Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
FLUIDVOLDEFNCPCS
Hochgeladen von
Eleazar Belgica100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
14 Ansichten2 SeitenNursing Care Plan - DEFICIENT FLUID VOLUME assessment. Provides information about overall fluid balance, renal function, and bowel disease control. Determines replacement needs and effectiveness of therapy.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenNursing Care Plan - DEFICIENT FLUID VOLUME assessment. Provides information about overall fluid balance, renal function, and bowel disease control. Determines replacement needs and effectiveness of therapy.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
14 Ansichten2 SeitenFLUIDVOLDEFNCPCS
Hochgeladen von
Eleazar BelgicaNursing Care Plan - DEFICIENT FLUID VOLUME assessment. Provides information about overall fluid balance, renal function, and bowel disease control. Determines replacement needs and effectiveness of therapy.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
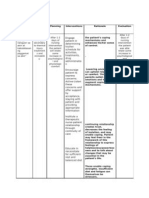
Nursing Care Plan – DEFICIENT FLUID VOLUME
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
PT: RC After 8 hours of nursing Independent:
Date: 9-9-2010 Risk for deficient interventions, the • Monitor intake and output • Provides information about After 8 hours of
fluid volume related patient will maintain (I&O). Note number, overall fluid balance, renal nursing
SUBJECTIVE: to diarrhea. adequate fluid volume character, and amount of function, and bowel disease interventions, the
as evidenced by moist stools. Estimate control, as well as patient was able to
“madalas ako mucous membranes, insensible fluid losses guidelines for fluid maintain adequate
dumumi” verbalized good skin turgor, and like diaphoresis. Measure replacement. fluid volume as
by patient. capillary refill. urine specific gravity and evidenced by moist
observe for oliguria. mucous
Objective: • Assess vital signs. Blood • Hypotension, tachycardia, membranes, good
pressure, pulse and fever can indicate response skin turgor, and
• Facial mask of temperature. to and or effect of fluid loss. capillary refill.
pain. • Indicates excessive fluid
loss or resultant
• Frequent watery dehydration.
stools. • Observe for excessively
dry skin and mucous
• V/S taken as membranes, decreased
follows: skin turgor, slowed
capillary refill. • Indicator of overall fluid and
nutritional status.
T: 37.7 • Weigh daily. • Colon is placed at rest for
PR:88 healing and to decrease
R: 20 intestinal fluid losses.
Bp: 110/80 • Inadequate diet and
• Maintain oral restrictions, decreased absorption may
bedrest and avoid lead to vitamin K deficiency
exertion. and defect in coagulation,
potentiating risk for
hemorrhage.
• Observe for overt • Excessive intestinal loss
bleeding and test stool may lead to electrolyte
daily for occult blood. imbalance.
• Maintenance of bowel rest
requires alternative fluid
replacement to correct loses
• Note generalized muscle or anemia.
weakness or cardiac • Determines replacement
dysrhythmias. needs and effectiveness of
Nursing Care Plan – DEFICIENT FLUID VOLUME
therapy.
Collaborative:
• Administer parenteral
fluids, blood transfusions
as indicated.
• Monitor laboratory
studies.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Gerontological NursingDokument13 SeitenGerontological NursingEleazar BelgicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newbie Case Digest - EthicsDokument1 SeiteNewbie Case Digest - EthicsEleazar BelgicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Funda HandoutDokument2 SeitenFunda HandoutEleazar BelgicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical-Surgical: Fluids & ElectrolytesDokument65 SeitenMedical-Surgical: Fluids & Electrolytesɹǝʍdןnos100% (32)
- ELNCPACTUALBURN1Dokument1 SeiteELNCPACTUALBURN1Eleazar BelgicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Operative Nursing Care: By: Eleazar B. Belgica BSNL Iii-2 Lorma CollegesDokument8 SeitenPre-Operative Nursing Care: By: Eleazar B. Belgica BSNL Iii-2 Lorma CollegesEleazar BelgicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver AnaphyDokument4 SeitenLiver AnaphyEleazar BelgicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holy EucharistDokument5 SeitenHoly EucharistAkyciel FariasNoch keine Bewertungen
- RN Exam July 2010Dokument754 SeitenRN Exam July 2010Lj Ferolino100% (1)
- Liver AnaphyDokument4 SeitenLiver AnaphyEleazar BelgicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Clinical Leaflet - QUS - v2Dokument2 SeitenClinical Leaflet - QUS - v2ultrasound tomNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange Related To Alveolar Wall Destruction EMPHYSEMADokument5 SeitenNCP Impaired Gas Exhange Related To Alveolar Wall Destruction EMPHYSEMAMa. Elaine Carla Tating50% (2)
- Uti StudiesDokument10 SeitenUti Studiesapi-302840362Noch keine Bewertungen
- Discuss Any Four Challenges Faced by Ovc and Their Intervention StrategiesDokument5 SeitenDiscuss Any Four Challenges Faced by Ovc and Their Intervention StrategiesJohn MugabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disability MatrixDokument21 SeitenDisability MatrixAngelika MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of A NHS Risk Rating MatrixDokument2 SeitenExample of A NHS Risk Rating MatrixRochady SetiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predicting and Controlling Influenza Outbreaks - Published Article - IJERSTE - Vol.12 Issue 2, Feb 2023Dokument4 SeitenPredicting and Controlling Influenza Outbreaks - Published Article - IJERSTE - Vol.12 Issue 2, Feb 2023dimple kharwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sq20-030 - Fact Sheet - Informed Consent - Nsqhs-8.9aDokument4 SeitenSq20-030 - Fact Sheet - Informed Consent - Nsqhs-8.9aPedro Medeiros JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Chart of Physical Education Teachers - AP GOVTDokument3 SeitenJob Chart of Physical Education Teachers - AP GOVTRamachandra Rao100% (1)
- GENDER Reseach 100%3Dokument46 SeitenGENDER Reseach 100%3Mesud GemechuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book - MOSBY'S DENTAL DRUG REFERENCE PDFDokument1.496 SeitenBook - MOSBY'S DENTAL DRUG REFERENCE PDFMohamed Faizal78% (9)
- Extend XT - Folleto ComercialDokument6 SeitenExtend XT - Folleto ComercialMuhamadZuhdiAlWaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Position Paper de l'UEFA Sur L'interdiction Du Gazon Synthétique Par l'ECHA 19 Juillet 2019Dokument8 SeitenPosition Paper de l'UEFA Sur L'interdiction Du Gazon Synthétique Par l'ECHA 19 Juillet 2019LeMonde.frNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 1 Concepts and Definitions 1.1 Disaster (I)Dokument25 SeitenUnit - 1 Concepts and Definitions 1.1 Disaster (I)RISHITHA LELLANoch keine Bewertungen
- g8 Health q3 LM Disease 130908005904 PDFDokument64 Seiteng8 Health q3 LM Disease 130908005904 PDFkenneth cannillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Consequences of Adverse Childhood Experiences: A Systematic ReviewDokument9 SeitenHealth Consequences of Adverse Childhood Experiences: A Systematic ReviewCocia Podina Ioana RoxanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burnout Among Secondary School Teachers in Malaysia Sabah: Dr. Balan RathakrishnanDokument8 SeitenBurnout Among Secondary School Teachers in Malaysia Sabah: Dr. Balan Rathakrishnanxll21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmaceuticals Manufacturing - What Do We Know About The Occupational Health and Safety Hazards For Women Working in The Industry PDFDokument61 SeitenPharmaceuticals Manufacturing - What Do We Know About The Occupational Health and Safety Hazards For Women Working in The Industry PDFCostas JacovidesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERAS Protocols For Thyroid andDokument9 SeitenERAS Protocols For Thyroid andOskar MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 10 Most (And Least) Prestigious Jobs in AmericaDokument12 SeitenThe 10 Most (And Least) Prestigious Jobs in AmericaParlindungan PardedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic ListDokument6 SeitenTopic ListEdwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Dan Siegel - Resources - Healthy Mind PlatterDokument4 SeitenDr. Dan Siegel - Resources - Healthy Mind PlatterInês Novais100% (4)
- Coordination Group For Mutual Recognition and Decentralised Procedures - Human (CMDH)Dokument12 SeitenCoordination Group For Mutual Recognition and Decentralised Procedures - Human (CMDH)aslkdjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prospectus: 1 ReservationsDokument8 SeitenProspectus: 1 ReservationsvarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prilosec (Omeprazole) MoreDokument3 SeitenPrilosec (Omeprazole) MoreLuis Arturo Andrade CoronadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Safety With Dance: Worksheet in Health Optimizing Physical Education 3 (HOPE3/PEH3)Dokument9 SeitenPersonal Safety With Dance: Worksheet in Health Optimizing Physical Education 3 (HOPE3/PEH3)Cregie Brillantes QuezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TheraDokument4 SeitenTheramaircusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food SafetyDokument2 SeitenFood SafetymacmanueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanDokument3 SeitenLab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanGiacen100% (3)
- Effects of Sprint Interval Training and Body.24Dokument8 SeitenEffects of Sprint Interval Training and Body.24Maxwell MartinsNoch keine Bewertungen