Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nursing Care Plan
Hochgeladen von
Aldrein Gonzales0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
895 Ansichten2 SeitenThe nursing care plan addresses a patient experiencing renal failure who presents with edema, fatigue, and weakness, and notes an assessment of fluid overload and compromised renal function. The plan includes monitoring intake and output, daily weighing, skin assessments for edema, oral fluid replacement within restrictions, and administering diuretics and antihypertensives as needed to manage fluid levels, reduce edema, and treat hypertension. The expected outcomes are appropriate urinary output, stable weight and vital signs, and resolution of edema.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe nursing care plan addresses a patient experiencing renal failure who presents with edema, fatigue, and weakness, and notes an assessment of fluid overload and compromised renal function. The plan includes monitoring intake and output, daily weighing, skin assessments for edema, oral fluid replacement within restrictions, and administering diuretics and antihypertensives as needed to manage fluid levels, reduce edema, and treat hypertension. The expected outcomes are appropriate urinary output, stable weight and vital signs, and resolution of edema.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
895 Ansichten2 SeitenNursing Care Plan
Hochgeladen von
Aldrein GonzalesThe nursing care plan addresses a patient experiencing renal failure who presents with edema, fatigue, and weakness, and notes an assessment of fluid overload and compromised renal function. The plan includes monitoring intake and output, daily weighing, skin assessments for edema, oral fluid replacement within restrictions, and administering diuretics and antihypertensives as needed to manage fluid levels, reduce edema, and treat hypertension. The expected outcomes are appropriate urinary output, stable weight and vital signs, and resolution of edema.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Student Nurses’ Community
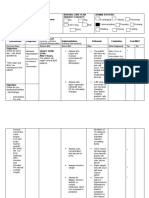
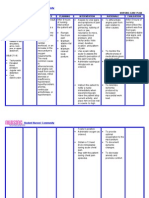
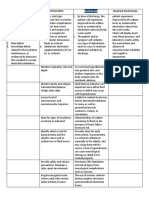
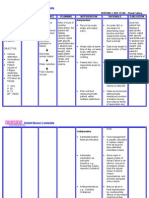
NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal Failure
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Independent
SUBJECTIVE: Fluid Volume Renal failure After 8 hours of Goal met,
“Namamanas excess r/t nursing • Record accurate • Accurate I&O is patient has
ako at ang hina Compromised intervention, the intake and output necessary for displayed
ng katawan ko” regulatory Decrease blood patient will (I&O). determining renal appropriate
(I have edema and mechanism flow to kidneys display function and fluid urinary output
I feel very weak) (renal failure) appropriate replacement needs with specific
as verbalized by urinary output and reducing risk of gravity/laborato
the patient Decrease with specific fluid overload ry studies near
perfusion in gravity/laborator normal; stable
kidney y studies near • Weigh daily at same • Daily body weight is weight, vital
OBJECTIVE: normal; stable time of day, on same best monitor of fluid signs within
weight, vital scale, with same status patient’s
• Venous Decrease signs within equipment and normal range;
distension urinary output patient’s normal clothing and absence of
• Generalized range; and edema.
edema absence of • Assess skin, face, • Edema occurs
• Patient Water retention edema. dependent areas for primarily in
reports of edema dependent tissues
Fatigue, of the body, e.g.,
weakness, Fluid volumes hands, feet,
and malaise excess lumbosacral area.
• V/S taken as Patient can gain up
follows to 10 lb (4.5 kg) of
fluid before pitting
T: 35˚C edema is detected
P: 50
R: 13 • Plan oral fluid • Helps avoid periods
BP: 130/90 replacement with without fluids,
patient, within minimizes boredom
multiple restrictions of limited choices,
and reduces sense
of deprivation and
Student Nurses’ Community
thirst
Collaborative
• Administer/restrict • Fluid management
fluids as indicated. is usually calculated
to replace output
from all sources
plus estimated
insensible losses
• Administer • Given early in
medication as oliguric phase of
indicated Renal Failure in an
Diuretics, e.g., effort to convert to
furosemide (Lasix), nonoliguric phase,
mannitol (Osmitrol) flush the tubular
lumen of debris,
reduce
hyperkalemia, and
promote adequate
urine volume.
• Antihypertensives, • May be given to
e.g., clonidine treat hypertension
(Catapres) by counteracting
effects of decreased
renal blood flow
and/or circulating
volume overload
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDokument2 SeitenNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDokument6 SeitenChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument2 SeitenNCPJhel NabosNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 1Dokument1 SeiteNCP 1hsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationDokument3 SeitenStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationNur faizah bt azmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDokument3 SeitenNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Dokument3 SeitenNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP HemoDokument2 SeitenNCP HemoJigs HechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Dokument2 SeitenCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis ADokument2 SeitenNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis APravesh Verma100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDokument2 SeitenRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care Plan ExampleDokument2 SeitenCare Plan Exampleincess27100% (1)
- Hepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALDokument2 SeitenHepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 1 Addisons DiseaseDokument5 SeitenNCP 1 Addisons DiseaseRenee RoSeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For HeadacheDokument1 SeiteNCP For HeadacheJohn MajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDokument4 SeitenNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument3 SeitenActivity Intolerancelouie roderos0% (1)
- Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1Dokument8 SeitenRisk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1kint manlangitNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDokument7 SeitenCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan NyaDokument3 SeitenAssessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan Nyaangel_pearl413100% (2)
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDokument3 SeitenSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDokument1 SeiteNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP LocDokument2 SeitenNCP LocMel RodolfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationDokument1 SeiteCholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationJess GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDokument15 SeitenAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRanusha AnushaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument4 SeitenNursing Care PlanKath RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP AnginaDokument3 SeitenNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- NCPDokument2 SeitenNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument13 SeitenNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- NCP Gastric CancerDokument6 SeitenNCP Gastric Cancerhayascent hilarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDokument2 SeitenNursing Diagnosis: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveLen meloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Dokument1 SeiteAssessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Jamaica Leslie NovenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument5 SeitenNCPRose AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDokument1 SeiteIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismneuronurseNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDokument2 Seiten"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- NCP - GlaucomaDokument1 SeiteNCP - GlaucomaKath CuevasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDokument7 SeitenNCP Liver CirrhosisIris Jimenez-BuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Acute PainDokument1 SeiteNCP - Acute PainjsthrNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP pAlPITATIONSDokument3 SeitenNCP pAlPITATIONSHazel PalomaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP MS DbiDokument2 SeitenNCP MS DbiSj EclipseNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP InfectionDokument3 SeitenNCP InfectionPrince AhmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Patient With Endotracheal TubeDokument1 SeiteNCP - Patient With Endotracheal TubeSelwynVillamorPatenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaDokument2 SeitenNursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaAbdallah AlasalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDokument9 SeitenFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- NCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaDokument2 SeitenNCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaChenime Añana0% (1)
- NCP BPHDokument8 SeitenNCP BPHjyaba0% (1)
- CholecystitisDokument1 SeiteCholecystitisDianne ParungaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. YingDokument1 SeitePatriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. Yingjanna mae patriarca100% (2)
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDokument2 SeitenCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNU49Dokument2 SeitenSNU49Nora BacolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveDokument3 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveMaverick LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan - Renal FailureDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan - Renal Failurederic87% (31)
- CKD NCPDokument2 SeitenCKD NCPMark Angelo Chan100% (13)
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMr. whiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRenie SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP AxelDokument10 SeitenNCP AxelTan TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Management Assignment #01: Submitted BY Shaheer Ahmed Khan (MS2019198019)Dokument15 SeitenEnergy Management Assignment #01: Submitted BY Shaheer Ahmed Khan (MS2019198019)shaheer khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5-People Should Manage Nature-Ts-Planning Guide-Grade 5Dokument1 SeiteUnit 5-People Should Manage Nature-Ts-Planning Guide-Grade 5api-457240136Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 1 - Digital - Systems - and - Binary - Numbers EE228 15-16Dokument81 SeitenChapter - 1 - Digital - Systems - and - Binary - Numbers EE228 15-16mohamed hemdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV (Martin A Johnson)Dokument7 SeitenCV (Martin A Johnson)kganesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- APA 6th Edition - Citation Styles APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, IEEE - LibGuDokument2 SeitenAPA 6th Edition - Citation Styles APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, IEEE - LibGuJan Louis SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- JICA Helmya DCC Building FFDokument4 SeitenJICA Helmya DCC Building FFMuhammad ElbarbaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tawjihi 7Dokument55 SeitenTawjihi 7api-3806314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Imamsha Maharaj Na Parcha NewDokument16 SeitenImamsha Maharaj Na Parcha NewNARESH R.PATELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distance Relay Setting CalculationDokument8 SeitenDistance Relay Setting Calculation1453h100% (7)
- RHEL 9.0 - Configuring Device Mapper MultipathDokument59 SeitenRHEL 9.0 - Configuring Device Mapper MultipathITTeamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Interactive AppsDokument17 SeitenBuilding Interactive AppsJRoman OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lorenzo JDokument2 SeitenLorenzo Japi-528402595Noch keine Bewertungen
- The History of The Photocopy MachineDokument2 SeitenThe History of The Photocopy MachineAndy WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level 2 Online BPDokument98 SeitenLevel 2 Online BProbertduvallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 SolutionDokument11 SeitenAssignment 1 SolutionKash TorabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WRhine-Main-Danube CanalDokument6 SeitenWRhine-Main-Danube CanalbillNoch keine Bewertungen
- SalivaDokument42 SeitenSalivaAtharva KambleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual G Ingles - V6Dokument68 SeitenManual G Ingles - V6Phùng Thế Kiên50% (2)
- Mooring OperationsDokument5 SeitenMooring OperationsHerickson BerriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checkpoints Before Transformer InstallationDokument3 SeitenCheckpoints Before Transformer InstallationBeaBustosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The London SchoolDokument3 SeitenThe London SchoolKhawla Adnan100% (5)
- RenewalPremium 1123186Dokument1 SeiteRenewalPremium 1123186Suhas Renu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Forms of Organizing Activity Games, Methodology of Conducting Activity Games in Physical Education LessonsDokument4 SeitenForms of Organizing Activity Games, Methodology of Conducting Activity Games in Physical Education LessonsAcademic JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- C3H Hawaii (Polynesian Islands) (Native Food in Hawaii)Dokument19 SeitenC3H Hawaii (Polynesian Islands) (Native Food in Hawaii)Yoon Yati ShinNoch keine Bewertungen
- LGDokument36 SeitenLGNanchavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastics Library 2016 enDokument32 SeitenPlastics Library 2016 enjoantanamal tanamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mucic Acid Test: PrincipleDokument3 SeitenMucic Acid Test: PrincipleKrizzi Dizon GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument14 SeitenHeat TreatmentAkhilesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Er. Nipesh RegmiDokument30 SeitenDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Er. Nipesh RegmiRosina AdhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34P S4hana1909 BPD en UsDokument18 Seiten34P S4hana1909 BPD en UsBiji RoyNoch keine Bewertungen