Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
B Vitamins 1
Hochgeladen von
api-2456927970 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
205 Ansichten1 SeiteB Vitamins are cofactors in Energy Metabolism. They help enzymes do their job better. Pantothenic acid, riboflavin and niacin helps break down fat for energy.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
b vitamins 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenB Vitamins are cofactors in Energy Metabolism. They help enzymes do their job better. Pantothenic acid, riboflavin and niacin helps break down fat for energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
205 Ansichten1 SeiteB Vitamins 1
Hochgeladen von
api-245692797B Vitamins are cofactors in Energy Metabolism. They help enzymes do their job better. Pantothenic acid, riboflavin and niacin helps break down fat for energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
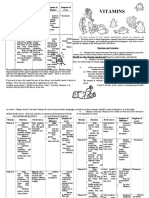
B Vitamins in Energy Metabolism
Energy Metabolism is the process in which the body breaks down nutrients for energy
and build up molecules that are needed for growth, repairing and maintaining the bodys tissues.
B vitamins are cofactors in energy metabolism, which help enzymes do their job better.
Glycolysis
Alanine
(amino acid)
Glucose, the main source of fuel for tissues
and cells, is broken down to pyruvate in the cytosol
Glucose
NAD +
PLP (vitamin B6) is involved in amino acid metabolism.
It has an important role in transamination, which is
making nonessential amino acids. When the body is
starved, it helps convert amino acids to pyruvate in
order to make energy for the body.
NADH
Pyruvate
Dehydrogenase
Complex
Pyruvate
Pyruvate enters the mitochondria, where it is
converted into a smaller molecule, acetyl CoA,
that can enter the TCA cycle for energy
production
NAD +
NADH
TPP (thiamin) activates pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Coenzyme A (pantothenic acid) is the substrate for Acetyl CoA.
Biotin is coenzyme for
pyruvate carboxylase.
Acetyl CoA
**Biotin helps make oxaloacetate,
which is the starting molecule for
the TCA cycle. It is also regenerated
at the end of the cycle.
Fatty acids
PLP
Amino acid
TCA Cycle
Oxaloacetate
NADH
Citrate
NAD +
Each step in this cycle is important to generate
energy from food, especially carbohydrates.
It must always be on to some degree in order
to deliver high-electron intermediate carriers to
the ETC for a constant ow of ATP production,
which is vital to tissues in the body.
NAD +
Acetyl CoA is modied in a series
of reactions to release its energy stored
in the chemical bonds and allow intermediate
carriers to pick up electrons and deliver them
to the electron transport chain
NADH
**Pantothenic acid, riboavin and niacin
helps break down fat for energy.
**Biotin helps make healthy fat in the skin.
FADH2
FAD
Acyl CoA synthetase (derived from
pantothenic acid) activates fatty acids
to enter beta-oxidation. In beta-oxidation,
FAD (riboavin) is coenzyme for acyl-CoA
dehydrogenase and NAD (niacin) is
coenzyme for beta-hydroxyacyl-CoA
dehydrogenase.
Biotin is coenzyme for acetyl CoA carboxylase,
which catalyzes fatty acid synthesis.
NAD +
TPP (thiamin) activates alpha-ketoglutarate
dehydrogenase complex and FAD (riboavin) activates
succinate dehydrogenase. Both are enzymes that facilitate
the next step in TCA cycle.
NADH
**Niacin and riboavin are intermediate electron carriers
that pick up electrons and bring them to the ETC, where
their high-energy electrons drive the making of ATP, the form
of energy that cells can use right away
Electron Transport Chain
Energy carried by the intermediate carriers is
brought to the electron transport chain, where
ATP, a usable form of energy, is made
KEY
TTP - thiamin
FAD - riboavin
NAD - niacin
PLP - vitamin B6
biotin - biotin
CoA - pantothenic acid
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportVon EverandFast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportNoch keine Bewertungen
- RN Pharmacology IV Push ReferanceDokument12 SeitenRN Pharmacology IV Push ReferanceMissK2216Noch keine Bewertungen
- PIN2215 Trigger Point InjectionsDokument3 SeitenPIN2215 Trigger Point InjectionsBob AdleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1097@01 JAA 0000522145 52305 AaDokument2 Seiten10 1097@01 JAA 0000522145 52305 AaAwal Safar M100% (1)
- Vitamin What The Vitamin Does Significant Food Sources B1 (Thiamin)Dokument4 SeitenVitamin What The Vitamin Does Significant Food Sources B1 (Thiamin)Safi BroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin Mineral Reference GuideDokument2 SeitenVitamin Mineral Reference GuideEleni KostaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin Function Food Sources Symptom of Deficiency Symptom of ExcessDokument3 SeitenVitamin Function Food Sources Symptom of Deficiency Symptom of ExcessBimo OmibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fat Soluble: Vitamins and Minerals Vitamins Vitamin Food Sources Health Benefit DeficiencyDokument2 SeitenFat Soluble: Vitamins and Minerals Vitamins Vitamin Food Sources Health Benefit DeficiencyJthan ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Matters Food Additives To AvoidDokument1 SeiteFood Matters Food Additives To AvoidPopescu Bogdan ConstantinNoch keine Bewertungen
- IV Push List PedsDokument5 SeitenIV Push List PedskrizzywhizzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intravenous Nutrient SolutionsDokument28 SeitenIntravenous Nutrient SolutionsElsayed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- AAP Module 9 SupplementDokument20 SeitenAAP Module 9 Supplementmaryelle conejarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parameter: ALT AST Parameter AlbuminDokument2 SeitenParameter: ALT AST Parameter AlbuminJoe-Anne Eliz WillsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFTrigger Point VisualDokument160 SeitenPDFTrigger Point VisualHealingForLife100% (2)
- 13 Antacids and Controllers UpdDokument63 Seiten13 Antacids and Controllers Updone_nd_onlyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition: Vitamin and MineralDokument15 SeitenNutrition: Vitamin and MineralSmkdpb PontianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table Vitamins PDFDokument3 SeitenTable Vitamins PDFthomasqilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals PDFDokument12 SeitenEndocrine Disrupting Chemicals PDFRocco LamponeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mindmap CH 5 Therapeutic ApproachesDokument1 SeiteMindmap CH 5 Therapeutic ApproachesKshitij DasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Mastery: Concepts and Methods From Peter Senge'sDokument21 SeitenPersonal Mastery: Concepts and Methods From Peter Senge'sMuhammad NajeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imaging of UroradiologyDokument32 SeitenImaging of UroradiologyAdib Ul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holistic Therapy Part 1Dokument8 SeitenHolistic Therapy Part 1Engy MoneebNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Appy Holistic Care Talk 24Dokument22 SeitenHow To Appy Holistic Care Talk 24Syifa FatiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1MENIEREDokument6 Seiten1MENIEREsunny_jr_Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine DisruptorsDokument50 SeitenEndocrine DisruptorsSnowangeleyes AngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic EFT Aka Tapping SequenceDokument4 SeitenBasic EFT Aka Tapping Sequences cNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analize LaboratorDokument2 SeitenAnalize LaboratorOana PaduraruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methylation Implications With Periodontal Disease 1 0Dokument107 SeitenMethylation Implications With Periodontal Disease 1 0David DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain Pathways IN HUMANSDokument189 SeitenPain Pathways IN HUMANSAshish VyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nine Types & Their Essential QualitiesDokument2 SeitenThe Nine Types & Their Essential QualitiesSarabjeet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- All About Skull PDFDokument28 SeitenAll About Skull PDFJoel SeradNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 6Dokument14 SeitenCSO Olympiad Book For Class 6harnil trivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders Due To Hormone Deficiency (Hyposecretion) : List of Hormonal DisordersDokument2 SeitenDisorders Due To Hormone Deficiency (Hyposecretion) : List of Hormonal Disordersritik shuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parathyroid GlandsDokument4 SeitenParathyroid GlandsMary Grace Buscargas PolancosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Vitamin D Pathway Genetic Variation and Circulating 25-Hydroxyvitamin D On Cancer Outcome. Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDokument19 SeitenThe Impact of Vitamin D Pathway Genetic Variation and Circulating 25-Hydroxyvitamin D On Cancer Outcome. Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDaniel AriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 03 12 - How-To-Fix-A-Broken-Diet-Infographic-Printer-3Dokument5 Seiten20 03 12 - How-To-Fix-A-Broken-Diet-Infographic-Printer-3sm V15Noch keine Bewertungen
- The - Top - 10 - Mistakes On PeptidesDokument11 SeitenThe - Top - 10 - Mistakes On PeptidesShamusORookeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpermatogenesisDokument31 SeitenSpermatogenesiselzenyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Effects of Prenatal Exposure PCBS, Dioxins, and Other Xenobiotics: Implications For Policy and Future ResearchDokument4 SeitenEndocrine Effects of Prenatal Exposure PCBS, Dioxins, and Other Xenobiotics: Implications For Policy and Future ResearchAgent Orange LegacyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal System: Term Meaning Term Meaning Body NeckDokument7 SeitenSkeletal System: Term Meaning Term Meaning Body NeckLaurel Vida Mentiza OrayleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ankle Block: Dr. S. Parthasarathy MD., DA., DNB, MD (Acu), Dip. Diab. DCA, Dip. Software StatisticsDokument27 SeitenAnkle Block: Dr. S. Parthasarathy MD., DA., DNB, MD (Acu), Dip. Diab. DCA, Dip. Software StatisticsRajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption and AssimilationDokument18 SeitenAbsorption and AssimilationNur Hidayatul Aliaa JustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 Metabolism and EnergyDokument35 Seiten2022 Metabolism and EnergyClaire WeerepasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menopause Symptoms Checklist: Symptom Yes No DetailsDokument1 SeiteMenopause Symptoms Checklist: Symptom Yes No DetailsBibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ankle Block AllyDokument14 SeitenAnkle Block AllyNur Aliah Amirah AmranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resiliency Training Presentation 1Dokument26 SeitenResiliency Training Presentation 1Bello NelsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Im Dude HandoutDokument1 SeiteIm Dude Handoutapi-535001113Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin Chart1Dokument2 SeitenVitamin Chart1api-281864644Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Phases of IV Fluid Therapy FinalDokument29 Seiten4 Phases of IV Fluid Therapy FinalLuqmanul Hakim Junaidden100% (1)
- 2nd Peroxisome Metabolism 20760414Dokument56 Seiten2nd Peroxisome Metabolism 20760414Rawbeena RamtelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic SystemLabDokument7 SeitenLymphatic SystemLabMax DelvalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDokument8 SeitenThoracic Outlet SyndromeJong-soo KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Lecture - Innate Immune Response (2022)Dokument56 SeitenIntegrated Lecture - Innate Immune Response (2022)Nabilah DENoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Disrupters A Threat To Women's HealthDokument5 SeitenEndocrine Disrupters A Threat To Women's Healthjl974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Infectious Disease Nplex ReviewDokument64 SeitenClinical Infectious Disease Nplex ReviewValeria AcevedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book About Cfs Titel Magical-Medicine Source Quelle Www-meactionuk-Org-uk) Magical-medicine-PDF Date 24-February-2010Dokument442 SeitenBook About Cfs Titel Magical-Medicine Source Quelle Www-meactionuk-Org-uk) Magical-medicine-PDF Date 24-February-2010xmrvNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 2-Minute Stress Solution:: 8 Easy Steps To Inner PeaceDokument2 SeitenThe 2-Minute Stress Solution:: 8 Easy Steps To Inner PeaceivandgpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism 4 D Hopeless :) : RemindersDokument22 SeitenMetabolism 4 D Hopeless :) : RemindersAina BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatty Acids SynthesisDokument30 SeitenFatty Acids SynthesisGhaidaa SadeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 9 Lipid MetabolismDokument28 SeitenUnit 9 Lipid MetabolismAthina100% (1)
- Amino Acids Lehninger - Biochemistry 4ed - NVDokument8 SeitenAmino Acids Lehninger - Biochemistry 4ed - NVShanmugapriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ps-2 Grade XII ChemistryDokument1 SeitePs-2 Grade XII Chemistrynishchala knNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dewar BenzeneDokument7 SeitenDewar BenzenechinuasfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To EnymesDokument34 SeitenIntroduction To EnymesMeshal NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry CurrentDokument48 SeitenOrganic Chemistry CurrentBierzo JomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of The Effect of The Temperature of Caustic Tower Operation On Red Oil Formation in Olefin UnitsDokument6 SeitenStudy of The Effect of The Temperature of Caustic Tower Operation On Red Oil Formation in Olefin UnitsLux Olan ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycolysis and Difference Between Aerobic and AnaeDokument12 SeitenGlycolysis and Difference Between Aerobic and Anaepc usageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohols and Phenols Class XII NotesDokument74 SeitenAlcohols and Phenols Class XII NotesAditya BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 233 Biochemistry Quiz 1 CaroroDokument2 SeitenChem 233 Biochemistry Quiz 1 CaroroBritney ClaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interrelationship Between Carbohydrate Protein Fat MetabolismDokument12 SeitenInterrelationship Between Carbohydrate Protein Fat MetabolismShailaja Neaupane100% (5)
- Alkane Test BankDokument16 SeitenAlkane Test BankAgot Barbero NorillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feed Fast CycleDokument19 SeitenFeed Fast Cyclesaraimran54100% (2)
- Protein ChemistryDokument3 SeitenProtein ChemistryAriane Manalo CerezoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholesterol and Human Health: Hongbao@msu - EduDokument5 SeitenCholesterol and Human Health: Hongbao@msu - EduMicki TaryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LipidsDokument48 SeitenLipidsNishamolKSNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEIDokument45 SeitenMEIFebri FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mosaic Model: 1 M.Bregar (Dante C.S.S.)Dokument34 SeitenFluid Mosaic Model: 1 M.Bregar (Dante C.S.S.)Akash ParabNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Introduction To MetabolismDokument6 Seiten2.1 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Introduction To Metabolismlovelots1234100% (1)
- 424 Spectra TablesDokument19 Seiten424 Spectra TablespradeepiitdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 Sup Plastic AddDokument8 Seiten2011 Sup Plastic AddAlexSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicinal Chemistry - II (Natural Products)Dokument4 SeitenMedicinal Chemistry - II (Natural Products)Aranga100% (1)
- Molecular Weight CalculatorDokument9 SeitenMolecular Weight Calculatornil82Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7.carbohydrates and GlycobiologyDokument18 Seiten7.carbohydrates and GlycobiologyTímea TóthováNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pet 4Dokument36 SeitenPet 4Martin GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Work, 217 Questions and Answers - MCQ's Tutorial Work, 217 Questions and Answers - MCQ'sDokument32 SeitenTutorial Work, 217 Questions and Answers - MCQ's Tutorial Work, 217 Questions and Answers - MCQ'syusser77.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nurul Aisyah BT Yusaffendy - 2020628694Dokument8 SeitenNurul Aisyah BT Yusaffendy - 2020628694ainaa' najwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer Additives and PlasticizersDokument25 SeitenPolymer Additives and PlasticizersDeva Raj100% (1)
- 18btc101j Biochem-Unit 1Dokument134 Seiten18btc101j Biochem-Unit 1nikteshgNoch keine Bewertungen
- BenzimidazolDokument145 SeitenBenzimidazolMartinez Fuentes PaulinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antioxidants & Free Radicals Hepatoprotective: DR - Dr.asep Sukohar, M.KesDokument29 SeitenAntioxidants & Free Radicals Hepatoprotective: DR - Dr.asep Sukohar, M.KesDhita Dwi NandaNoch keine Bewertungen