Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
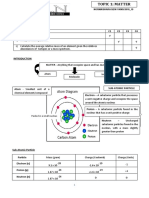
Chapter 4.3-Orbital Overlap & Hybridisation
Hochgeladen von
Supia Nazma0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
39 Ansichten3 SeitenUse valence bond theory to explain the bonding in HCl and show how the bond is formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. I. Ii. Describe the hybridisation process and determine the geometry of the following species.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Chapter 4.3-Orbital Overlap & Hybridisation[1]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenUse valence bond theory to explain the bonding in HCl and show how the bond is formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. I. Ii. Describe the hybridisation process and determine the geometry of the following species.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
39 Ansichten3 SeitenChapter 4.3-Orbital Overlap & Hybridisation
Hochgeladen von
Supia NazmaUse valence bond theory to explain the bonding in HCl and show how the bond is formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. I. Ii. Describe the hybridisation process and determine the geometry of the following species.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
TUTORIAL 4.
3 : HYBRIDISATION AND ORBITAL OVERLAP
3.
(a)
Describe the formation of sigma and pi bonds.
(b)
Use valence bond theory to explain the bonding in HCl and show how the
bond is formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals.
(a)
What is meant by hybridisation of atomic orbitals?
(b)
Name the hybridisation of the carbon atoms in the following molecules.
i.
CH3CH3
ii.
CH3CH=CH2
Describe the hybridisation process and determine the geometry of the
following species.
(a)
BeH2
(b)
BH3
(c)
PF5
(d)
SeF4
(e)
SCl6
(f)
ICl2-
(g)
ICl4+
TUTORIAL 4.3 : HYBRIDISATION AND ORBITAL OVERLAP
Objective questions
1
Two carbon atoms form a linear shaped ethene, C2H4, molecule when bonded with
four other hydrogen atoms. Prior to bonding, the carbon atom
A
does not hybridise.
undergoes sp hybridisation.
undergoes sp2 hybridisation.
undergoes sp3 hybridisation.
According to the valence bond theory, the formation of the covalent bond in the HBr
is due to the overlap between
H
Br
1s
2s
1s
3p
2s
2p
2s
3s
What is the hybridisation for central atom in IF4 ?
A
sp2
sp3
sp3d
sp3d2
What is the hybridisation of carbon atom in hydrogen cyanide, HCN?
A sp
B. sp2
C. sp3
D. sp3d
The hybridisation of the central atom in the following molecules is same EXCEPT?
A. NH3
B. H2O
C. AlCl3
D. C2H6
TUTORIAL 4.3 : HYBRIDISATION AND ORBITAL OVERLAP
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesVon EverandChirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesF. Richard KeeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Berikan 2 Persamaan Dan 2 Perbedaan Ikatan O-O Dalam O Dan ODokument2 SeitenBerikan 2 Persamaan Dan 2 Perbedaan Ikatan O-O Dalam O Dan OrisnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical BondingDokument5 SeitenChemical BondingYanti FarhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSS Chemistry Part 11 Chemistry of Carbon CompoundsDokument47 SeitenNSS Chemistry Part 11 Chemistry of Carbon CompoundsFelix YueNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 4Dokument24 SeitenNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 4AaseesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 12 Organic WSDokument5 SeitenCH 12 Organic WSRaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDokument21 SeitenChapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesNitish MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Class 11 CBSE Important QuestionsDokument21 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Class 11 CBSE Important QuestionsNitish MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valence-Bond Method ExercisesDokument1 SeiteValence-Bond Method ExercisesHạ Thi LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon and Its CompoundDokument15 SeitenCarbon and Its CompoundrahulsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Topic 4: Ionic, Covalent and Metallic BondingDokument3 SeitenTest Topic 4: Ionic, Covalent and Metallic BondingAshutosh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Letter 202/1/2017: General Chemistry 1BDokument10 SeitenTutorial Letter 202/1/2017: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSBE Sample Paper For Class 11 Chemistry ErDokument4 SeitenCSBE Sample Paper For Class 11 Chemistry ErSujata SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Exam - Class 11 - Chemistry Question PaperDokument4 SeitenAnnual Exam - Class 11 - Chemistry Question PaperADITIYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Sch3u Review 20923 42 04Dokument4 SeitenSch3u Review 20923 42 04limichael000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Questions - Weeks 345 - 3rdedDokument5 SeitenPractice Questions - Weeks 345 - 3rdedJon LevinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 R - 5 Set - 2Dokument4 SeitenClass 12 R - 5 Set - 2santhosNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSS Chemistry Part 6 Microscopic World IIDokument20 SeitenNSS Chemistry Part 6 Microscopic World IISabrina WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch1 2 3 ExercisesDokument11 SeitenCh1 2 3 ExercisesMancini100% (1)
- Chem S6Dokument4 SeitenChem S6sugi mugiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Compounds MCQsDokument10 SeitenCarbon Compounds MCQssenjicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry worksheetDokument5 SeitenChemistry worksheet987f7gjvt7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isucceed Sample Question Paper 20 Chemistry 12Dokument5 SeitenIsucceed Sample Question Paper 20 Chemistry 12Gajanan100% (1)
- 11 Chemistry PP Ch4 Chemical Bonding Molecular StructureDokument6 Seiten11 Chemistry PP Ch4 Chemical Bonding Molecular StructureJwalant100% (1)
- kk mid semi 1Dokument26 Seitenkk mid semi 1chikondikosamu24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class X Chemistry Sample Paper IDokument11 SeitenClass X Chemistry Sample Paper IshomitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TS - JR - Ipe Chemistry Important Questions - 01-03-2023Dokument6 SeitenTS - JR - Ipe Chemistry Important Questions - 01-03-2023bittu060606Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 231 Spring 2023 Exam 1.docx63ed278f8b08f4482Dokument7 SeitenChemistry 231 Spring 2023 Exam 1.docx63ed278f8b08f4482francisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry WorksheetDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheetkuldeep kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques Shobhit NirwanDokument43 SeitenOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques Shobhit NirwanTanmoy GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios Estructura MolecularDokument4 SeitenEjercicios Estructura MolecularDANNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon and Its ComponentsDokument17 SeitenCarbon and Its ComponentsS.SreerevanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet - Covalent Bonding & Intermolecular ForcesDokument5 SeitenWorksheet - Covalent Bonding & Intermolecular ForcesJohn Theodore KotselasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Examination Class Xi Chemistry (2020-2021) SubjectiveDokument3 SeitenAnnual Examination Class Xi Chemistry (2020-2021) SubjectiveLavyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JR. Che. IMP. QDokument10 SeitenJR. Che. IMP. QabhichowdarykondaveetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial #4: Unit 1 Fundamentals in Chemistry Shapes of MoleculesDokument2 SeitenTutorial #4: Unit 1 Fundamentals in Chemistry Shapes of MoleculesMel ManningNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHM 092 Tutorial 4 Chemical BondingDokument4 SeitenCHM 092 Tutorial 4 Chemical BondingAin Syakirah AzleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry II: s- and p- Block Elements ExamDokument2 SeitenInorganic Chemistry II: s- and p- Block Elements Exam5940 sankalp rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Assignment 4 Class 11Dokument3 SeitenChemistry Assignment 4 Class 11Nayan ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- T12 Introduction To Organic Chemistry 27-34Dokument8 SeitenT12 Introduction To Organic Chemistry 27-34饶宝珍Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exemplar 123Dokument10 SeitenExemplar 123Padhai karle Serious se lomduNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class XI Chemistry ExamDokument4 SeitenCBSE Class XI Chemistry Examalex scottNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument14 SeitenChemistryGutsy Studs7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class-Xii Haloalkanes and Haloarenes (Assignment-2)Dokument4 SeitenClass-Xii Haloalkanes and Haloarenes (Assignment-2)Hardik GulatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon and its compounds worksheetDokument3 SeitenCarbon and its compounds worksheetashish gandreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2Dokument47 SeitenChap 2h2300147Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet For Chemical BondingDokument2 SeitenWorksheet For Chemical Bondingaaradhyajain2106Noch keine Bewertungen
- JR - Chemistry Important Questions 2023Dokument9 SeitenJR - Chemistry Important Questions 2023Srilakshmi MNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 Intro Organic Chem Tutorial (Teachers)Dokument14 Seiten2009 Intro Organic Chem Tutorial (Teachers)Tommy Jing Jie NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Organic Chemistry Important Questions 2022-23Dokument15 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Organic Chemistry Important Questions 2022-23Divye DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLASSIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY QUESTIONSDokument8 SeitenCLASSIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY QUESTIONSADITYA SONINoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 ScienceDokument2 SeitenCBSE Class 10 ScienceschoolhelpmentorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding Board Level Assignment: 1. Which of The Following Has Maximum Bond Angle? HDokument7 SeitenChemical Bonding Board Level Assignment: 1. Which of The Following Has Maximum Bond Angle? HLightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Snsir JR Chemistry Imp QuestionsDokument4 SeitenSnsir JR Chemistry Imp Questionssriram vadrevu100% (1)
- 11-Chemistry-Sample-Papers-2018-2019-Set-3 (1)Dokument3 Seiten11-Chemistry-Sample-Papers-2018-2019-Set-3 (1)fatema19447Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry - Mock ExamDokument3 SeitenOrganic Chemistry - Mock ExamAashif MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic ChemistryDokument3 SeitenOrganic Chemistrydivijno12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryVon EverandOrganometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryF. G. A. StoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collision Theory States That For A Reaction To OccurDokument9 SeitenCollision Theory States That For A Reaction To OccurSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATTER: ISOTOPES AND MASS SPECTROMETRYDokument35 SeitenMATTER: ISOTOPES AND MASS SPECTROMETRYSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instantaneous Rate: Is Determined From A Graph of Time Versus Concentration by Drawing A Line Tangent To The CurveDokument13 SeitenInstantaneous Rate: Is Determined From A Graph of Time Versus Concentration by Drawing A Line Tangent To The CurveSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Metallic BondsDokument13 Seiten2 Metallic BondsSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz PHASE EQUILIBRIA (Set 2)Dokument4 SeitenQuiz PHASE EQUILIBRIA (Set 2)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry: 1. Concept of EnthalphyDokument2 SeitenThermochemistry: 1. Concept of EnthalphySupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KMK Quiz on Gas Laws and Relative Molecular MassDokument4 SeitenKMK Quiz on Gas Laws and Relative Molecular MassSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz C8 Set 4Dokument2 SeitenQuiz C8 Set 4Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Kuliah TermoDokument9 SeitenExercise Kuliah TermoSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz PHASE EQUILIBRIA (Set 3)Dokument4 SeitenQuiz PHASE EQUILIBRIA (Set 3)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 1.1 2021 LectureDokument4 SeitenQuiz 1.1 2021 LectureSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 5.1 Gas (Set 1)Dokument2 SeitenQuiz 5.1 Gas (Set 1)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Density of An Aqueous Solution Containing 18Dokument1 SeiteThe Density of An Aqueous Solution Containing 18Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1: DH DH DH For The Following ReactionDokument4 SeitenExercise 1: DH DH DH For The Following ReactionSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise MassSpecDokument1 SeiteExercise MassSpecSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Born HaberDokument17 SeitenExercise Born HaberSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 5.2 Liquid (Set 2)Dokument2 SeitenQuiz 5.2 Liquid (Set 2)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Exercises - Measurement of ConcentrationDokument1 SeiteExtra Exercises - Measurement of ConcentrationSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz C6 Set 2Dokument2 SeitenQuiz C6 Set 2Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz C6 Set 4Dokument2 SeitenQuiz C6 Set 4Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Born HaberDokument17 SeitenExercise Born HaberSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 5.3 Solid (Set 3)Dokument2 SeitenQuiz 5.3 Solid (Set 3)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 5.1 Gas (Set 1)Dokument2 SeitenQuiz 5.1 Gas (Set 1)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Equilibrium Quiz Set 3Dokument1 SeiteChemical Equilibrium Quiz Set 3Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz C6 Set 1Dokument2 SeitenQuiz C6 Set 1Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KMK Quiz on Gas Laws and Relative Molecular MassDokument4 SeitenKMK Quiz on Gas Laws and Relative Molecular MassSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz C5 STATES OF MATTER (Set 5)Dokument2 SeitenQuiz C5 STATES OF MATTER (Set 5)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gases (B)Dokument115 SeitenGases (B)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1.1 (PG 1-2)Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 1.1 (PG 1-2)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid StateDokument46 SeitenLiquid StateSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen