Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NCP Tuberculosis
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous XvwKtnSrMR50%(2)50% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (2 Abstimmungen)
10K Ansichten3 SeitenCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
50%(2)50% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (2 Abstimmungen)
10K Ansichten3 SeitenNCP Tuberculosis
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous XvwKtnSrMRCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
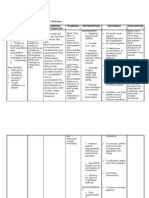
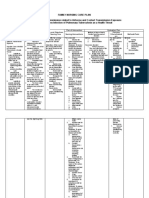
FAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN
Risk for Infection Transmission related to Airborne and Contact Transmission Exposure
Possible Cross Infection of Pulmonary Tuberculosis as a Health Threat
Nursing Diagnoses, Plan of Intervention Evaluation Plan
Health Conditions, Goals and Objectives Method of Nurse-Family Outcome
Supporting Data Cues
Family Nursing of Nursing Care Nursing Interventions Contact and Resources Criteria/Indicat Methods/Tools
Problems Needed ors
Risk for Infection M. J. and J. Goal: After the nursing The nurse will: Method: Home visit The family will be Methods:
Transmission related to have been diagnosed intervention, Mrs. L will 1. Discuss the 1. Discussion able to: 1. Asking
Airborne Transmission with MDR-TB. not acquire the disease nature of pulmonary 2. Demonstration 1. Discuss questions
Exposure Mrs. L has been tuberculosis at least 3 2. Interview
diagnosed before with Objectives: At the end of Rationale: To have a Resources Needed: important 3. Verbal feedback
Possible Cross Infection minimal PTB. the nursing intervention, background of what 1. Human resources: concepts 4. Discussion
of Pulmonary Mrs. L takes care the family members will causes the disease Time and effort both of the regarding the 5. Return
Tuberculosis a Health of her diseased children. be able to: and how it develops nurse and the family nature of Demonstra-tion
Threat Mrs. L verbalized 1. Discuss the a. Caused by 2. Material resources: multidrug
1. Inability to that her children are not nature of multidrug Mycobacterium a. Image of the human resistant Tool: Checklist
make decisions with infectious because resistant tuberculosis respiratory tract with and tuberculosis
respect to taking they’ve already tested tuberculosis b. May be dormant without tuberculosis 2. Enumer
appropriate health negative in their sputum 2. Enumerate the or active b. Handout on proper ate at least 5
action due to: smear and culture. signs and symptoms c. Destroyed by handwashing technique signs and
a. Failure to Mrs. L verbalized of PTB antibodies or c. Germicidal soap symptoms of
comprehend the that PTB cannot be 3. Explain how engulfed by PTB
nature/magnitude transmitted through the the tubercle bacilli macrophages 3. Explain
of the sharing of utensils can be transmitted d. Form tubercles the 2 ways
problem/condition to another person especially at the how the
M. J. and J. have
b. Lack 4. Enumerate the lung apex tubercle bacilli
not strictly complied with
of/inadequate ways of diagnosing e. May be/develop can be
the treatment regimen for
knowledge as to a person with PTB drug resistant/ce transmitted to
their illness. They missed
alternative courses 5. Recognize the 2. Enumerate the another
some days of treatment.
of action open to importance of signs and symptoms person
them The house compliance with the of PTB 4. Enumer
2. Inability to measures 4 x 6 m, is treatment Rationale: To detect ate the 4
provide adequate poorly lit by the sun, and 6. Discuss the the presence of the ways of
nursing care to the has fairly well ventilation. ways of preventing disease as early as diagnosing a
sick member of the The three sleep disease possible person with
family due to lack in the same room transmission a. Cough with or PTB and give
of/inadequate distanced only a few feet 7. Demonstrate without sputum 1 advantage
knowledge about the apart. proper handwashing or hemoptysis and 1
disease/health The residences technique for more than 3 disadvantage
condition are not congested but weeks for each
are adjacent to each b. Low-grade fever 5. Explain
other providing less c. Poor appetite the 2 reasons
space for light and air to d. Weight loss why it is
enter the house. e. Chest and/or important to
M. J.’s physical upper back pain comply with
examination revealed f. Night sweats the treatment
inspiration-expiration g. Chills 6. Discuss
ratio of 1:1 and h. Tendency to at least 5
diminished breath fatigue easily ways of
sounds and dullness i. Pallor preventing
over the right lung field. 3. Explain how the disease
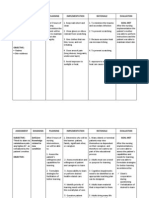
pathogen can be transmission
transmitted to another 7. Demons
person trate proper
Rationale: To serve handwashing
as foundation for technique
disease prevention correctly
a. Airborne
transmission –
tubercle bacilli
suspended in
dirt in the air
b. Contact
transmission –
droplet
transmission via
coughing,
sneezing,
speaking,
spitting
4. Enumerate the
ways of diagnosing a
person with PTB
Rationale: To be
aware of the various
diagnostic
procedures and their
advantages and
disadvantages
a. Sputum smear
b. X-ray
c. Sputum culture
d. PPD skin test
5. Recognize the
importance of
compliance with the
treatment
Rationale: To reduce
the complications and
cost of treatment
a. Prevent
development of
drug resistance
b. Efficient
treatment
6. Discuss the
ways of preventing
infection transmission
Rationale: To know
the different ways of
preventing the spread
of the infection
a. Isolation
b. Keeping
distance when
talking
c. Covering the
mouth when
sneezing or
coughing
d. Proper hygiene
e. Handwashing
f. Use of alcohol
or hand sanitizer
g. Boost immunity
h. Provide
adequate
sunlight
i. Provide
adequate
ventilation
7. Demonstrate
proper handwashing
technique
Rationale: To
decrease the risk of
contact transmission
8. Discuss ways
on how to boost the
immunity
Rationale: To
reinforce the body’s
natural capability to
destroy the pathogen
a. Eat foods rich in
vitamin C
(oranges,
ponkan, apples,
dalanghita,
calamansi,
cabbage)
b. Avoid exposure
to smoke and
dust
c. Drink adequate
amount of fluids
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- FNCP TB As A Health DeficitDokument5 SeitenFNCP TB As A Health Deficitkuu faalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Pulmonary TuberculosisDokument6 SeitenNCP - Pulmonary TuberculosisastrijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PTB NCPDokument12 SeitenPTB NCPNiel LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for a Patient with Tuberculosis (TBDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan for a Patient with Tuberculosis (TBVen Belista86% (14)
- NCP - TBDokument2 SeitenNCP - TBPahw BaluisNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP TBDokument6 SeitenNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis For AsthmaDokument6 SeitenNursing Diagnosis For AsthmaTINAIDA33% (3)
- Pulmonary TuberculosisDokument6 SeitenPulmonary Tuberculosisjenilay0% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Mapagod at Manghina" As: Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With AsthmaDokument2 SeitenMapagod at Manghina" As: Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With AsthmaKian Herrera100% (1)
- Case Study of Pneumonia With Underlying Covid 19Dokument41 SeitenCase Study of Pneumonia With Underlying Covid 19Angel CauilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Dokument1 SeiteChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Loss of AppetiteDokument5 SeitenNCP Loss of AppetiteStenneli Gumban Trojillo50% (2)
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPDharline Abbygale Garvida Agullana100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PneumoniaDokument28 SeitenNCP PneumoniaW'ton Borbe83% (6)
- Hernandez NCP Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenHernandez NCP Drug StudyEliza Joyce HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Dokument3 SeitenNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline ChaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDokument3 SeitenNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument3 SeitenAssessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceNelle Agni100% (1)
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentDokument4 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentIrish Eunice FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisDokument2 SeitenNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisFatima Zainab Matlih IdjiraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defining Characteristics Nursing Diagnosis Scientifc Analysis Plan of Care Nursing Interventions RationaleDokument3 SeitenDefining Characteristics Nursing Diagnosis Scientifc Analysis Plan of Care Nursing Interventions Rationalesbo100% (1)
- Rabi PurDokument3 SeitenRabi PurDiana Laura LeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute PancreatitisDokument2 SeitenAcute PancreatitisAkocmeme Sanchez100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Pulmonary TuberculosisDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Pulmonary TuberculosisLionel Richie Pedraza50% (2)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument10 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle Acena100% (2)
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDokument1 SeiteImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hiv NCPDokument2 SeitenHiv NCPHeindrich Cardenas0% (1)
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDokument1 SeiteHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For PCAPCDokument6 SeitenNCP For PCAPCEnrique Lu100% (1)
- Pneumonia NCPDokument5 SeitenPneumonia NCPElbert Aquitania Mutuc RN100% (2)
- Cap MRDokument4 SeitenCap MRKit BarcelonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesDokument20 SeitenAssessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesZamranosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP and Learning Objectives For MeaslesDokument7 SeitenNCP and Learning Objectives For MeaslesKhemz Dalde Lim67% (6)
- Pleural EffusionDokument5 SeitenPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case NCPDokument25 SeitenCase NCPJoher Bolante Mendez100% (1)
- Family Nursing Care Plan CriteriaDokument7 SeitenFamily Nursing Care Plan CriteriaAnonymous K99UIf1Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PTBDokument2 SeitenNCP PTBKath TalubanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chickenpox Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenChickenpox Nursing Care PlanBruno MercuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prostate Cancer NCPDokument1 SeiteProstate Cancer NCPKathleen Dimacali0% (1)
- Body Weakness NCPDokument1 SeiteBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 2Dokument2 SeitenNCP 2Neil Abraham Mendoza Lalap100% (2)
- SB: Sedentary Lifestyle Is A Medical Term Used To Denote A Type of Lifestyle With No or Irregular Physical Activity. ADokument4 SeitenSB: Sedentary Lifestyle Is A Medical Term Used To Denote A Type of Lifestyle With No or Irregular Physical Activity. ACamz ZernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing care plan for client with UTI and feverDokument3 SeitenNursing care plan for client with UTI and feverTheresa AbrilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Diarrhea - FeunrmfDokument7 SeitenNCP - Diarrhea - FeunrmfJk SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument4 SeitenNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaKannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Nursing NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy LaboratoryDokument3 SeitenCollege of Nursing NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy LaboratoryArriane Desepeda100% (1)
- NCP Risk For Infection TuberculosisDokument3 SeitenNCP Risk For Infection TuberculosisWen SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- FNCP 2Dokument3 SeitenFNCP 2Mae DacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Knowledge Deficit FINALDokument8 SeitenNCP Knowledge Deficit FINALJOSHUA JOSE TERCEnONoch keine Bewertungen
- FNCP2Dokument4 SeitenFNCP2Macky RobentaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Communicable Disease Control Program IDokument9 Seiten10 Communicable Disease Control Program IJennica JaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FNCP - TB As A Health DeficitDokument6 SeitenFNCP - TB As A Health DeficitIngrid Paula Nicolas100% (4)
- College of Our Lady of Mt. Carmel Public Health Course SyllabusDokument4 SeitenCollege of Our Lady of Mt. Carmel Public Health Course Syllabus;'SiLeNt';Noch keine Bewertungen
- Family nursing problems for hyperthermia and arthritisDokument5 SeitenFamily nursing problems for hyperthermia and arthritisYoongiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FNCP CHN Health ThreatDokument5 SeitenFNCP CHN Health ThreatYoongiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAQs On CARPDokument15 SeitenFAQs On CARPMichelleOgatisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magna Financial v. ColarinaDokument3 SeitenMagna Financial v. ColarinaAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Inter-Country Adoption ReportDokument8 SeitenInter-Country Adoption ReportAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Statutory Monetary Benefits 2016 PDFDokument75 SeitenHandbook of Statutory Monetary Benefits 2016 PDFAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- DO 18-A Uniform ImplementationDokument3 SeitenDO 18-A Uniform ImplementationAl BaljonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simex v. CADokument3 SeitenSimex v. CAAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Onapal v. CA FPIB v. CADokument5 SeitenOnapal v. CA FPIB v. CAAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR0% (1)
- Comparison of Laws On IncentivesDokument28 SeitenComparison of Laws On IncentivesAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Union Bank vs. CIRDokument6 SeitenUnion Bank vs. CIRAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNB v. PinedaDokument3 SeitenPNB v. PinedaAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Memo On Uniform Implementation of DO 174Dokument3 SeitenMemo On Uniform Implementation of DO 174Anonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (2)
- Alhambra Cigar v. SECDokument3 SeitenAlhambra Cigar v. SECAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candijay v. CADokument2 SeitenCandijay v. CAAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cosare v. BroadcomDokument4 SeitenCosare v. BroadcomAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salcedo v. ComelecDokument4 SeitenSalcedo v. ComelecAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- People v. CarantoDokument4 SeitenPeople v. CarantoAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Salcedo v. ComelecDokument4 SeitenSalcedo v. ComelecAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSC V BelaganDokument3 SeitenCSC V BelaganAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Concerning Oil Platforms (Iran V US)Dokument9 SeitenCase Concerning Oil Platforms (Iran V US)Anonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC vs. CADokument2 SeitenCBC vs. CAAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Realty V CADokument3 SeitenIntegrated Realty V CAAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Rules of The Geneva Conventions and Their Additional ProtocolsDokument32 SeitenBasic Rules of The Geneva Conventions and Their Additional ProtocolsInternational Committee of the Red Cross100% (1)
- Hassan v. COMELEC ruling on election failureDokument2 SeitenHassan v. COMELEC ruling on election failureAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iglesia Evangelica v. Bishop LazaroDokument3 SeitenIglesia Evangelica v. Bishop LazaroAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Marohombsar v. AlontoDokument2 SeitenMarohombsar v. AlontoAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nieva v. Alvarez-EdadDokument2 SeitenNieva v. Alvarez-EdadAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merrill v. CADokument2 SeitenMerrill v. CAAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR50% (2)
- Compiled Digests Letters of CreditDokument9 SeitenCompiled Digests Letters of CreditAnonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICC Elements of Crimes PDFDokument50 SeitenICC Elements of Crimes PDFKaye de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Syllabus (Spit) 2015Dokument15 SeitenTax Syllabus (Spit) 2015Anonymous XvwKtnSrMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPCHILD English Parent 5.0 WatermarkedDokument9 SeitenCPCHILD English Parent 5.0 WatermarkedAz-Zahraa NaasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Responsible Use of Media and Information ModuleDokument3 SeitenResponsible Use of Media and Information ModuleDarlene Dacanay DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behavior TherapyDokument4 SeitenBehavior TherapyMarianne DalmacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Macros PDFDokument6 SeitenWhat Are Macros PDFkulsoomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Household Chemical Poisoning GuideDokument9 SeitenHousehold Chemical Poisoning GuideAshley DayagNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Perception of Community Towards The ImplementedDokument7 SeitenThe Perception of Community Towards The ImplementedRia-Nette CayumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabian - Lit Analysis Feminism ApproachDokument1 SeiteFabian - Lit Analysis Feminism ApproachFabian Regine G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ground HandlingDokument46 SeitenGround HandlingIshwar ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Emotion and the Human Brain Are Deeply IntertwinedDokument6 SeitenHow Emotion and the Human Brain Are Deeply IntertwinedBruno XavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cover Letter For EportfolioDokument1 SeiteCover Letter For Eportfolioapi-302255572Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Nutritional Adequacy of Plant-Based Diets - Tom Sanders, ProcNutrSoc 1999Dokument6 SeitenThe Nutritional Adequacy of Plant-Based Diets - Tom Sanders, ProcNutrSoc 1999Richard PatonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everyday Activities. For Example, Walking or Cycling ToDokument1 SeiteEveryday Activities. For Example, Walking or Cycling ToVivian NajeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maritex Aquapure Bearing Material SDSDokument5 SeitenMaritex Aquapure Bearing Material SDSHovanTaTarianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lofgren 2014Dokument16 SeitenLofgren 2014Casulo De GenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 11 v3 LatestDokument50 SeitenMODULE 11 v3 LatestBrigette Kim Lumawas100% (3)
- 3f PDFDokument4 Seiten3f PDFYidne GeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurs3021h Summer 2022 Midterm Evaluation WeigaDokument15 SeitenNurs3021h Summer 2022 Midterm Evaluation Weigaapi-547521437Noch keine Bewertungen
- Podologia 3Dokument5 SeitenPodologia 3ositos.amorositos26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Interview Assignment - Writing in Biological SciencesDokument5 SeitenInterview Assignment - Writing in Biological Sciencesapi-708250948Noch keine Bewertungen
- A.bsfhsjsjsjgsg-WPS OfficeDokument3 SeitenA.bsfhsjsjsjgsg-WPS OfficeGJ MagbanuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alaskan Tlingkit TribeDokument1 SeiteAlaskan Tlingkit TribeRenz Calex Cojamco SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Theories and Nightingale's Environmental TheoryDokument36 SeitenNursing Theories and Nightingale's Environmental TheoryRIJMOND AARON LAQUINoch keine Bewertungen
- Q3 M3 - 3is - Selecting Relevant LiteratureV4 1 FinalDokument21 SeitenQ3 M3 - 3is - Selecting Relevant LiteratureV4 1 FinalMarivic Omosura ItongNoch keine Bewertungen
- InSimu ReportDokument10 SeitenInSimu ReportCiprian CeianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canton Mayor Thomas Bernabei's StatementDokument2 SeitenCanton Mayor Thomas Bernabei's StatementRick ArmonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Einstein and Twain Through ConversationsDokument19 SeitenUnderstanding Einstein and Twain Through ConversationsnonnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Category 2 RRLDokument2 Seiten1 Category 2 RRLGlydel Anne C. LincalioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material-Minimum-Requirements: Valid For The Complete Assortment of GoodsDokument2 SeitenMaterial-Minimum-Requirements: Valid For The Complete Assortment of GoodsTahir NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID Testing Labs 16072021Dokument192 SeitenCOVID Testing Labs 16072021AMIT KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uts MidtermsDokument5 SeitenUts MidtermsdanglapenmaryjayNoch keine Bewertungen