Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Poverty and Brain Development Flow Chart
Hochgeladen von
api-316442609Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Poverty and Brain Development Flow Chart
Hochgeladen von
api-316442609Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
POVERTY AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT CONCEPT MAP/ FLOW CHART REVISED
Poverty and Brain Development Concept Map/ Flow Chart Revised
Haleigh Hudson
University of St. Thomas
Running Head: POVERTY AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT CONCEPT MAP/ FLOW CHART REVISED
Poverty and Brain Development Concept Map/ Flow Chart Revised
I chose to revise my poverty and brain development concept map/ flow chart. Although the critique I received was excellent, I
felt like I needed to revise this concept map because the information needed to become more visually professional as well as be
explained more thoroughly, and also, I needed to make the concept map/ flow chart more concise in its purpose. The original concept
map/ flow chart is the first one in the document, and the revised concept map/ flow chart is the second one in the document.
The first thing I wanted to do was make the concept map more visually appealing to the reader. Although the original one
seemed to flow easily, it seemed very simple. I felt that it was too simple. I added more elaborated components and points to the
second concept map. The second concept map takes the specific points a little further, but it is still easy to read and follow. I also
changed the shapes on the second map, so the map would appear more professional.
The second thing I wanted to do in revising the concept map/ flow chart was reference the specific articles I received my
information from as I did not do this in the original work. I wanted the reader to know the specific names of both of the articles in
case the reader wanted to read the original articles in their entirety.
Thirdly, I wanted to include more specific statistics in my second concept map/ flow chart as well as provide more detail
regarding specific reasoning brought up in the original articles. When I went back and studied the first work, I noticed that I only
included statistics from the article Brain Scans Reveal How Poverty Hurts Childrens Brains. In the second concept map I added
Running Head: POVERTY AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT CONCEPT MAP/ FLOW CHART REVISED
data relating to how children from poor families scored on standardized tests. This information came from the article Association of
Child Poverty, Brain Development, and Academic Achievement.
Finally, I wanted the concept map to be more finished and have the overall conclusions tied together from both articles. In my
original concluding point from the first map, I used information from the article Brain Scans Reveal How Poverty Hurts Childrens
Brains. The other article, Association of Child Poverty, Brain Development, and Academic Achievement, provided a final thought
of how to avoid the impacts of poverty on brain development and achievement.
My second concept map/ flow chart is much more developed, and I didnt rely too much on the information from just one
article. I took the topic discussed in both articles and provided the information in a concept map/ flow chart that is engaging to the
reader, is easy to follow, and is informational and educable.
Running Head: POVERTY AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT CONCEPT MAP/ FLOW CHART REVISED
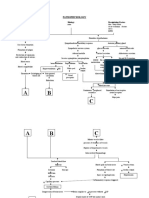
Efects
In children from poverty, gray
matter volumes 7-10 % lower than
what would be expected for normal
development (Tozzi).
Poverty and Brain Development
Nutritional Deficits
Federal Poverty
Line Below
$24,000
ed with school readiness skills, with the largest influence observed among children from the poorest households (Hair, Hanson, W
Crowded environments/ unstable homes may disrupt sleep
Conclusions
The influence of poverty on childrens learning
and achievement is mediated by structured
brain development (Hair, Hanson, Wolf, and
Pollak).
Link Between Income and Achievement
Exposure
Less stimulation from parents and lack of things like crayons, childrens books or games
Running Head: POVERTY AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT CONCEPT MAP/ FLOW CHART REVISED
Brain Scans
Reveal How
Poverty Hurts
Childrens Brains
Articles
Poverty Line
= $24,000 or
Less
Statistics
What accounts for the
diferences?
1. Less stimulation from
parents (Parents may
2. Lack of
work multiple jobs and
crayons,
arent home as much)
childrens
games, or books
Gray Matter:
Children in families below the
poverty line had gray matter
volumes 7 10% lower than
would be expected for normal
development
Association of
Child Poverty,
Brain
Development, and
Academic
Achievement
Statistics
Tozzi
Children from lowincome households
scored 4 7% lower on
standardized tests
As much as 20% of the
gap in test scores
could beof poverty on childrens learning
The influence
could beand
explained
by
achievement
is meditated by structural bran
maturational development.
lags in the
To avoid long-term costs of
3. Sleep disruptions
Conclusions
and
frontal andimpaired
temporalacademic functioning,
households
related to crowded4. Nutritional deficits
Relevance
lobes
below 150% of the federal poverty level should
homes lives that due to neighborhoods
beHair,
targeted
for additional resources aimed at
Hanson,
may be unstable that might not have
remediating
early childhood environments.
Wolfe, and
The
diferences
in development
grocery
stores
with Conclusions
and
Pollack
dont
students
fresh
foodmean poorer
Relevance
cant catch up in
the right
circumstances.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Endangered Minds: Why Children Dont Think And What We Can Do About IVon EverandEndangered Minds: Why Children Dont Think And What We Can Do About IBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (27)
- Unessay Cover Letter-3Dokument4 SeitenUnessay Cover Letter-3api-437668808Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Importance of Cognition in LearningVon EverandThe Importance of Cognition in LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genes, Brains, and Human Potential: The Science and Ideology of IntelligenceVon EverandGenes, Brains, and Human Potential: The Science and Ideology of IntelligenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnglishDokument23 SeitenEnglishEmmanuel ChichesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mind Mapping: Activity 1: Grades 5-8Dokument7 SeitenMind Mapping: Activity 1: Grades 5-8James WarrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copeland 1: Commented (CC1) : I Included This in My Introduction ToDokument5 SeitenCopeland 1: Commented (CC1) : I Included This in My Introduction Toapi-558306215Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neurodiversity Discovering The Extraordinary Gifts of Autism, ADHD, Dyslexia, and Other Brain Differences 2010Dokument356 SeitenNeurodiversity Discovering The Extraordinary Gifts of Autism, ADHD, Dyslexia, and Other Brain Differences 2010Antonio Donini100% (3)
- Romania's Abandoned Children: Deprivation, Brain Development, and the Struggle for RecoveryVon EverandRomania's Abandoned Children: Deprivation, Brain Development, and the Struggle for RecoveryBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Welcome to Your Child's Brain: How the Mind Grows from Conception to CollegeVon EverandWelcome to Your Child's Brain: How the Mind Grows from Conception to CollegeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (12)
- Capstone Project Draft ProposalDokument4 SeitenCapstone Project Draft Proposalapi-580341048Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wolf, P. (2003) - Brain Research and Education - Fad or Foundation 1Dokument4 SeitenWolf, P. (2003) - Brain Research and Education - Fad or Foundation 1Jésica SokolovskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardwired for Life: Human Understanding Beyond Surface PersonalityVon EverandHardwired for Life: Human Understanding Beyond Surface PersonalityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardwiring vs. Rewiring: Shaping the Mindset, Skillset, and Behaviors During Early Childhood Development StagesVon EverandHardwiring vs. Rewiring: Shaping the Mindset, Skillset, and Behaviors During Early Childhood Development StagesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retro Baby: Timeless Activities to Boost Development—Without All the Gear!Von EverandRetro Baby: Timeless Activities to Boost Development—Without All the Gear!Noch keine Bewertungen
- BNW Chapter 2 1Dokument2 SeitenBNW Chapter 2 1api-588923200Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research Essay Outline - EditedDokument5 SeitenResearch Essay Outline - Editedelizabeth michaelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brainbow 5 15 16 No 3Dokument5 SeitenBrainbow 5 15 16 No 3api-251160397Noch keine Bewertungen
- wp1 1Dokument11 Seitenwp1 1api-553186141Noch keine Bewertungen
- What's The Catch?, 2nd ed.: How to Avoid Getting Hooked and ManipulatedVon EverandWhat's The Catch?, 2nd ed.: How to Avoid Getting Hooked and ManipulatedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example Mind Map Literature ReviewDokument4 SeitenExample Mind Map Literature Reviewaflslcqrg100% (1)
- Ericka Bradley wp2-2Dokument6 SeitenEricka Bradley wp2-2api-616221007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Boosting Brain Power: 52 Ways to Use What Science Tells UsVon EverandBoosting Brain Power: 52 Ways to Use What Science Tells UsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Top Brain, Bottom Brain: Surprising Insights into How You ThinkVon EverandTop Brain, Bottom Brain: Surprising Insights into How You ThinkBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- Mind Mapping: Improve Memory, Learning, Concentration, Organization, Creativity, and Time Management: Mind Hack, #5Von EverandMind Mapping: Improve Memory, Learning, Concentration, Organization, Creativity, and Time Management: Mind Hack, #5Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Education That Works: The Neuroscience of Building a More Effective Higher EducationVon EverandEducation That Works: The Neuroscience of Building a More Effective Higher EducationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of A Whole New Mind by Daniel Pink :Why Right-Brainers Will Rule the Future: A Comprehensive SummaryVon EverandSummary of A Whole New Mind by Daniel Pink :Why Right-Brainers Will Rule the Future: A Comprehensive SummaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Children with Autism to Mind-Read: The WorkbookVon EverandTeaching Children with Autism to Mind-Read: The WorkbookBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Teenage Brain Thesis StatementDokument5 SeitenTeenage Brain Thesis StatementHelpWithYourPaperAurora100% (2)
- Report of TET Answer Key Errors of TGT Arts 2013 Sent To HPBOSE by Vijay Kumar HeerDokument8 SeitenReport of TET Answer Key Errors of TGT Arts 2013 Sent To HPBOSE by Vijay Kumar HeerVIJAY KUMAR HEERNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 5Dokument5 Seiten1 5api-673690908Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Blind Child's Pathway to Learning: Developing Cognition Without SightVon EverandA Blind Child's Pathway to Learning: Developing Cognition Without SightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bright Not Broken: Gifted Kids, ADHD, and AutismVon EverandBright Not Broken: Gifted Kids, ADHD, and AutismBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Online Education EssayDokument8 SeitenOnline Education Essayafabfetiu100% (2)
- Developing Multiple Intelligences in Young LearnersDokument10 SeitenDeveloping Multiple Intelligences in Young LearnersTevynNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Play Prescription: Using Play to Support Internalizing BehaviorsVon EverandThe Play Prescription: Using Play to Support Internalizing BehaviorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Young Minds Wasted: Reducing Poverty By Enchancing Intelligence, In Known Ways.Von EverandYoung Minds Wasted: Reducing Poverty By Enchancing Intelligence, In Known Ways.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hurt 2.0 (): Inside the World of Today's TeenagersVon EverandHurt 2.0 (): Inside the World of Today's TeenagersBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (25)
- wp3 Reflection and Grading (Final Revised)Dokument7 Seitenwp3 Reflection and Grading (Final Revised)api-281194852Noch keine Bewertungen
- I Search EditDokument7 SeitenI Search Editapi-253977101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Apa Short Research Paper ExampleDokument6 SeitenApa Short Research Paper Examplefvgjcq6aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annette Karmiloff-Smith - Precis - Beyond - ModularityDokument32 SeitenAnnette Karmiloff-Smith - Precis - Beyond - ModularityVinícius AugustoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reveleslesliegafinal 1Dokument8 SeitenReveleslesliegafinal 1api-283985342Noch keine Bewertungen
- Super Creativity - Tony BuzanDokument16 SeitenSuper Creativity - Tony BuzanHenrik Sundgren0% (1)
- Essay 2 Final Draft 1Dokument8 SeitenEssay 2 Final Draft 1api-611013571Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Research Dossier 5Dokument7 SeitenFinal Research Dossier 5api-509440366Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Children Succeed: Grit, Curiosity, and the Hidden Power of CharacterVon EverandHow Children Succeed: Grit, Curiosity, and the Hidden Power of CharacterBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (204)
- Gray Matter, Matters: Reflections on Child Brain Injury and Erroneous Educational PracticesVon EverandGray Matter, Matters: Reflections on Child Brain Injury and Erroneous Educational PracticesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes on Child Study (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Von EverandNotes on Child Study (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Schema FrendDokument11 SeitenSchema FrendRubab MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDokument5 SeitenNUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebral PhysiologyDokument27 SeitenCerebral PhysiologyArmaanjeet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Basic Academic EnglishDokument4 SeitenTugas Basic Academic EnglishAhmad Saiful BahriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nöropunktur Nörobilim Akupunkturunun Klinik El Kitabı, İkinci BaskıDokument175 SeitenNöropunktur Nörobilim Akupunkturunun Klinik El Kitabı, İkinci BaskıMaji Reyhan100% (1)
- Mark The Letter A, B, C, or D On Your Answer Sheet To Indicate The Correct Answer To Each of The Following QuestionsDokument20 SeitenMark The Letter A, B, C, or D On Your Answer Sheet To Indicate The Correct Answer To Each of The Following QuestionsVũ Minh ThànhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Inggris Jevva Edya S (2304140040)Dokument7 SeitenAssignment Inggris Jevva Edya S (2304140040)jevvaesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Focus4 2E Students Book With Answers PDF Phrase Word 2Dokument1 SeiteFocus4 2E Students Book With Answers PDF Phrase Word 2oleksandrgusar471Noch keine Bewertungen
- Polarising Brain OrganoidsDokument2 SeitenPolarising Brain OrganoidsDaniel KachkinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measureable Changes in The Neuro-Endocrinal Mechanism Following Spinal Manipulation - 2015Dokument6 SeitenMeasureable Changes in The Neuro-Endocrinal Mechanism Following Spinal Manipulation - 2015Renan O. Pravatta PivettaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remote Viewing - Part 2 - Sex MagicDokument2 SeitenRemote Viewing - Part 2 - Sex Magicstop-organized-crime50% (2)
- Siva SutraDokument197 SeitenSiva Sutraaade100% (6)
- How Electromagnetically-Induced Cell Leakage May Cause AutismDokument4 SeitenHow Electromagnetically-Induced Cell Leakage May Cause AutismodhiseoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dory in The Lens of PsychologyDokument3 SeitenDory in The Lens of PsychologyPoetic PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How The Brain Works The Facts Visually Explained-101-150Dokument50 SeitenHow The Brain Works The Facts Visually Explained-101-150TôThànhPhongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frontal Lobes - Bedside Testing: Pridmore S. Download of Psychiatry, Chapter 27. Last Modified: April, 2013. 1Dokument8 SeitenFrontal Lobes - Bedside Testing: Pridmore S. Download of Psychiatry, Chapter 27. Last Modified: April, 2013. 1RathavishwarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Integrate The Curricula Fogarty Robin J Pete BrianDokument153 SeitenHow To Integrate The Curricula Fogarty Robin J Pete Brianmila syukria100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- Last Minute RevisionDokument229 SeitenLast Minute RevisionSelvaArockiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson-5: How The Human Brain WorksDokument14 SeitenLesson-5: How The Human Brain Worksprecious maningasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurobiologic Theories and PsychopharmacologyDokument7 SeitenNeurobiologic Theories and PsychopharmacologyhoneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laserburn - Adventurer's Companion PDFDokument28 SeitenLaserburn - Adventurer's Companion PDFJMMPdosNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOTOR IMAGERY Tarek Abo Ayoub-1 PDFDokument5 SeitenMOTOR IMAGERY Tarek Abo Ayoub-1 PDFTarek Abo ayoubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify The Part of The BrainDokument2 SeitenIdentify The Part of The BrainClement Mar ClimacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Customers ThinkDokument16 SeitenHow Customers ThinkPatricio Javier ÓrdenesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Music EssayDokument5 SeitenMusic Essayapi-431080375Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Grades 5-6 Book 3Dokument65 SeitenAnatomy Grades 5-6 Book 3Miha MargineanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edoc - Pub - 4 Secret Techniques of In10se The October Man Sequ PDFDokument14 SeitenEdoc - Pub - 4 Secret Techniques of In10se The October Man Sequ PDFbaek2mo340Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neuroscience and Social Work Practice The Missing Link - NodrmDokument201 SeitenNeuroscience and Social Work Practice The Missing Link - NodrmHipatia Al83% (6)
- The Strain Pitch BibleDokument21 SeitenThe Strain Pitch BiblePayal Davda MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Memory Treasure by Krishan Cha HalDokument61 SeitenMemory Treasure by Krishan Cha Halnasreen100% (3)