Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
2 Electric Circuits Note
Hochgeladen von
api-2660212170 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
209 Ansichten3 SeitenThese pages are about different kinds of Electrical Circuits and how to draw them. Electrical Circuits may be divided into two main types - Series and Parallel Circuits. Series circuits use an electric cell to drive the electric current through the circuit. Parallel circuits use one or more electrical components such as bulbs and motors.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
2 electric circuits note
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThese pages are about different kinds of Electrical Circuits and how to draw them. Electrical Circuits may be divided into two main types - Series and Parallel Circuits. Series circuits use an electric cell to drive the electric current through the circuit. Parallel circuits use one or more electrical components such as bulbs and motors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
209 Ansichten3 Seiten2 Electric Circuits Note
Hochgeladen von
api-266021217These pages are about different kinds of Electrical Circuits and how to draw them. Electrical Circuits may be divided into two main types - Series and Parallel Circuits. Series circuits use an electric cell to drive the electric current through the circuit. Parallel circuits use one or more electrical components such as bulbs and motors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
Electricity is very important in everyday life. People use electricity to
light their homes, shops and factories. Electricity is needed to make
TVs, telephones, radios and computers work. Electricity is needed to
control traffic lights and to make runway signals work.
These pages are about different
kinds of electrical circuits and how
to draw them.
Circuit symbols
Conductors and insulators
When you work with electrical circuits you need to
use symbols to show how you have arranged your
equipment.
A conductor is a material which lets electrons move
through it easily. Conductors contain free-moving
electric charges (positive and negative charges). All
metals conduct electricity, and so does graphite (a
form of carbon). Examples of metal conductors are
copper, aluminium, iron, etc.
Symbol
Electrical
component
Cell
Picture
Battery
two or more
cells
together
Lamp
An insulator is a material which does not let
electrons move through it. Electrical insulators do not
contain free-moving electric charges, but can acquire
static electric charges by rubbing. Non-metals
(rubber, wool, glass, silk and amber) are insulators,
and so are materials like wood or plastic, which are
mainly made from non-metals.
Bulb
Electrical conductors are used to make electrical
wires, whereas electrical insulators (plastic and
rubber) are used to make protective coverings in
wires and electrical devices.
Switch
(open)
Electrons were discovered in 1897 by a scientist
called Sir Joseph Thomson. Before then people
had imagined that electricity was an invisible
fluid which flowed through wires. To make it
easier to talk about electricity, they decided
that this fluid flowed out of the + end of a cell
and when back into the end.
motor
Ammeter
Now that we know about electrons, we also
know that the electrons come out of the end
of the battery and go back in the + end.
Bulbs, switches and motors are all electrical
components.
Electrical Circuits
Series and Parallel Circuits
An electrical circuit is the path along which electric
charges flow. It consists of an electrical source (e.g.
an electric cell) which drives the electric current
through the circuit, connecting wires and one or
more electrical components such as electric bulbs
and switches.
Electrical circuits may be divided into two main types
series circuits and parallel circuits.
A series circuit is one that connects electrical
components end to end, one after another to form a
single loop. The current flowing through each
electrical component in a series circuit is the same.
Switches can be used to control electricity.
In a closed circuit, the switch is closed and the circuit
is completed. There is a continuous path for electric
current to flow.If the circuit is broken, no current can
flows in the circuit. This called an open circuit.
If you put more lamps into a series circuit, the lamps
will be dimmer than before.
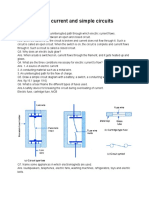
(a) Closed circuit
In a series circuit, if a lamp
breaks or a component is
disconnected, then the
circuit is broken and all the
components stop working.
(b) Open circuit
Circuit diagrams
A circuit diagram must be drawn using the symbols
which are used to represent electrical components.
A parallel circuit is one that splits into two or more
branches. The current flowing through each branch in
the parallel circuit may be the same or different, but
it is definitely less than the current flowing out from
the source.
Some guidelines for drawing circuits:
Wires must be straight lines
Draw component symbols then add the wires.
Use a ruler to draw wires connecting each
component.
Unlike a series circuit, the lamps stay bright if you add
more lamps in parallel.
The circuit diagram on the right uses the symbols for
a cell and a bulb. Notice the wires are straight lines.
In a parallel circuit, if a lamp breaks or a component
is disconnected from one parallel wire, the
components on different branches keep working.
Try drawing a circuit diagram of the open and closed
circuits on this page.
SUMMARY
Conductors are materials which allow electrons to move through them
Insulators are materials which do not allow electrons to move through
them
A complete circuit is needed for an electric current to flow
Series circuits have components arranged one after the other
Parallel circuits have components arranged in separate branches of the
circuit.
1.
What do these words mean?
a. Cell
b. Battery
c. Component
d. Conductor
e. Insulator
2.
(a) Name an insulating material.
(b) Name a conducting material.
3.
4.
(a) Why are electrical wires made of
metal?
(b) Why do they usually have a plastic
coating on the outside?
(a) Draw two bulbs and a cell in a
series circuit.
(b) Draw two bulbs and a cell in a
parallel circuit.
5.
(a) Which switches have to be pressed
to make bulb 2 come on?
(b) Which bulbs will come on if you
press switch B?
(c) Which bulbs will come on if you
press switches A and C?
A
B
6.
Mr. Smith has some Christmas tree
lights. One bulb is missing and the
other light will not come on until
he has replaced the bulb.
(a) Are the lights on a series or a
parallel circuit?
(b) Explain why.
7.
(a) Are the lights in your house on
a series circuit or a parallel
circuit?
(b) Explain why.
Two way switches are used on stair
cases so that the light can be
switched on or off from upstairs or
downstairs. Find out what a circuit
with a two-way switch would look
like and explain how it works. Draw
a diagram of the circuit too.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ElectricityDokument22 SeitenElectricityanu.pavansuresh30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics for Artists: Adding Light, Motion, and Sound to Your ArtworkVon EverandElectronics for Artists: Adding Light, Motion, and Sound to Your ArtworkBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Portfolio in ScienceDokument13 SeitenPortfolio in ScienceMarkLesterEstrellaMabagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electrical Symbols and Their MeaningsDokument5 SeitenBasic Electrical Symbols and Their MeaningsJasjeet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- COT ElectricityDokument23 SeitenCOT ElectricityArlene Tuyor Agunod0% (1)
- Chapter 03Dokument20 SeitenChapter 03Pramod MoryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christmas Lights vs Home LightsDokument9 SeitenChristmas Lights vs Home LightsJoel Christian Salentes100% (1)
- Electric CircuitsDokument50 SeitenElectric CircuitsClaudineNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSS 11 - Module 5 - Plan and Prepare Termination Connection of Electrical WiringDokument17 SeitenCSS 11 - Module 5 - Plan and Prepare Termination Connection of Electrical WiringJoy100% (1)
- Factory Hygiene ProcedureDokument5 SeitenFactory Hygiene ProcedureGsr MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity and MagnetismDokument22 SeitenElectricity and MagnetismLakwatserong GuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etp ListDokument33 SeitenEtp ListMohamed MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.02 Electric CircuitsDokument21 Seiten5.02 Electric Circuitsfouad alkasehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit ElectrcityDokument23 SeitenCircuit Electrcityapi-246410374Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science q3 w5 Co1Dokument20 SeitenScience q3 w5 Co1Julieta AlbercaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Grade 4 Unit 5 Making CircuitsDokument9 SeitenScience Grade 4 Unit 5 Making CircuitsPhairouse Abdul SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 6 - Electricty &circuits - NotesDokument5 SeitenClass 6 - Electricty &circuits - NotesAntony Judice ANoch keine Bewertungen
- P503 - CircuitsDokument53 SeitenP503 - Circuitstai057482Noch keine Bewertungen
- TLEDokument6 SeitenTLEPoseidon NipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Current and Circuits NotesDokument9 SeitenElectric Current and Circuits Notes13srivastava.nimishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1 W2 Series and Parallel CircuitDokument7 SeitenQ1 W2 Series and Parallel CircuitLouis Miguel LauritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GURUJI - Infrared Sensor Using Opamp IC LM324.Epub - Sanet.stDokument23 SeitenGURUJI - Infrared Sensor Using Opamp IC LM324.Epub - Sanet.stJuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Revision Notes: Electrical Circuits ExplainedDokument2 SeitenStudent Revision Notes: Electrical Circuits Explainedjessalyn iladaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument19 SeitenUntitledMs LusianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Science.3Dokument17 SeitenIntegrated Science.3J-Den MoffattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Current and Circuit Class 7 LessonDokument5 SeitenElectric Current and Circuit Class 7 Lessonlushlife231Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 01 05 VI Science 1Dokument4 Seiten2022 01 05 VI Science 1KITE GLOBALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotics Reviewer Quarter 1Dokument16 SeitenRobotics Reviewer Quarter 1Dane Gian Angelo TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2tech Unit 4 Electrical CircuitsDokument41 Seiten2tech Unit 4 Electrical Circuitsannadominguez740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric CircuitsDokument10 SeitenElectric CircuitsDante Gabriel Recide INoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 12 Electricity and Circuit 1Dokument31 SeitenCH 12 Electricity and Circuit 1POOJA SUSHILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity and Circuits Related Questions (CH 12)Dokument50 SeitenElectricity and Circuits Related Questions (CH 12)Srijan MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuit - Class 7, Electric Current and Its Effects, ScienceDokument9 SeitenElectric Circuit - Class 7, Electric Current and Its Effects, Sciencesmi_santhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science QNADokument17 SeitenScience QNAShourjya SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serries ParallelDokument13 SeitenSerries ParallelNoel SeniegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE-2-Electric Circuit ComponentsDokument20 SeitenMODULE-2-Electric Circuit ComponentsRichard Dela PenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UIIS W Revision Notes Electric Current and Its EffectsDokument5 SeitenUIIS W Revision Notes Electric Current and Its Effectsjonathanshiroj10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inte Term 2 Week 6 Electricity and LightingDokument6 SeitenInte Term 2 Week 6 Electricity and LightingSheridan DyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-14 Electric Current and Its EffectsDokument5 SeitenCh-14 Electric Current and Its Effectstanshikha dharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuits & ComponentsDokument3 SeitenElectric Circuits & ComponentsLionel DsouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuits QRDokument60 SeitenCircuits QRDon Mariano Marcos Elementary SchoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symbols and CircuitsDokument11 SeitenSymbols and CircuitsJoel OkohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes 1: 1. Basic Elements and Components in Electric CitcuitsDokument27 SeitenLecture Notes 1: 1. Basic Elements and Components in Electric CitcuitsAlejandro Ca MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuits Lab GuideDokument5 SeitenElectric Circuits Lab GuideAtif MehfoozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity and Circuits - Question and Answers: Answer The FollowingDokument5 SeitenElectricity and Circuits - Question and Answers: Answer The FollowingkashviNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Electronic Circuit and Their SymbolsDokument3 SeitenWhat Are The Electronic Circuit and Their SymbolsEmilyn PaculbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParallelDokument2 SeitenParallelKhushal PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLE 9 - 3Q - Electrical PlansDokument23 SeitenTLE 9 - 3Q - Electrical Plansjayson cajateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Current and Its Effects - NoteDokument6 SeitenElectric Current and Its Effects - NoteToshit Kumar NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS Q 1 WEEK 3 Ste 9Dokument6 SeitenLAS Q 1 WEEK 3 Ste 9KimmmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2 Module 2 Activities: Grade 9 Seatwork ActivityDokument5 SeitenQ2 Module 2 Activities: Grade 9 Seatwork ActivityIsiah Milan GloriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charges at RestDokument58 SeitenCharges at RestVinod ChackoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MigirubbbbnDokument4 SeitenMigirubbbbnehigie300ezekielNoch keine Bewertungen
- English For EEE - NTK - 2017Dokument50 SeitenEnglish For EEE - NTK - 2017Vũ Việt HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Series and Parallel CircuitsDokument2 SeitenUnderstanding Series and Parallel CircuitsbobNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPRS Module 3 - Basic ElectronicsDokument43 SeitenCPRS Module 3 - Basic ElectronicsLawrence Cada NofiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity and Circuits NotesDokument5 SeitenElectricity and Circuits NotesThwayyiba PKNoch keine Bewertungen
- REFLECTIONDokument7 SeitenREFLECTIONariannerose gonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 6 Electricity and Circuit Exercise Question and Answer Plus Inner(Extra) Question and AnswerDokument7 SeitenClass 6 Electricity and Circuit Exercise Question and Answer Plus Inner(Extra) Question and Answerdebasishnath9593913213Noch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Basic Electrical ComponentsDokument17 Seiten14 Basic Electrical ComponentsShimpy MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series CircuitsDokument3 SeitenSeries CircuitsEnglish TeacherNoch keine Bewertungen
- G6 Electricity and Magnetism - Revision Booklet and ANSDokument21 SeitenG6 Electricity and Magnetism - Revision Booklet and ANSAhad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affordable Care Act Tax - Fact CheckDokument26 SeitenAffordable Care Act Tax - Fact CheckNag HammadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPIM101 4 UpdatedDokument61 SeitenOPIM101 4 UpdatedJia YiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corena s2 p150 - Msds - 01185865Dokument17 SeitenCorena s2 p150 - Msds - 01185865Javier LerinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review 5Dokument4 SeitenLiterature Review 5api-463653994Noch keine Bewertungen
- PDS-1st PageDokument1 SeitePDS-1st PageElmer LucreciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 13 AminesDokument3 SeitenUnit 13 AminesArinath DeepaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BUSN7054 Take Home Final Exam S1 2020Dokument14 SeitenBUSN7054 Take Home Final Exam S1 2020Li XiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Frequency Voltage Probe Non-Availability on GeMDokument2 SeitenHigh Frequency Voltage Probe Non-Availability on GeMjudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afar Partnerships Ms. Ellery D. de Leon: True or FalseDokument6 SeitenAfar Partnerships Ms. Ellery D. de Leon: True or FalsePat DrezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule of Charges General Banking 2022Dokument18 SeitenSchedule of Charges General Banking 2022Shohag MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Grants Final/Terminal/Exit Progress Report: Instructions and Reporting FormDokument13 SeitenResearch Grants Final/Terminal/Exit Progress Report: Instructions and Reporting FormBikaZee100% (1)
- Alexander Lee ResumeDokument2 SeitenAlexander Lee Resumeapi-352375940Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exp19 Excel Ch08 HOEAssessment Robert's Flooring InstructionsDokument1 SeiteExp19 Excel Ch08 HOEAssessment Robert's Flooring InstructionsMuhammad ArslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Localization Strategy in Vietnamese Market: The Cases ofDokument25 SeitenLocalization Strategy in Vietnamese Market: The Cases ofHồng Thy NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- December 2018: Russian Journal of Agricultural and Socio-Economic SciencesDokument339 SeitenDecember 2018: Russian Journal of Agricultural and Socio-Economic Sciencesnahla saviraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statement of PurposeDokument2 SeitenStatement of Purposearmaan kaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- JWCh06 PDFDokument23 SeitenJWCh06 PDF007featherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Companies Choose Corporate Bonds Over Bank LoansDokument31 SeitenWhy Companies Choose Corporate Bonds Over Bank Loansতোফায়েল আহমেদNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kunci Jawaban Creative English 3BDokument14 SeitenKunci Jawaban Creative English 3BLedjab Fatima67% (3)
- BILL OF SALE Pre ApproveDokument1 SeiteBILL OF SALE Pre ApprovedidinurieliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RS-RA-N01-AL User Manual of Photoelectric Total Solar Radiation TransmitterDokument11 SeitenRS-RA-N01-AL User Manual of Photoelectric Total Solar Radiation TransmittermohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Infrastructure ProjectsDokument1 SeiteCase Study Infrastructure ProjectsAnton_Young_1962Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluke - Dry Well CalibratorDokument24 SeitenFluke - Dry Well CalibratorEdy WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book Two - 2da. EdiciónDokument216 SeitenBook Two - 2da. EdiciónJhoselainys PachecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASM Architecture ASM Disk Group AdministrationDokument135 SeitenASM Architecture ASM Disk Group AdministrationVamsi ChowdaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- cp2021 Inf03p02Dokument242 Seitencp2021 Inf03p02bahbaguruNoch keine Bewertungen
- NH School Employee Criminal Record Check FormDokument2 SeitenNH School Employee Criminal Record Check FormEmily LescatreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical PropertiesDokument30 SeitenMechanical PropertiesChristopher Traifalgar CainglesNoch keine Bewertungen