Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hearing Aid
Hochgeladen von
Gyan ChaharOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hearing Aid
Hochgeladen von
Gyan ChaharCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
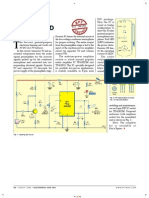
circuit
ideas
DIP package.
Here the IC is
wired in bridge
Hearing Aid S.C. DW
IVEDI
configuration to
drive the 32-ohm
general-purpose
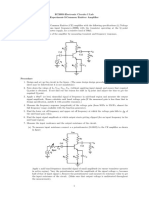
T.K. Hareendran Resistor R1 biases the internal circuit of monophonic ear-
the low-voltage condenser microphone phone. Red LED
T
his low-cost, general-purpose for proper working. The audio output (LED1) indicates
electronic hearing aid works off from the preamplifier stage is fed to the the power status.
3V DC (2x1.5V battery). input of the medium-power amplifier Resistor R8 lim-
In this circuit, transistor T1 and as- circuit via capacitor C2 and volume its the operating
sociated components form the audio control VR1. current of LED1.
signal preamplifier for the acoustic The medium-power amplifier The audio
signals picked up by the condenser section is wired around popular output of this Fig. 2: Enclosure
microphone and converted into cor- audio amplifier IC TDA2822M (not circuit is 10 to 15
responding electrical signals. Resistor TDA2822). This IC, specially designed mW and the quiescent current drain is
R5 and capacitor C3 decouple the for portable low-power applications, below 1 mA. The circuit can be easily
power supply of the preamplifier stage. is readily available in 8-pin mini assembled on a veroboard. For easy as-
Fig. 3: Pin descriptions of cond.
mic, C1740 and BC547
sembling and maintenance,
use an 8-pin DIP IC socket
for TDA2822M. Proposed
enclosure (with earphone
socket) for the assembled
unit is shown in Fig. 2.
Note. The complete
kit is available at
Kits‘n’Spares.
Fig. 1: Hearing aid circuit
9 6 • au g u s t 2 0 0 6 • e l e c t ro n i c s f o r yo u w w w. e f y m ag . co m
CMYK
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Analog Electronic Circuit Engineering PDFDokument434 SeitenAnalog Electronic Circuit Engineering PDFSeang Hok Yiev100% (3)
- Sound System at Ustc Auditorium Sl. Image Qty. No. Description of ItemsDokument9 SeitenSound System at Ustc Auditorium Sl. Image Qty. No. Description of ItemsMilin Anik'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audiometric Testing of AdultsDokument6 SeitenAudiometric Testing of AdultssofiameNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Performance UWB Planar Antenna Design ProWong NSYSUDokument30 SeitenHigh Performance UWB Planar Antenna Design ProWong NSYSUAdnan MirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective.: Audio EqualizersDokument6 SeitenObjective.: Audio EqualizersFernando Aarón Ortiz RicárdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspects of Hearing Aids Fitting ProceduresDokument150 SeitenAspects of Hearing Aids Fitting ProceduresakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Hearing Aid DevelopmentDokument10 SeitenDigital Hearing Aid Developmentaka_1010Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Principles of Hearing Aid AudiologyDokument350 Seiten1 - Principles of Hearing Aid AudiologyCarlos GoodwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hearing AidDokument4 SeitenHearing AiddnllkzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Spectrum Analyser in Your Shack PDFDokument4 SeitenA Spectrum Analyser in Your Shack PDFbaymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ground LoopDokument86 SeitenGround LoopZulu Bravo MikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desktop Fitting Guide Target 6.0Dokument11 SeitenDesktop Fitting Guide Target 6.0Abdul BaseerNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEARING LOSS GUIDEDokument46 SeitenHEARING LOSS GUIDEgibreilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enhancement of Mobile Tele-Health System Via GSMDokument5 SeitenEnhancement of Mobile Tele-Health System Via GSMarunnehru_aucseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuning a Radio with FiltersDokument42 SeitenTuning a Radio with FiltersMaphikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hearing Aids FinalDokument9 SeitenHearing Aids FinalVishal GauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otoacoustic Emissions From MedscapeDokument5 SeitenOtoacoustic Emissions From MedscapeMin-Joo Esther ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rehabilitation Esophageal Speech & Artificial LarynxDokument50 SeitenRehabilitation Esophageal Speech & Artificial LarynxKUNNAMPALLIL GEJO JOHN100% (2)
- Hearing Aid PDFDokument43 SeitenHearing Aid PDFBILAL DIFNoch keine Bewertungen
- BranchesDokument350 SeitenBranchespmjoshir50% (2)
- Masking Frequency Selectivity and The Critical BandDokument80 SeitenMasking Frequency Selectivity and The Critical Bandعلی احمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kenneth Kaliski Slides 6.7.11Dokument21 SeitenKenneth Kaliski Slides 6.7.11Northeast Wind Resource Center (NWRC)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustical ParametersDokument26 SeitenAcoustical ParametersFederico Nahuel CacavelosNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB Implementation of Acoustic Echo Cancellation AlgorithmsDokument81 SeitenMATLAB Implementation of Acoustic Echo Cancellation AlgorithmsTridev Padhi100% (1)
- Bob PhaseDokument7 SeitenBob Phasealecs serbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voicecourse StrobosDokument35 SeitenVoicecourse StrobospocepocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equal Loudness LevelDokument16 SeitenEqual Loudness LevelssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figures For Chapter 5: Earmolds and EarshellsDokument27 SeitenFigures For Chapter 5: Earmolds and EarshellsnabillsharmasisirNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Economical Hearing Aid LoopDokument10 SeitenAn Economical Hearing Aid LoopTimotheus Michael VowlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earmolds and Hearing Aid Shells - A Tutorial - Hearing ReviewDokument12 SeitenEarmolds and Hearing Aid Shells - A Tutorial - Hearing ReviewAhiawortor KplorlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poor Mans Hearing AidDokument1 SeitePoor Mans Hearing Aidvinay reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audio Signal Processing: A MATLAB ProgramDokument19 SeitenAudio Signal Processing: A MATLAB ProgramAkhiJarodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individualizing The Hearing Aids Needs AssessmentDokument36 SeitenIndividualizing The Hearing Aids Needs Assessmentapi-349133705100% (1)
- Samsung Bluetooth Hearing Aid Test Results (FCC Application)Dokument53 SeitenSamsung Bluetooth Hearing Aid Test Results (FCC Application)Gina SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditory Neuropathy MorletDokument20 SeitenAuditory Neuropathy MorletOxanaBitcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSR Thresholds PDFDokument7 SeitenASSR Thresholds PDFDaniela Garrido GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Hearing Aid DeviceDokument7 SeitenDesign Hearing Aid DeviceThương TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hearing Aid System Using MatlabDokument6 SeitenHearing Aid System Using MatlabAbhishek ChedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 3Dokument3 SeitenAss 3Matthew JoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Am 03Dokument30 SeitenAm 03Mudit AryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sound Spring06Dokument11 SeitenSound Spring06toolman1588Noch keine Bewertungen
- As 60118.14-2007 Hearing Aids Specification of A Digital Interface DeviceDokument8 SeitenAs 60118.14-2007 Hearing Aids Specification of A Digital Interface DeviceSAI Global - APACNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slow Auditory Evoked Potentials (1 InterligneDokument8 SeitenSlow Auditory Evoked Potentials (1 Interligner.boniver524Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cochlear Rotation and Its RelevanceDokument7 SeitenCochlear Rotation and Its RelevanceDrTarek Mahmoud Abo KammerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing Loudness Models in MatlabDokument5 SeitenImplementing Loudness Models in MatlabPro AcousticNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna FundamentalDokument54 SeitenAntenna FundamentalMardan KadivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Portable Hearing Aid Based On FPGADokument4 SeitenDesign of Portable Hearing Aid Based On FPGAsenthilvlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Line Derivation Perry Marshall PDFDokument20 SeitenTransmission Line Derivation Perry Marshall PDFmerrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hearing With Bone-Anchored Hearing Aid BAHA PDFDokument8 SeitenHearing With Bone-Anchored Hearing Aid BAHA PDFpro4ksaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna FundamentalsDokument45 SeitenAntenna FundamentalsAllanki Sanyasi RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loudspeaker Impedance With Sia Smaartlive: Paul D. HendersonDokument7 SeitenLoudspeaker Impedance With Sia Smaartlive: Paul D. HendersonGabo CodornizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Pyramidal Horn Antenna For UWB ApplicationsDokument3 SeitenDesign of Pyramidal Horn Antenna For UWB ApplicationsAmador Garcia IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- The Marchand Balun: Past and Ever PresentDokument28 SeitenThe Marchand Balun: Past and Ever Presenthadi545nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cochlear ImplantDokument33 SeitenCochlear ImplantNithiyah DevarajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2W 4W SystemDokument7 Seiten2W 4W SystemmaanbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Patch's Shapes On Microstrip Monopole AntennaDokument40 SeitenAnalysis of Patch's Shapes On Microstrip Monopole AntennaSuryana DevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ounding and Shielding For Sound and Video PDFDokument37 SeitenOunding and Shielding For Sound and Video PDFMoyGar2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- White Paper KEFDokument15 SeitenWhite Paper KEFhificompassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spy EarDokument1 SeiteSpy EarAsad AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonic DetectorDokument2 SeitenUltrasonic DetectorRev. Matthew100% (3)
- CI-1 Aug06Dokument1 SeiteCI-1 Aug06Sai KiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Musical Light Chaser: IdeasDokument2 SeitenMusical Light Chaser: IdeasJaveed AhamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening BugDokument1 SeiteListening BugDiksha Tulsi67% (3)
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - 5295 Bank Clerk Sample 2010Dokument7 Seiten(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - 5295 Bank Clerk Sample 2010Gyan ChaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume FormatDokument2 SeitenResume FormatRamesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advertisemen CSDokument8 SeitenAdvertisemen CSpiyushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isdr Publication Floods Chapter2Dokument23 SeitenIsdr Publication Floods Chapter2Gyan ChaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hearing AidDokument1 SeiteHearing AidGyan ChaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feedback TopologyDokument6 SeitenFeedback Topologyilg1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tba120 ReceiverDokument4 SeitenTba120 ReceiverUruguayoGonzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problemas CH6 PDFDokument11 SeitenProblemas CH6 PDFJuan227100% (1)
- Digital Electronics (K-Wiki - Data Converters)Dokument11 SeitenDigital Electronics (K-Wiki - Data Converters)SUNOBHAINoch keine Bewertungen
- EC1 Lab Exp3 PDFDokument2 SeitenEC1 Lab Exp3 PDFRitu RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Depletion-mode MOSFET devices explainedDokument3 SeitenDepletion-mode MOSFET devices explainedshohobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi Stage AmplifiersDokument9 SeitenMulti Stage AmplifiersMuhammed ThameemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Pulse CircuitsDokument74 Seiten2 Pulse CircuitsWaqar Ahmad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic Gate Delay and Transition Time AnalysisDokument24 SeitenLogic Gate Delay and Transition Time AnalysisKarthick NpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detectors: Single-SidebandDokument8 SeitenDetectors: Single-SidebandIsrael MaurenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trescientos Uno Flanger: Resistors Trim Pots Parts ListDokument1 SeiteTrescientos Uno Flanger: Resistors Trim Pots Parts ListYeremia OyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LC Filter DesignDokument41 SeitenLC Filter DesignPhạm Tuấn AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIT Refreshing Test TitleDokument2 SeitenCIT Refreshing Test TitleMani BharathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verifying Thevenin's, Norton's and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremsDokument6 SeitenVerifying Thevenin's, Norton's and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremsPias OfficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics - Contd.: Rijil RamchandDokument24 SeitenDigital Electronics - Contd.: Rijil RamchandAshna JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital-to-Analog (D/A) Converters Lec8 1 Introduction To D/A ConvertersDokument4 SeitenDigital-to-Analog (D/A) Converters Lec8 1 Introduction To D/A ConvertersKhalifa EltayebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuits - Lab - Handbook RA ZJSUDokument8 SeitenCircuits - Lab - Handbook RA ZJSUlanxinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vdic 2Dokument142 SeitenVdic 2api-3735399100% (3)
- ESC201 UDas Lec24Corrected OpAmp Aps PDFDokument6 SeitenESC201 UDas Lec24Corrected OpAmp Aps PDFPk KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dressler ARA-2000 Active Antenna - What's Inside ?Dokument7 SeitenDressler ARA-2000 Active Antenna - What's Inside ?chumengue snachezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15ecl48 VTU Raghudathesh Astable Monostable MultivibratorDokument4 Seiten15ecl48 VTU Raghudathesh Astable Monostable MultivibratorraghudatheshgpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eup3482aeup3482a PDFDokument11 SeitenEup3482aeup3482a PDFfabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18CSS201J Analog and Digital ElectronicsDokument34 Seiten18CSS201J Analog and Digital ElectronicsPriyansh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Complex Circuits": Markham District High SchoolDokument12 Seiten"Complex Circuits": Markham District High SchoolJayan OommenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shouding: Features General DescriptionDokument7 SeitenShouding: Features General DescriptionJuan SenatoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12v, 7ah Smart Battery Charger With PCB Diagram - Engineering ProjectsDokument3 Seiten12v, 7ah Smart Battery Charger With PCB Diagram - Engineering ProjectsDhanraj PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter: Amplitude Stabilization of The Harmonic OscillatorDokument10 SeitenChapter: Amplitude Stabilization of The Harmonic OscillatordheenadayalanNoch keine Bewertungen