Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
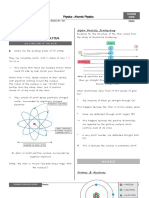
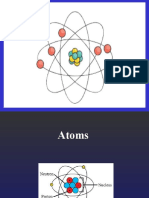
Atomic Structure
Hochgeladen von
Sk. Salahuddin AhammadOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Atomic Structure
Hochgeladen von
Sk. Salahuddin AhammadCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
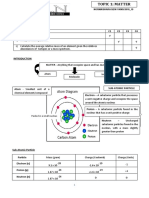
Atomic Structure
• Contains the electrons
• Makes up most of the volume of the atom
• Negatively charged (electrons are negative)
• Electrons are small and essentially have no
mass, so the electron cloud is mostly empty
space
• Contains the protons and neutrons
• Positively charged (positive protons, neutral
neutrons)
• Small
• Contains all of the mass of the atom
• Extremely dense
Mass
Basic Electrostatics:
Where Found Charge Number
Proton Opposite charges attract and identical charges repel
Nucleus +1 1
Neutron Ø Electrons and protons attract each other
Nucleus 0 1
Ø Protons repel other protons
Electron Electron Cloud -1 0
Ø Electrons repel other electrons
Ø Neutrons are neutral and should neither repel
nor attract any particles
Definitions
q Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the
properties of that element
q Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of Nuclear Forces:
an atom Powerful short range forces in the nucleus that hold
q Mass number: the total number of protons and neutrons the nuclear particles (protons and neutrons) together.
in the nucleus of an atom These forces overcome the electrostatic repulsion of
q Isotopes: Atoms of the same element that differ in mass protons.
number (differing numbers of neutrons)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Your Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2Von EverandYour Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- O The Smallest Unit Of: An ElementDokument61 SeitenO The Smallest Unit Of: An ElementBrian Laurence BarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atom Atom: Electron, The Proton and The NeutronDokument29 SeitenAtom Atom: Electron, The Proton and The Neutronrehab ebraheemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 11 ReviewDokument14 SeitenGrade 11 ReviewAiza Casinillo CabatinganNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Physical Chemistry Y12 LolDokument29 Seiten3.1 Physical Chemistry Y12 LolcallumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Model Comparison SheetDokument2 SeitenAtomic Model Comparison SheetEamon BarkhordarianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 CchemDokument1 Seite1.1 CchemcallumNoch keine Bewertungen
- The AtomDokument22 SeitenThe Atomalbi veshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subatomic Particles of AtomsDokument8 SeitenSubatomic Particles of AtomsRose Ann Marie BabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic PhysicsDokument17 SeitenAtomic PhysicsOrangess GirlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Atom: Made By:dr. Isha Jaiswal Moderator: Dr. S.P.MishraDokument37 SeitenStructure of Atom: Made By:dr. Isha Jaiswal Moderator: Dr. S.P.MishraRafael OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Level Edexcel ChemistryDokument22 SeitenA-Level Edexcel ChemistryElyssa Mcpe100% (1)
- Ch. 44: Quarks, Leptons and The Big Bang The Fundamental ParticlesDokument4 SeitenCh. 44: Quarks, Leptons and The Big Bang The Fundamental ParticlesvaibhavdkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Atomic StructureDokument21 Seiten1.1 Atomic StructureBhPO2023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic BondingDokument13 SeitenAtomic BondingDanica Sphynx BonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument23 SeitenUnit 1mtayyab zahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- (TC) C2 Atomic Structure and Electronic ConfigurationDokument5 Seiten(TC) C2 Atomic Structure and Electronic Configurationthanat amornratchnondNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA Chemistry Unit 1: S.L.O.P Shed Loads of Practice! Atomic Structure & The Periodic TableDokument11 SeitenAQA Chemistry Unit 1: S.L.O.P Shed Loads of Practice! Atomic Structure & The Periodic TableImama FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 It The Production, Properties and Interactions of X-RaysDokument14 Seiten11 It The Production, Properties and Interactions of X-Raysroma ulinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthDokument218 SeitenUnit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthBlopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Lecture 1 F22Dokument16 SeitenChapter 2 - Lecture 1 F22Ali AtwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem I Chapter 02Dokument9 SeitenChem I Chapter 02M GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transes ECEDokument14 SeitenTranses ECEI AM CHESCA (IamChesca)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inorg Chem ReviewerDokument24 SeitenInorg Chem ReviewerKier PanugaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleus and Elementary Particles: Lesson OneDokument9 SeitenNucleus and Elementary Particles: Lesson Onemohy711Noch keine Bewertungen
- AtomsDokument6 SeitenAtomsshreyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1. A Simple Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge and Isotopes PDFDokument4 Seiten1.1. A Simple Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge and Isotopes PDFUloko ChristopherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atom, Molecule and Stoichiometry 2023 OnlineDokument10 SeitenAtom, Molecule and Stoichiometry 2023 OnlineGan Ee HengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radioactivity-General ChemistryDokument26 SeitenRadioactivity-General Chemistry7assan1300Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics II q3Dokument7 SeitenGeneral Physics II q3Glaiza Mae GalizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDokument4 SeitenLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic TheoryDokument2 SeitenAtomic TheoryRaymond EdgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Matter 1.1 Atoms and Molecules: Packed in A Small NucleusDokument35 SeitenChapter 1: Matter 1.1 Atoms and Molecules: Packed in A Small NucleusSupia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled Notebook PDFDokument28 SeitenUntitled Notebook PDF石上 優Noch keine Bewertungen
- 197 Review Notes 1 PDFDokument23 Seiten197 Review Notes 1 PDFKIMBERLY ANNE DIAZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms, Ions, IsotopesDokument9 SeitenAtoms, Ions, IsotopesHaizel MahendruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 (Atomic Structure and History of Atom)Dokument15 SeitenChapter 3 (Atomic Structure and History of Atom)Tunku Hilman Al-nordinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number-1Dokument38 SeitenAtoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number-1joseph dave pregonerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms Inside OutDokument19 SeitenAtoms Inside OutRicky AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and BondingDokument5 SeitenStructure and Bonding0406privNoch keine Bewertungen
- File 2657Dokument6 SeitenFile 2657Alexandra LupuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Atoms - The Inside StoryDokument4 Seiten4 Atoms - The Inside Storypianosheet123Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENCHML130 1 Energy 5 Nuclear 1Dokument27 SeitenENCHML130 1 Energy 5 Nuclear 1G7 SJ-01 Cabataña, MichailaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Thirteen Nuclei: Page 1 of 8Dokument8 SeitenChapter Thirteen Nuclei: Page 1 of 8MT๛ LUCIFERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3: Atomic Structure: Atoms MoleculesDokument2 SeitenChapter 3: Atomic Structure: Atoms Moleculesonlooker.eternityNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Atom: General ChemistryDokument9 SeitenThe Atom: General ChemistryKian Ceasar DeolazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presetation On Atomic StructureDokument11 SeitenPresetation On Atomic StructurebashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson-3 BDokument13 SeitenLesson-3 BJames Roy Bacolina DugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asc0304 Chemistry 1 Chapter 2: Atomic StructureDokument17 SeitenAsc0304 Chemistry 1 Chapter 2: Atomic StructurehadassahhadidNoch keine Bewertungen
- A105 ESE Revision SlidesDokument22 SeitenA105 ESE Revision Slides65scgdwmbkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 页面提取自-Chemistry for the IB Diploma Coursebook, 2nd EditionDokument1 Seite页面提取自-Chemistry for the IB Diploma Coursebook, 2nd EditionEshowbooks EbooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 01 Fundamentals of ElectricityDokument4 SeitenLecture 01 Fundamentals of ElectricityOnofre Algara Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry FactsheetsDokument415 SeitenChemistry FactsheetsAmbrose Aaron DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science MidtermsDokument4 SeitenPhysical Science MidtermsKimberly MedranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Organizer Science - AtomsDokument1 SeiteVisual Organizer Science - AtomswaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision-Map Chapter 4Dokument1 SeiteRevision-Map Chapter 4Megha BishtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number 1Dokument48 SeitenAtoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number 1Marielle GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- RDT103 PrelimsDokument4 SeitenRDT103 PrelimsRoshanlene ArellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic StructureDokument2 SeitenAtomic StructureArwind RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Polyatomic IonsDokument1 SeiteList of Polyatomic IonsSk. Salahuddin Ahammad100% (1)
- DNASeq ProcessDokument1 SeiteDNASeq ProcessSk. Salahuddin AhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathodic Protection: The BasicsDokument8 SeitenCathodic Protection: The BasicsbookbumNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Polyatomic IonsDokument1 SeiteList of Polyatomic IonsSk. Salahuddin Ahammad100% (1)
- Thermal InsulationDokument28 SeitenThermal Insulationferozbabu100% (2)
- How To Eliminate Foam in Coating Formulations - ArticleDokument4 SeitenHow To Eliminate Foam in Coating Formulations - ArticleMoatz HamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Problems Normal ShocksDokument7 SeitenClass Problems Normal ShocksNO oneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Contents: Methods To Study The Mineral Requirements of PlantsDokument28 SeitenChapter Contents: Methods To Study The Mineral Requirements of Plantskrish masterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular MotionDokument6 SeitenCircular MotionRasoolKhadibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main Work, Energy and Power Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDokument5 SeitenJEE Main Work, Energy and Power Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadSancia SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3 Biological MoleculesDokument6 SeitenLab 3 Biological Moleculesjohn NisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Stress Analysis of Rectangular Plate Due To Convection Using Finite Element MethodDokument7 SeitenThermal Stress Analysis of Rectangular Plate Due To Convection Using Finite Element Methodزهرة اللوتسNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate of ReactionsDokument30 SeitenRate of Reactionsanwar9602020100% (1)
- DPP 1 State of MatterDokument2 SeitenDPP 1 State of MatterLucky YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 250ml Volumetric Analysis Standards and SolutionsDokument6 Seiten250ml Volumetric Analysis Standards and SolutionsSham SajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 215 Myers: The Heck ReactionDokument8 SeitenChem 215 Myers: The Heck ReactiondubstepoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Misconceptions in Physics StudentsDokument6 SeitenMisconceptions in Physics StudentsAnonymous Zk2vW6ylNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 18 Ethylene GlycolDokument6 SeitenLecture 18 Ethylene GlycolJayraj DaymaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2 Coulombs Law APEMDokument3 SeitenCH 2 Coulombs Law APEMJames FlaughNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dielectric Behavior of Single Crystals: Articles You May Be Interested inDokument7 SeitenDielectric Behavior of Single Crystals: Articles You May Be Interested inmuthuphysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE BIOLOGY Exercises 01 Principles of BiologyDokument6 SeitenIGCSE BIOLOGY Exercises 01 Principles of Biologyngole_96Noch keine Bewertungen
- Postharvest Biology and Technology: A A A B C A D DDokument10 SeitenPostharvest Biology and Technology: A A A B C A D DRestrepo JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baking Soda LabDokument6 SeitenBaking Soda LabAubrey KemberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ab-Initio Simulations of Materials Using VASP PDFDokument35 SeitenAb-Initio Simulations of Materials Using VASP PDFjie shiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of CeramicsDokument80 SeitenStructure of CeramicsAmir Nazri KaibingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chlorination Guide Presentation PDFDokument168 SeitenChlorination Guide Presentation PDFAmit nayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leader Online Test Series For Jee Main 2020Dokument2 SeitenLeader Online Test Series For Jee Main 2020Aman KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1: How Does The Concept of Atomic Number Led To The Sysnthesis of New Elements in The LaboratoryDokument17 SeitenLesson 1: How Does The Concept of Atomic Number Led To The Sysnthesis of New Elements in The LaboratoryAngelica Bag-ao100% (1)
- WEBB 1999 Solubility and Diffusion of Carbon Dioxide in PolymersDokument6 SeitenWEBB 1999 Solubility and Diffusion of Carbon Dioxide in Polymerspstedile1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1Dokument16 SeitenExperiment 1Izhharuddin100% (2)
- Homework 07 ProblemsDokument6 SeitenHomework 07 ProblemsBrianna ChapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daiy Test Preparation - QuizzizDokument11 SeitenDaiy Test Preparation - QuizzizJulyantho TundeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 1 - Surface Hardening Processes PDFDokument16 SeitenChapter - 1 - Surface Hardening Processes PDFRajaSekarsajja100% (2)
- 2.1 Compound MeasuresDokument38 Seiten2.1 Compound MeasuresMejd BenkortbiNoch keine Bewertungen