Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bab 1: Pengenalan Kepada Fizik Bahagian A: Period Time For 10 Oscillations
Hochgeladen von
lapokOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bab 1: Pengenalan Kepada Fizik Bahagian A: Period Time For 10 Oscillations
Hochgeladen von
lapokCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
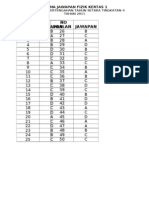
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
126
BAB 1: PENGENALAN KEPADA FIZIK
BAHAGIAN A
NO. 1
(a)
NO. 2
(b)
NO.
(a) 5
(a)
(c) 3
(b)(i)
NO.
(b)
(b)(ii)
(a)
(c)(i)
NO.
(b) 4
(c)(ii)
(a)
(c)
(b)(i)
(c)
(b)(ii)
(c)(iii)
(c)
ANSWER
45C
-Q
ANSWER
ANSWER
- To reduce
zero
error/systematic
/ avoid parallax
error error
The
period
of oscillation depends
on length of the pendulum
Thermal
44.0
s equilibrium
ANSWER
When
length
increase,
the
period
also increase
TOTAL
44
Scalar
quantity
investigate
To
the
relationship
between
the
period
the
length
ANSWER
0.1 20
A
Manipulated
:
length
Mass
0.30 A
Responding
2.2 s
Diagram
1.3 : period of oscillation
TOTAL
Gravitational
g.
increase
Has
smallest acceleration,
division of scale
Retort
stand
with clamp,
100 cm
thread,
bob,value is calculated
TOTAL
Repeated
readings
are taken
andofthe
average
meter rule, 2 blocks of clamp wood, protractor and
TOTAL
stop stopwatch
(c)(iv)
(c)(v)
1. The apparatus is set up as shown in the diagram
2. Measure the length of the pendulum, l = 60.0 cm by using
meter rule.
3. Give the pendulum bob a small displacement 10o.Time for 10
oscillations is measured by using a stop watch.
Calculate the average time.
Period=
time for 10 oscillations
10
4. Experiment is repeated by using l = 50.0 cm, 40.0 cm, 30.0
cm and 20.0 cm
(c)(vi)
MARK
1
1
MARK
MARK
1
1
MARK
1
4
1
1
MARK
1
1
1
1
3
1
1
1
5
1
4
l/ cm
60.0
50.0
40.0
30.0
20.0
T/ s
1
(c)(vii)
TOTAL
12
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
127
KERTAS 3 (BAHAGIAN B)
BAB 2: DAYA DAN GERAKAN
BAHAGIAN A
NO. 1
(a)
ANSWER
MARK
1
gravitational force
W= mg
(b)
1
W= (500) (10)
5 000 N
(c)
1
(d)(i)
1
(d)(ii)
(d)(iii)
Fx : to pull the car to move forward
Fy : to lift the car
10 000 cos 30
use smaller angle between cable and bar / the
horizontal component, Fx
(e)
1
increase the force applied// (accept any suitable
method)
TOTAL
NO. 2
(a)
(b)(i)
ANSWER
rate of change of velocity
The mass must be high
10
MARK
1
1
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
128
so that the vehicles becomes more stable
the engine capacity must be high
1
1
so the power is higher
the diameter of the tyre must be bigger
1
1
so the pressure is low // more stable
Q
1
1
(b)(ii)
(b)(iii)
(c)
(d)(i)
500
10
1
1
5 ms-2
1st section : graph shows uniform acceleration
2nd section : graph shows uniform velocity
1
(d)(ii)
1
TOTAL
12
BAHAGIAN B
NO. 3
(a)(i)
(a)(ii)
(a)(iii)
(b)
ANSWER
Crumple zone
Easily crumple in order to lengthen the collision time
Absorb impulsive force during accident
To increase the time interval of impact
To minimize the energy transferred to the passenger
Both car are moving with high speed
Both car applying emergency brake in high speed
Car in Diagram 10.2 are without ABS and skidded on the road
Car in Diagram 10.3 with ABS are not skidded on the road.
ABS brake avoid skidding when braking.
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
129
CHARACTERISTICS
1. Build up from light weight
and high strength material
but easily crumple.
3. Build up from high strength
material such as steel bar
(c)
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
EXPLANATION
2. It will prolong the time of
collision// Reduce the
impulsive force
4. Prevents the collapse of the
front and back of the car into
the passenger compartment.
Also gives good protection
from a side-on collision.
5. Shatter-proof windscreen
6. Prevents the windscreen from
10
shattering
7. Air bag
8. Acts as a cushion for the head
and body in an accident and
thus prevents injuries to the
driver and passengers.
9. Safety seat belt
10. Prevents the passengers from
being thrown out of the car.
Slows down the forward
movement of the passengers
when the car stops abruptly.
TOTAL
20
BAHAGIAN C
NO. 4
(a)
ANSWER
Rate of change of momentum
Impulsive force to 1/time
To increase the time of impact
(b)
Helmet to protect the head
Jacket to protect the body
Glove to protect the hand
(c)(i)
v=
160 1000
60 60
= 44.4ms-1
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max 4m
1
130
a=
a=
(c)(ii)
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
vu
t
44.40
10
a = 4.44ms-2
F = ma
= (202)(4.44)
= 896.88N
CHARACTERISTICS
1
1
REASON
2. Motorcycle does not
1. With ABS
(d)
3. Bigger with of tyre
5. Smaller mass
7. Lower seat height
stop immediately/ can
be controlled if
direction changes/
does not move
sideways / more
friction with ABS.
4. Bigger surface area,
better support / low
pressure acts on the
tyres/ more friction
when breaks.
6. Lighter, can move
faster / low inertia.
8. Lower centre of
gravity/ more stable/
safer when turn
10
9. R
10. It has ABS, bigger width of tyre, smaller mass, and
lower seat height.
TOTAL
20
KERTAS 3 (BAHAGIAN B)
NO. 5
(a)
(b)
(c)(i)
(c)(ii)
ANSWER
The length of catapult rubber depends on the force
The bigger the force, the longer the extension of the catapult
rubber
To investigate the relationship between the force and
extension of a spring
MV: force
RV: extension
CV: length of the spring// diameter of the spring// type of
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
131
spring
Spring, retort stand, ruler, slotted weight
State a functional arrangement of the apparatus
1. Measure the initial length of the spring, lo
2. Put one slotted mass,m1= 20g at the end of the spring
3. Measure the length of the spring, l1
4. Calculate extension of the spring, x= l1 lo
5. Repeat the experiment for the mass 40g, 60g, 80g and
(c)(iii)
(c)(iv)
(c)(v)
1
1
1
1
1
100g
F (N) // m (g)
X (cm)// l (cm)
(c)(vi)
(c)(vii)
TOTAL
BAB 3: DAYA DAN TEKANAN
BAHAGIAN A
NO. 1
(a)
ANSWER
Pascals Principle
When the small piston is pressed down, the
MARK
1
1
pressure is exerted on the liquid and
(b)
transmits uniformly to the large piston
The force is produced and pushes the chair
up
Some of the force is used to compress air
(c)
1
bubbles
(d)
F
20
500
100
12
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
132
F = 100 N
Increase the cross sectional area of the big
(e)
piston// Decrease the size of the small piston
To increase the force multiplier// Use
stronger alloy for liquid// To withstand higher
pressure without cracking
Enlarge the size of the seat
To accommodate the larger bodies of adults//
Strengthened the seat to withstand the
1
1
heavier adults without damage
TOTAL
NO. 2
(a)
ANSWER
10
MARK
1
1
Gravitational force
(a)(i)
1
(a)(ii)
Buoyant force = weight
FB = Vg
(b)(i)
(b)(ii)
(c)(i)
FB = 1020 x 600 x 10
FB = 6 120 000 N
FB = W = 6 120 000 N
Ship base cross section area is wide
Increase buoyant force // increase the
volume of liquid displaced
(c)(ii)
(d)
Volume of the air space in the ship is high
Reduce the density of the ship
P
TOTAL
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
12
133
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
BAHAGIAN B
NO. 3
(a)(i)
(a)(ii)
(b)
ANSWER
Force per unit area
Pressure on piston Q is equal to pressure on piston R
Cross sectional area of piston Q is less than R
Force acted on piston Q less than R
The greater the area, the greater the force
Pascal's principle
aerofoil shape
The air speed on the tipper surface is greater than the
air speed on the lower surface.
The pressure on the lower surface is greater than the
pressure on the upper surface.
Different in pressure produce the lift force
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
134
CHARACTERISTICS
1. Thick wall
2. Water pressure
3. High density
increase with depth
4. Increase mass / can
material
submerge easily
5. Strong material
(c)
REASON
7. Aerodynamic shape
9. Ballast tank
6. Does not break easily
8. Reduce water
Max=10
resistance
10. To increase or reduce
weight
11. Sonar transmitter and 12. To estimate distance
receiver
and depth
TOTAL
20
BAHAGIAN C
NO. 4
(a)(i)
(a)(ii)
ANSWER
Archimedes principle states that the buoyant force on an
object immersed in a fluid is equal to the weight of fluid
displaced by the object.
The balloon acted by two forces: Upthrust and the weight
of the balloon
The density of helium gas is less than the density of
surrounding air
Upthrust equals to the weight of the air displaced by the
balloon
Upthrust is higher than the weight of the balloon
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
135
CHARACTERISTICS
1. Large balloon
3. Use 2 burners //
Many burners
(b)
5. Synthetic nylon
7. High temperature of
the air in the balloon
(c)(i)
(c)(ii)
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
REASON
2. To produce bigger
buoyant / upthrust //
Increase the volume of
the air displaced
4. To produce bigger
flame // heat up the gas
in the balloon faster
6. Light-weight, strong and
air-proof material
8. Reduce the density
//weight of the air in the
balloon
9. Q
10. Large balloon, use 2 burners / many burners, use
synthetic nylon and has high temperature of the air in
the balloon
W = FB
m x 10 = (10 x 2 x 10-6) x 1000 x 10
m = 0.02 kg /20 g
20 = (12 x 2)
= 0.83 g cm-3
TOTAL
10
1
1
1
1
1
20
KERTAS 3 (BAHAGIAN B)
NO. 5
(a)
(b)
(c)(i)
(c)(ii)
(c)(iii)
ANSWER
The wall of the dam is thicker at the bottom of the dam.
Water pressure increases with depth
To investigate the relationship between the pressure in a liquid
and the depth.
MV: Depth of liquid, y
RV: Pressure in liquid, h
CV: density,
Measuring cylinder, thistle funnel, rubber tube, manometer,
and retort stand.
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
136
(c)(iv)
(c)(v)
1. The measuring cylinder is completely filled with water.
2. The thistle funnel is connected to the manometer with a
rubber tube.
3. The thistle funnel is lowered with the water to a depth
y=10.0 m
4. The manometer reading, h is measured.
5. Step 3 is repeated with values of depth y = 20.0m, 30.0
cm, 40.0 cm and 50.0 cm.
y (cm)
10
20
30
40
50
(c)(vi)
1
1
1
h (cm)
1
(c)(vii)
TOTAL
12
BAB 4: HABA
BAHAGIAN A
NO. 1
(a)
(a)(ii)
(a)(iii)
(b)(i)
ANSWER
Kelvin, K
To obtain two fix points high and low
Opaque// easy to see// does not stick
20.0 cm
16.9
100
20.0
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
(b)(ii)
1
84.5oC
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
137
TOTAL
NO. 2
ANSWER
MARK
To measure mass of ice melted by heat from
(a)
surrounding
(b)
168 g
(c)
Latent heat
H
m
56800
0.168
L=
(d)
1
338 095 Jkg
-1
(e)
Heat loss to surrounding
(f)
Wrap filter funnel with wool
1
8
TOTAL
BAHAGIAN B
NO. 3
(a)
(b)
(c)
ANSWER
Thermal equilibrium
The amount of heat energy is the same
c of Diagram 9.1(a) is greater than Diagram 9.1(b)
Temperature in diagram 9.1(a) is greater than in
Diagram 9.1(b)
The rate of heat loss in Diagram 9.1(b) is greater than in
Diagram 9.1(a)
The smaller the c of container, the greater the rate of
heat loss
Initially, more heat flow from water to the container than
from container to the water
nett heat flow is from water to the containers
when thermal equilibrium is reached nett heat flow is
zero
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
138
the temperature of water = temperature of container
1
CHARACTERISTICS
High specific capacity of
REASON
Small change in temperature
inner box
Material X made of good
// keep hot longer time.
heat insulator
(d)
prevent heat from flow out
Max=10
Low density of material X
Low mass // light
Low density of outer box
Low mass // light
Shiny colour of outer box
Reflect heat from outside
TOTAL
20
BAHAGIAN C
NO. 4
(a)(i)
(a)(ii)
(b)(i)
(b)(ii)
ANSWER
temperature of the coolant decreases
speed of the molecules decreases
distance between molecules decreases
when coolant changes from a liquid to a gas, latent heat
is required
latent heat is obtained from the interior of the refrigerator
Q = Pt
= 48 x 5 x 60 // 14 400 J
Q = mc
14 400 = (500 x 10-3)(c) (80 40)
c = 720 J kg-1 oC
Heat supplied by liquid = heat received by water
(500 x 10-3) (4 200) (80 - ) = (1) (4 200) ( - 25)
= 29.34 oC
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
139
CHARACTERISTICS
1. Plate x asbestos
3. Liquid Y oil
(c)
5. Material Z tissue
7. Immersion heater
has high power
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
REASON
2. A good heat insulator
4. Good heat contact
between thermometer
and the aluminium
block//
to
ensure
thermal
equilibrium
between thermometer
and aluminium block
6. Reduce/ prevent heat
lost to the surrounding
8. Can
increase
the
temperature
faster//
fast to heat// supply
more heat energy
Max=10
m
9. S is chosen
10. Because...(repeat characteristics //reason)
TOTAL
20
KERTAS 3 (BAHAGIAN B)
NO. 5
(a)
(b)
(c)(i)
(c)(ii)
(c)(iii)
ANSWER
Volume depends on temperature // temperature influences
volume
If the temperature increases, the volume increases
To investigate the relationship between volume and
temperature
MV: temperature
RV : volume
CV: mass of gas// pressure
Capillary tube, sulphuric acid, thermometer, ice and Bunsen
burner
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
140
(c)(iv)
(c)(v)
1. Put some ice in the beaker and stir until the
temperature is . Record the reaching of temperature.
2. Read and record the length of air trapped.
3. Repeat the experiment 4 times with the difference
1
1
temperature.
(c)(vi)
(oC)
1
2
3
4
5
l (cm)
1
(c)(vii)
TOTAL
12
BAB 5: CAHAYA
BAHAGIAN A
NO. 1
(a)
(b)(i)
(b)(ii)
(c)
(d)(i)
(d)(ii)
(e)
ANSWER
Refraction
Object distance 5.1 is greater than 5.2
Image distance 5.1 is less than 5.2
Image must be on the retina.
Concave lens/cekung
Convex lens/cembung
Correct shape of lens (concave) drawn in the
box
Light rays diverge after passing through
concave lens then converge on the retina after
passing through eye lens.
TOTAL
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
141
NO. 2
ANSWER
The incidence angle in denser medium which can
produce a 90o refracted angle
(a)
MARK
1
(b)(i)
The ray is reflected twice
Direction of ray is correct
(b)(ii)
n=
1
sin 42
n=
1
0.669
1
1
1
1
n=1.491.50
(b)(iii)
Total internal Reflection
refractive index of the inner core is greater than
the outer cladding
total internal reflection can occur
An optical fibre is very small in diameter
hence a bundle of optical fibres can transmit
more information.
Optical fibre has high flexibility
Easy to install in narrow space
TOTAL
(c)(i)
(c)(ii)
(c)(iii)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
12
BAHAGIAN B
NO. 3
(a)
(b)
ANSWER
Focal length in Diagram 9.1 is longer
Lens in Diagram 9.1 is thinner
Power of lens in Diagram 9.1 is lower
The thinner the lens the longer the focal length
The thinner the lens the higher the power of lens
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1
(c)(i)
At u < f
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
142
1
1
1
(c)(ii)
(d)
CHARACTERISTICS
1. Type of the Projection
lens: convex(cembung)
3. Surface of the reflector:
black
REASON
2. Can produce real
image
5. Power of the bulb: high
6. Can produce bright light
7. Distance between LCD
to the screen: far
9. Body material: Lower
Density
8. Can produce large
image
4. Can absorb heat
Max=10
m
10. Easy to carry
TOTAL
20
BAHAGIAN C
NO. 4
(a)
(b)
(c)
ANSWER
Image cannot be caught /formed on a screen
Position of principal axis, object, focal point and concave
(cekung)mirror
Parallel ray reflected to the focal point (A)
Light ray from C reflected along the same path (B)
Extension of (A) and(B) until they meet
Draw upright image where they meet
Virtual, laterally inverted, diminished
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1+1
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
143
CHARACTERISTICS
1. Type of window
glass
3. Use multiple
reflectors
(d)
5. Type of lid used is
clear glass lid
7. Use dark aluminium
pot suspended in a
clear pot
REASON
2. Withstand high
temperature// higher
melting point// glass
trap radiant heat better
than plastics
4. Reflect more sunlight//
concentrating more
light into the box
6. Allow food to be
observed while it is
cooking without
removing the lid
8. Trap the heat inside//
trap heated air next to
the pot//isolating the
air inside the cooker
from the air
outside//very even
heating// sun is able to
shine into the sides
and bottom of the pot
Max=10
m
9. S is chosen
10. Because.....(1357//2468)
(e)(i)
30o
(e)(ii)
60o 15o
450
1
1
TOTAL
20
KERTAS 3 (BAHAGIAN B)
NO. 5
(a)
(b)
(c)(i)
(c)(ii)
(c)(iii)
ANSWER
The object distance affects the size of the image
The greater the object distance, the smaller the size of the
image
To investigate the relationship between the object distance
and the size of the image
MV: object distance, u
RV: size of the image, H
Focal length of the lens / type of lens
Cardboard with a cross-wire in triangular cut-out, light bulb,
lens holder, convex lens, concave lens, white screen
MARK
1
1
1
1
1
1
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
144
(c)(iv)
(c)(v)
1. The convex lens is placed at distance of, u = 15 cm from
the object
2. The screen is adjusted until a sharp image is formed on it.
The size of the image, H is measured.
3. The procedure is repeated with values of u = 20 cm, 25
cm, 30 cm, 35 cm and 40 cm.
u (cm)
1
1
1
H (cm)
15
(c)(vi)
20
25
30
35
(c)(vii)
1
TOTAL
12
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Skema Fizik Kertas 2 Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun SBP 2011 Ting 4Dokument8 SeitenSkema Fizik Kertas 2 Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun SBP 2011 Ting 4nurul atiqah100% (2)
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsVon EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- BB Skema P2 B&C 2011Dokument15 SeitenBB Skema P2 B&C 2011Shahrul AnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualVon EverandPressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- BWM Final 2014 Draft 1Dokument17 SeitenBWM Final 2014 Draft 1hero100% (1)
- Physics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaDokument9 SeitenPhysics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaLeeZiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progress in Aeronautical Sciences: Volume 3Von EverandProgress in Aeronautical Sciences: Volume 3Antonio FerriBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Skema Fizik Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011 Tingkatan 4Dokument11 SeitenSkema Fizik Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011 Tingkatan 4jeglila50% (4)
- Ship Construction & Stability (Time Allowed - 3 Hours) INDIA (2001) Afternoon Paper Total Marks 100Dokument5 SeitenShip Construction & Stability (Time Allowed - 3 Hours) INDIA (2001) Afternoon Paper Total Marks 100Bhupender RamchandaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Jawapan Kertas 2 PDFDokument5 SeitenSkema Jawapan Kertas 2 PDFdarwishmajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Air Decks To Reduce Subdrillings in Escondida MineDokument8 SeitenUse of Air Decks To Reduce Subdrillings in Escondida MineRoberto NoriegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 484, April 11, 1885Von EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 484, April 11, 1885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 Section B and C Sample QuestionsDokument30 SeitenPaper 2 Section B and C Sample Questionscikgusuriyati100% (4)
- Design Project On Reincarnation of Concorde: Anna University: Chennai 600 025Dokument67 SeitenDesign Project On Reincarnation of Concorde: Anna University: Chennai 600 025srajbooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naval Architecture18Dokument6 SeitenNaval Architecture18Thiet PhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization of Landing Gear Fairings: Group7 Daniel Ablog, Michael Fuget, Seunghyun Ko, and Keisuke TsujitaDokument16 SeitenOptimization of Landing Gear Fairings: Group7 Daniel Ablog, Michael Fuget, Seunghyun Ko, and Keisuke TsujitaROBERTO CARLOS NARVAEZ AGUILARNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 The Foiling OptimistDokument12 Seiten03 The Foiling OptimisttoncipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics P2 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangDokument9 SeitenPhysics P2 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangCikgu FaizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- WarehouseDokument51 SeitenWarehouseAnonymous q0irDXlWAm100% (2)
- API 650 Design TanksDokument34 SeitenAPI 650 Design TanksSyedZainAli100% (13)
- Marking Scheme Essay Question: Answer Q1Dokument5 SeitenMarking Scheme Essay Question: Answer Q1jesunathan44@yahoo.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12P305 2016 AugDokument2 Seiten12P305 2016 AugArun PanneerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air LubDokument5 SeitenAir LubnavalntuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FreeseDokument15 SeitenFreeseBrandon HaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of A Pressure Waves Mitigation DevicDokument14 SeitenUse of A Pressure Waves Mitigation Devicyassentaha20000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Volume 7 - Flight PlanningDokument55 SeitenVolume 7 - Flight PlanningBui Duc Hai100% (7)
- Shell Structure: 5.1 Thickness of Shell PlatesDokument8 SeitenShell Structure: 5.1 Thickness of Shell PlatesJuan SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Numerical Investigation of Air Lubrication EffectDokument8 SeitenA Numerical Investigation of Air Lubrication EffectnaufragatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOCK EXAM - Aerodynamics 2017Dokument6 SeitenMOCK EXAM - Aerodynamics 2017Klint TayagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Built-In Buoyancy Computation - Worked Example - Revision 1.3Dokument19 SeitenBuilt-In Buoyancy Computation - Worked Example - Revision 1.3Ikhwan ShafiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Physics Part A: Objective QuestionDokument8 SeitenChapter 1: Introduction To Physics Part A: Objective QuestionMohamad Rizal MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 295 CH 14 MCDokument3 Seiten295 CH 14 MCDulshan GunawardanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculations Tank S6Dokument19 SeitenCalculations Tank S6Joshue Adele100% (1)
- Consolidation Test1Dokument6 SeitenConsolidation Test1Ramesh BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Physics Trial 08 - SchemeDokument9 Seiten02 Physics Trial 08 - SchemeSyafiq HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assingment 1 (Resistance, Propulsion and Machinery)Dokument25 SeitenAssingment 1 (Resistance, Propulsion and Machinery)Brudden NáuticaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TR3 2Dokument15 SeitenTR3 2oriasedelmor10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Penang Trial SPM 2013 Physics K2 Skema PDFDokument8 SeitenPenang Trial SPM 2013 Physics K2 Skema PDFbdy3372Noch keine Bewertungen
- 183 FullDokument14 Seiten183 Fullmechengg01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gas AbsorptionDokument26 SeitenGas AbsorptionNemo Cyzar LiisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pascal, Des & BernoulliDokument15 SeitenPascal, Des & BernoulliNor Hidaya Md SaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Essay AnswerDokument6 SeitenChapter 2 Essay AnswerMamat BuznamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Bladed PropellerDokument8 Seiten7 Bladed Propellerfef123123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis of Midway PaperDokument6 SeitenSynopsis of Midway Paperknowme73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Level - 4 - Chapter 1 - Current TrendsDokument21 SeitenLevel - 4 - Chapter 1 - Current TrendsyangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlling Operation of Ship and Care For Persons On Board at Operational LevDokument3 SeitenControlling Operation of Ship and Care For Persons On Board at Operational LevGiri VenkatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDI13 Storage Tank Design As Per IS803 and API650Dokument36 SeitenTDI13 Storage Tank Design As Per IS803 and API650zefiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 95SCS-4 Sr. No. 6 Examination of Marine Engineer OfficerDokument3 Seiten95SCS-4 Sr. No. 6 Examination of Marine Engineer OfficerBhupender RamchandaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDI13 Storage Tank Design As Per IS803 and API650Dokument36 SeitenTDI13 Storage Tank Design As Per IS803 and API650Faizal Sattu100% (3)
- A New Method of Atmospheric Reentry For Space Shuttles: Alexander BolonkinDokument7 SeitenA New Method of Atmospheric Reentry For Space Shuttles: Alexander BolonkinHimanshu DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Experiment 3: Mohd Ashraf Mohd IsmailDokument29 SeitenLaboratory Experiment 3: Mohd Ashraf Mohd IsmailMohd Ashraf Mohd IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank of College Physics Chapter 9Dokument17 SeitenTest Bank of College Physics Chapter 9MarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Chemical & MechanicalDokument25 SeitenChapter 1 Chemical & MechanicalcykinNoch keine Bewertungen
- SURAHHHHHHHHHHHDokument6 SeitenSURAHHHHHHHHHHHsuraj kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Year Physics From 4 2009 - Scheme p1p2Dokument12 SeitenMid Year Physics From 4 2009 - Scheme p1p2Rosmini Abdul RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Paper2keynoteDokument18 SeitenPhysics Paper2keynoteLeong Sin Yee100% (1)
- Rehab Hip 3 PDFDokument6 SeitenRehab Hip 3 PDFlapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws & Definition PDFDokument2 SeitenLaws & Definition PDFlapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healing Hamstring InjuriesDokument7 SeitenHealing Hamstring Injuriesetelosztas108Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answering Question Techniques Physics SPM 4531-2Dokument7 SeitenAnswering Question Techniques Physics SPM 4531-2wengsung50% (2)
- Gluteal Strain Exercises - tcm28-180752Dokument4 SeitenGluteal Strain Exercises - tcm28-180752lapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physic Form 4 FormulaDokument17 SeitenPhysic Form 4 Formulaadria_elnes100% (2)
- Physics SPM Paper 1, 2 and 3 Tips - 153 DEFINITION and AnswerDokument6 SeitenPhysics SPM Paper 1, 2 and 3 Tips - 153 DEFINITION and AnswerCikgu Faizal75% (4)
- SPM 2013 Physics Paper 3 Section BDokument2 SeitenSPM 2013 Physics Paper 3 Section BlapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answering Technique Paper 3 Physics SPMDokument1 SeiteAnswering Technique Paper 3 Physics SPMped88% (8)
- Physics p3 ExperimentDokument18 SeitenPhysics p3 ExperimentJosh, LRT88% (17)
- Model Heuristics eDokument113 SeitenModel Heuristics elapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answering Questions Technique Physics SPM Paper 3Dokument10 SeitenAnswering Questions Technique Physics SPM Paper 3wengsung100% (13)
- Precautionary Steps For Investigative ExperimentsDokument8 SeitenPrecautionary Steps For Investigative Experimentsatie5050Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 6: Gelombang Bahagian ADokument20 SeitenBab 6: Gelombang Bahagian AlapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 P2Dokument22 SeitenChapter 6 P2Arif Ahmad100% (1)
- F5 CH 1 TeacherDokument15 SeitenF5 CH 1 TeacherIzrin AyobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 1: Pengenalan Kepada Fizik Bahagian A: Period Time For 10 OscillationsDokument19 SeitenBab 1: Pengenalan Kepada Fizik Bahagian A: Period Time For 10 OscillationslapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersDokument14 SeitenSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersChinWynn.com80% (5)
- Chapter 6 P2 AnswersDokument8 SeitenChapter 6 P2 AnswersNirmala SundrarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 RadioactivityDokument23 SeitenNota Padat Fizik F5 Radioactivityslokkro97% (33)
- Rutin KPD Bukan Rutin eDokument3 SeitenRutin KPD Bukan Rutin elapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 6: Gelombang Bahagian ADokument20 SeitenBab 6: Gelombang Bahagian AlapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Physics Chapter 1 - StudentDokument17 SeitenForm 5 Physics Chapter 1 - StudentPavithiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hots SainsDokument51 SeitenHots SainsRiduan SeliminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asking Effective QuestionsDokument8 SeitenAsking Effective Questionsjrogenski9000Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Higher Order Thinking Questions Preso PDFDokument34 Seiten1 - Higher Order Thinking Questions Preso PDFlapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initial Exercises For Gluteal StrainsDokument13 SeitenInitial Exercises For Gluteal StrainslapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initial Exercises For Gluteal StrainsDokument13 SeitenInitial Exercises For Gluteal StrainslapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Problems 1,2,3Dokument3 SeitenTutorial Problems 1,2,3Chloe OlazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MD1-0-E-505!06!00001 Generator Transformer Sizing CalculationDokument19 SeitenMD1-0-E-505!06!00001 Generator Transformer Sizing Calculationtvpham12350% (2)
- Forces SlopesDokument6 SeitenForces SlopesXolani MoffatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 11 Physics - Chapter 10 ElectrostaticsDokument24 SeitenMaharashtra Board Solutions Class 11 Physics - Chapter 10 ElectrostaticsManveer SingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cargo Calculations - Tanker WorkDokument24 SeitenCargo Calculations - Tanker WorkVasil Raykov100% (1)
- 24 04 11 PDFDokument6 Seiten24 04 11 PDFMostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radioactivity - PDFDokument8 SeitenRadioactivity - PDFWhite Heart100% (2)
- Recent Progress Toward A Three-Dimensional Unstructured Navier-Stokes Flow SolverDokument21 SeitenRecent Progress Toward A Three-Dimensional Unstructured Navier-Stokes Flow SolverDanielle HaysNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Wireless Channel 1Dokument43 SeitenThe Wireless Channel 1Anil FkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDokument48 SeitenFluid Mechanics PDFrakib hasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- JKCET Medical 2015 Answer Key Phy CheDokument12 SeitenJKCET Medical 2015 Answer Key Phy CheRuchi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regenerative CycleDokument9 SeitenRegenerative CycleJon Vincent BallesteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematic Viscosity, Units & DimensionDokument7 SeitenKinematic Viscosity, Units & DimensionPrithwish Kr SutradharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concave and Convex LensDokument7 SeitenConcave and Convex LensannmarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: Water: The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsDokument6 SeitenChapter 2: Water: The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsMariam EidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridge AerodynamicsDokument25 SeitenBridge AerodynamicsJoseAngelFernandezOrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project Finite Element AnalysisDokument41 SeitenFinal Project Finite Element AnalysisAkhil KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- PACO IE3 MotorDokument24 SeitenPACO IE3 Motoriqxca azmyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- E1 - Heat Transfer LabDokument5 SeitenE1 - Heat Transfer LabManu K VasudevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit One Formulae and Definitions Module 1: Mechanics D: Base Quantity Base Unit ImensionsDokument27 SeitenUnit One Formulae and Definitions Module 1: Mechanics D: Base Quantity Base Unit ImensionsUnexpected TheoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADOMIAN Decomposition Method For Solvin1Dokument18 SeitenADOMIAN Decomposition Method For Solvin1Susi SusilowatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet - 01-Pages-27-72Dokument46 SeitenSheet - 01-Pages-27-72Hemant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Exe3 SolDokument2 Seiten1 Exe3 SolTarak BENSLIMANENoch keine Bewertungen
- VLC Technical Seminar ReportDokument11 SeitenVLC Technical Seminar ReportjashwanthmekalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Montalk - Dimensional Shift - The Physics of 2012 - Fringe ScienceDokument4 SeitenMontalk - Dimensional Shift - The Physics of 2012 - Fringe ScienceKamal HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cheat Sheet SurfaceDokument2 SeitenCheat Sheet SurfaceArchita VNoch keine Bewertungen
- 003 - Option B Chapter 14 Engineering Physics PDFDokument62 Seiten003 - Option B Chapter 14 Engineering Physics PDFyuke kristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimisation of Bench-BermDokument25 SeitenOptimisation of Bench-BermMacarena Ulloa MonsalveNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Engineering - Civil Engineering Department: Carig CampusDokument6 SeitenCollege of Engineering - Civil Engineering Department: Carig CampusShanaia Kate AsutenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Materials and MechanicsDokument2 SeitenComposite Materials and MechanicsroscillaNoch keine Bewertungen