Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Surgical Management
Hochgeladen von
nj_pink081794Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Surgical Management
Hochgeladen von
nj_pink081794Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
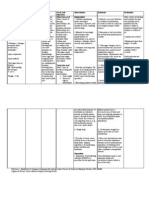
OSTEOMYELITIS
Surgical Management
Drain the infected area. Opening up the area around infected bone
allows surgeon to drain any pus or fluid that has accumulated in
response to the infection.
Remove diseased bone and tissue. In a procedure called
debridement, the surgeon removes as much of the diseased bone as
possible, taking a small margin of healthy bone to ensure that all the
infected areas have been removed. Surrounding tissue that shows
signs of infection also may be removed.
Restore blood flow to the bone. The surgeon may fill any empty
space left by the debridement procedure with a piece of bone or other
tissue, such as skin or muscle, from another part of the body. The graft
helps body repair damaged blood vessels and form new bone.
Amputate the limb. As a last resort, surgeons may amputate the
affected limb to stop the infection from spreading further.
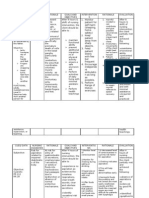
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Surgical Management
If medications fail to prevent or slow joint damage, the patient and the
doctor may consider surgery to repair damaged joints. Surgery may help
restore your ability to use your joint. It can also reduce pain and correct
deformities.
Total joint replacement (arthroplasty). During joint replacement
surgery, the surgeon removes the damaged parts of the joint and inserts a
prosthesis made of metal and plastic.
Tendon repair. Inflammation and joint damage may cause tendons around
the joint to loosen or rupture. The surgeon may be able to repair the tendons
around the joint.
Removal of the joint lining (synovectomy). If the lining around the joint
(synovium) is inflamed and causing pain, the surgeon may recommend
removing the lining of the joint.
Joint fusion (arthrodesis). Surgically fusing a joint may be recommended
to stabilize or realign a joint and for pain relief when a joint replacement isn't
an option.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- NCP Risk For InfectionDokument2 SeitenNCP Risk For Infectionnj_pink08179460% (5)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Age NCPDokument4 SeitenAge NCPnj_pink081794Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Drug Silver Sulfadiazine FlamazineDokument2 SeitenDrug Silver Sulfadiazine Flamazinenj_pink081794100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Dengue NCPDokument3 SeitenDengue NCPnj_pink08179456% (9)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Pneumonia WordDokument2 SeitenPneumonia Wordnj_pink081794Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- NCP ChoreaDokument4 SeitenNCP Choreanj_pink081794100% (2)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Patho Chronic SinusitisDokument1 SeitePatho Chronic Sinusitisnj_pink081794Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)