Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Introduction Lab 1
Hochgeladen von
AmeerRashid0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
21 Ansichten2 Seitencc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldencc
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
21 Ansichten2 SeitenIntroduction Lab 1
Hochgeladen von
AmeerRashidcc
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
INTRODUCTION
Gaseous diffusivity or gas dispersion apparatus, which involves diffusion with
bulk flow, is one of the laboratory equipment that have been designed to allow
measurement of molecular diffusivities. From this model, it will make the students
become more familiar with the basic notions or concepts of mass transfer theory. This
apparatus is a bench mounted apparatus for the determination of diffusion coefficients of
a vapour in air, which uses the method of measuring the rate of evaporation of a liquid
through a stagnant layer into a flowing air stream, comprising a precision bore capillary
tube, which may be filled from a syringe and the top of which means are provided to pass
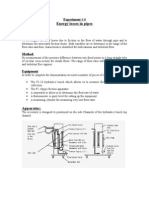
air (or an inert gas) stream to remove vapour. The apparatus also consist an air pump, a
travelling microscope with accurate focus adjustment and mounted for vertical axis
movement against a Vernier scale and a thermostatically controlled water bath, in which
to place the capillary tube, capable of accurate temperature control.
Figure 1: Gas Diffusion Apparatus
The experimental capabilities of this apparatus are direct measurement of mass
transfer rates in the absence convective effects. Gas laws was used to calculate
concentrations differences in terms of partial pressures while Ficks Law was used to
measure diffusion coefficients in the presence of a stationary gas, measurement of the
effect of temperature on diffusion coefficients and gaining familiarity with the use of
laboratory instruments to achieve accurate measurements of data required for industrial
process design.
The diffusivity of the vapour of a volatile liquid in air can be conveniently
determined by Winklemanns method in which liquid is contained in a narrow diameter
vertical tube, maintained at a constant temperature, and an air stream is passed over the
top of the tube to ensure the partial pressure of the vapour is transferred from the surface
of the liquid to the air stream by molecular diffusion. The molecular diffusivity, D, is a
kinetic parameter associated with static and dynamic conditions of a process. All the
complexity and unwieldiness of many calculations is, indeed, connected with the
determination of this quantity.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Osmosis Beaker KeyDokument2 SeitenOsmosis Beaker Keyapi-26466818259% (44)
- Bernoulli's Principle Demonstration (Lab Report)Dokument17 SeitenBernoulli's Principle Demonstration (Lab Report)Arey Ariena94% (110)
- Experiment 3 Bernoulli's TheoremDokument26 SeitenExperiment 3 Bernoulli's TheoremSaber Minato Azrul100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Heat IntegrationDokument25 SeitenChapter 3 - Heat IntegrationAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Testing of CheckvalveDokument10 SeitenDynamic Testing of Checkvalveamirthraj74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report For Venturi MeterDokument9 SeitenLab Report For Venturi MeterRichard Puni89% (44)
- Energy Losses in Pipes: Experiment # 4Dokument4 SeitenEnergy Losses in Pipes: Experiment # 4محمد جوادNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calibration of An Orifice Plate Flow Meter (Fluid Exp 8)Dokument7 SeitenCalibration of An Orifice Plate Flow Meter (Fluid Exp 8)hayder alaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruments Training & Calibration PDFDokument95 SeitenInstruments Training & Calibration PDFSreedhar PayyavulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Instrumentation in RefineryDokument15 SeitenBasic Instrumentation in RefinerySahil SahniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banan Fiber PDFDokument19 SeitenBanan Fiber PDFtulasi saladiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Distillation ProcessDokument6 SeitenBasic Distillation ProcessAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bernoulli S Principle Demonstration Lab ReportDokument17 SeitenBernoulli S Principle Demonstration Lab ReportpehweihaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gaseous Diffusion CoefficientDokument17 SeitenGaseous Diffusion CoefficientAddiaAzizan93% (14)
- Bernouli's Theorem DemonstrationDokument14 SeitenBernouli's Theorem DemonstrationAlohaaSwezzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Air Flow in The ChannelDokument7 SeitenDetermination of Air Flow in The ChannelAmalinaAznanNoch keine Bewertungen
- H9 User Manual A3Dokument88 SeitenH9 User Manual A3Michael Tanglao0% (1)
- Blending of Coals in Power StationsDokument20 SeitenBlending of Coals in Power StationsPankaj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract/SummaryDokument6 SeitenAbstract/SummaryZati TarhiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion CompileDokument11 SeitenDiffusion CompileSharing CaringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Transfer Lab.: Name: Mohammed Sobhi Anoon No. Experiment: 1 DataDokument14 SeitenMass Transfer Lab.: Name: Mohammed Sobhi Anoon No. Experiment: 1 DataMohammed AlkhafajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planner - Lab Gas DiffusionDokument5 SeitenPlanner - Lab Gas DiffusionJames EdwardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty of Engineering and Green Technology Bachelor of Engineering (HONS) Petrochemical EngineeringDokument9 SeitenFaculty of Engineering and Green Technology Bachelor of Engineering (HONS) Petrochemical EngineeringDevakan BalaganeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No.4: Venturi Meters Che 34 (Novermber 14,2016)Dokument4 SeitenExperiment No.4: Venturi Meters Che 34 (Novermber 14,2016)Kenneth AndrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Diffusion ExperimentDokument18 SeitenGas Diffusion ExperimentMuhammad NasrulNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB (Bernoulli's Theorem Demonstration)Dokument26 SeitenLAB (Bernoulli's Theorem Demonstration)Nurul AinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Regime Identification in A Two-Phase Flow Using Wavelet TransformDokument9 SeitenFlow Regime Identification in A Two-Phase Flow Using Wavelet TransformMuammer AlssayhNoch keine Bewertungen
- VenturimeterDokument24 SeitenVenturimeterYashArnatNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTIONDokument26 SeitenINTRODUCTIONFatimah Rahima JingonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Flow MeterDokument4 SeitenIntroduction Flow MeterohdausNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level SystemDokument6 SeitenLevel SystemMervin GautaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 5Dokument2 SeitenExpt 5The Banana-agNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Report F3: Coefficient of Difusivity: ObjectivesDokument7 SeitenLaboratory Report F3: Coefficient of Difusivity: ObjectivesCristhianRondónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment: Flow Tthrough Venturi MeterDokument4 SeitenExperiment: Flow Tthrough Venturi MeterMuhammadZAmjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 51 Me Lab 1Dokument8 Seiten51 Me Lab 1John Paul MorilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Permeability, Diffusivity and Solubility of Nitrogen, Helium, Methane, CO2, CH2O in Dense Polymeric Membranes Using A New On-Line Permeation ApparatusDokument12 SeitenGas Permeability, Diffusivity and Solubility of Nitrogen, Helium, Methane, CO2, CH2O in Dense Polymeric Membranes Using A New On-Line Permeation ApparatusCinthiaCevallosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coeficientes de DifusiónDokument12 SeitenCoeficientes de DifusiónAyrton BriceñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Lab 3Dokument3 SeitenMass Lab 3hamza A.laftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids: Experimental Study of A Gas-Liquid Flow in Vacuum Air-Lift Column Using An Optical Bi-ProbeDokument18 SeitenFluids: Experimental Study of A Gas-Liquid Flow in Vacuum Air-Lift Column Using An Optical Bi-ProbeRohan PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument5 Seiten2Lawrence De LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)Dokument19 SeitenInternational Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)International Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Validation of Custody Transfer Metering Skid at Site After Laboratory ProvingDokument8 SeitenValidation of Custody Transfer Metering Skid at Site After Laboratory Provingkamala 123Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Method For Particle Size Amplification by Water Condensation in A Laminar Thermally Diffusive FlowDokument10 SeitenA Method For Particle Size Amplification by Water Condensation in A Laminar Thermally Diffusive FlowoksanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Diffusion UnitDokument20 SeitenGas Diffusion Unitsolehah misniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACT 6 Venturi GRP 1Dokument8 SeitenACT 6 Venturi GRP 1Michael Alex MabaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wetted Wall Column AssignDokument3 SeitenWetted Wall Column AssignMuhammad MubasherNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Multiphase Flow: H. Shaban, S. TavoularisDokument12 SeitenInternational Journal of Multiphase Flow: H. Shaban, S. TavoularisAkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bernoulli's Theorem: TitleDokument3 SeitenBernoulli's Theorem: TitleShahiera ShafieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab1 - Verification of Bernoullis PrincipleDokument20 SeitenLab1 - Verification of Bernoullis PrincipleAbenezer Tasew0% (1)
- Experiment - Flow Through Porous Medium (Darcy's Law Apparatus)Dokument5 SeitenExperiment - Flow Through Porous Medium (Darcy's Law Apparatus)Piyush AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Wire Mesh Sensor As A Two-Phase Flow MeterDokument33 SeitenThe Wire Mesh Sensor As A Two-Phase Flow MeterHassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid LABDokument9 SeitenFluid LABKayfe sayfadeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Level MeasurementDokument15 Seiten1-Level MeasurementAhmed KamelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty of Chemical EngineeringDokument32 SeitenFaculty of Chemical EngineeringArif HanafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure TransducersDokument7 SeitenPressure Transducersaem2070Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 (Thermofluids Lab)Dokument32 SeitenLab 4 (Thermofluids Lab)Adnan Nanda0% (1)
- Farmacopeea Europeana Ed. 10 Cap. 2. 2. 28.Dokument2 SeitenFarmacopeea Europeana Ed. 10 Cap. 2. 2. 28.Alex-Bogdan VișaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLOW METER DEMONSTATION ReportDokument15 SeitenFLOW METER DEMONSTATION ReportAbenezer TasewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Permeability Specific SurfaceDokument3 SeitenAir Permeability Specific SurfaceYourMotherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids Laboratory:) Venture Meter (Dokument8 SeitenFluids Laboratory:) Venture Meter (aulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Dozen Ways To Measure Fluid Level and How They Work - SensorsDokument14 SeitenA Dozen Ways To Measure Fluid Level and How They Work - SensorsmeetsushelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flowmeter DEMONSTRATIONDokument20 SeitenFlowmeter DEMONSTRATIONAfiq IkhwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wet Wall AbsorptionDokument11 SeitenWet Wall Absorptionhagt813Noch keine Bewertungen
- Respiration Calorimeters for Studying the Respiratory Exchange and Energy Transformations of ManVon EverandRespiration Calorimeters for Studying the Respiratory Exchange and Energy Transformations of ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrothermal Analysis in Engineering Using Control Volume Finite Element MethodVon EverandHydrothermal Analysis in Engineering Using Control Volume Finite Element MethodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeram Landfill - Chapter 8Dokument32 SeitenJeram Landfill - Chapter 8AmeerRashid100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Solid WasteDokument2 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Solid WasteAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feedforward PDFDokument21 SeitenFeedforward PDFAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multivariable Control SystemDokument39 SeitenMultivariable Control SystemAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline Thesis 25 Sep 2017Dokument60 SeitenGuideline Thesis 25 Sep 2017AmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Project QuestionDokument1 SeiteMini Project QuestionAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Aim of This Experiment 1 Is To Differentiate Between Plant Cell and Animal CellDokument1 SeiteThe Aim of This Experiment 1 Is To Differentiate Between Plant Cell and Animal CellAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 5 - Tracing Chemicals Tru PFDDokument14 SeitenCHAPTER 5 - Tracing Chemicals Tru PFDAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 - HeuristicsDokument40 SeitenChapter 11 - HeuristicsAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,990,074: Gross Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999Dokument5 SeitenUnited States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,990,074: Gross Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999AmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Kamariah EH2214A GRP 5 N 6Dokument4 SeitenDR Kamariah EH2214A GRP 5 N 6AmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE555 Procedure Lab 2Dokument9 SeitenCHE555 Procedure Lab 2AmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 PolymersDokument17 SeitenChapter 7 PolymersAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- LabReport Gas DiffusionDokument21 SeitenLabReport Gas DiffusionAmeerRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019.01.28 - HUSSEIN - ZPhys - Chem - Physico-Chem AuCu Clusters - SUpporting InformationDokument19 Seiten2019.01.28 - HUSSEIN - ZPhys - Chem - Physico-Chem AuCu Clusters - SUpporting InformationAlejandra AwimbaweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Komposit UHMWPE Sebagai Alternatif Bantalan Rel Kereta Api: Abel Evan, Alia Kristika, Farid Mulia LatiefDokument11 SeitenKomposit UHMWPE Sebagai Alternatif Bantalan Rel Kereta Api: Abel Evan, Alia Kristika, Farid Mulia LatiefAlia KristikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vt-420 Vitalband: Bitumen Flashing TapeDokument1 SeiteVt-420 Vitalband: Bitumen Flashing Tapesakha abdussalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- JURNAL FixxDokument8 SeitenJURNAL FixxNci Ncisri.mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Chemical Engineering For Renewable EnergyDokument16 SeitenRole of Chemical Engineering For Renewable EnergyAayush KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wbi11 01 Que 20240109Dokument28 SeitenWbi11 01 Que 20240109tongshuo066Noch keine Bewertungen
- Defoamer PDFDokument3 SeitenDefoamer PDFEveline PatriciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.physical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WaterDokument203 Seiten1.physical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WaternikhilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science Summative Exam. First QuarterDokument5 SeitenPhysical Science Summative Exam. First QuarterIsagani WagisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics NotesDokument5 SeitenThermodynamics NotesRaheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM D6209-98 Determination of Gaseous and Particulate Policyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient AirDokument14 SeitenASTM D6209-98 Determination of Gaseous and Particulate Policyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient AirFredi Cari CarreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fosroc Product GuideDokument194 SeitenFosroc Product GuideinbarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iplex GuideDokument70 SeitenIplex GuidebalotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Af 163-2Dokument10 SeitenAf 163-2lacsmm982Noch keine Bewertungen
- GUID - 9 en-USDokument9 SeitenGUID - 9 en-USrx bafnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination Compounds Theory Sheet-244 PDFDokument36 SeitenCoordination Compounds Theory Sheet-244 PDFJatin SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Pharmaceutics Lecture NotesDokument64 SeitenIntegrated Pharmaceutics Lecture NotesSolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSC CGL Model Paper - 17 Solution PDFDokument7 SeitenSSC CGL Model Paper - 17 Solution PDFsandeep kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 3: Naming Compounds: Chapter 5: Molecules and CompoundsDokument21 SeitenSection 3: Naming Compounds: Chapter 5: Molecules and CompoundsCheri BulahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Armstrong Electric Single Point and Retrofi T Purger Installation and Operation ManualDokument16 SeitenArmstrong Electric Single Point and Retrofi T Purger Installation and Operation ManualCALGERINoch keine Bewertungen
- Edited PPT On Carboxylic AcidDokument51 SeitenEdited PPT On Carboxylic AcidRenante DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- E7215 2 11 16 - WHC KatalogversionDokument4 SeitenE7215 2 11 16 - WHC KatalogversionQuy HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Processes: Performance Comparison of Industrially Produced Formaldehyde Using Two DiDokument12 SeitenProcesses: Performance Comparison of Industrially Produced Formaldehyde Using Two DiMohammed FaiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydroscout Manual E34 Revision 3Dokument21 SeitenHydroscout Manual E34 Revision 3Omar Ernesto EscuderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SyllabusDokument4 SeitenSyllabusemhufafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Regarding Types of PlasticsDokument2 SeitenQuestion Regarding Types of PlasticsFadhlul HadiNoch keine Bewertungen