Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Yoga Therapy For Teachers D1 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Andreea Simona CosteOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Yoga Therapy For Teachers D1 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Andreea Simona CosteCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
DAY 1
Lower back, hips, knees and the feet
Common causes of aches & pains in the lower body:
Lower back pain, knee pain, knee injuries, issues in the hips & feet
YOGA as THERAPY
What role does yoga have in terms of wellness or therapeutic treatments?
From a yogic point of view, problems in the body arises from imbalances of the mind
Undigested emotions / feelings accumulates: depletes prana, the vital energiesLow prana
weakens the body, toxins accumulate both mentally and physically
Disease develops
Mental: Loneliness, isolation, depression, tension, stress, anger, jealousy
Physical: Over-eating, over-working, drugs, alcoholic ways to numb feelings and emotions
Emotional stress / tension = physical
- Neck & shoulder stiffness
- high blood pressure / heart diseases
Suppressed expression / emotions = physical
- sore throat
- heart diseases
How Yoga can help
BODY
Asana physical poses for mobility, strength & stability
BREATH
Pranayama breath modification with mental focus to help facilitate circulation & healing
MIND
Meditation, visualization & chanting to remove
negativity & bring in positive thoughts
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www.paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
Physical benefits of Yoga Therapy:
stretches, tones and strengthens the body
- brings nourishment and rejuvenation of the muscles, tendons, ligaments, bones & joints
- encourages circulation, stimulates metabolism
- increasing stamina in the body and clarity in the mind; youth & vitality
Assists recovery in common physical injuries
Prepares the body for sports, e.g. marathon, triathlons, golfing etc
Physical & Mental benefits of Yoga Therapy
When the body starts to benefit from the asana practice:
- the mind starts to settle down
- letting go of unnecessary burden & thoughts
- relieves tension & stress
- restores mind (mental) & body (physical)
to optimal balance and
well-being
What is Pain?
An indication that something is not right
A perception of pain in the brain, can be mental tension
Not muscle soreness, which is fatigue or giving too much force to the muscles, usually dull
ache esp. when pressed, comes afterwards
Pain usually happens when you are doing it
Back off if it is painful
Pain from stretching should not exist
Pain from Tension /stretching is not right
Tension: tissues are not elastic enough for the bones to move apart,
i.e.
not flexible enough can lengthen in time
Pain from Compression may not cause damage but should still be avoided cannot change!
Compression : bones hitting against bones, stopping any further movement
Cramps or Spasms: not long term damages, only a protection mechanism of the body
- response to sudden movements or out of use: spasms freezes up muscles to protect body
from movements that may hurt the body
- bad blood circulation or muscle fatigue, dehydration
Can also be caused by lack of minerals such as magnesium, potassium & calcium
Rare, but can be due to nerve malfunction, such as spinal chord injury
Gently stretch to release the spasm
Ensure adequate hydration before exercise
Ensure balanced intake of minerals such as magnesium, potassium and calcium
ease into your practice slowly
Relax, breathe!
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www. .paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
ACHES & PAINS
Age & hereditary: born with (scoliosis), growing older / degeneration
Pathologies / Illness
Posture / Alignment: habit of sitting, standing, improper alignment during exercise
Injuries: lack of endurance & stability from lack of use & misalignment
Wear-and-Tear: Daily life & exercise
Mental Tension & Anger
Injuries during Yoga
often when going in and / or out of an asana
The 3 most vulnerable areas for injury in Yoga: Neck, lower back, & knees
The 2 main ways of injury:
- doing something wrong fast; hits right away,
e.g. over stretching/ tearing hamstrings
- doing something wrong repeatedly, no immediate pain, damage builds up,
e.g. Wear-Tear in incorrect twisting of knee
PREVENTION & TREATMENT OF INJURIES
Maintain proper Alignment at all times
Before any movement of the spine, always activate the Core Muscles to protect lower back
Be Mindful & present during practice
Breathe
1. RICE: Rest Ice Compression Elevation
Rest when there is any Inflammation!!!!
2. REHABILITATION: Yoga Therapy
SAFETY IN YOGA
I can go more, I can go more, I can go more, I can go more..can I?
Find our potential for improvement AND
Accept that we do have limitations
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www.paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
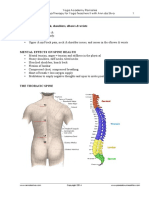
THE SPINE
Four major sections:
Cervical C1 to C7
Thoracic T1 to T12
Lumbar L1 to L5
Sacrum fused S1 to S5
Vertebrae
joints & disks
Curves
Vertebra
Multi-segmented structure
Vertebral Body
Lamina & Pedicle
Spinal Canal
Spinous Process
Transverse Processes x2
Facet joints x4
Separated by Intervertebral discs
Intervertebral Disc
Made of water, collagen, & gel
Annulus
-hard, tough
-rotational stability
-compressive stress
Nucleus
-soft, moist, gel-like
-transmits stress & weight from vertebra to vertebra
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www. .paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
Curves of the Spine
Spring-like, shock absorber
Allows the spine to bend and give
Weight bearing Strength
Better muscle attachment for flexibility,
momentum & stability
Flat spine = harder working muscles
Big range of normal curve angles
Cervical
curve
Lumbar
curve
Thoracic
curve
Sacral
curve
Exaggerated curves of the spine
Kyphosis
-over curvature of the thoracic
-hunchback
-rounded shoulders, tight chest
Lordosis
-over curvature of the lumbar
-swayback
-hypermobility = risk
Planes of Spinal Movement
Flexion -forward bend
- Restricted by soft tissues, can bend too deep
- Risk of compressing nerves
Extension -backward bend
- Restricked joints & bones, generally safer
- No nerves to compress
Lateral Flexion / Extension
- sideways bend
Rotation
- twists
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www.paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
Flexion and Extension
Side bends & Rotation
side bends almost always involve rotation
stretching 50% and unloading of the other 50% fibers of the Annulus
Strain on the Intervertebral disc
Intradiscal Pressure raises during sleep due to water uptake = risk!
95% of disc prolapse caused by repetitive Flexion esp. with Rotation
Neutral Spine
Key concept in modern sports rehab
not too curved and not too flat
Weight load is distributed evenly along the whole spine
Maximum force to go forward in sports
Performance & safety
No 100% perfect shape of spine
Common spine problems
Usually in the Lumbar spine as it supports the entire spine = stability!
Also common in Cervical spine as it supports the weight of the skull = stability!
Less frequent in the Thoracic as it is less mobile due to rib cage = mobility!
May or may not manifest in pain along spine
Pain/numbness can extend down arms/legs
Common causes
Usually chronic, keeps coming back & triggered by a particular traumatic incident
Age & Lifestyle: lack of exercise, diet, smoking, causing degeneration, prone to injuries
Injuries from lack of endurance & stability
Poor posture: misalignment, repeatedly
Stability & Mobilization with Alignment is the key to prevent & rehabilitate back
problems
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www. .paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
Common treatment for Back Pain
Anti-inflammatory pain medication (NSAIDS)
Injection of cortisone into the spine
Rehabilitation: Yoga Therapy, Physical Therapy
Chiropractic treatments
Change of habits / lifestyle
Correct posture
Surgery rare: incontinence, weakness or numbness, to relieve compression & pain
Strengthening the Spine Muscles
Strengthening is protective
Stretching is releasing, feels good and helps to prevent immobility
BALANCE between the two!
Strengthen = weight bearing
Endurance & Stamina = lower weight, reps
Erector Spinae
Abdominal Muscles
Key Muscles for Spine Stability
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www.paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
THE LUMBAR SPINE
Supports the weight load of the whole Spine
The largest segments of the vertebral column
very mobile, needs Stabilization
Most problems appear here
Interconnected to Sacro-illiac joint problems
Sciatica
most common pain and discomfort caused by a problem in the lumbar region
Pain, weakness, numbness or tingling sensations, usually one side
Injury or pressure on the sciatic nerve
A symptom of another medical condition, not a condition on its own
Causes of Sciatica
Disc Herniation
Spondylolithesis
Spinal Stenosis
Piriformis Syndrome
Sacroiliac Joint Disorder
Pelvic injury or fracture
Tumors
Usually only one-sided
Worsen after standing, or sitting,
or when sneezing, coughing
Damaged
Sciatic
nerve
Weakened
knee (pain
running down
back of legs to
toes)
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www. .paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
Disc Herniation
Slipped disc
Disc protrusion
Most often in Lumbar spine
Tear in the Annulus
Bulging out of the Nucleus
Pain due to inflammation/nerve
May cause nerve compression
Can cause Sciatica, but not common
Therapy for Disc Herniation
Pain-free, neutral spine
Extension from neutral
prevent immobilization
Core stability
Movement that extend the pain away spine
- big NO as nerve compression is more severe
Avoid deep ROM in morning due to IDP
Numbness, bladder & bowel control problems
Spondylolysis & Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolysis: fracture of Pars Interarticularis
Spondylolisthesis: forward slippage of the vertebra due to breakage of this boney ring
Usually L5 and Sacrum, sometimes L4
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www.paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
10
Spondylolysis & Spondylolisthesis
Hypermobility
Can be Hereditary
Stress fractures typically due to repetitive load
Hyperlordosis gymnasts, dancers
Can be caused by Disc Hernation
Spondylolysis can usually heal on its own
Spondylolisthesis may require surgery
Therapy for Spondylolisthesis
Stabilize
Avoid Hyper-extension (over back bend)
Core Strengthening!
Avoid SLR (straight leg raising) psoas load
Explore Flexion with awareness
Neurological deficits (paralysis, weakness, numbness, or increasing pain)
Spinal Stenosis
Aging: enlarged joints,
Thickened ligament
Disc Herniation
Facet joint fracture
trauma
Vertebral slip - Spondylolisthesis
Can be hereditary narrow spinal chord
Pressure on the spinal cord or nerves
Can cause neurological deficit:
Pain, numbness, tingling or loss of mobility
Lumbar: when nerve roots in lower back is compressed, can cause sciatica, affects walking,
gait & distance
Cervical: dangerous as spinal cord is compressed, serious symptoms, major body weakness
& paralysis
Therapy for Spinal Stenosis
Emphasis on flexion, may decrease pain
Laminotomy to increase space by removing a bit of the bone / disc
Post surgery:
o -Stabilize
o -Maintain neutral Spine
o -Regain normal function
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www. .paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
11
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Pain in the SI joint
Cartilage damaged or worn (degenerative arthritis/osteoarthritis)
pregnancy (hormonal)
Stress of joint (repetitive)
Trauma (missed step)
Common: leg length discrepancy, back pain
Therapy for SI-Joint Dysfunction
Stabilization, strength, endurance of surrounding muscles, e.g. glutes, core
Mindful self mobilization may help to reposition the SI-joint
Reduce / correct load in daily habits
Avoid asymmetric FWD bends, and end range
Warm oil
Avoid too frequent manual adjustments!
Severe cases: surgery to fuse the SI-joint
The MUSCULAR SYSTEM
Three types of muscles tissues:
SKELETAL, SMOOTH, CARDIAC
- elastic, flexible, stretches
Three types of connective tissues:
TENDONS, LIGAMENTS, FASCIAE
less flexible, only gradual lengthening
They make up about half of the weight & bulk of the body
TENDONS connective tissues
Bundles of fibrous connective tissue, collagen
Tough, flexible, gradual lengthening
Dries, shortens, becomes brittle if not used
Connects muscles to bones
Body movement
Example: Achilles tendon, hamstrings
LIGAMENTS
Bundles of fibrous connective tissue, collagen
Tough, flexible, gradual lengthening
Dries, shortens, becomes brittle if not used
Connects bone to bone
Stabilizes, supports & controls movements of the joints
overstretched, double-jointed, risk of injury Example: Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL),
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www.paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
12
FASCIAE
Bundles of fibrous connective tissue, collagen
Bands or layers of stringy elastic tissues, stretches
Dries, shortens, becomes brittle if not used
Surrounds muscles to muscles, covers bones, blood vessels, nerves, everywhere
Some binds structures for stability or protection
Some layers on to allow smooth gliding movements
Example: Plantar fascia
TENDINITIS / TENDONITIS
Inflammation of a tendon, e.g. Achilles
Common in the limbs, not often hips /torso
Repetitive strain injury, mostly wear & tear
Aches & pains, joint stiffness
Burning sensation around joint or inflamed tendon
Can have swelling
R.I.C.E.
MUSCLES OF THE HIP
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www. .paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
13
The ILIOPSOAS & PSOAS
The Iliopsoas: two muscles
Iliacus: main hip flexor
Psoas: only muscle thatattaches leg to spine
Short psoas: tilts the pelvis, look of shorter leg, knee &back pain,
Wear-tear, over holding
Mindful stretching
The ILIOTIBIAL BAND
fibrous reinforcement of the fascia lata muscles
Assists in moving the hips
Stabilizes the knee inextension & partial flexion
Used constantly in walking, running etc
Overuse = ITB Syndrome
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
Pain in outer knee
Possible pain in hip
Training /overuse
Anatomical (arches, foot supination/strike)
Muscle imbalance
R.I.C.E. then: stretch
The HAMSTRINGS
group of three muscles on back of the thigh, connects the hip to the knee, walking
Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus
Extension of the legs
Flexion of knee
Stretches over time
Can be torn
Takes time to heal
R.I.C.E. then stretch
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www.paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
14
JOINTS
When two or more bones come together
There are three types of joints:
FIXED JOINTS
Held together by a tough fiber that doesnt allow movement, also called Fibrous Joints
e.g. the skull
SLIGHTLY MOVABLE JOINTS
Separated by cartilage, allowing small range of movement, also called: Cartilaginous Joints
e.g the joints between the vertebrae
MOVABLE JOINTS
With lubricating synovial fluids inside a
synovial membrane that wraps around the joint
great freedom of movement
Two main types: Hinge, Ball & Socket
Also Synovial Joints
HINGE JOINTS
Allow movement in one direction
E.g. the knees, elbows & fingers
BALL & SOCKET JOINTS
Allow the greatest freedom of movement, the round end of one long bone fits into the
hollow of another E.g. hips and shoulders
OSETOPOROSIS
Progressive bone disease, Porous bones
Production of new bones cannot keep up with the loss of bone mass
Risk of bone fracture, even from sneezing, coughing, falling!
Often in hips, wrist or spine
Stooped posture, loss of height, collapsed vertebrae, fractures
Age, race, sex, family history, menopause, bone reserve from youth
Hormonal and /or glandular issues
Dietary: low calcium, eating disorders, nutrient absorption problems
Medication: long term corticosteroid use can interfere with bone-regrowth
Lifestyle: lack of exercise, alcohol & tobacco use can reduce calcium absorption
Calcium supplements
Moderate & mindful weight bearing, e.g. Standing poses, warriors etc
Lifestyle changes: avoid smoking & alcohol consumption
Being present,
avoid falling!
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www. .paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
15
OSETOARTHRITIS
Degenerative joint disease, most common type of arthritis, Wear-and-Tear arthritis
Cartilage in the joints are worn down
Often in lower back, knees & hips
Pain & stiffness, loss of flexibility, tenderness
Gradually worsens, no real cure
Can only slow down deterioration, relieve pain & improve function
Glucosamine, supplements
nourish the joints with gently cycles of moderate weight loading & unloading
Mindful rotation & movements to encourage circulation & range of motion
Gentle stretching / pulling of the muscles
ANATOMY OF THE HIP
ISSUES OF THE HIP JOINT
Osteoporosis
Hip Fracture
Osteoarthritis in the Hip:
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www.paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
16
THE KNEE JOINT
Femur: Thigh bone
Tibia: Shin bone
Fibula: Calf bone
Patella: knee cap
ACL: Anterior cruciate ligament
PCL: Posterior cruciate ligament
LCL: Lateral collateral ligament
MCL: Medial collateral ligament
Knee cap (Patella): protects the interior parts of the knee joint
Patella tendon: also known as Patella Ligament connects from the quadriceps, through the
Knee cap to the tibia, the shin bone (bone to bone),
it provides and controls extension of the knee joint
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL): connects the thigh bone to the shin bone in the center
of the knee. Limits rotation and forward motion
- most commonly injured or torn, resulting
in instability of the knee
- E.g. falls that caused the knee
to twist or pivot: skiing, soccer
- In yoga, fast, forceful twist of
knee, or forceful overextending such as lunges
- Immediate symptoms
- Slow healing, or, surgery
Medial collateral ligament (MCL): runs down the inside of the knee, connects the thigh
bone to the shin bone
Lateral collateral ligament (LCL): runs down the outside of the knee, connects the thigh
bone to the calf bone
Together they limit and stabilize sideways movement of the knee
Injured by sideways force to knee
Slow, timely healing process
All soft tissues around & nearest the knee joint, tendons &ligaments, are for stabilizing and
protecting the knee
Meniscus: two pads of cartilaginous tissues in the knee joint, to disperse the weight
of the body & reduce friction during movement
Injured either by acute tearing fromsudden trauma in sports, or a Slow Wear-andTear
In Yoga: misalignment, e.g. hyper-extension or hyper-flexion of knee, esp. when
weight bearing
Symptoms slow or recurring
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www. .paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
17
OTHER ISSUES IN THE KNEE
Patellar Tendinitis:
Jumpers Knee repetitive overloading
& extending of the knee
Osteoarthritis in the Knee
ISSUES IN THE CALVES
Gastrocnemius Muscle
tearing of inner calves, or Tennis Leg
A pop, sharp pain
Slow healing, depending on severity, surgery
R.I.C.E.
stretching & strengthening
ISSUES IN THE ACHILLES TENDON
Calcaneal Tendon
A pop, sharp pain
Slow healing, according to severity, surgery
R.I.C.E., then stretching & strengthening
PLANTAR FASCITIS
Progressive, degenerative damage to Plantar Fascia Ligament, may not have inflammation
Weight bearing, overuse, inadequate arch support in shoes, esp when running/ flip flops
can cause, possibly caused by Flatfeet
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www.paradoxumrealitas.com
Yoga Academy Romania
Yoga Therapy for Yoga Teachers I with Ann da Silva
18
R.I.C.E.
Stretch Achilles Tendon & Plantar Fascia
Ligament
Strengthen Calves
Orthotics (shoes) with arch & foot support
Surgery (detaching the Plantar Fascia
Ligament from the heel bone) = Flatfeet!!
FLATFLEET
Collapsed Arch in the feet
Related to Plantar Fascitis, age, weight bearing,
improper shoes
Feet Pronation
Can cause pain in back, knees, hips and neck
same treatment as Plantar Fascitis
FEET PRONATION
www.anndasilva.com
Copyright 2014
www. .paradoxumrealitas.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Yoga Therapy For Teachers D2 PDFDokument9 SeitenYoga Therapy For Teachers D2 PDFAndreea Simona CosteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficient Yoga Sets at Pain in the Back and for the Development of Spine Elasticity (Mindfulness Therapy): YOGA PLACE BooksVon EverandEfficient Yoga Sets at Pain in the Back and for the Development of Spine Elasticity (Mindfulness Therapy): YOGA PLACE BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific View AsanasDokument3 SeitenScientific View AsanasRavi KiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skillful Sequencing Part 1Dokument4 SeitenSkillful Sequencing Part 1crhlakarrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Svastha Yoga of Krishnamacharya: Therapy ProgramDokument7 SeitenSvastha Yoga of Krishnamacharya: Therapy ProgramUwe HeimNoch keine Bewertungen
- YOGA Lesson 12Dokument8 SeitenYOGA Lesson 12Sandeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yoga Open NotesDokument8 SeitenYoga Open NotesInsight MndyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therapeutic Role of Yoga in Type 2 Diabetes PDFDokument11 SeitenTherapeutic Role of Yoga in Type 2 Diabetes PDFNEW GENERATIONSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yoga Practical PaperDokument8 SeitenYoga Practical PaperjosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pranayama & TypesDokument58 SeitenPranayama & TypesShekhar BIshtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Yoga Philosphy PDFDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Yoga Philosphy PDFNishant DhimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC Yoga Syllabus PDFDokument50 SeitenMSC Yoga Syllabus PDFsankuj5354Noch keine Bewertungen
- AasanaDokument38 SeitenAasanakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Just-for-Fun Yoga and Anatomy Quiz Answer Sheet With ResultsDokument6 SeitenJust-for-Fun Yoga and Anatomy Quiz Answer Sheet With ResultsGovind KaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balancing Tridosh Through YogaDokument52 SeitenBalancing Tridosh Through Yogaराहुल आपटेNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hip Opening AsanasDokument4 SeitenHip Opening Asanasmangaldas0% (1)
- La942 990309 Releasing Childhood AngerDokument7 SeitenLa942 990309 Releasing Childhood AngerAmina Satrovic100% (1)
- Module 4Dokument110 SeitenModule 4Priyanka Nambiar100% (1)
- Postnatal FormDokument3 SeitenPostnatal FormMihaelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compare Various Yogic PracticesDokument4 SeitenCompare Various Yogic PracticesghjghguhggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yoga - PPT FinalDokument31 SeitenYoga - PPT FinalSanjay YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why We Use Props - Yoga Rahasya 2004Dokument5 SeitenWhy We Use Props - Yoga Rahasya 2004Diego Baldi50% (2)
- Yoga For Body, Breath, Mind: A Guide To Personal Reintegration - A.G. MohanDokument4 SeitenYoga For Body, Breath, Mind: A Guide To Personal Reintegration - A.G. Mohanpyhybehe0% (2)
- Yoga Ayurveda PDF For StudentsDokument14 SeitenYoga Ayurveda PDF For StudentsTijana MilenovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warm Up Before YogaDokument9 SeitenWarm Up Before YogaShyam_Nair_9667Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shat KarmaDokument3 SeitenShat KarmaMisterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yoga Asanas ListDokument12 SeitenYoga Asanas Listchinuuu85br5484Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bakasana PDFDokument5 SeitenBakasana PDFJoaquínNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laghu Shankha Prakshalana - Final BnysDokument9 SeitenLaghu Shankha Prakshalana - Final Bnyssureshbabubnys100% (1)
- KHYF Yoga Therapy India 2017 2020 V2Dokument14 SeitenKHYF Yoga Therapy India 2017 2020 V2Jacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- KYM - YTTP Prospectus 2020-21 PDFDokument23 SeitenKYM - YTTP Prospectus 2020-21 PDFVidhya Murali100% (1)
- Dinacharya PDFDokument3 SeitenDinacharya PDFKrishnaswamy JajimoggalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sun Salutations Step-by-Step: Pranamasana (Prayer Pose)Dokument3 SeitenSun Salutations Step-by-Step: Pranamasana (Prayer Pose)Viktória MolnárNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iyn 29Dokument56 SeitenIyn 29rajendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sirsasana Father of All AsanasDokument2 SeitenSirsasana Father of All AsanasHaseebNoch keine Bewertungen
- KHYF Viniyoga Therapy Europe 2018-20-21Dokument15 SeitenKHYF Viniyoga Therapy Europe 2018-20-21lakshmi narsimhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yoga in The Treatment of Neurotic Disorders PDFDokument10 SeitenYoga in The Treatment of Neurotic Disorders PDFDejana AnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Yoga Poses To Strengthen Your Lower BackDokument4 Seiten5 Yoga Poses To Strengthen Your Lower BackgnareshbabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIATICA - Rev. Durga GlassonDokument25 SeitenSCIATICA - Rev. Durga GlassonAissmsIomPuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiological Responses To Iyengar YogaDokument17 SeitenPhysiological Responses To Iyengar Yogaapi-3718530100% (1)
- A Presentation By: Joan CabacunganDokument14 SeitenA Presentation By: Joan CabacunganGodwin CabacunganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kriya - Strenghthening The Immune SystemDokument8 SeitenKriya - Strenghthening The Immune SystemJavier Gómez AbascalNoch keine Bewertungen
- AllAboutYoga PDFDokument29 SeitenAllAboutYoga PDFValeria BensoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yoga of HealingDokument41 SeitenThe Yoga of Healingsillyminds100% (1)
- Ist Level: Energy From YogaDokument3 SeitenIst Level: Energy From Yogashailesh tandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yoga Benefits of AsanasDokument4 SeitenYoga Benefits of AsanaskparvezaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yoga Poses and What They AchieveDokument1 SeiteYoga Poses and What They AchieveVenketeshwar SwamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100-Hour Ashtanga YogaDokument3 Seiten100-Hour Ashtanga YogaShree HariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yoga Therapy in The Treatment of Chronic Low Back Pain (PDFDrive)Dokument79 SeitenYoga Therapy in The Treatment of Chronic Low Back Pain (PDFDrive)Anan Sari100% (1)
- Yoga in Health and DiseaseDokument3 SeitenYoga in Health and DiseaseRagavendrasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Yogic Approach To Wellness PDFDokument66 SeitenA Yogic Approach To Wellness PDFpatrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yoga For Weight LossDokument18 SeitenYoga For Weight Losshemanth_chaturvedulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- YOGADokument17 SeitenYOGAPriya GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yoga and Meditation - Digital Report - Bhavanya - TTGI200118Dokument23 SeitenYoga and Meditation - Digital Report - Bhavanya - TTGI200118bhavanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backbend Poses: Dhanurasana (Bow Pose)Dokument5 SeitenBackbend Poses: Dhanurasana (Bow Pose)yogavashisthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shatkarma - The 6 Cleansing and Detox TechniquesDokument3 SeitenShatkarma - The 6 Cleansing and Detox TechniquesTinglingNoch keine Bewertungen
- DaviesTotal Soccer Fitness PDFDokument167 SeitenDaviesTotal Soccer Fitness PDFGaston Saint-Hubert100% (2)
- Soccer DVDManualDokument28 SeitenSoccer DVDManualAndreea Simona CosteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Yoga - An Illustrated Guide To Over 100 Yoga Poses and Meditations PDFDokument233 SeitenEssential Yoga - An Illustrated Guide To Over 100 Yoga Poses and Meditations PDFAndreea Simona Coste100% (2)
- Essential Yoga - An Illustrated Guide To Over 100 Yoga Poses and Meditations PDFDokument233 SeitenEssential Yoga - An Illustrated Guide To Over 100 Yoga Poses and Meditations PDFAndreea Simona Coste100% (2)
- Factoring Problems-SolutionsDokument11 SeitenFactoring Problems-SolutionsChinmayee ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Group DynamicsDokument12 SeitenFundamentals of Group DynamicsLimbasam PapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Quiz 5 Module 3 Financial MarketsDokument5 SeitenPractice Quiz 5 Module 3 Financial MarketsMuhire KevineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bos 22393Dokument64 SeitenBos 22393mooorthuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awake! - 1964 IssuesDokument769 SeitenAwake! - 1964 Issuessirjsslut100% (1)
- XT 125Dokument54 SeitenXT 125ToniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Tadka InstituteDokument15 SeitenPhysics Tadka InstituteTathagata BhattacharjyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monologues For Danimations - Adam SorrellDokument2 SeitenMonologues For Danimations - Adam SorrellCharlie Smith-McMahonNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINS1612 Capital Markets and Institutions S12016Dokument15 SeitenFINS1612 Capital Markets and Institutions S12016fakableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coca-Cola Femsa Philippines, Tacloban PlantDokument29 SeitenCoca-Cola Femsa Philippines, Tacloban PlantJuocel Tampil Ocayo0% (1)
- Pier Cap Corbel 30m SGDokument3 SeitenPier Cap Corbel 30m SGSM ConsultantsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minneapolis Police Department Lawsuit Settlements, 2009-2013Dokument4 SeitenMinneapolis Police Department Lawsuit Settlements, 2009-2013Minnesota Public Radio100% (1)
- Athletic KnitDokument31 SeitenAthletic KnitNish A0% (1)
- The Organization of PericentroDokument33 SeitenThe Organization of PericentroTunggul AmetungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Singleton v. Cannizzaro FILED 10 17 17Dokument62 SeitenSingleton v. Cannizzaro FILED 10 17 17Monique Judge100% (1)
- Four Year Plan DzenitaDokument4 SeitenFour Year Plan Dzenitaapi-299201014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solar SystemDokument3 SeitenSolar SystemKim CatherineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robbins FOM10ge C05Dokument35 SeitenRobbins FOM10ge C05Ahmed Mostafa ElmowafyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MKTG4471Dokument9 SeitenMKTG4471Aditya SetyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research Chapter 1Dokument27 SeitenBusiness Research Chapter 1Toto H. Ali100% (2)
- Computer Awareness: Special Edition E-BookDokument54 SeitenComputer Awareness: Special Edition E-BookTanujit SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SJK (T) Ladang Renchong, PagohDokument2 SeitenSJK (T) Ladang Renchong, PagohAinHazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive Technology945Dokument35 SeitenAssisted Reproductive Technology945Praluki HerliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multigrade Lesson Plan MathDokument7 SeitenMultigrade Lesson Plan MathArmie Yanga HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naresh Kadyan: Voice For Animals in Rajya Sabha - Abhishek KadyanDokument28 SeitenNaresh Kadyan: Voice For Animals in Rajya Sabha - Abhishek KadyanNaresh KadyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Net 2020Dokument48 SeitenNet 2020Krishan pandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vulnerabilidades: Security Intelligence CenterDokument2 SeitenVulnerabilidades: Security Intelligence Centergusanito007Noch keine Bewertungen
- HDFCDokument60 SeitenHDFCPukhraj GehlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCSE Sample QuestionsDokument19 SeitenMCSE Sample QuestionsSuchitKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aptitude For Civil ServicesDokument17 SeitenAptitude For Civil Servicesnagarajuvcc123Noch keine Bewertungen