Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCP
Hochgeladen von
dericOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCP
Hochgeladen von
dericCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Student Nurses Community
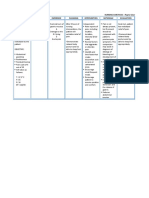
NURSING CARE PLAN Liver Cirrhosis
ASSESSMENT
SUBJECTIVE:
Napansin ko na
lumalaki ang tiyan ko
as verbalized by the
patient.
OBJECTIVE:
Pallor
Weak in
appearance
Jaundice
Abdominal
distention noted
Bipedal edema
Irritability noted
DOB with RR of 29
bpm
Abdominal girth of
32
DIAGNOSIS
Fluid volume
excess r/t
compromised
regulatory
mechanism
secondary to
cirrhosis of the
liver as manifested
by pallor, weak in
appearance,
jaundice,
abdominal
distention, edema,
irritability, DOB
with RR of 29 and
abdominal girth of
32
PLANNING
After 6 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient will
demonstrate
stabilized fluid
volume and
decreased
edema and
abdominal girth.
INTERVENTIONS
Monitor vital sign
Measure intake and
output
Monitor BP
Assess respiratory
status
Monitor abdominal
girth
Provide occasional
ice chips if NPO
Restrict sodium and
fluids as ordered
Administer
medications as
indicated:
Diuretics
Potassium
Assist with
paracentesis
procedure
RATIONALE
Established baseline data
Reflects circulating
volume status,
developing fluid shifts,
and in response to
therapy
BP elevations are usually
associated with fluid
volume excess
Indicative of pulmonary
congestion/edema
Reflects accumulation of
fluid (ascites)
Decreases sensation of
thirst, especially when
fluid intake is restricted
Sodium may be restricted
to minimize fluid
retention in extravascular
spaces. Fluid restriction
may be necessary to
prevent dilutional
hyponatremia
Used with caution to
control edema and
ascites, block effect of
aldosterone, and increase
water excretion while
sparing potassium
Serum and cellular
potassium are usually
EVALUATION
After 6
hours of nsg.
interventions,
the patient
demonstrated
stabilized fluid
volume and
decreased
edema and
abdominal
girth.
Goal met.
Student Nurses Community
depleted because of liver
disease
Done to remove ascites
fluid
Student Nurses Community
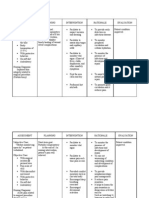
Nursing Care Plan
Assessment
Subjective: Wala akong
ganang kumain as
verbalized
Objective:
Weak in
appearance
Refusal to eat
Irritability noted
Poor muscle tone
Jaundice noted
Emaciated
Abdominal
distention noted
Pallor noted
Diagnosis
Imbalance
nutrition: less than
body requirements
r/t loss of appetite
secondary to
ascites as
evidenced by
refusal to eat,
weak in
appearance,
irritability, poor
muscle tone,
emaciated and
abdominal
distention
Planning
After 5 hrs of
nsg.
Interventions,
patients
appetite will
improve from 2
tbsp to at least 5
tbsp per meal.
Interventions
Monitor vital signs
Assist in oral hygiene
before meals.
Discuss eating habits
including food
preferences.
Serve favorite foods
that are not
contraindicated.
Prevent or minimize
unpleasant odors
during meal time.
Serve foods that are
attractive and
palatable.
Recommend small,
frequent meals
Restrict intake of
caffeine, gasproducing or spicy and
excessively hot or cold
foods
Provide assistance
with activities as
needed. Promote
undisturbed rest
periods, especially
Rationale
For baseline data
A clean mouth
enhances appetite
To appeal to client
likes and dislikes
To stimulate the
appetite
May have
negative effect on
appetite
To stimulate the
appetite
Poor tolerance to
larger meals may
be due to
increased intraabdominal
pressure/ascites
Aids in reducing
gastric irritation &
abdominal
discomfort that
may impair oral
intake/digestion
Conserving energy
reduces metabolic
demands on the
liver and promotes
Evaluation
After 8 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patients appetite
improved from 2
tbsp to 5 tbsp per
meal.
Goal met.
Student Nurses Community
before meals
Advise to consume
nutritious foods
cellular
regeneration.
Student Nurses Community
Nursing Care Plan
Assessment
Subjective:
Sumasakit ang tiyan
ko as verbalized with a
pain scale of 6 out of 10
where in:
0 - no pain
1 2 mild pain
3 4 moderate pain
5 6 severe pain
7 8 very severe pain
9 10 worst possible
Objective:
Facial grimace
noted
Irritability noted
Restlessness noted
Anxiety noted
Fatigued
Clenched fist
Beaten look
Agitation noted
Pallor
Grunting
Guarding of body
part (right
hypochondriac)
Diagnosis
Acute pain related
to liver
enlargement
secondary to
ascites as
evidenced by facial
grimace,
irritability,
restlessness,
anxiety, fatigued,
clenched fist,
beaten look,
agitation, pallor,
grunting, guarding
of body part and
verbalization of
pain with a pain
scale of 6/10
Planning
After 2 hours of
nursing
interventions,
pain will be
lessened with a
scale of 1-10,
from 6/10 to
1/10.
Interventions
Monitor VS
Perform pain
assessment
(COLDSPA) every
time pain occurs
Encourage
verbalization of
feeling of pain
Instruct use of
relaxation exercise
such as listening to
music
Provide comfort
measures such as
back rubbing &
changing position
Teach the patient
relaxation
techniques like deep
breathing
Provide quiet and
calm environment
Rationale
Pain alters VS
To rule out
development of
complications by
knowing alleviating
and precipitating
factors
Pain is subjective &
cant be assessed
through
observation alone
Promotes
relaxation and
diverts attention
from pain
To prove nonpharmacological
management
To alleviate pain
Noisy environment
stimulates
irritation
Evaluation
After 2 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient was
relieved from pain
Goal met.
Student Nurses Community
Nursing Care Plan
ASSESSMENT
SUBJECTIVE:
Nahihirapan
akong huminga as
verbalized
OBJECTIVE:
Dyspnea
Tachypnea with RR
of 30, irregular,
shallow
Weak in
appearance
Anxiety noted
Irritability noted
Restlessness noted
Lethargic
Pallor
DIAGNOSIS
Altered breathing
pattern r/t
decreased lung
expansion
secondary to intraabdominal fluid
collection (ascites)
as manifested by
dyspnea,
tachypnea with RR
of 30, irregular and
shallow, weak in
appearance,
anxiety, irritability,
restlessness,
lethargy and pallor
PLANNING
INTERVENTIONS
After 6 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient will be
relieved from
dyspnea and
breathing pattern
will return to
normal.
Monitor V/S
Monitor respiratory
rate, rhythm and
depth
Auscultate breath
sounds, noting
crackles, wheezes
and rhonchi
Investigate
changes in LOC
Keep head of bed
elevated. Position
on sides
Encourage
frequent
repositioning and
deep-breathing
exercises
Provide
supplemental O2
as indicated
RATIONALE
For baseline data
Rapid shallow
respirations/dyspn
ea may be present
because of hypoxia
or fluid
accumulation in
the abdomen
Indicates
developing
complications and
increasing risk of
infection
Changes in
mentation may
reflect hypoxemia
and respiratory
failure
Facilitates
breathing by
reducing pressure
on the diaphragm
Aids in lung
expansion and
mobilizing
secretions
May be necessary
to treat/prevent
hypoxia
EVALUATION
After 6 hours of
nsg. interventions,
patient was
relieved from
dyspnea and
breathing pattern
returned to normal
Goal met.
Student Nurses Community
Nursing Care Plan
ASSESSMENT
SUBJECTIVE:
Nanghihina na
ako, ayoko na
mag-gagalaw as
verbalized
OBJECTIVE:
Pallor
Body malaise
noted
Diaphoresis
Inability to
concentrate
Inability to perform
usual ADLs
Weak in
appearance
Limited ROM
Difficulty initiating
movements
DIAGNOSIS
Activity intolerance
r/t generalized
body weakness
secondary to
progressive
disease state as
manifested by
pallor, body
malaise,
diaphoresis,
inability to
concentrate,
inability to perform
usual ADLs, weak
in appearance,
limited ROM and
difficulty initiating
movements
PLANNING
INTERVENTIONS
After 8 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient will
participate
willingly in
necessary activity,
will learn how to
conserve energy
and verbalize relief
from fatigue.
Evaluate pts
current activity
tolerance
Adjust activity and
reduce intensity of
task that may
cause undesired
physiological
changes
Increase exercise
and activity levels
gradually
Teach methods to
conserve energy
such as sitting
than standing
while dressing
Demonstrate/Assis
t the patient while
doing ADL
Give the patient
information that
provides evidence
progress
Encourage client to
RATIONALE
Provide
cooperative
baseline
To prevent over
exertion
Enhances activity
tolerance
Helps minimize
waste of energy
Protect patient
from injury
To sustain pts
motivation
Provides for sense
of control and
feeling of
accomplishment
EVALUATION
After 8 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient participated
willingly in
necessary
activities, learned
how to conserve
energy and
verbalized relief
from fatigue
Goal met
Student Nurses Community
do whatever
possible e.g. selfcare
Student Nurses Community
Nursing Care Plan
ASSESSMENT
SUBJECTIVE:
Mawawala ba pa
tong laki ng tiyan
ko? as verbalized
OBJECTIVE:
Anxiety noted
Fear of rejection
Irritability noted
Restlessness noted
Feeling of
helplessness
Negative feelings
about body
DIAGNOSIS
Disturbed body
image r/t altered
physical
appearance as
evidenced by
anxiety, fear,
irritability,
restlessness,
feeling of
helplessness and
negative feelings
about the body
PLANNING
After 8 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient will
verbalize
understanding of
changes and
acceptance of self
in the present
situation.
INTERVENTIONS
Discuss
situation/encourag
e verbalization of
fears and
concerns. Explain
relationship
between nature of
disease
and symptoms.
RATIONALE
Support and
encourage patient;
provide care with a
positive, friendly
attitude
Encourage family
to verbalize
feelings, visit
freely/participate
in care
Patient is very
sensitive to body
changes and may
also experience
feelings of guilt
when cause is
related to
alcohol (70%) or
other drug use.
Caregivers
sometimes allow
judgmental
feelings to affect
the care of patient
and need to make
every effort to help
patient feel valued
as a person.
Family members
may feel guilty
about patients
condition
and may be fearful
of impending death.
They need
nonjudgmental
emotional support
and free access to
patient.
Participation in care
helps them feel
EVALUATION
After 8 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient verbalized
understanding of
changes and
acceptance of self
in the present
situation.
Goal met
Student Nurses Community
useful and
promotes trust
between staff,
patient.
Nursing Care Plan
ASSESSMENT
DIAGNOSIS
PLANNING
INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Student Nurses Community
Subjective:
Lagi akong
nangangati at
parang mahapdi
balat ko as
claimed
Objective:
Pruritus noted
Dry skin
Erythema noted
Scaly skin
Risk for impaired
skin integrity r/t
altered circulation
secondary to
accumulation of
bile salts as
evidenced by
pruritus, erythema,
dry and scaly skin
After 7 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient will
maintain skin
integrity and
identify individual
risk factors and
demonstrate
behaviors/techniqu
e to prevent skin
breakdown.
Inspect skin
surface/pressure
points routinely.
Gently massage
bony prominences
or areas of
continued stress
Encourage/assist
with repositioning
on a regular
schedule while in
bed, chair and
active passive
ROM exercises as
appropriate
Keep linen dry and
free of wrinkles
Suggest clipping
finger nails short
Edematous tissues
are more prone to
breakdown and to
the formation of
decubitus ulcers.
Ascites may
stretch the skin to
the point of tearing
in severe cirrhosis
Repositioning
reduces pressure
on edematous
tissues to improve
circulation.
Exercises enhance
circulation and
improve, maintain,
joint mobility
Moisture
aggravates
pruritus and
increases risk of
skin breakdown
Prevents client from
inadvertently
injuring the skin
especially while
sleeping
After 3 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient maintained
skin integrity and
identified individual
risk factors and
demonstrated
behaviors/techniqu
es to prevent skin
breakdown.
Goal met
Student Nurses Community
Nursing Care Plan
Assessment
Subjective:
Nahiirapan akong
umihi as
verbalized
Objective:
Anxiety noted
Irritability noted
Restlessness noted
Small, frequent
voiding
Facial grimace
noted upon
urination
Excessive
diaphoresis when
trying to void
Urgency
Diagnosis
Impaired urinary
elimination r/t
bladder distention
secondary to
ascites as
evidenced by
anxiety, irritability,
restlessness, small
and frequent
voiding, facial
grimace upon
urination,
excessive
diaphoresis when
trying to void, and
urgency
Planning
After 8 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient will empty
bladder regularly
with decrease pain
and difficulty.
Interventions
Rationale
Palpate bladder.
Investigate reports
of discomfort,
fullness, inability to
void
Provide routine
voiding measures
like privacy,
normal positioning,
running water in
sink, pouring warm
water over
abdomen
Perception of
bladder fullness,
distention of
bladder above
symphysis pubis
indicates urinary
retention
Promotes
relaxation urinary
muscles and may
facilitate voiding
efforts
Evaluation
After 8 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient voided
regularly and
without difficulty.
Goal met
Student Nurses Community
Nursing Care Plan
Assessment
Subjective:
Anu kaya tong
sakit ko, san ko
nakuha to? as
verbalized
Objective:
Restlessness noted
Irritability noted
Confused look
Statement of
misconception
Development of
preventable
complications
Frequent questions
Diagnosis
Knowledge deficit
regarding
condition,
prognosis,
treatment and
discharge needs r/t
information
misinterpretation
as evidenced by
restlessness,
irritability,
confused look,
statement of
misconception,
development of
preventable
complications and
frequent questions
Planning
After 8 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient will
verbalize
understanding of
disease process,
prognosis,
potential
complications and
identify necessary
lifestyle changes
and participate in
care.
Interventions
Review disease
process/prognosis
and future
expectations
Stress importance
of avoiding alcohol.
Give information
about community
services available
to aid in alcohol
rehabilitation if
indicated.
Emphasize the
importance of
good nutrition.
Recommendavoida
nce of highprotein/salty foods,
onions, and
strongcheeses.
Provide written
dietary instructions
Rationale
Provides
knowledge base
from which patient
can make informed
choices
Alcohol is the
leading cause in
the development
of cirrhosis
Proper dietary
maintenance and
avoidance of foods
highin sodium and
protein aid in
remission of
symptoms andhelp
prevent ammonia
buildup and further
liver
damage.Written
instructions are
helpful for patient
to refer to at home
Evaluation
After 8 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient verbalized
understanding of
disease process,
prognosis, potential
complications and
identified
necessary lifestyle
changes and
participate in care.
Goal met
Student Nurses Community
Nursing Care Plan
Assessment
Subjective:
Hirap ako
makatulog as
claimed
Objective:
Sunken eyeballs
Fatigue
Mood alterations
Agitated
Body weakness
noted
Lethargic
Diagnosis
Disturbed sleep
pattern r/t changes
in activity pattern
secondary to
psychologic stress
as evidenced by
sunken eyeballs,
fatigue, mood
alterations,
agitation, body
weakness, lethargy
Planning
After 4 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient will
establish adequate
sleep pattern and
report rested.
Interventions
Evaluate level of
stress
Rationale
Advise to reduce
fluid intake at
night
Increasing
confusion,
disorientation, and
uncooperative
behavior may
interfere with
attaining restful
sleep
Provide soft music
or white noise if
available
Decreases need to
get up to go to
bathroom during
sleep
Reduces sensory
stimulation by
blocking out other
environmental
sounds that could
interfere with restful
sleep
Evaluation
After 4 hours of
nursing
interventions,
patient established
adequate sleep
pattern and
reported rested.
Goal met
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDokument2 SeitenNCP Liver Cirrhosismarlx5100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver CirrhosisDokument14 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosisken93% (75)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Liver CirrhosisDokument2 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN - Liver Cirrhosisderic100% (27)
- NCP For Liver CirrhosisDokument25 SeitenNCP For Liver CirrhosisWendy Escalante100% (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis Nursing Care PlansDokument17 SeitenLiver Cirrhosis Nursing Care Plansmarsan12Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Liver Cirrhosis Nursing Care PlansDokument4 Seiten8 Liver Cirrhosis Nursing Care PlansAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDokument7 SeitenNCP Liver CirrhosisIris Jimenez-BuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPJose Escobar100% (3)
- Liver Cirrhosis NCPDokument3 SeitenLiver Cirrhosis NCPSharmaine MadlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Cirrhosis NCPDokument21 SeitenLiver Cirrhosis NCPJeco Valdez100% (4)
- Case Study CholecystitisDokument27 SeitenCase Study Cholecystitismeed0290% (10)
- Case: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceDokument7 SeitenCase: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceLovelyn GanirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan-AscitesDokument10 SeitenNursing Care Plan-AscitesKayki Louise75% (4)
- Liver Cirrhosis NCP 1Dokument6 SeitenLiver Cirrhosis NCP 1Paolo Rafael D EsguerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy NCPDokument9 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy NCPderic88% (8)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument6 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- NCP Urinary Tract InfectionDokument19 SeitenNCP Urinary Tract InfectionYudistiro Adi Nugroho100% (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis - NCPDokument18 SeitenLiver Cirrhosis - NCPIshmael Solamillo83% (6)
- NCP. FistulectomyDokument2 SeitenNCP. Fistulectomymitchelley80% (10)
- Lung Cancer N C P BY BHERU LALDokument2 SeitenLung Cancer N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For "Hepatitis"Dokument12 SeitenNursing Care Plan For "Hepatitis"jhonroks86% (14)
- CASE STUDY Intestinal ObstructionDokument68 SeitenCASE STUDY Intestinal ObstructionMaria Paula Bungay91% (22)
- Nursing Diagnoses For PT With Altered Level of ConsciousnessDokument5 SeitenNursing Diagnoses For PT With Altered Level of Consciousnessmikaela_pascua95% (40)
- Liver NCPDokument5 SeitenLiver NCPMerrill HansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standing Order-Diarrhea DraftDokument1 SeiteStanding Order-Diarrhea DraftKatelyn Brissey50% (2)
- NCP PancreatitisDokument2 SeitenNCP PancreatitisJeanelle Generoso100% (1)
- NCP-Esophageal Varices Pleural EffusionDokument6 SeitenNCP-Esophageal Varices Pleural Effusiontinatin98933% (3)
- Esophageal CADokument25 SeitenEsophageal CADan Kenneth86% (7)
- Hypospadia CompletedDokument92 SeitenHypospadia Completedgideon A. owusu100% (1)
- NCP of Renal CalculiDokument3 SeitenNCP of Renal Calculidextroid1289% (9)
- NCP Acute Pain RT CancerDokument3 SeitenNCP Acute Pain RT CancerCharissa Magistrado De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleDokument5 SeitenNCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleMika Saldaña100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - CancerDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan - CancerChristineAla0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Chronic PancreatitisDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Chronic PancreatitisAnne B. Buenvenida100% (2)
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDokument7 SeitenCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - TBDokument2 SeitenNCP - TBPahw BaluisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subjective: No Subjective Cues. ObjectiveDokument2 SeitenSubjective: No Subjective Cues. Objective1S VILLEGAS GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role Av Aids in Clinical TeachingDokument16 SeitenRole Av Aids in Clinical Teachingtankmp100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis For TonsillitisDokument3 SeitenNursing Diagnosis For TonsillitisVaneca Go67% (9)
- NCP BPHDokument8 SeitenNCP BPHjyaba0% (1)
- NCP LymphomaDokument4 SeitenNCP LymphomaRene John Francisco100% (2)
- NCP For Pain - NephrolithiasisDokument3 SeitenNCP For Pain - NephrolithiasisDepia Leah NgislawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDokument3 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- Abdominal PainDokument2 SeitenAbdominal Paindelan7dust78% (18)
- NCP Loss of AppetiteDokument5 SeitenNCP Loss of AppetiteStenneli Gumban Trojillo50% (2)
- Appebon With IronDokument2 SeitenAppebon With IronLindsay Grace MandarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Appendectomy Nursing Care PlansDokument8 Seiten4 Appendectomy Nursing Care PlansMarin Andrei100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On AppendicitisDokument15 SeitenCase Study On AppendicitisKristelle BonitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Renal Tissue PerfusionDokument2 SeitenIneffective Renal Tissue PerfusionHendra Tanjung100% (4)
- NCP Pleural EffusionDokument7 SeitenNCP Pleural EffusionEjie Boy Isaga100% (2)
- NCPDokument5 SeitenNCPJusTin Cargason100% (1)
- Nephrolithiasis - NCPDokument9 SeitenNephrolithiasis - NCPAia Javier83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan - Using NandaDokument16 SeitenNursing Care Plan - Using NandaWardinatul ImanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDokument8 Seiten7 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsHikaru Takishima91% (23)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument5 SeitenNursing Care PlanAnju Luchmun100% (2)
- NCP Risk For FallDokument20 SeitenNCP Risk For FallRen Ren Determinado86% (7)
- NCPDokument7 SeitenNCPAbbie TantengcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Alcoholic NeuropathyDokument5 SeitenNCP Alcoholic NeuropathyPeachy Marie Anca100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlansDokument10 SeitenNursing Care PlansClaire Alcantara50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic86% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic71% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Breastfeeding NCPDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Breastfeeding NCPderic76% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (24)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Tabel IcdDokument214 SeitenTabel IcdSusilo HendroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast Sarcoidosis An Extremely Rare Case of Idiopathic Granulomatous MastitisDokument3 SeitenBreast Sarcoidosis An Extremely Rare Case of Idiopathic Granulomatous MastitisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geriatrics RehabDokument30 SeitenGeriatrics RehabNasroon BhambhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Medical Emergencies: Jude D. Positos, RNDokument27 SeitenCommon Medical Emergencies: Jude D. Positos, RNNenen PositosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Women May Be Better Equipped To Fight COVIDDokument46 SeitenWhy Women May Be Better Equipped To Fight COVIDjudith retanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimal Management of Collagenous Colitis A Review 021016Dokument9 SeitenOptimal Management of Collagenous Colitis A Review 021016Eliza DNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Vector Control ProgramDokument35 SeitenIntegrated Vector Control ProgramKeerthi VasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenSample Nursing Care Planhyunbin18100% (4)
- DiabetesDokument6 SeitenDiabetesnayraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ThesisDokument47 SeitenFinal ThesisMohammed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 7 (GIT & Hepatobiliary Case Simulation)Dokument41 SeitenGroup 7 (GIT & Hepatobiliary Case Simulation)Zil Kamleshkumar PanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elc501 - Group Portfolio ForumDokument11 SeitenElc501 - Group Portfolio ForumAhmad SyamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Breast DiseasesDokument64 SeitenCommon Breast Diseasesamirahmei100% (1)
- د. هالة Dermatitis-1 (Muhadharaty)Dokument7 Seitenد. هالة Dermatitis-1 (Muhadharaty)adwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetic Emergencies PDFDokument20 SeitenDiabetic Emergencies PDFhenry leonardo gaona pinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osce, BaselDokument302 SeitenOsce, Baselbpjavi78% (9)
- WK 4 Respiratory 2023Dokument38 SeitenWK 4 Respiratory 2023Basmala HebaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects and Costs of Real-Time Cardiac Telerehabilitation - Randomised Controlled Non - Inferiority TrialDokument8 SeitenEffects and Costs of Real-Time Cardiac Telerehabilitation - Randomised Controlled Non - Inferiority TrialarwitarahayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Isthmic SpondylolisthesisDokument9 SeitenAdult Isthmic SpondylolisthesisAlex CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Values: Interpreting Chemistry and Hematology For Adult PatientsDokument36 SeitenLab Values: Interpreting Chemistry and Hematology For Adult PatientsBrian Johnson100% (1)
- Medical and Surgical NursingDokument9 SeitenMedical and Surgical NursingWilmaBongotanPadawilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perinatology Clinics 2008, Vol.35, Issues 4, Neuroprotection in The NewbornDokument210 SeitenPerinatology Clinics 2008, Vol.35, Issues 4, Neuroprotection in The NewbornJhonny MarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toxoplasmosis2019 PDFDokument69 SeitenToxoplasmosis2019 PDFDavid Felipe Cardona GuarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Life TestimoniesDokument87 Seiten4 Life TestimoniesBhavin VoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education: School Contingency PlanDokument14 SeitenDepartment of Education: School Contingency PlanClerica RealingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DORO - Cranial Stabilization and Retractor SystemsDokument32 SeitenDORO - Cranial Stabilization and Retractor SystemsBooBleGooMNoch keine Bewertungen
- KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline On The.9Dokument93 SeitenKDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline On The.9PD18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Colorectal CancerDokument23 SeitenCase Study Colorectal CancerLeogalvez BedanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeopathy and PaediatricsDokument15 SeitenHomeopathy and PaediatricsCristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological Changes of A Pregnant WomanDokument4 SeitenPsychological Changes of A Pregnant WomanEuna Patricia AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen