Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Strategies To Support Students Learning Project Chart 2
Hochgeladen von
api-313085898Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Strategies To Support Students Learning Project Chart 2
Hochgeladen von
api-313085898Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
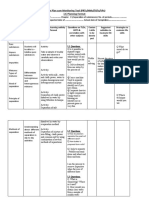
INTELLECTUAL HANDICAP
INTELLECTUAL HANDICAP (CONT)
MODERATE-SEVERE CODE 24
PROFOUND CODE 23 * Support to student must be
MODERATE-SEVERE CODE 24
PROFOUND CODE 23 * Support to student must be
continuous
continuous
1. Ensure that material/task demanded
is at their level
5. Encourage interaction between
students & involve peers as classroom
role models (peer scaffolding from
stronger student, group work/projects)
2. Teach specific strategies & remind
students to apply them (rehearsal,
labeling, chucking, practice, apply, review)
3. Involve students in active learning
process (practice, apply, review, selfmonitoring)
4. Focus on content that is meaningful
to the students (interests and
familiarities of student, scaffolding on
previous knowledge)
6. Emphasize self-reliance (selfmanagement, problem solving, etc.)
7. Create environment that
encourages verbal communication and
interaction with language
8. Provide concrete examples of
instruction in social skills & seek
understanding for inappropriate
behavior (use peer reinforcement)
9. Use technology to support learning
(I-PADS, Computers, etc.)
LEARNING DISABILITIES:
MATHEMATICS
CODE LD (Ex. Dyscalculia)
1. Model correct ways of applying
theories and use a wide range of
examples for students to practice on
2. Give consistent feedback &
establish realistic goals for progress
(providing information about their present
performance and what they need to learn)
3. Monitor progress on weekly basis
(through graphing or visual display so that
student can chart and see how they are
performing)
4. Break tasks down into manageable
parts and provide explicit step-by-step
instructions (problem-solving checklists)
NON-VERBAL LEARNING DISORDER
(NLD)
NON-VERBAL LEARNING DISORDER
(NLD)(CONT)
5. Computer-assistance instruction to
learn arithmetic computation and
problem solving skills (I-PADS ,
Computers, etc.)
LEARNING DISABILITIES: READING
COMPREHENSION
CODE LD
CODE LD
CODE LD (I.e. Dyslexia)
1. Break tasks down into manageable
parts and provide explicit step-by-step
instructions (incremental due dates,
checklists, etc.)
5. Always keep in mind the goal of the
evaluation (do not burden student with
difficulty handwriting when oral response
could be substituted in plan of written
work)
1. Break tasks down into manageable
parts (Use clear objectives, checklists,
incremental due dates)
*These are the students who are likely to follow a
modified program*
2. Teach verbal feedback strategies:
Ask student to repeat directions or
information
Provide structure
Ensure all steps of a task are
understood
3. Capitalize on students strengths to
memorize and absorb
information/material
4. Provide clear outlines that are not
too visually overwhelming
6. Provide student with opportunities
to interact with peers and encourage
leadership roles to instill sense of
responsibility (role-playing, group work)
7. Avoid punitive measures and
replace them with constructive
criticism and clear, consistent
expectations
2. Discuss connections between the
concepts being read and the students
background, interests etc.
3. Inform the students of effective
strategies to use (finding key words,
annotations, self-questioning, summarizing,
story-mapping etc.)
KWL Strategy
Accessing what I Know
Determining what I Want to
know
Recalling what I did Learn
4. Monitor understanding of texts &
performance (gauging questioning using
5 Ws, check homework, communicate with
parents, daily schedule)
5. *IEP includes a reader
INTELLECTUAL HANDICAP
INTELLECTUAL HANDICAP (CONT)
MODERATE-SEVERE CODE 24
PROFOUND CODE 23 * Support to student must be
MODERATE-SEVERE CODE 24
PROFOUND CODE 23 * Support to student must be
continuous
continuous
1. Ensure that material/task demanded
is at their level
5. Encourage interaction between
students & involve peers as classroom
role models (peer scaffolding from
stronger student, group work/projects)
2. Teach specific strategies & remind
students to apply them (rehearsal,
labeling, chucking, practice, apply, review)
3. Involve students in active learning
process (practice, apply, review, selfmonitoring)
4. Focus on content that is meaningful
to the students (interests and
familiarities of student, scaffolding on
previous knowledge)
6. Emphasize self-reliance (selfmanagement, problem solving, etc.)
7. Create environment that
encourages verbal communication and
interaction with language
8. Provide concrete examples of
instruction in social skills & seek
understanding for inappropriate
behavior (use peer reinforcement)
9. Use technology to support learning
(I-PADS, Computers, etc.)
LEARNING DISABILITIES:
MATHEMATICS
CODE LD (Ex. Dyscalculia)
1. Model correct ways of applying
theories and use a wide range of
examples for students to practice on
2. Give consistent feedback &
establish realistic goals for progress
(providing information about their present
performance and what they need to learn)
3. Monitor progress on weekly basis
(through graphing or visual display so that
student can chart and see how they are
performing)
4. Break tasks down into manageable
parts and provide explicit step-by-step
instructions (problem-solving checklists)
PHYSICAL DISABILTIIES GENERAL
STRATEGIES
PHYSICAL DISABILTIIES LEARNING
STRATEGIES
5. Computer-assistance instruction to
learn arithmetic computation and
problem solving skills (I-PADS ,
Computers, etc.)
LEARNING DISABILITIES: WRITTEN
EXPRESSION
SEVERE-MOTOR DEFICIENCY CODE 36
SEVERE-MOTOR DEFICIENCY CODE 36
Code LD (I.e. Dysgraphia)
* Support to student must be continuous
* Support to student must be continuous
*These are the students who are likely to follow a
modified program*
MOTOR OR ORGANIC IMPAIRMENT CODE 33
1. Prepare students for entry/re-entry
of fellow student who has sustained
motor or organic impairment(s)
discuss any changes in physical functioning
or personality
2. Modify classroom to ensure safety
and address specific needs of the
student
3. Minimize visual and auditory
distractions that may interfere with
attention to task
4. Be familiar with specific equipment
that might be needed (communicative
devices, wheelchair, etc.)
5. Be familiar with effects and
administration procedures of
prescribed medications
MOTOR OR ORGANIC IMPAIRMENT CODE 33
1. Use a multimodal approach
(overheads, videos, hands-on activities)
when presenting instructions
2. Teach/allow students to use
different strategies to help with their
physical condition (font size, desk size
checklists, etc.)
3. Emphasize key points in instruction
(repetition, use prompts, cues)
5. Break down tasks into steps
(incremental due dates, checklists etc.)
6. Ensure student is included in all
activities to whatever extent possible
(group work, co-operative learning)
1. Teach students how to plan out and
write down their ideas
(planning/brainstorming sheet, outline,
graphic organizers, sticky notes)
2. Give consistent feedback on written
work
3. Have student revise and edit work
before submitting it (peer-editing
checklist, communicate with parents the
strategy of reading students work before
they submit it)
4. Imitate and model the correct way
of spelling or structuring sentence
(students compare incorrect words with
correct words in order to remember)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- 3shape Grammars1Dokument94 Seiten3shape Grammars1OSHIN BALASINGH100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Top 10 Best Medical Schools in The PhilippinesDokument15 SeitenTop 10 Best Medical Schools in The PhilippineshandyatamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Module 4 Critical ThinkingDokument9 SeitenModule 4 Critical Thinkingapi-265152662Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Visible ThinkingDokument2 SeitenVisible Thinkingorellnairma88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Teacher Evaluation Records for Magarao-Bombon DistrictDokument11 SeitenTeacher Evaluation Records for Magarao-Bombon DistrictRey Albino83% (6)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Detailed Lesson Plan inDokument7 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan inEmieVillafloresMolina100% (1)
- Mestizo Racism in EcuadorDokument20 SeitenMestizo Racism in EcuadorCamilo Andrés Ávila Ceballos100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Group VideoDokument2 SeitenGroup Videoapi-294800788100% (2)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- ARTICLEDokument2 SeitenARTICLEIasmi IasminaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Accreditation and CertificationDokument6 SeitenAccreditation and Certificationesprote buzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Prelude To Mapping The Practice of Process DramaDokument13 SeitenA Prelude To Mapping The Practice of Process DramaDespina KalaitzidouNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Human SciencesDokument4 SeitenSchool of Human Sciencesnm.nandita5938Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Lesson Plans For 3-6 3-10Dokument2 SeitenLesson Plans For 3-6 3-10api-653098428Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Fins3635 Options Futures and Risk Management Techniques s12012 (February 23)Dokument12 SeitenFins3635 Options Futures and Risk Management Techniques s12012 (February 23)aunglinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Chapter 5Dokument2 SeitenChapter 5iqra mehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- SMEA-Form Class-Adviser 4th QDokument7 SeitenSMEA-Form Class-Adviser 4th QDaryl RagasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Political Concepts and Agricultural EducationDokument4 SeitenPolitical Concepts and Agricultural EducationJay R ChivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: 6 Mathematics 7 3rd 90 December 12, 2017Dokument5 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: 6 Mathematics 7 3rd 90 December 12, 2017Sheryl Mendoza LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShamaDokument1 SeiteShamajjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Students' problems in English speaking and strategies to overcome themDokument48 SeitenStudents' problems in English speaking and strategies to overcome themAmal DhainyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReflectionDokument12 SeitenReflectionimran acopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Science Classroom Becoming An Elementary Middle School Science Teacher 1st Edition Goldston Test Bank PDFDokument6 SeitenYour Science Classroom Becoming An Elementary Middle School Science Teacher 1st Edition Goldston Test Bank PDFa433484312Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experienced Training Professional Seeking New OpportunityDokument2 SeitenExperienced Training Professional Seeking New OpportunityahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Scanning Exercise Alifa Nuzul NabilaDokument3 SeitenScanning Exercise Alifa Nuzul NabilaAlifa Nuzul NabilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae of (Name) : Personal InformationDokument4 SeitenCurriculum Vitae of (Name) : Personal InformationataqueesquimalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Performance of Feu Pre-Service Sped Teachers in Ie-Formulated Comprehensive Examination and Its InfluenceDokument10 SeitenThe Performance of Feu Pre-Service Sped Teachers in Ie-Formulated Comprehensive Examination and Its InfluenceStephanie GañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 58 Circular 2021Dokument2 Seiten58 Circular 2021Chitman SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposed Three-Storey School Building The Problem and Its Setting 1Dokument4 SeitenProposed Three-Storey School Building The Problem and Its Setting 1Jeffry VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Spelling Homework 3rd GradeDokument6 SeitenSpelling Homework 3rd Gradeafnaxdxtloexll100% (1)
- "Picturing Poetry": Grade Level/Subject: Targeted: CCSS - ELA-Literacy - RL.6.7Dokument4 Seiten"Picturing Poetry": Grade Level/Subject: Targeted: CCSS - ELA-Literacy - RL.6.7api-290076952Noch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)