Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fact Sheet
Hochgeladen von
api-2927456340 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
100 Ansichten4 SeitenOriginaltitel
fact sheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
100 Ansichten4 SeitenFact Sheet
Hochgeladen von
api-292745634Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
FACT SHEET FOR BROCHURES
GEOGRAPHIC REGIONS COVERED:
o West-Central Europe
o Northern Europe
o Russia
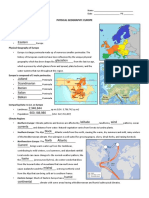
A. WEST CENTRAL EUROPE-GEOGRAPHY, WATER, AND CLIMATE
Physical geography of West-Central Europe-important landforms:
o Northern European Plain stretches from Atlantic coast to
Eastern Europe
o Central Uplands stretch from the Massif Central plateau
region in France, the Jura Mountains on the French-Swiss
border to the Black Forest of Germany
This area is also known for having productive
coalfields which make the Central Uplands a difficult
area to farm
Major water features
o North Sea and English Channel to the north
o Bay of Biscay and Atlantic Ocean to the west
o Mediterranean Sea to the south
o Major Rivers that cross the region include
Danube
Rhine
Navigable rivers such as these allow ships to pass
through them due to their width and depth
Climate of this region
o Contains a warm ocean current that flows along Europes
northwestern coast-this is known as marine west coast
climate
o At higher elevations, the clmate is colder and wetter
o Southern France has a Mediterranean climate
o Climate is an important natural resource of this area
Energy and minerals are not evenly distributed across the region
Besides climate, the Alps serve as another important natural
resource due to the number of tourists who come to hike and ski
B. NORTHERN EUROPE-GEOGRAPHY, WATER, AND CLIMATE
Physical Geography of Northern Europe
o Two regions make up Northern Europe
British Isles
Include Republic of Ireland, and the UK (Scotland,
England, Wales and Northern Ireland)
Scandanavia
Includes Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and
Denmark
o Different Types of Terrain
Hills and Mountains-rough rocky hills and low mountains cover
much of Northern Europe
Farmlands and Plains-fertile farmland and flat plaains stretch
across Northern Europe; Ireland has green rolling hills and
England has wide valleys
Glaciers have impacted the lakes and coastlines of Northern
Europe by causing great fjords to form; an example is Norways
Sogne Fjord which is over 100 miles long and miles deep
o Natural Resources
Primary resources of Northern Europe include energy resources,
forests and soils, and surrounding areas
Energy: energy sources include
oil and natural gas from under the North Sea
hydroelectric energy produced by lakes and rivers
geothermal energy produced in Iceland due to the steam
from the hot springs
Forests and Soils: forests produce timber and the soils produce
fertile land used for farming
Seas and Oceans: fishing is a major natural resource that
benefits much of Northern Europe
o Climate
Much of Northern Europe is above the Arctic Circl and has high
latitudes
However the North Atlantic Drift causes for this region to have
fairly mild climates
Much of Northern Europe has a marine west coast climate like
Denmark, the British Isles and western Norway
Central Norway, Sweden and southern Finland have a humid
continental climate
C. RUSSIA-GEOGRAPHY, WATER, AND CLIMATE
A. Landforms:
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
Ural Mountains are the mountain range in Russia where
Europe and Asia meet
Europe is West and Asia is East
Russia is the worlds largest country
The capital of Russia is Moscow
East side of Russia has a rising plain that forms the Ural
Mountains
West side of Russia contains the Northern European Plain
South of the Northern European Plain are the Carpathians
mountain range
Moscow is the fertile plain in between the Ural Mountains and
Europe where most Russians live.
It is also the nations
capital.
Siberia is the vast area between the Ural Mountains to the west
and the Pacific Ocean to the east
Ring of Fire is part of the Russian Far East or Eastern Siberia,
the area circling the Pacific; it is known for its volcanoes and
earthquakes
B. Major Bodies of Water:
o Volga River is the longest river in Europe and it winds
southward to the Caspian Sea, forming the core of Russias
river network
o Ob, Yenisey and Lena Rivers flow northward toward the
Arctic Ocean
o The rivers are frozen for much of the year making shipping
and trade difficult and causing for Russias ports to close for
part of the year.
o Lake Baikal, in south-central Siberia, is the worlds deepest
lake and deep enough to hold all five of the American Great
Lakes
C. Climate
o Known for having long snowy winters and short summers
o Northern coast is tundra and much of the ground is frozen,
called permafrost
o Most of the regions moisture comes from the Atlantic Ocean
o South of the tundra is the vast forest of evergreen trees
called taiga
D. Natural Resources
o Northern European Plain and steppe provide rich fertile soil
for farming
o Taiga provides wood for building and paper products
Metals like copper and gold are also found here
o Main energy resources of Russia are coal, hydroelectric
power, natural gas and oil. Oil comes from large oil fields
and from under the Caspian Sea
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- World Builder's GuidebookDokument162 SeitenWorld Builder's Guidebookdinglenuts100% (4)
- Landform Cards 19 ADokument100 SeitenLandform Cards 19 ANina StratukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography of Asia Ppt. BheyDokument55 SeitenGeography of Asia Ppt. BheyLeanne Joie Lozano100% (2)
- BeachesAndCoasts Davis and FitzgeraldDokument521 SeitenBeachesAndCoasts Davis and FitzgeraldanibalNoch keine Bewertungen
- East Iceland - Official Tourist Guide 2014-2015Dokument196 SeitenEast Iceland - Official Tourist Guide 2014-2015cavrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contemporary Issues in Estuarine Physics - CompletoDokument328 SeitenContemporary Issues in Estuarine Physics - CompletoDolores AristaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Illustrated Glossary of Land and Water FormsDokument5 SeitenIllustrated Glossary of Land and Water FormsnastaranarastehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Norway Fisheries Case JudgmentDokument17 SeitenNorway Fisheries Case JudgmentKiko Rimban100% (1)
- Be A Better Campaign MasterDokument134 SeitenBe A Better Campaign MasterLoba100% (4)
- Rowan of RinDokument18 SeitenRowan of RinClara PartoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology of Longyearbyen-Jochmann EngDokument36 SeitenGeology of Longyearbyen-Jochmann EngLeo Rescia100% (1)
- VikingsDokument22 SeitenVikingsAnonymous ldZphWiVn100% (1)
- The Physical Geography of Europe - The LandDokument25 SeitenThe Physical Geography of Europe - The LandRehab OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eu6Dokument1 SeiteEu6tjapa006Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Alps: The Alps Are A Small Segment of A DiscontinuousDokument5 SeitenThe Alps: The Alps Are A Small Segment of A DiscontinuousTeddy DumitracheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area II - Europe, Africa and Middle EastDokument3 SeitenArea II - Europe, Africa and Middle EastSheila MarchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Russia and Central Asia Geography NotesDokument4 SeitenRussia and Central Asia Geography NotessirgivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WGEODokument5 SeitenWGEOJaymore BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Europe Study Sheet: Pehel JainDokument11 SeitenEurope Study Sheet: Pehel JainToxic MokshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo TestDokument6 SeitenGeo TestRiju SushreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EuropeDokument27 SeitenEuropeAinon Mardiya DiatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7 (Europe) - CDokument13 SeitenCH 7 (Europe) - CXain RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Africa, Asia, America, Europe & Oceania: A Concise Comparison of the ContinentsDokument11 SeitenAfrica, Asia, America, Europe & Oceania: A Concise Comparison of the ContinentsRaimerlopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Eastern Hemisphere-2017Dokument18 SeitenThe Eastern Hemisphere-2017ERICA CHARRIS PAYARES100% (1)
- Learning(ratta)Dokument5 SeitenLearning(ratta)Manayay GehlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Europe: Location, Area, Political and Physical Features A. Give Geographical Reasons. Europe Is Rightly Called The Peninsula of Peninsulas'Dokument3 SeitenEurope: Location, Area, Political and Physical Features A. Give Geographical Reasons. Europe Is Rightly Called The Peninsula of Peninsulas'Nargis FarhaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our WorldDokument29 SeitenOur Worldapi-288228945Noch keine Bewertungen
- Europe's Realm ReviewerDokument2 SeitenEurope's Realm ReviewerJhamae Rose AbulogNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Outline of The Peoples Socialist Republic of AlbaniaDokument80 SeitenAn Outline of The Peoples Socialist Republic of Albaniaerosion343Noch keine Bewertungen
- 08WGC Chapter 14Dokument56 Seiten08WGC Chapter 14Natalia ShubinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography Take Home ExamDokument4 SeitenGeography Take Home ExamDominic BenjaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Europe's Mountain Ranges, Peninsulas, and Coastal FeaturesDokument3 SeitenEurope's Mountain Ranges, Peninsulas, and Coastal FeaturesJude AldonsNoch keine Bewertungen
- EuropeDokument5 SeitenEuropeAmicus CuriaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human GeographyDokument11 SeitenHuman GeographyAmicus CuriaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Northern and Southern European Physical GeographyDokument20 SeitenNorthern and Southern European Physical Geographyapi-395831257Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide 4th Six Wks TestDokument2 SeitenStudy Guide 4th Six Wks Testapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Poland's diverse topography from Baltic coast to Carpathian MountainsDokument2 SeitenPoland's diverse topography from Baltic coast to Carpathian MountainshafizsulemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kami Export - Jayden Weil - GRWC12S01Dokument4 SeitenKami Export - Jayden Weil - GRWC12S01jNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.rivers, 3.climate, 4.vegetation and 5.agricultureDokument23 Seiten2.rivers, 3.climate, 4.vegetation and 5.agriculturemadhaviyogi16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Russia's Diverse Landscapes and ClimateDokument1 SeiteRussia's Diverse Landscapes and ClimateMarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASIADokument6 SeitenASIASanatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Russia Kit LametDokument6 SeitenRussia Kit LametGauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- LN - 10 - 46 - Climate of ContinentsDokument39 SeitenLN - 10 - 46 - Climate of ContinentsPantulu MurtyNoch keine Bewertungen
- John Haldon - Palgrave Atlas of Byzantine History 1-13 OCRDokument7 SeitenJohn Haldon - Palgrave Atlas of Byzantine History 1-13 OCRAnathema Mask100% (1)
- Microsoft Word - 38 - Physical Geography - Europe Notes PDFDokument2 SeitenMicrosoft Word - 38 - Physical Geography - Europe Notes PDFBoxInABoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Europe Overview - GeographyDokument5 SeitenEurope Overview - Geographyapi-434008934Noch keine Bewertungen
- Albania's Geography in 40 CharactersDokument5 SeitenAlbania's Geography in 40 CharactersEmpire100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Water FormsDokument8 SeitenWater FormsBasco Martin JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Masses: Logronio, Robert M. BSED-General Science 4BDokument20 SeitenAir Masses: Logronio, Robert M. BSED-General Science 4BStiffany Rose Nillama TinambunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOCIALES Tema 7 InglesDokument1 SeiteSOCIALES Tema 7 InglesMiriam MGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography Lesson 5Dokument5 SeitenGeography Lesson 5Debsruti SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KO Rivers and Mountains Year 4Dokument1 SeiteKO Rivers and Mountains Year 4meteaydNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeographyDokument2 SeitenGeographyjam_davidpack7oNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate of Anglo-AmericaDokument13 SeitenClimate of Anglo-AmericaChemutai EzekielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Documents 2Dokument1 SeiteDocuments 2Rechel SartorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESS - Grade 7 - Term 1 - PPT 2Dokument6 SeitenESS - Grade 7 - Term 1 - PPT 2Doha ElegeimyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography of Sea Aliagha8Dokument3 SeitenGeography of Sea Aliagha8liaganovruzovNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEOGRAPHY OF BRITAINDokument10 SeitenGEOGRAPHY OF BRITAINDaria MurashkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB 9-10 PDFDokument2 SeitenGB 9-10 PDFAnonymous 7TZxdum5cNoch keine Bewertungen
- WESTERN EUROPE - Summary - 8thDokument2 SeitenWESTERN EUROPE - Summary - 8thRuby RamírezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pacific Maritime Location (I.e. Provinces)Dokument8 SeitenPacific Maritime Location (I.e. Provinces)VLONENoch keine Bewertungen
- World Geography Asia NotesDokument12 SeitenWorld Geography Asia NotesYogaj DarshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NORTH AMERICA - NotesDokument11 SeitenNORTH AMERICA - NotesNirvaan SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.2 Geography Rhine LandsDokument109 SeitenS.2 Geography Rhine Landstreva givenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Russia PowerpointDokument23 SeitenRussia PowerpointVanessa MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compilation: 21 CenturyDokument12 SeitenCompilation: 21 CenturyNordian Ashley MapantasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography of The Regions of Canada Example For Presentation-2Dokument10 SeitenGeography of The Regions of Canada Example For Presentation-2Paola RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography - Unit 6 - North America Q&ADokument3 SeitenGeography - Unit 6 - North America Q&ANairahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Physical Features of China RegionsDokument13 SeitenMain Physical Features of China RegionsHema Aher- MoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Semester Exam Study Guide CWCDokument3 Seiten2016 Semester Exam Study Guide CWCapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Semester Exam Schedule 2015-2016Dokument1 Seite2nd Semester Exam Schedule 2015-2016api-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 33 Vocab Capitals ContentDokument3 SeitenWeek 33 Vocab Capitals Contentapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- North Africa Presentation RubricDokument1 SeiteNorth Africa Presentation Rubricapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6th 6 Weeks Test Study GuideDokument2 Seiten6th 6 Weeks Test Study Guideapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 30 Brochure DirectionsDokument2 SeitenWeek 30 Brochure Directionsapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 34 VocabularyDokument1 SeiteWeek 34 Vocabularyapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 36 Brochure DirectionsDokument2 SeitenWeek 36 Brochure Directionsapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 33 Brochure DirectionsDokument2 SeitenWeek 33 Brochure Directionsapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 34 ContentDokument2 SeitenWeek 34 Contentapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5th Six Weeks Study GuideDokument2 Seiten5th Six Weeks Study Guideapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 32 Vocab People ContentDokument2 SeitenWeek 32 Vocab People Contentapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 29 ContentDokument3 SeitenWeek 29 Contentapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 29 VocabularyDokument1 SeiteWeek 29 Vocabularyapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 28 VocabularyDokument1 SeiteWeek 28 Vocabularyapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 28 ContentDokument2 SeitenWeek 28 Contentapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure AssignmentDokument1 SeiteBrochure Assignmentapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure RubricDokument1 SeiteBrochure Rubricapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 27 ContentDokument2 SeitenWeek 27 Contentapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 27 VocabularyDokument1 SeiteWeek 27 Vocabularyapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Directions For Social Studies BrochuresDokument1 SeiteDirections For Social Studies Brochuresapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 26 ContentDokument2 SeitenWeek 26 Contentapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Grade Syllabus ProckDokument6 Seiten6th Grade Syllabus Prockapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 26 VocabularyDokument1 SeiteWeek 26 Vocabularyapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 23 4th Six Weeks OverviewDokument4 SeitenWeek 23 4th Six Weeks Overviewapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exhibit Rules Verification SheetDokument2 SeitenExhibit Rules Verification Sheetapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide 4th Six Wks TestDokument2 SeitenStudy Guide 4th Six Wks Testapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 21 ContentDokument3 SeitenWeek 21 Contentapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 21 VocabularyDokument1 SeiteWeek 21 Vocabularyapi-292745634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geography - Unit 7 - EuropeDokument32 SeitenGeography - Unit 7 - EuropeSamanvitha RaaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iceland Complete Classic Circle Tour: Full Itinerary & Trip DetailsDokument9 SeitenIceland Complete Classic Circle Tour: Full Itinerary & Trip DetailsManfredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bodies of Water PicDokument4 SeitenBodies of Water PicLD MARY M. POLICARPIONoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Sheet 4 - GSP22T04S-ark6d2Dokument38 SeitenAnswer Sheet 4 - GSP22T04S-ark6d2rohit95patnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography Picture DictionaryDokument71 SeitenGeography Picture Dictionaryshaikh AijazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Britainbritishse 00 MackuoftDokument418 SeitenBritainbritishse 00 MackuoftZelia GregoriouNoch keine Bewertungen
- EuropeDokument5 SeitenEuropeAmicus CuriaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography Picture DictionaryDokument4 SeitenGeography Picture DictionaryEva Andersen VargaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oils Spill Response Capacity-NunavutDokument54 SeitenOils Spill Response Capacity-NunavutNunatsiaqNewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glacial Landforms-1Dokument11 SeitenGlacial Landforms-1Satarupa BandyopadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sea Level Changes or EustatismDokument6 SeitenSea Level Changes or Eustatismkalule elvisNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 1 Ocean and Coastal Habitat - SECTION 9 Coastal LandformsDokument35 SeitenMODULE 1 Ocean and Coastal Habitat - SECTION 9 Coastal Landformspoiu987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Driving Guide to Norway - Get Your Permit, Rent a Car, Road Rules & Top DestinationsDokument4 SeitenDriving Guide to Norway - Get Your Permit, Rent a Car, Road Rules & Top DestinationsTupy TupasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Landforms Scavenger Hunt Geography ProjectDokument2 SeitenLandforms Scavenger Hunt Geography ProjectNatalia ShubinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEOGRAPHY - Lesson 4-6Dokument8 SeitenGEOGRAPHY - Lesson 4-6VINCE FRANCIS MESANA FAMORCANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marine Ecosystems Estuary and Coastal WetlandsDokument20 SeitenMarine Ecosystems Estuary and Coastal WetlandsTime NextNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tom Finch's Monkeyand How He Dined With The Admiral by Hutcheson, John ConroyDokument51 SeitenTom Finch's Monkeyand How He Dined With The Admiral by Hutcheson, John ConroyGutenberg.orgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submerged TunnelDokument18 SeitenSubmerged TunnelRakesh HNoch keine Bewertungen
- SiphonophoresDokument12 SeitenSiphonophoresNicolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Norway's Fiords RevealedDokument3 SeitenNorway's Fiords RevealedGabriel Salazar LozadaNoch keine Bewertungen