Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
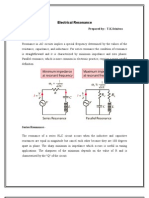
Parallel Resonance
Hochgeladen von
tahia0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
98 Ansichten10 SeitenElectrical circuit 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenElectrical circuit 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
98 Ansichten10 SeitenParallel Resonance
Hochgeladen von
tahiaElectrical circuit 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
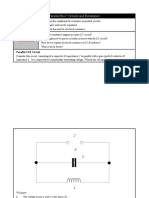
Parallel circuit to series circuit:
Series to parallel:
Parallel resonant circuit has the
Basic configuration as fig. 20.21
Unlike series resonance, impedance is relatively
high at parallel resonance.
For the figure, resonance occurs when =
and resonant frequency has the same format
obtained for series resonance.
Resultant total current will be in phase with the
applied voltage.
Power factor is unity
If there is a resistance in series with an inductor,
it does have an important impact on the parallel
resonant condition.
First effort is to find a parallel
network equivalent for the R-L
branch.
Similar case is for R-C series circuit.
If the susceptances are replaced by their equivalent values,
= 2 2
2 + 2
+
2
1/2
=
2 + 2 2 + 2
Therefore, the quantities that may be varied are L, C, f, and
From =
2 1/2
[
]
2 2
1
, if we solve for :
So, within limits there are definite values of
which will bring the circuit to resonance at
some particular values of f, L, C and .
Also for resonance,
=
2
2
1
2 2
In contrast to series circuit, where resistances
have no part in determining the resonant
frequency, resistances in parallel circuit are of
significant importance.
It can be understood that with a certain current
in capacitive branch, some sufficiently large value
of will prevent a resultant current in inductive
branch from flowing which can be as much as the
current in C-branch even when L=0.
Inserting L will do nothing but make current
smaller.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Parallel Resonance and Parallel RLC Resonant CircuitDokument9 SeitenParallel Resonance and Parallel RLC Resonant CircuitRoboconDKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module7 ResonanceDokument93 SeitenModule7 ResonanceTatsumaki TornadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series Resonance Circuits PDFDokument16 SeitenSeries Resonance Circuits PDFnpavankNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResonanceDokument27 SeitenResonanceAiza GhanchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power FactorDokument13 SeitenPower Factorafnanriaz100% (2)
- Series and Parallel ResonanceDokument15 SeitenSeries and Parallel ResonanceEuric CalityNoch keine Bewertungen
- RLC CircuitDokument9 SeitenRLC CircuitHemangee PurohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series Resonance in A Series Resonant CircuitDokument10 SeitenSeries Resonance in A Series Resonant CircuitProsenjit ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELE 201 - RC CircuitsDokument26 SeitenELE 201 - RC CircuitsIB MasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probsetreso 1Dokument34 SeitenProbsetreso 1Edmark AldeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resonance: University of Babylon Basic of Electrical Engineering Lecture NotesDokument25 SeitenResonance: University of Babylon Basic of Electrical Engineering Lecture NotesSaad AlwashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smith ChartDokument11 SeitenSmith ChartVishalPolowaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resonance CircuitsDokument5 SeitenResonance CircuitsmoooNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE 211 - Lecture Note2Dokument9 SeitenEEE 211 - Lecture Note2ujirhonicholasNoch keine Bewertungen
- FinalProject-Circuits Lab 2Dokument15 SeitenFinalProject-Circuits Lab 2Lynn CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- American International University-Bangladesh Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Title: Analysis of Series ResonanceDokument12 SeitenAmerican International University-Bangladesh Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Title: Analysis of Series ResonanceChowdhury MithilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series ResonanceDokument29 SeitenSeries ResonanceSubhadeep BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication 7 11266 628Dokument25 SeitenPublication 7 11266 628abelndayambekwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of ResonanceDokument4 SeitenApplications of ResonancesrinupidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Basic Elements&PhasorDokument19 SeitenThe Basic Elements&Phasorcontact.hestonNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCA Lab Report 12Dokument12 SeitenLCA Lab Report 12ayleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Lab Assignment: Series and Parallel Resonance CircuitDokument21 SeitenCommunication Lab Assignment: Series and Parallel Resonance CircuitUsama AkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Resonance?: An AC Circuit Containing A Resistor, A Capacitor and An InductorDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Resonance?: An AC Circuit Containing A Resistor, A Capacitor and An InductorKaran SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series Resonance in A Series RLC Resonant CircuitDokument22 SeitenSeries Resonance in A Series RLC Resonant CircuitvenkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical-7 SeriesRLC REsonanceDokument5 SeitenPractical-7 SeriesRLC REsonanceJay SathvaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN - Unit IIIDokument31 SeitenEN - Unit IIIsunnypritam2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 3 SinglePhase AC CctsDokument20 SeitenChap 3 SinglePhase AC CctsbackuponecolosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 - Parallel ResonanceDokument14 Seiten7 - Parallel ResonanceSenjuti DeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Steady State Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis Part 2 1Dokument19 SeitenChapter 3 Steady State Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis Part 2 1temesgen adugnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap1 Lect3Dokument7 SeitenChap1 Lect3Ibraheem MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impedance MatchingDokument19 SeitenImpedance Matchingbharathi83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel RLC Circuits and Resonance: Learning ObjectiveDokument26 SeitenParallel RLC Circuits and Resonance: Learning Objectiveandrew smithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline: Prototype Series and Parallel Resonant CircuitsDokument36 SeitenOutline: Prototype Series and Parallel Resonant CircuitsspandanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Ph AC CircuitsDokument27 Seiten1Ph AC CircuitsChristopher OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RLC NotesDokument4 SeitenRLC Noteskerala pscNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPLM #6 - Resonance and BandwidthDokument60 SeitenSPLM #6 - Resonance and BandwidthSherwin Pagpaguitan100% (1)
- Circuits Resonance: Laguna State Polytechnic University Sta Cruz, LagunaDokument14 SeitenCircuits Resonance: Laguna State Polytechnic University Sta Cruz, Lagunasherina rebongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Resonance Circuit Concepts: Series Resonant Circuits Parallel Resonant CircuitsDokument20 SeitenBasic Resonance Circuit Concepts: Series Resonant Circuits Parallel Resonant CircuitsHardik MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RLC Resonant Circuits: Prepared By: - Zanyar AwezDokument24 SeitenRLC Resonant Circuits: Prepared By: - Zanyar AwezSul SyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resonant Circuits and Mutual Inductances: + V R L CDokument5 SeitenResonant Circuits and Mutual Inductances: + V R L CKodali JayachandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electric Circuit 2 Own SourceDokument6 SeitenFundamentals of Electric Circuit 2 Own SourceLemss DeveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes For BeeDokument15 SeitenNotes For BeeSagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCR Circuits: Learning Objectives of This Experiment Is That Students Will Be Able ToDokument6 SeitenLCR Circuits: Learning Objectives of This Experiment Is That Students Will Be Able ToAryan sahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESO 210 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: Lecture-13 Three Phase AC CircuitsDokument34 SeitenESO 210 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: Lecture-13 Three Phase AC CircuitsAmit MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Circuits-CHDDokument32 SeitenAc Circuits-CHDsalman104alviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2Dokument32 SeitenLab 2AyeshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module2 - RLC and Impedance ConceptDokument74 SeitenModule2 - RLC and Impedance ConceptTatsumaki TornadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series RLC ResonanceDokument2 SeitenSeries RLC ResonanceSreekanth SreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- RLC Series and ParallelDokument8 SeitenRLC Series and ParallelFaizanAshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- The RCL Circuit and Ac Series ResonanceDokument5 SeitenThe RCL Circuit and Ac Series ResonancePrince LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series RLC CircuitDokument15 SeitenSeries RLC CircuitMohan MaheshawariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Basic Concepts - Professor J R Lucas 2.1 Single Phase PowerDokument9 SeitenReview of Basic Concepts - Professor J R Lucas 2.1 Single Phase PowerNormanSulimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEE Modile II Lecture 16Dokument21 SeitenBEE Modile II Lecture 16Jasmine HansdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1. 3Φ TransformersDokument220 Seiten1. 3Φ TransformersKyambi MutiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STD Xii: AC CircuitsDokument22 SeitenSTD Xii: AC CircuitsAmish ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resonance in RLC Series and Parallel Circuit: ObjectivesDokument10 SeitenResonance in RLC Series and Parallel Circuit: Objectivesayesha amjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency Selective NetworksDokument23 SeitenFrequency Selective NetworksRaghu RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE351 Lect4 2020Dokument31 SeitenPE351 Lect4 2020Abdul RazzaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 6Dokument5 SeitenExp 6tahiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 1Dokument4 SeitenExp 1tahiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 5Dokument6 SeitenExp 5tahiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Ramadan PlannerKidsDokument39 SeitenMy Ramadan PlannerKidstahiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Electrical Circuit LabDokument71 SeitenAc Electrical Circuit LabtahiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThesisBook-Chapter 1Dokument6 SeitenThesisBook-Chapter 1tahiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter of Recommendation: Transmission Line Fault Detection Using Android Application Via BluetoothDokument2 SeitenLetter of Recommendation: Transmission Line Fault Detection Using Android Application Via BluetoothtahiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Requisition List - 1002Dokument5 SeitenLab Requisition List - 1002tahiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8Dokument5 SeitenLab 8tahiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Electronics 2 - Exp2Dokument9 SeitenAnalog Electronics 2 - Exp2tahiaNoch keine Bewertungen