Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
H81Hmt Example Sheet 6 (Radiation)
Hochgeladen von
Xiao ThAmOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
H81Hmt Example Sheet 6 (Radiation)
Hochgeladen von
Xiao ThAmCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
H81HMT EXAMPLE SHEET 6 (RADIATION)
1. Based on slide 30 and 31 in the lecture notes, derive the expression Q12 for
a. Large (infinite) parallel planes
b. Long (infinite) concentric cylinders
c. Small convex object in a large cavity
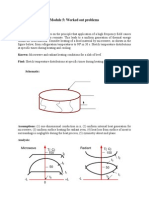
2. A heated plate of D = 0.2 m diameter has one of its surfaces insulated and the other is
maintained at T = 550 K. If the hot surface has an emmissivity of 0.9 and is exposed
to a surrounding area at 300K, calculate the heat loss by radiation. [Ans: 131.9W]
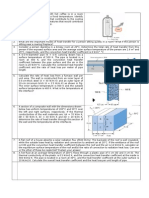
3. A fluid flows through a long tube of 20mm diameter with outer surface at 77K and
= 0.02. The tube is concentric with a larger tube of 50 mm diameter at 300K and =
0.05. The space between the surfaces is evacuated. Calculate the heat transfer rate by
the fluid per unit length of the tube. [Ans: -0.5 W/m]
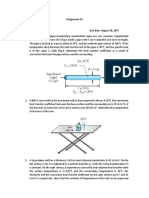
4. The following diagram shows a sphere placed inside a large oven.
Taking into account of heat convection, calculate the net heat transfer to the sphere when
its temperature is 300K. What is the major assumption used in this calculation [19.85 W]?
5. A procedure for measuring the thermal conductivity of solid can be done by placing a
sample at the bottom of a large furnace (see below). The sample is of thickness L and
is placed in a square container of width W on a side and the sides are insulated. The
wall of the furnace is maintaned at Tw. Neglecting convection effects, under steady
state condition, determine the thermal conductivity of the solid [2.93 W/m.k].
Sides insulated
300K
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Files-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315Dokument44 SeitenFiles-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315AndrestorpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Files-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315Dokument44 SeitenFiles-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315TortelliniTimNoch keine Bewertungen
- HT Notes For ESEDokument25 SeitenHT Notes For ESEM BhurleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mee40001 Thermodynamics 2 / Semester 2 2017 Assignment 1 DUE DATE: 25.09.2017 Mark: 5 % of Final Mark Answer All QuestionsDokument1 SeiteMee40001 Thermodynamics 2 / Semester 2 2017 Assignment 1 DUE DATE: 25.09.2017 Mark: 5 % of Final Mark Answer All QuestionsAndy NgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass Transfer 2011-Midterm Solutions FinalDokument11 SeitenHeat and Mass Transfer 2011-Midterm Solutions FinalJaspreet SandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIN-305 Heat & Mass Transfer Tutorial - 8Dokument2 SeitenMIN-305 Heat & Mass Transfer Tutorial - 8Akhilesh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHG 2314 Heat Transfer Operations Winter 2012: Assignment 3Dokument3 SeitenCHG 2314 Heat Transfer Operations Winter 2012: Assignment 3Clinton OkereNoch keine Bewertungen
- End-Semester Question PaperDokument4 SeitenEnd-Semester Question PaperRabey The physicistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 7Dokument4 SeitenAss 7Puneet MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.tutorial HMTDokument5 Seiten4.tutorial HMTdearsaswatNoch keine Bewertungen
- HT AssignDokument2 SeitenHT AssignSai Chand Arkham KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass Transfer QuizDokument7 SeitenHeat and Mass Transfer Quizdsathiya0% (1)
- Mae 3314 HW 4Dokument1 SeiteMae 3314 HW 4john_andrews_1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- (An Autonomous Institute Under VTU) Manandavadi Road, Mysore-570008, Karnataka, IndiaDokument2 Seiten(An Autonomous Institute Under VTU) Manandavadi Road, Mysore-570008, Karnataka, IndiaMohammed Maaz100% (1)
- Second AssignmentDokument2 SeitenSecond AssignmentNitish NehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 2-Heat ConductionDokument4 SeitenExample 2-Heat Conductionqusai almshaqbehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D EDokument4 SeitenHeat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D ERotten AppleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4363 112 Heat TransferDokument6 Seiten4363 112 Heat Transferyogesh_b_kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1 Schematic of A Hair DryerDokument2 SeitenFigure 1 Schematic of A Hair DryerIcy45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument7 SeitenAssignment 1AdarshpatankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution of Transient 2D Heat Conduction Problem Using Freefem++Dokument4 SeitenSolution of Transient 2D Heat Conduction Problem Using Freefem++Chicca PantanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial SheetDokument5 SeitenTutorial Sheetpradeep.kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2-1Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 2-1chandan rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 HMTDokument7 SeitenAssignment 1 HMTAnkit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- We M5Dokument14 SeitenWe M5knyogishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Donnee Exo SupplDokument5 SeitenDonnee Exo SupplMohamud LhafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios TransferenciaDokument5 SeitenEjercicios TransferenciaPablo RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Dokument4 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Guru PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMT Tutorial 1Dokument3 SeitenHMT Tutorial 1mofoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated ProblemsDokument3 SeitenUpdated Problemsmahmoud koriemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A03505 Heat TransferDokument4 Seiten9A03505 Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Exam.2.2Dokument3 SeitenModel Exam.2.2Srinivasan PichandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass Transfer Unit - I: 2 Conductivity 0 0Dokument14 SeitenHeat and Mass Transfer Unit - I: 2 Conductivity 0 0Christopher MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer AssinmentDokument4 SeitenHeat Transfer AssinmentbaruaoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Problem Sheet PDFDokument3 SeitenHeat Transfer Problem Sheet PDFDerek101johnson100% (1)
- Assignment 01Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 01Adan SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass Transfer WorksheetDokument5 SeitenHeat and Mass Transfer WorksheetBISRAT YIHUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam EditedDokument2 SeitenExam Editedsaad alzubedyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1-13 PDFDokument27 SeitenTutorial 1-13 PDFPavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Qtns HT 1Dokument61 SeitenBig Qtns HT 1Pranay TinkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial - 2 Steady State Heat Conduction: at K KDokument2 SeitenTutorial - 2 Steady State Heat Conduction: at K KDr. Santosh BopcheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer II Mid QPDokument2 SeitenHeat Transfer II Mid QPRambabuDaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems On RadiationDokument3 SeitenProblems On RadiationSuraj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 HT Assignment 01 2023 24 IisemDokument2 Seiten13 HT Assignment 01 2023 24 IisemrakiravaishuNoch keine Bewertungen
- To UploadDokument2 SeitenTo Uploadsmg26thmayNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDB3033 - Heat TransfersDokument8 SeitenMDB3033 - Heat TransfersKamarul Aiman ShariffuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 HEATDokument1 SeiteAssignment 1 HEATDevesh RehanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TransferDokument6 SeitenHeat Transferkevinjorgeramos100% (1)
- Heat Transfer (HT) QueDokument6 SeitenHeat Transfer (HT) QueAshutosh KushwanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HT Pyq SolvedDokument11 SeitenHT Pyq Solveddatirshreya6Noch keine Bewertungen
- MEL301 Heat and Mass Transfer Tutorial Sheet #2Dokument5 SeitenMEL301 Heat and Mass Transfer Tutorial Sheet #2PeeyushiRaghavNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW3Dokument1 SeiteHW3cathycathycheung KA MANNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME311 Assignment 1 ConductionDokument4 SeitenME311 Assignment 1 ConductionPradumn DixitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8S 2105 Mepc22 1Dokument2 Seiten8S 2105 Mepc22 1Challa YachendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Von EverandSteam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Noch keine Bewertungen
- PsychodramaDokument5 SeitenPsychodramaAkhila R KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Souvenir Mushrooms 1986Dokument106 SeitenSouvenir Mushrooms 1986Ankit MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation and Comparison of Highly Soluble Sodium Stearyl Fumarate With Other Lubricants in VitroDokument8 SeitenEvaluation and Comparison of Highly Soluble Sodium Stearyl Fumarate With Other Lubricants in VitroSvirskaitė LaurynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSE TBT Schedule - Apr 2022Dokument1 SeiteHSE TBT Schedule - Apr 2022deepak bhagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wrestling Strength and ConditioningDokument12 SeitenWrestling Strength and ConditioningTintin BilatbatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kristen Swanson's Theory of CaringDokument12 SeitenKristen Swanson's Theory of CaringAlexandria David50% (2)
- IJARIE Paper 17936 PDFDokument7 SeitenIJARIE Paper 17936 PDFArbelyn RoblesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nato Code Numbers: Scope of ListDokument6 SeitenNato Code Numbers: Scope of ListRain HeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 TitrimetryDokument7 Seiten04 TitrimetryDarwin Fetalbero ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENG 110-Task 4 (Unintended Messages)Dokument2 SeitenENG 110-Task 4 (Unintended Messages)Erika Noreen Dela RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Showalter Female MaladyDokument13 SeitenShowalter Female MaladyKevin Sebastian Patarroyo GalindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- African Traditional Medicine A PrimerDokument5 SeitenAfrican Traditional Medicine A PrimerEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wound Dressing ChecklistDokument3 SeitenWound Dressing ChecklistBUAHIN JANNA100% (1)
- CV TemplateDokument5 SeitenCV TemplateLopezDistrict FarmersHospitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Grass Cutter MachDokument21 SeitenSolar Grass Cutter MachAnonymous I13s99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pinoy Ree - EeDokument138 SeitenPinoy Ree - EeChilvin ChipmunkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respirator LangmanDokument10 SeitenRespirator LangmanSavu MalinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Cholesterol DietDokument10 SeitenLow Cholesterol Dietkevintotz73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ocean StarDokument36 SeitenOcean Starrobertshepard1967Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nutritional Classification of BacteriaDokument7 SeitenNutritional Classification of BacteriaRalphpinno SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOCDokument14 SeitenTOCAthirah HattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FPGA-based System For Heart Rate Monitoring PDFDokument12 SeitenFPGA-based System For Heart Rate Monitoring PDFkishorechiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Liberal Policy ResolutionsDokument86 Seiten2016 Liberal Policy ResolutionsCPAC TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Destructive & Nondestructive TestingDokument38 SeitenIntroduction To Destructive & Nondestructive Testingshubham sinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SwivelDokument29 SeitenSwivelluisedonossaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSA11 CholelithiasisDokument3 SeitenCSA11 CholelithiasisBerlon LacsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tips To Diagnose & Address Common Horse AilmentsDokument6 SeitenTips To Diagnose & Address Common Horse AilmentsMark GebhardNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Prosecution of Kim Jong Il - Accountability in A Post 9-11 WorldDokument21 SeitenThe Prosecution of Kim Jong Il - Accountability in A Post 9-11 WorldimpunitywatchNoch keine Bewertungen
- RSA 12 - Laser Attacks Safety GuidelinesDokument19 SeitenRSA 12 - Laser Attacks Safety Guidelinesrona putriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draw-Through or Blow-Through: Components of Air Handling UnitDokument23 SeitenDraw-Through or Blow-Through: Components of Air Handling Unityousuff0% (1)