Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ME345 Lecture 31
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP50 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
15 Ansichten8 SeitenME345 Lecture 31
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenME345 Lecture 31
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
15 Ansichten8 SeitenME345 Lecture 31
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5ME345 Lecture 31
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 8
M E 345
Spring 2009 Professor John M. Cimbala Lecture 31
04/01/2009
Today, we will:
Continue our discussion about first-order dynamic systems: discuss half-life.
Finish reviewing the pdf module: Dynamic System Response (2nd-order systems)
Do some more example problems dynamic system response
Do some review example problems for Exam 2
Example: Dynamic system response
Given: The following second-order ODE:
d 2 y dy
5 2 +
+ 1000 y = x ( t )
dt
dt
The forcing function is a step function (sudden jump):
x(t) = 0 for t < 0
x(t) = 25 for t > 0
(a) To do: Calculate the natural frequency and damping ratio of this system.
(b) To do: Calculate the equilibrium response (as t , what is y?).
Solution:
(1)
Example: Review for Exam 2
Given:
The integer 13 (base 10).
To do:
Write this integer in 4-bit binary format.
Solution:
Example: Review for Exam 2
Given:
The integer 0001 0111 (8-bit binary).
To do:
Write this integer in base 10 format.
Solution:
Example: Review for Exam 2
Given:
Two integers in 8-bit binary format:
A = 0010 0110
B = 1101 1001
To do:
Solution:
Add A + B and write the result in base 10 format.
Example: Review for Exam 2
Given: Voltage data are sampled digitally at a sampling frequency of 250 Hz.
To do: For each frequency in the signal, calculate the perceived frequency from the
acquired data.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
f = 120 Hz.
f = 200 Hz.
f = 300 Hz.
f = 380 Hz.
f = 500 Hz.
Solution:
4.0
4.2
4.4
4.6
3.6
3.8
f /ffolding
2.0
2.2
2.4
1.6
1.8
0
0.2
0.4
3.4
4.8
3.2
5.0
3.0
2.6
2.8
1.4
0.6
fa /ffolding
1.2
0.8
f /ffolding
1.0
Example: Review for Exam 2
Given: Tom samples a voltage signal digitally for 4.00 seconds at a sampling frequency of
500 Hz. He plugs the data into MatLab, calculates an FFT, and plots the frequency spectrum.
To do:
(a) Calculate the frequency resolution of his frequency spectrum.
(b) Repeat if Tom uses Excel instead of MatLab.
(c) Repeat if Tom wants to improve the frequency resolution of his FFT, so he samples at
the same frequency, but for a longer time. He samples the voltage signal digitally at a
sampling frequency of 500 Hz and takes 4096 data points.
Solution:
Example: Review for Exam 2
Given:
Veronica needs to measure a signal that ranges between 0.20 V and +0.80 V.
The signal is to be sampled by an 12-bit A/D converter that has an input range of 0 to 5 V.
For maximum resolution, the signal is to be conditioned such that it fits the full input range
of the A/D converter (add a DC offset to the signal, and then amplify the modified signal).
To do:
(a) Calculate the required DC offset and amplification (gain).
(b) Veronica uses inverting op-amp circuits for the DC offset and gain. If a 10.0 k resistor
is used as R1 in her inverting amplifier, what resistor should she use for R2?
(c) Calculate the smallest change in input voltage that Veronica can measure.
Solution:
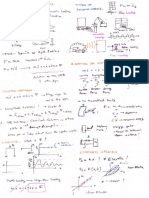
Example: Review for Exam 2
Given: A 2.00 V DC voltage is applied as the input voltage, i.e., Vin = 2.00 V DC. Where
op-amps are used, the power supplied to the op-amps is +15 V and 15 V DC.
To do:
For each case, identify the circuit and calculate the output voltage Vout.
R
Vin
Vin
C
Vout
(a)
Vn
Vin
Vp
(b)
2R
Vn
Vo
Vout
2R
Vin
Vn
Vin
Vp
(e)
Vout
(d)
7R
Vo
Vp
(c)
Vout
Vn
Vo
Vout
Vin
Vp
Vo
Vout
6.00 V
(f)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Lawn-Boy Service Manual 1950-88 CompleteDokument639 SeitenLawn-Boy Service Manual 1950-88 Completemasterviking83% (35)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Learner's Book Answers: Unit 1 CellsDokument31 SeitenLearner's Book Answers: Unit 1 CellsLyaz Antony91% (91)
- Vector Mechanics Engineers Statics 8th BeerDokument8 SeitenVector Mechanics Engineers Statics 8th Beercerebro50% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- CE 7014 Chap2 Part 5Dokument23 SeitenCE 7014 Chap2 Part 5Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5100% (1)
- IEC Certification Kit: Model-Based Design For EN 50128Dokument31 SeitenIEC Certification Kit: Model-Based Design For EN 50128Ícaro VianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpreting The Venus CycleDokument2 SeitenInterpreting The Venus Cyclemurx2100% (1)
- Summary Good To GreatDokument5 SeitenSummary Good To GreatAziz ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic - Concepts - in - Pharmaceutical - Care CLINICAL PHARMACYDokument17 SeitenBasic - Concepts - in - Pharmaceutical - Care CLINICAL PHARMACYPrincess RonsableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lister Hr3 ManualDokument119 SeitenLister Hr3 ManualRichard Gomez Cueva100% (2)
- Crystal Gallery: AccountabilityDokument15 SeitenCrystal Gallery: AccountabilityJitesh ManwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bianca Premo - The Enlightenment On Trial - Ordinary Litigants and Colonialism in The Spanish Empire-Oxford University Press (2017)Dokument385 SeitenBianca Premo - The Enlightenment On Trial - Ordinary Litigants and Colonialism in The Spanish Empire-Oxford University Press (2017)David Quintero100% (2)
- Simulation & Role PlayDokument10 SeitenSimulation & Role Playpreeti sharma100% (2)
- IB Biology Lab Report TemplateDokument6 SeitenIB Biology Lab Report TemplatebigbuddhazNoch keine Bewertungen
- A HandBook On Finacle Work Flow Process 1st EditionDokument79 SeitenA HandBook On Finacle Work Flow Process 1st EditionSpos Udupi100% (2)
- CCPCTCGlobal Data Final1Dokument1 SeiteCCPCTCGlobal Data Final1Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Turer Ce5802-2018Dokument13 SeitenDr. Turer Ce5802-2018Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors 18 00309Dokument14 SeitenSensors 18 00309Md. Tuhin KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Svgexport 27Dokument1 SeiteSvgexport 27Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Burj Khalifa ImportantDokument42 SeitenBurj Khalifa ImportantAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 1Dokument5 SeitenClass 1Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Svgexport 27Dokument1 SeiteSvgexport 27Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bridge MeasureDokument19 SeitenBridge MeasureThanh Nhan LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton Raphson Alcoa Graphical Method C#Dokument3 SeitenNewton Raphson Alcoa Graphical Method C#Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Source Code Example Root Finding Visual StudioDokument5 SeitenSource Code Example Root Finding Visual StudioAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Encryption Source CodeDokument5 SeitenEncryption Source CodeAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sdcard 30c3 PubDokument61 SeitenSdcard 30c3 PubAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Specification: IEC/TS 60815-1Dokument7 SeitenTechnical Specification: IEC/TS 60815-1Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2D Truss Solution Via MatlabDokument18 Seiten2D Truss Solution Via MatlabChandra JyotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metu Thesis TemplateDokument16 SeitenMetu Thesis TemplateAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abrahamson SHA Stateoftheart PDFDokument27 SeitenAbrahamson SHA Stateoftheart PDFAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- BMWDokument1 SeiteBMWAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics of CM Ers02 Deformation StrainDokument28 SeitenKinematics of CM Ers02 Deformation StrainAchmad Rachmad TullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- TempDokument4 SeitenTempAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iast Lect04Dokument13 SeitenIast Lect04Takis ApostolidesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 4Dokument1 SeiteAssignment 4Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE 7014 Week1 IntroDokument40 SeitenCE 7014 Week1 IntroAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- TM Chap15 Strain PDFDokument22 SeitenTM Chap15 Strain PDFRicardo ColosimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WeekI PDFDokument3 SeitenWeekI PDFAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- WeekI PDFDokument3 SeitenWeekI PDFAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE 7014 Chap2 Part 2Dokument51 SeitenCE 7014 Chap2 Part 2Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dakshin Dinajpur TP ListDokument5 SeitenDakshin Dinajpur TP ListDeb D Creative StudioNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP35N K Tube Technical Data SheetDokument2 SeitenMP35N K Tube Technical Data Sheetstrip1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research TopicsDokument15 SeitenResearch TopicsmalinksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Science: Lecture #1Dokument22 SeitenData Science: Lecture #1khanjan varmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey 2 Module 2Dokument76 SeitenSurvey 2 Module 2veereshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied-Signed Product Cordial Labeling and - Santhi.mDokument6 SeitenApplied-Signed Product Cordial Labeling and - Santhi.mImpact JournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOEFL - Longman TOEFL-534-540Dokument7 SeitenTOEFL - Longman TOEFL-534-540Diah Agustina RatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Third Space Learning Ratio GCSE WorksheetDokument11 SeitenThird Space Learning Ratio GCSE WorksheetDrichy Obi-EmelonyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Actor and Actress Adjudication Rubric 41950cb9a3Dokument3 SeitenBest Actor and Actress Adjudication Rubric 41950cb9a3Sarah Jhoy SalongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Chapter 2Dokument5 SeitenTutorial Chapter 2Naasir SheekeyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring PovertyDokument47 SeitenMeasuring PovertyPranabes DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fema 310Dokument12 SeitenFema 310Anil BasnetNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTTPHeader LiveDokument199 SeitenHTTPHeader LiveDenys BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC68 HC05 B4 UDokument253 SeitenMC68 HC05 B4 Uflo724Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor Lab ManualDokument36 SeitenMicroprocessor Lab ManualsivagamasundhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- USDP Shehzore02Dokument39 SeitenUSDP Shehzore02Feroz GullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in Contact Center Services NC IIDokument12 SeitenReviewer in Contact Center Services NC IIRonalei TañedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rack Interface Module 3500 20SDokument71 SeitenRack Interface Module 3500 20SmaheshNoch keine Bewertungen