Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
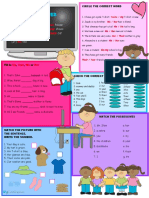
Simple Past
Hochgeladen von
Meshal Al-mutairiOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Simple Past
Hochgeladen von
Meshal Al-mutairiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
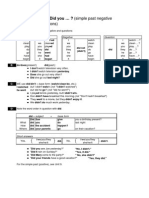
Simple past
Negative question:
The simple past, past simple or past indenite, sometimes called the preterite, is the basic form of the past
tense in Modern English. It is used principally to describe
events in the past, although it also has some other uses.
Regular English verbs form the simple past in -ed; however there are a few hundred irregular verbs with dierent
forms.
Did I/you/he/she/it/we/they not help?
Didn't I/you/he/she/it/we/they help?
2 Usage
The term "simple" is used to distinguish the syntactical
construction whose basic form uses the plain past tense The simple past is used for a single event (or sequence of
alone, from other past tense constructions which use aux- such events) in the past, and also for past habitual action:
iliaries in combination with participles, such as the past
He took the money and ran.
perfect and past progressive.
I visited them every day for a year.
Formation
It can also refer to a past state:
Regular verbs form the simple past in -ed; however there
I knew how to ght even as a child.
are a few hundred irregular verbs with dierent forms.
For details see English verbs: Past tense.
For action that was ongoing at the time referred to, the
Most verbs have a single form of the simple past, indepen- past progressive is generally used instead (e.g. I was cookdent of the person or number of the subject (there is no ing). The same can apply to states, if temporary (e.g. the
addition of -s for the third person singular as in the simple ball was lying on the sidewalk), but some stative verbs do
present). However, the copula verb be has two past tense not generally use the progressive aspect at all see Uses
forms: was for the rst and third persons singular, and of English verb forms: Progressive and in these cases
were in other instances. The form were can also be used the simple past is used even for a temporary state:
in place of was in conditional clauses and the like; for
information on this, see English subjunctive. This is the
The dog was in its kennel.
only case in modern English where a distinction in form
I felt cold.
is made between the indicative and subjunctive moods in
the past tense.
However, with verbs of sensing, it is common in such circumstances to use could see in place of saw, could hear
in place of heard, etc. For more on this, see can see.
Questions, other clauses requiring inversion, negations
with not, and emphatic forms of the simple past use the
auxiliary did. For details of this mechanism, see dosupport. A full list of forms is given below, using the
(regular) verb help as an example:
If one action interrupts another, then it is usual for the
interrupted (ongoing) action to be expressed with the past
progressive, and the action that interrupted it to be in the
simple past:
Basic simple past:
Your mother called while you were
cooking.
I/you/he/she/it/we/they helped
Expanded (emphatic) simple past:
The simple past is often close in meaning to the present
perfect. The simple past is used when the event happened
at a particular time in the past, or during a period which
ended in the past (i.e. a period that does not last up until the present time). This time frame may be explicitly
stated, or implicit in the context (for example the past
tense is often used when describing a sequence of past
events).
I/you/he/she/it/we/they did help
Question form:
Did I/you/he/she/it/we/they help?
Negative:
I/you/he/she/it/we/they did not (didn't) help
1
4
I was born in 1980.
We turned the oven o two minutes ago.
I came home at 6 o'clock.
When did they get married?
We wrote two letters this morning.
(the simple past is appropriate here
if it is no longer morning)
She placed the letter on the table,
sighed, and left the house.
Contrast these examples with those given at Uses of English verb forms: Present perfect. Note also that for past
actions that occurred before the relevant past time frame,
the past perfect is used.
Various compound constructions exist for denoting past
habitual action. The sentence When I was young, I played
football every Saturday might alternatively be phrased using used to (... I used to play ...) or using would (... I would
play...).
The simple past also has some uses in which it does not refer to a past time. These are generally in condition clauses
and some other dependent clauses referring to hypothetical circumstances, as well as certain expressions of wish:
If he walked faster, he would get
home earlier.
I wish I knew what his name was.
I would rather she wore a longer
dress.
For more details see the sections on conditionals,
dependent clauses and expressions of wish in the article
on uses of English verb forms.
For use of the simple past (and other past tense forms) in
indirect speech, see Uses of English verb forms: Indirect
speech. An example:
He said he wanted to go on the
slide.
See also
English verbs
Uses of English verb forms
Preterite
Past tense
Other tenses:
Simple present
Present perfect
REFERENCES
4 References
iStudyEnglishOnline (2013). Past Simple Uses &
Explanations
ingilizceturkce.gen.tr (2014). Past Simple with Exercises
Text and image sources, contributors, and licenses
5.1
Text
Simple past Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simple_past?oldid=722812891 Contributors: Sinuhe, Netspy, Kwamikagami, Anthony Appleyard, Bgwhite, SmackBot, Chris the speller, Nick Levine, Ckatz, Bungeh, Twas Now, Fabrictramp, Tgeairn, Katharineamy,
VolkovBot, Flyer22 Reborn, Rodarmor, Denisarona, Mild Bill Hiccup, Akira-otomo, WikHead, Addbot, Thaejas, Moosehadley, Trevas,
Luckas-bot, Der Meister, Xqbot, Zad68, Carveone, Telofy, Calbannin, le ottante, Petr Kulaty, EmausBot, WikitanvirBot, CaptRik,
Azkm, ZroBot, F, Waterfalls12, Donner60, ClueBot NG, Widr, Tony Tan, Victor Yus, The Illusive Man, JYBot, Sancar1983, JaconaFrere, Futrer, Sunsann, Nelsonkam, ScrapIronIV, 3 of Diamonds and Anonymous: 53
5.2
Images
5.3
Content license
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pre-Intermediate Progress Test 1Dokument6 SeitenPre-Intermediate Progress Test 1Carlos Berrospe73% (11)
- ASHRAE - District Cooling Best Guide PDFDokument175 SeitenASHRAE - District Cooling Best Guide PDFPERICOGARCA100% (7)
- English Test: Snapshot IntermediateDokument4 SeitenEnglish Test: Snapshot IntermediateLiliana GheorgheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Unit 7 Welcome 1Dokument3 SeitenTest Unit 7 Welcome 1Valentina PrepaskovskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 35 Basic Mistakes To AvoidDokument16 Seiten35 Basic Mistakes To AvoidMariam Ikram100% (3)
- Auden Henry William 1867 A Minimum of GreekDokument192 SeitenAuden Henry William 1867 A Minimum of Greekthersites100% (1)
- World at NightDokument10 SeitenWorld at NightSHIVAJI CHOUDHURYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real English: 1. Complete The Chart. Personal Pronouns Possessive AdjectivesDokument7 SeitenReal English: 1. Complete The Chart. Personal Pronouns Possessive AdjectivesvericliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name and surname:……………………………...... Date:……………………… 1. Преведи ги реченицитеDokument2 SeitenName and surname:……………………………...... Date:……………………… 1. Преведи ги реченицитеOlgica KarovskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pismena 1-Osmo OddDokument2 SeitenPismena 1-Osmo OddLjupka Banar PoposkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar and Vocabulary Test - March 2019Dokument2 SeitenGrammar and Vocabulary Test - March 2019VYXNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Test For 7-8th GradeDokument2 SeitenEnglish Test For 7-8th GradeRozalija RamovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Past Vs PR PerDokument13 SeitenSimple Past Vs PR PerSaadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Втора Писмена Работа По Англиски ЈазикDokument1 SeiteВтора Писмена Работа По Англиски ЈазикВиолетаЦветковиќ100% (1)
- Present Perfect Tense PPPDokument38 SeitenPresent Perfect Tense PPPSandra Sánchez OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 6 9Dokument3 SeitenTest 6 9Pavle JovanoskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Grammar 1o ESODokument4 SeitenReview Grammar 1o ESOConchin TarazonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pet Buster Test Kl. 9Dokument1 SeitePet Buster Test Kl. 9Selajdin IslamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Simple - All FormsDokument1 SeitePast Simple - All FormsrenataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn English Grammar - Present Simple and ContinuousDokument2 SeitenLearn English Grammar - Present Simple and ContinuousBranka Telenta0% (1)
- Perfect Tenses PracticeDokument3 SeitenPerfect Tenses PracticeJuan Pablo Moreno BuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suffix and Prefix Exercise 1Dokument8 SeitenSuffix and Prefix Exercise 1Rodrigo CarvalhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is This?: Robert SusuanDokument2 SeitenWhat Is This?: Robert SusuanElizabeta KosteskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write Affirmative, Negative or Question Form in The Present Continuous TenseDokument3 SeitenWrite Affirmative, Negative or Question Form in The Present Continuous TenseMima TrenevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Continuous Tense TestDokument2 SeitenPast Continuous Tense TestN. R.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name & Surname: - DateDokument2 SeitenName & Surname: - DateAndrijana DimitrievaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Test For 8th Grade Group 2Dokument2 SeitenEnglish Test For 8th Grade Group 2Rozalija RamovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future Tenses Quiz: Fill in The Blanks With The Most Appropriate Verb FormsDokument4 SeitenFuture Tenses Quiz: Fill in The Blanks With The Most Appropriate Verb Formspochaco4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Complete The Sentences Using Both Present Perfect and Present Perfect ContinuousDokument1 SeiteComplete The Sentences Using Both Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuousgominola_92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vtora Pisena Rabota Po Angliski Jazik Za Osmo 2Dokument2 SeitenVtora Pisena Rabota Po Angliski Jazik Za Osmo 2Sara JovanovskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Possessive-Adjectives-With-Key 2Dokument1 SeitePossessive-Adjectives-With-Key 2Daniela AmistadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 VII - Grade November, 2014: 1. Choose The Right WordDokument2 SeitenTest 1 VII - Grade November, 2014: 1. Choose The Right WordLjupka Banar PoposkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prva Pismena Rabota Po Angliski Jazik Za Osmo Oddelenie 2010Dokument2 SeitenPrva Pismena Rabota Po Angliski Jazik Za Osmo Oddelenie 2010Sara JovanovskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 10: Simple Past Negative and QuestionsDokument2 SeitenUnit 10: Simple Past Negative and QuestionsYulia LogunovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEST 4b Messages 3Dokument2 SeitenTEST 4b Messages 3Sirma Stavreska0% (1)
- Present Simple Grammar Test HomeworkDokument2 SeitenPresent Simple Grammar Test HomeworkjurgitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Test For 8th GradeDokument2 SeitenEnglish Test For 8th GradeRozalija RamovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Трето одделение 2011 тест 2Dokument3 SeitenТрето одделение 2011 тест 2Nikola NedelkovskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Simple or Past ContinuousDokument2 SeitenPast Simple or Past ContinuousNoelia0% (2)
- Cleft Sentences: Sit Dolor AmetDokument13 SeitenCleft Sentences: Sit Dolor AmetDan HayesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises Relative ClausesDokument1 SeiteExercises Relative ClausesTünde PintilieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfred's Typical American School DayDokument2 SeitenAlfred's Typical American School DayMónica MeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Help environment by recycling and saving energyDokument2 SeitenHelp environment by recycling and saving energyMarina NikolovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homophones Circling P 2 IntermediateDokument2 SeitenHomophones Circling P 2 IntermediateSaturos Jadilyn Rose100% (1)
- Circle The Correct Answers:: English Test (Units 5 & 6) NameDokument2 SeitenCircle The Correct Answers:: English Test (Units 5 & 6) NameTanya SpirovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7-Present Perfect and Simple PastDokument9 SeitenUnit 7-Present Perfect and Simple PastĐỗ Ngọc Mỹ NhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academic Writing Course Present Tenses ReviewDokument8 SeitenAcademic Writing Course Present Tenses ReviewjorghelaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Tutorial VerbsDokument3 SeitenSummer Tutorial VerbsPeterAndrewRegenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech - Exercise ADokument4 SeitenReported Speech - Exercise ASara •Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Worksheet Second ConditionalDokument2 SeitenGrammar Worksheet Second Conditionaljanebennet3000Noch keine Bewertungen
- English Grammar SuffixesDokument4 SeitenEnglish Grammar SuffixesVicSana KazakevichNoch keine Bewertungen
- ТЕСТ 2. 8мо ДеветолеткаDokument2 SeitenТЕСТ 2. 8мо ДеветолеткаAleksandra Koceva-MojsoskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pet Buster Worksheet GuideDokument2 SeitenPet Buster Worksheet Guideandy100% (1)
- English TestDokument2 SeitenEnglish TestElizabeta KosteskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cat and The BellDokument17 SeitenThe Cat and The Bellmarijabogatinovska100% (1)
- Put The Verbs Into The Correct Tense (Simple Past or Past Progressive)Dokument1 SeitePut The Verbs Into The Correct Tense (Simple Past or Past Progressive)Reka HillierNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Nastavno Livche Relative Pronouns Exercises PET BusterDokument2 Seiten11 Nastavno Livche Relative Pronouns Exercises PET BusterZorica Arnaudova100% (1)
- g1 Ordering Comparing NumbersDokument2 Seiteng1 Ordering Comparing NumbersChistine Rose EspirituNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Perfect ReviewDokument2 SeitenPast Perfect ReviewCarlaCarolinaFortuna100% (1)
- Exam 2 EsoDokument5 SeitenExam 2 EsoLourdes Rubio CallejónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Test Messages ADokument2 SeitenFinal Test Messages ABiljana PetrovskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Past, Past Simple or Past Indefinite,: Preterite Past Tense Modern EnglishDokument4 SeitenSimple Past, Past Simple or Past Indefinite,: Preterite Past Tense Modern Englishبارق نوارNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Zainab WaleedDokument4 SeitenEnglish Zainab Waleedmercure19100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Past Simple TenseDokument17 SeitenPast Simple TenseAPRILIA NURULNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concealed Ducted Split Units R22 24-60 MBH 50HzDokument20 SeitenConcealed Ducted Split Units R22 24-60 MBH 50HzMeshal Al-mutairi100% (1)
- 062 071 Boldt and KeenDokument10 Seiten062 071 Boldt and KeenMeshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NGEDokument40 SeitenNGEMeshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vana Seçimi Control Valve Selection Practical GuideDokument7 SeitenVana Seçimi Control Valve Selection Practical GuideÖmer EmelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adm Apn001 en 121801Dokument8 SeitenAdm Apn001 en 121801Meshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duct Sizing-Static BalanceDokument24 SeitenDuct Sizing-Static BalancemohdnazirNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Energy Conservation in Buildings Code MEW-R6-2014 PDFDokument38 SeitenThe Energy Conservation in Buildings Code MEW-R6-2014 PDFPERICOGARCA100% (1)
- SHT CostBenefitAnalysisDokument21 SeitenSHT CostBenefitAnalysisMeshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adm Apn060 en - 110116Dokument8 SeitenAdm Apn060 en - 110116Meshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Getting StartedDokument78 SeitenGetting StartedMeshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duct Design 2016Dokument14 SeitenDuct Design 2016Meshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling Load Sheet PDFDokument91 SeitenCooling Load Sheet PDFKagitha Tirumala100% (1)
- APP CMC047 en Material Std62Dokument93 SeitenAPP CMC047 en Material Std62Meshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ashare 62 2001Dokument40 SeitenAshare 62 2001Trương Văn Cường100% (2)
- Manual For The Design of Pipe Systems and Pumps - GEADokument56 SeitenManual For The Design of Pipe Systems and Pumps - GEABeomHee LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duct DesignDokument9 SeitenDuct DesignjaswanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edr Designbriefs ChillerplantDokument28 SeitenEdr Designbriefs ChillerplantAnonymous PkeI8e84RsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Expansion CalculationsDokument2 SeitenPipe Expansion CalculationsMeshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydronics 102 System Components: Technical FeatureDokument10 SeitenHydronics 102 System Components: Technical FeatureMeshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amca 300Dokument46 SeitenAmca 300tesbtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Turbine Buy OnkarDokument965 SeitenSteam Turbine Buy OnkarSandip Kumar100% (5)
- 1 s2.0 S0038092X14000474 MainDokument11 Seiten1 s2.0 S0038092X14000474 MainMeshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Piping and Pump CarrierDokument64 SeitenWater Piping and Pump CarrierMeshal Al-mutairi100% (5)
- PM Handbook6Dokument61 SeitenPM Handbook6Meshal Al-mutairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigeration HandoutDokument144 SeitenRefrigeration HandouthamooodiiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Passive Voice 3Dokument4 SeitenThe Passive Voice 3LalitheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giao An Day Phu Dao Anh 9Dokument65 SeitenGiao An Day Phu Dao Anh 9mr hanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 04 - ArticlesDokument9 SeitenUNIT 04 - ArticlesDumitrita TabacaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Tenses in A TabloDokument4 SeitenAll Tenses in A Tabloahmtozkn100% (1)
- English Language, Word FormationDokument27 SeitenEnglish Language, Word FormationShaip DautiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30 The Passive VoiceDokument7 Seiten30 The Passive VoiceOvidiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Plan - English Year 6Dokument2 SeitenDaily Lesson Plan - English Year 6thilagarajandran1993Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Verb?: Click Here To Find Out...Dokument26 SeitenWhat Is A Verb?: Click Here To Find Out...Shereen Jungco Tabug100% (1)
- F. Y. B. A. Compulsory English (W. E. f-2013 - 2014) : Prescribed Text: Visionary Gleam: A Selection of Prose andDokument6 SeitenF. Y. B. A. Compulsory English (W. E. f-2013 - 2014) : Prescribed Text: Visionary Gleam: A Selection of Prose andAnurima DeshpandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Year 4Dokument33 SeitenEnglish Year 4EmellianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of Speech ExercisesDokument3 SeitenParts of Speech ExercisesbatutamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 01 Gopal Parts of SpeechDokument8 Seiten01 01 Gopal Parts of SpeechRadha KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irrigular Verbs CompletoDokument4 SeitenIrrigular Verbs CompletoMichele Vieira de OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food - Cooking Verbs - QuantitiesDokument2 SeitenFood - Cooking Verbs - QuantitiesJulie NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tips For ACT English PDFDokument19 SeitenTips For ACT English PDFJayvis Gonsalves100% (1)
- UPSR English Paper TipsDokument15 SeitenUPSR English Paper TipsAl ShamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ielts Writing Task VocabularyDokument10 SeitenIelts Writing Task VocabularyAlezdihar SeihatNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 25 Grammar Capsule - Prepositions For The PerplexedDokument3 SeitenJune 25 Grammar Capsule - Prepositions For The PerplexedAkanksha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Simple IrregularDokument11 SeitenPast Simple IrregularmsoldugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gerund PPT FixDokument33 SeitenGerund PPT FixfinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Test Unit 5Dokument1 SeiteQuick Test Unit 5Dini Haiti Zulfany0% (1)
- Adjectives AR 2Dokument10 SeitenAdjectives AR 2Bri Kate O'DonoghueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 117 The Simple Present and The Present ContinuousDokument45 Seiten117 The Simple Present and The Present ContinuousPiroska Szolnoki33% (3)
- Part TOEFLDokument7 SeitenPart TOEFLFrisca Rahma DwinantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irregular VerbsDokument3 SeitenIrregular Verbsapi-327991691Noch keine Bewertungen
- DELTA Terminology PDFDokument3 SeitenDELTA Terminology PDFlola's booksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjectives and Adverbs: Eugenia Ida Edward UB00102 Communicative English GrammarDokument17 SeitenAdjectives and Adverbs: Eugenia Ida Edward UB00102 Communicative English GrammarVLxiaoyu Ivy Chai50% (2)