Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes Good
Hochgeladen von
Anitesh DharamCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes Good
Hochgeladen von
Anitesh DharamCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
24/04/2016
HOME
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
CBSE
STUDY MATERIAL
CLASSES
ICSE / ISC
STATE BOARDS
NCERT
MOCK TESTS
TALENT SEARCH EXAMS & OLYMPIADS
ENTRANCE EXAMS
RESOURCES
HC VERMA SOLUTIONS
GOT A QUESTION? ASK US HERE!
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes :
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
October 22, 2014 by Anuj William Leave a Comment
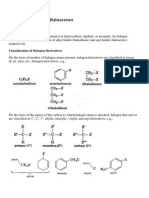
The replacement of hydrogen atom(s) in hydrocarbon, aliphatic or aromatic, by halogen atom(s) results in
the formation of alkyl halide (haloalkane) and aryl halide (haloarene), respectively.
Classi1cation of Halogen Derivatives
On the basis of number of halogen atoms present, halogen derivatives are classi1ed as mono, di, tri, tetra,
etc., halogen derivatives, e.g.,
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
1/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
On the basis of the nature of the carbon to which halogen atom is attached, halogen derivatives are
classi1ed as 1, 2, 3, allylic, benzylic, vinylic and aryl derivatives, e.g.,
General Methods of Preparation of Haloalkanes
1. From Alcohols
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
2/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
In Grooves method, ZnC12 is used to weaken the C-OH bond. In case of 3 alcohols, ZnC12 is not required.
The reactivity order of halogen acids is HI > HBr > HCl.
Darzen procedure is the best method for preparing alkyl halides from alcohols since both the by products
(SO2 and HCl) are gaseous andescape easily.
2. Free Radical Halogenation of Alkanes
Addition of Hydrogen Halides on Alkenes
1. Finkelstein Reaction
2. Swarts Reaction
H3C Br + AgF H3C F + AgBr
Hg2F2, COF2 and SbF3 can also be used as a reagent for Swarts reaction.
3. Hunsdiecker Reaction
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
3/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
Physical Properties of Haloalkanes
1. Boiling point orders
1. R I > R Br > R CI > R F
2. CH3 (CH2)2 CH2Br > (CH3)2 CHCH2Br > (CH3)3CBr
3. CH3CH2CH2 > CH3CH2X > CH3X
2. Bond strength of haloalkanes decreases as the size of the halogen atom increases. Thus, the order of
bond strength is
CH3F > CR3Cl > CR3Br > CH3I
3. Dipole moment decreases as the electronegativity of the halogen decreases.
4. Haloalkanes though polar but are insoluble in water as they do not form hydrogen bonding with water.
5. Density order is
RI > RBr > RCl > RF (For the same alkyl group)
CH3I > C2H5I > C3H7I
Chemical Reactions of Haloalkanes
1. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions (SN reactions)
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
4/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
kCN is predominantly ionic and provides cyanide ions in solution, which is ambident nucleophile and bind
with carbon side to form as the major product, while AgCN is covalent and form isocyanide as the major
product.
Like KCN, KNO2 form R-ONO while AgNO2 produces R-NO2 as product. Vinyl chloride is less reactive
towards nucleophilic substitution reactions due to resonance.
Nucleophilic substitution reactions are of two types
(a) SN1 type (Unimolecular nucleophilic reactions proceed in two steps:
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
5/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
Rate, r = k [RX). It is a 1rst order reaction.
Reactivity order of alkyl halide towards SN1 mechanism
3 > 2 > 1
Polar solvents, low concentration of nucleophiles and weak nucleophiles favour SN1 mechanism.
In SN1 reactions, partial racemisation occurs due to the possibility of frontal as well as backside attack on
planar carbocation.
(b) SN2 type (Bimolecular nucleophilic substitution) These reactions proceed in one step and is a second
order reaction withr = k[RX] [Nu].
During SN2 reaction, inversion of con1guration occurs (Walden inversion) i.e., starting with dextrorotatory
halide a laevo product is obtained and vice-versa, e.g.,
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
6/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
Reactivity of halides towards SN2 mechanism is
1 > 2 > 3
Rate of reaction in SN2 mechanism depends on the strength of the attacking nucleophile. Strength of some
common nucleophiles is
:CN > : I > : OR > : OH > CH3COO: > H2O > F
Non-polar solvents, strong nucleophiles and high concentration of nucleophiles favour SN2 mechanism.
Relative rates of some alkyl halides in SN1 and SN2 reactions are in the order
Resonating structure of benzyl carbocations are
Relative reactivity of alkyl halides for same alkyl group is
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
7/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
RI > RBr > RCI > RF
2. Elimination Reactions
Dehydrohalogenation is a elimination reaction in which halogen is from -carbon atom and the
hydrogen from the -carbon according to Saytzeff rule, e.g.,
Ease of dehydrohalogenation among halides
3 > 2 > 1
3. Reduction
4. Reaction with Metals
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
8/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
Grignard reagent is never isolated in the solid state as it explodes in dry state. So it is used as ethereal
solution.
5. lsomerisation
General Methods of Preparation of Aryl Halides
1. By Halogenation of Aromatic Hydrocarbons
It is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
2. By Side Chain Halogenation
(It involves free radical mechanism.)
3. From Benzene Diazonium Salt
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
9/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
4. From Phenol
Physical Properties of Aryl Halides
1. Aryl halides are colourless liquids or colourless solids with characteristic odour.
2. Boiling point generally increases with increase in the size of aryl group or halogen atom. Boiling point
order
Ar I > Ar Br > Ar Cl > Ar F
3. The melting point of p -isomer is more than 0- and m-isomer.
This is because of more symmetrical nature of p-isomer.
4. Due to resonance in chlorobenzene, C-CI bond is shorter and hence, its dipole moment is less than that
ofcyclohexylchloride.
Chemical Properties of Aryl Halides
1. Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction
Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction. Their low reactivity is attributed due
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
10/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
to the following reasons:
1. Due to resonance, C-X bond has partial double bond character.
2. Stabilisation of the molecule by delocalisation of electrons.
3. (Instability of phenyl carbocation.
However, aryl halides having electron withdrawing groups (like NO2, -SO3H, etc.) at ortho and para
positions undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction easily.
Presence of electron withdrawing group (-NO2) increases the reactivity.
2. Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
Halogens are deactivating but O, p-directing. Thus, chlorination, nitration, sulphonation and Friedel Crafts
reaction give a mixture of o- and P- chloro substituted derivatives.
(i) Halogenation
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
11/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
(ii) Nitration
(iii) Sulphonation
(iv) Friedel-Crafts reaction
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
12/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
3. Reaction with Metals
(i) Wurtz Fittig reaction
(ii) Fitting reaction
(iii) Ullmann reaction
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
13/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
Dlhalogen Derivatives
Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) is widely used as a solvent, as a propellant in aerosols. Direct contact of
dichloromethane in humans causes intense burning and milk redness of the skin.
Trihalogen Derivatives
1. Chloroform [Trichloromethane, CHCl3]
Methods of preparation
Properties
1. Oxidation of CHCl3gives poisonous gas phosgene (carbonyl chloride).
To avoid this oxidation CHCl3 iI .toreci in dark brown bottles and 1lled to the brim. 1% ethanol is added to
chloroform which converts harmful phosgene gas into diethyl carbonate.
2. CHCl3 is widely used in the production of freon refrigerant R-22.
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
14/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
3. On nitration, it gives tear producing insecticide substance chloropicrin.
2. Iodoform (tri-iodornethane, CHl3)
Iodoform is prepared by iodoform reaction.
Compounds containing either CH3CO- or CH3CH(OH) group form yellow colour iodoform with I2 and NaOH.
Iodoform when comes in contact with organic matter, decomposes easily to free iodine, an antiseptic. Due
to its objectionable smell, it hasbeen replaced by other formulations containing iodine.
Polyhalogen Derivatives
1. Tetrachloromethane (Carbon Tetrachloride, CCl4 )
Preparation
CCI4 is a colourless, non-inammable, poisonous liquid, soluble in alcohol and ether.
Uses
Carbon tetrachloride is used
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
15/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
1. as a solvent for oils, fats, resins
2. in dry cleaning
3. as 1re extinguisher under the name pyrene.
2. Freons
The chlorouorocarbon compounds of methane and ethane are collectively known as freons. These are
usually produced for aerosol propellants, refrigeration and air conditioning purposes. Carbon tetra chloride
when reacts with antimony triuoride in the presence of SbCl5as catalyst, dichlorouromethane (freon) is
obtained.
3. DDT (p, p-Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane)
DDT is the 1rst chlorinated organic insecticide. Its stability and fat solubilityis a great problem.
It is prepared from chloral and chlorobenzene in the presence of conc. H2SO4
4. Perchloroethane (C2Cl6)
It is used as moth repellant and is also known as arti1cial camphor.
All CBSE Notes for Class 12 Chemistry
Maths Notes
Physics Notes
Biology Notes
If you have any query regarding this topic please post your queries HERE
Filed Under: CBSE
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
16/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
Tagged With: CBSE 12 Notes, CBSE Class Notes, CBSE Notes, Class 12 Notes, Class 12th Notes, Free CBSE Notes, Free
Notes
YOURREACTION?
Happy
Angry
Amused
Indifferent
Excited
232
37
32
30
22
PoweredbyVICOMI
RELATED POSTS
STAY UPDATED!
Get all updates and information in your Inbox. Enter your email below:
E-Mail Address
GO
5 comments
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
17/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
5Comments
Sortby Newest
Addacomment...
MontyTembhurne
Itisanexcellentinformation
LikeReplyMar31,201611:56pm
ShubhamDubeySTUDENTOFCLASS11SCIENCE~MATH~COMPatM.J.R.P.PublicSchool.Ghazipur
Goodit'shelpful
LikeReplyMar8,20164:09pm
VishalJain
itsucksit'salmostsimilartothenotessummerisedinulike.....
LikeReplyMar5,20168:00pm
VishalKumarNachiketanPublicSchool
grt
LikeReply
1Dec2,20159:48am
SiddhantMishra
ilikeit...
LikeReplyNov17,20152:22am
FacebookCommentsPlugin
Search the site ...
STAY UPDATED!
Get all updates and information in your
Inbox. Enter your email below:
E-Mail Address
GO
CBSE Date Sheet
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
18/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
MOCK TESTS
IMO Mock Test | IEO Mock Test | NSO Mock Test
PSA Online Mock Test
KVPY Online Mock Test
NTSE Online Mock Test
IMPORTANT ENTRANCE EXAMS
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
19/21
24/04/2016
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
Copyright 2014 - AglaSem Schools - AglaSem EduTech Pvt. Ltd.
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
20/21
24/04/2016
http://schools.aglasem.com/55441
CBSEClass12ChemistryNotes:HaloalkanesandHaloarenes
21/21
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokument24 SeitenChapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesSuhas GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes: Classification of Halogen DerivativesDokument16 SeitenHaloalkanes and Haloarenes: Classification of Halogen Derivativeskaushik247Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokument159 SeitenPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- HaloalkanesDokument12 SeitenHaloalkanesMo_Bash1Noch keine Bewertungen
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES (FULLY SOLVED) FOR CBSE (IIT-JEE) EXAMS (2021-2022Dokument38 SeitenHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES (FULLY SOLVED) FOR CBSE (IIT-JEE) EXAMS (2021-2022Ananth DharanidharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- S Block ElementsDokument11 SeitenS Block Elements19ucha023 19ucha023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokument2 SeitenHaloalkanes and HaloarenesVisakh Suku SNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 02Dokument47 Seiten12 Chemistry Impq CH10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 02Swaroop SurendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HaloalkanesDokument13 SeitenHaloalkanesChingYan TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactions of HaloalkanesDokument10 SeitenReactions of Haloalkanesapi-504683923Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 14.0: Haloalkanes (Alkyl Halides)Dokument12 SeitenTopic 14.0: Haloalkanes (Alkyl Halides)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDokument28 SeitenHaloalkanes & HaloarenesFam IlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haloalkanes QDokument7 SeitenHaloalkanes Qlucylovesbooks6770Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokument7 Seiten12 Chemistry Notes Ch10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesShouvik sinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name Reaction 3569Dokument38 SeitenName Reaction 3569Ashish AmbekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mrs. Preetha - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - WS005Dokument4 SeitenMrs. Preetha - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - WS005Vikram MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Classification and PropertiesDokument24 SeitenAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Classification and PropertiesMadhureemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry: Chapter OutlineDokument68 SeitenChemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry: Chapter OutlineMaden betoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn: Chapter-10 Haloalkanes & Haloarenes Class-XII Subject-ChemistryDokument32 SeitenLearn: Chapter-10 Haloalkanes & Haloarenes Class-XII Subject-Chemistryprajaktac506Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organometallic CompoundsDokument66 SeitenOrganometallic CompoundsJon Ho100% (1)
- 20 HaloalkanesDokument7 Seiten20 HaloalkanesizabelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkyl Halides and Nucleophilic SubstitutionDokument53 SeitenAlkyl Halides and Nucleophilic SubstitutionRaja DanishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehydes & Ketones DPP 4Dokument2 SeitenAldehydes & Ketones DPP 4Vishal_93100% (1)
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Dokument1 SeiteCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Shreyash KolekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH2.2 - AlkeneDokument48 SeitenCH2.2 - AlkeneNur Ain SyuhadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST Columba's School Class 12 - Chemistry: Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokument3 SeitenST Columba's School Class 12 - Chemistry: Haloalkanes and HaloarenesKushar Dev Chhibber100% (1)
- CBSE Class XII Chemistry Test on Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokument2 SeitenCBSE Class XII Chemistry Test on Haloalkanes and HaloarenesyeateshwarriorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - Class XII - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokument8 SeitenAssignment - Class XII - Haloalkanes and Haloarenesgarv khoslaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic 6 CDokument26 SeitenOrganic 6 CDr.Rajarshi PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redox RxnsDokument30 SeitenRedox RxnsJolaine ValloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes McqsDokument2 SeitenAlkanes McqsMuhammad Ahtisham AsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes Chapter-12-Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDokument26 SeitenLecture Notes Chapter-12-Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsSHUBHAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resonance and Inductive Effects in Organic ChemistryDokument36 SeitenResonance and Inductive Effects in Organic Chemistryeagl33yeNoch keine Bewertungen
- HaloalkanesDokument6 SeitenHaloalkanesDoc_CrocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sn1 MechanismDokument24 SeitenSn1 MechanismDian MustikasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Organic Chemistry For IITDokument21 SeitenGeneral Organic Chemistry For IITParas Thakur83% (6)
- Alkenes and AlkynesDokument2 SeitenAlkenes and AlkynesLewis AlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questio10Dokument21 SeitenMultiple Choice Questio10Achiket Anand DesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The SDokument9 SeitenOrganic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The Ssweta KushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel & Cambridge Syllabus: Unit 4: Carbonyl Compounds Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherDokument8 SeitenEdexcel & Cambridge Syllabus: Unit 4: Carbonyl Compounds Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherMaliha Ishrat JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Reactions and MechanismsDokument38 SeitenOrganic Reactions and Mechanismszarna nirmal rawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- D AND F BLOCK ELEMENT NotesDokument5 SeitenD AND F BLOCK ELEMENT NotesM AroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coii Niii Cuii and Criii Complexes of Heterocyclic Schiff Base Ligand Synthesis Spectroscopic and Thermal StudyDokument5 SeitenCoii Niii Cuii and Criii Complexes of Heterocyclic Schiff Base Ligand Synthesis Spectroscopic and Thermal StudyIJARP Publications100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Final NotesDokument30 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Final Notespawan khandweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis, Characterization of New Schiff Base and Some Metal Complexes Derived From Glyoxylic Acid and O-PhenylenediamineDokument12 SeitenSynthesis, Characterization of New Schiff Base and Some Metal Complexes Derived From Glyoxylic Acid and O-PhenylenediamineAndzhiita SaampeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Polarity: AP ChemistryDokument13 SeitenMolecular Polarity: AP ChemistryArvie Guevarra ToqueroNoch keine Bewertungen
- (CHEM) Chemical ReactionsDokument32 Seiten(CHEM) Chemical Reactionssodiumboyupinthishoe100% (2)
- FLAME TESTS: IDENTIFY METAL IONS BY COLOURDokument4 SeitenFLAME TESTS: IDENTIFY METAL IONS BY COLOURFelicia CharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ-S BlockDokument4 SeitenMCQ-S Blocktgs100Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Chemistry Ncert Ch09 Coordination Compounds Part 01 QuesDokument43 Seiten12 Chemistry Ncert Ch09 Coordination Compounds Part 01 Queshumayun khalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carborane Synthesis MethodsDokument17 SeitenCarborane Synthesis MethodsJulienne Stephanie Fabie100% (1)
- Anic Chemistry Carbonyl CompoundsDokument6 SeitenAnic Chemistry Carbonyl Compoundseamcetmaterials100% (1)
- Reaksi SN-1, SN-2, E-1, Dan E-2.Dokument64 SeitenReaksi SN-1, SN-2, E-1, Dan E-2.Annik QurniawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The S-Block ElementsDokument51 SeitenThe S-Block ElementsDiksha TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Delocalization and ResonanceDokument9 SeitenElectron Delocalization and ResonanceMariana LizethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic reactive intermediatesVon EverandOrganic reactive intermediatesSamuel McManusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsVon EverandOrganometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transition Metal ToxicityVon EverandTransition Metal ToxicityG. W. RichterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week Wise Plan - Period - 2 (June, July, August, Sep)Dokument4 SeitenWeek Wise Plan - Period - 2 (June, July, August, Sep)Anitesh DharamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al KynesDokument28 SeitenAl KynesAnitesh Dharam100% (1)
- Gaurav Essay GovernanceDokument24 SeitenGaurav Essay GovernanceAnitesh DharamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class8 Geography Unit03 NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionDokument16 SeitenClass8 Geography Unit03 NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionvbjai72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vision 2016 Report Stats Brief FinalDokument14 SeitenVision 2016 Report Stats Brief FinalAnitesh DharamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gautams EssayDokument2 SeitenGautams EssayAnitesh DharamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The JEE Dilemma - InsIghT, IIT BombayDokument7 SeitenThe JEE Dilemma - InsIghT, IIT BombayAnitesh DharamNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Typical Group DiscussionDokument1 SeiteA Typical Group DiscussionrudceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rust-inhibiting yellow primer for steelDokument2 SeitenRust-inhibiting yellow primer for steelPancho JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polybond PVA: PVA Based Bonding Agent and AdmixtureDokument2 SeitenPolybond PVA: PVA Based Bonding Agent and AdmixtureHtun ZarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herbicide - WikipediaDokument112 SeitenHerbicide - WikipediaBashiir NuurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coal and Petroleum - 8thDokument15 SeitenCoal and Petroleum - 8thVijay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: Sodium HydroxideDokument10 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: Sodium HydroxideJuan del CarmenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Chemistry Atoms First 1st Edition Burdge Full DownloadDokument17 SeitenTest Bank For Chemistry Atoms First 1st Edition Burdge Full Downloaderichughesbdnxfgqyra100% (41)
- Tutorial Chapter 9-AnswersDokument7 SeitenTutorial Chapter 9-AnswersNKMS:)Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Goes Into Safety FootwearDokument4 SeitenWhat Goes Into Safety FootwearBeshoy RedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Grade 12 Vol 3 PDFDokument229 SeitenChemistry Grade 12 Vol 3 PDFG.KAPILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerogen Solo Instruction Manual ROWDokument38 SeitenAerogen Solo Instruction Manual ROWHernán ÁlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02-Effect of Water Impurities in BoilersDokument4 Seiten02-Effect of Water Impurities in BoilersBikas SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqa 7405 2 W MS PDFDokument30 SeitenAqa 7405 2 W MS PDFdenookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids BiosynthesisDokument56 SeitenAmino Acids BiosynthesisDeea LobonțiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Body LotionDokument8 SeitenThesis Body Lotionuiconvbaf100% (2)
- bài về nhà bếp 33Dokument10 Seitenbài về nhà bếp 33Cún CúnNoch keine Bewertungen
- A + B A + B: Acid Conjugate Base Conjugate Acid BaseDokument7 SeitenA + B A + B: Acid Conjugate Base Conjugate Acid BaseKatrina CagungunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Nanomaterials in Fuel Cells: June 2014Dokument41 SeitenApplications of Nanomaterials in Fuel Cells: June 2014AdvikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOP's For CIPDokument4 SeitenSOP's For CIPFaisal RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empirical & Molecular Formula 2 QPDokument8 SeitenEmpirical & Molecular Formula 2 QPjade.davis0019Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coffee Roasting Thesis PDFDokument100 SeitenCoffee Roasting Thesis PDFitell_sri75% (4)
- Metakaolin ReviewDokument22 SeitenMetakaolin ReviewRAGHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle Regulation - Control Points (Part I)Dokument24 SeitenCell Cycle Regulation - Control Points (Part I)Amara TargaryenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yield Point in Drilling Mud Formula, Factors & Application - Drilling ManualDokument9 SeitenYield Point in Drilling Mud Formula, Factors & Application - Drilling Manualphucbm bmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Ke-Software Engineering Laboratory Laporan Basis DataDokument6 SeitenTugas Ke-Software Engineering Laboratory Laporan Basis DataUfie RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ubc 2014 Spring Jiang HaoDokument129 SeitenUbc 2014 Spring Jiang HaovaibhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOWSIL™ 87 Additive and DOWSIL™ 88 Additive For Decorative CoatingsDokument2 SeitenDOWSIL™ 87 Additive and DOWSIL™ 88 Additive For Decorative CoatingsLong An DoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of The Use of Ceramic Filters in Steel CastingDokument6 SeitenEffect of The Use of Ceramic Filters in Steel CastingBrijesh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT-JAM 2006 With Solution PDFDokument24 SeitenIIT-JAM 2006 With Solution PDFgaurav100% (1)
- Chemical Changes LabDokument5 SeitenChemical Changes LabGildardo SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiclazurilDokument5 SeitenDiclazurilDatih PurwasihNoch keine Bewertungen