Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ib Lab - Lenz's Law (DCP Ce)
Hochgeladen von
ringo_tigerOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ib Lab - Lenz's Law (DCP Ce)
Hochgeladen von
ringo_tigerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
International Baccalaureate Physics 4/PSOW
The Motion of a Magnet Falling in a Metal Tube
(by Gary Piech, modified at ISM)
IB Criteria Assessed
Aim: Data Collection and Processing,
1. To find the motion of a magnet in free fall in a metal tube. Conclusion and Evaluation
2. Use the data that you collected to Illustrate Lenz’s and Criteria Aspect Level
Faraday's Law. assessed 1 2 3 awarded
D
DCP
CE
ISM score
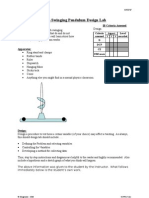
Diagram: Method:
1. Obtain a long aluminum or copper tube, which has
magnet
fixed coils attached to it.
2. Attach a wire from the top of the first coil to the
Logger Pro interface box leads.
3. Run a second wire from the bottom of the first coil to
the top of the second coil. Then run a wire from the
bottom of the second coil to the top of the third coil.
These coils Continue this until you have all the coils connected in
are in series series.
4. Connect the bottom wire of the last coil to the 2nd
lead from the Logger Pro.
Laptop collecting 5. Open the Logger Pro Software. Open the
voltage
and time data Experiments file. Open the voltage file.
6. Estimate the time that the magnet takes to fall through
the tube. Add about 5 seconds to this and set this as
your horizontal axis. Voltage will be your vertical
axis.
7. Hit Collect, then drop the magnet in the pipe.
8. Measure the distance from the first coil to all the other
coils
9. Construct a well labelled data table for you data.
Theory:
Lenz’s Law and Faraday’s Law both allow one to predict aspects of induced current when there is a changing
magnetic field.
Data Processing and Presentation:
• Collect appropriate data.
• Plot a suitable graph from which you can analyze the motion of the magnet as it falls through the tube.
Conclusion and Evaluation:
• Using your graph, analyze the type of motion of the falling magnet.
• Using your knowledge of the laws of electromagnetic induction, explain why this type of motion occurs.
• Evaluate the method, including any modifications you had to make to overcome problems. Include an
evaluation of the apparatus used.
• Suggest ways in which the procedure could be modified in order to improve it for the future.
The above information was given to the student by the instructor. What follows
immediately below is the student’s own work.
© Dickinson / Dingrando - ISM 4734836.doc
International Baccalaureate Physics 4/PSOW
Internal Assessment Marking Form
Criteria Aspect 1 Aspect 2 Aspect 3 Grade
Defining the Problem and Controlling the Variables: Developing a method for
selecting variables: collecting data:
Formulates a focused Designs a method for the Develops a method that
problem/research question effective control of the allows for the collection of
c=2
and identifies the relevant variables. sufficient relevant data.
variables.
Design (D)
Formulates a Designs a method that Develops a method that
problem/research question makes some attempt to allows for the collection of
p=1 that is incomplete or control the variables. insufficient relevant data.
identifies only some
relevant variables.
Does not identify a Designs a method that does Develops a method that
problem/research question not control the variables. does not allow for any
n=0
and does not identify any relevant data to be
relevant variables. collected.
Recording raw data Processing raw data Presenting processed data
Data Collection and Processing (DCP)
Records appropriate Processes the quantitative Presents processed data
quantitative and associated raw data correctly. appropriately and, where
qualitative raw data, relevant, includes errors
c=2
including units and and uncertainties.
uncertainties where
relevant.
Records appropriate Processes quantitative raw Presents processed data
quantitative and associated data, but with some appropriately, but with
p=1 qualitative raw data, but mistakes and/or omissions. some mistakes and/or
with some mistakes or omissions.
omissions.
Does not record any No processing of Presents processed data
appropriate quantitative quantitative raw data is inappropriately or
n=0 raw data or raw data is carried out or major incomprehensibly.
incomprehensible. mistakes are made in
processing.
Concluding Evaluating procedure(s) Improving the
investigation
Conclusion and Evaluation (CE)
States a conclusion, with Evaluates weaknesses and Suggests realistic
justification, based on a limitations. improvements in respect of
c=2
reasonable interpretation of identified weaknesses and
the data. limitations.
States a conclusion based Identifies some weaknesses Suggests only superficial
on a reasonable and limitations, but the improvements.
p=1
interpretation of the data. evaluation is weak or
missing.
States no conclusion or the Identifies irrelevant Suggests unrealistic
conclusion is based on an weaknesses and limitations. improvements.
n=0
unreasonable interpretation
of the data.
© Dickinson / Dingrando - ISM 4734836.doc
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 3º ESO Criterion B Summative ConductivityDokument4 Seiten3º ESO Criterion B Summative ConductivityPacificHennNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2a Assessment 2Dokument20 SeitenPhysics 2a Assessment 2api-357692508Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Guide #2 Coulombs LawDokument3 SeitenLab Guide #2 Coulombs LawJoriel CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction LessonDokument6 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction LessonVictorino Victorino ButronNoch keine Bewertungen
- COSC 4223 - Basic ElectronicsDokument4 SeitenCOSC 4223 - Basic ElectronicsDon Lenard Eleccion PescaderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 113 Ee 37Dokument4 Seiten113 Ee 37ahmad72mizanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher/Technician Determining Young Modulus For A MetalDokument4 SeitenTeacher/Technician Determining Young Modulus For A MetalKasam ANoch keine Bewertungen
- A1 EP 14ED23 RevisedDokument8 SeitenA1 EP 14ED23 Revisednghiemnguyen100% (1)
- Black BoxDokument6 SeitenBlack BoxAnonymous L21MIUqANoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering Fundamentals Course SpecDokument4 SeitenElectrical Engineering Fundamentals Course SpecSarah KandilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Conductors - Practical InvestigationDokument3 SeitenAnalysis of Conductors - Practical InvestigationUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Theory SkillsDokument2 SeitenAtomic Theory SkillsshiftingphasesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual PH516 Jan-May-2024 v1Dokument37 SeitenManual PH516 Jan-May-2024 v1Main DdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tle Ict Cy W8Dokument5 SeitenTle Ict Cy W8sheenamarie.cerenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annotated Lab ReportDokument6 SeitenAnnotated Lab ReportSolomon MensahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rocket Design Lab, Arjun, For EARCOSDokument5 SeitenRocket Design Lab, Arjun, For EARCOSringo_tiger100% (1)
- Course Out-LineDokument24 SeitenCourse Out-LinemandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee4007 Ee4007a Ee4007b SDF 2023Dokument3 SeitenEe4007 Ee4007a Ee4007b SDF 2023funnylearn08Noch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE Cables in Shallow Troughs-R4Dokument9 SeitenIEEE Cables in Shallow Troughs-R4zwerr100% (1)
- Electronic Circuits and Analysis-I Lab ECE 217 Credits:2Dokument49 SeitenElectronic Circuits and Analysis-I Lab ECE 217 Credits:2vj86Noch keine Bewertungen
- SRM Lab ManualDokument102 SeitenSRM Lab ManualAnshul SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- AFM Atomic Force MicroscopyDokument24 SeitenAFM Atomic Force MicroscopyYogesh KhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 SA Communcation Through Distance A IDokument3 SeitenGrade 9 SA Communcation Through Distance A Id.baidarbekovNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Fabrication Lab Manual StudentsDokument32 SeitenRF Fabrication Lab Manual StudentsTajinder Singh100% (4)
- Electric and Electronic Technology BDA14303 Group Project SEM 2 2021/2022Dokument4 SeitenElectric and Electronic Technology BDA14303 Group Project SEM 2 2021/2022Muhd YusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- week 8Dokument3 Seitenweek 8Diana Joy Ancheta CldheiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEVEL 1 - No.5 - Suspension Cable Bridge System PDFDokument4 SeitenLEVEL 1 - No.5 - Suspension Cable Bridge System PDFliayanajemainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report 1Dokument11 SeitenReport 1Rohan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE 9-SY 2022-2023-Q2-W5-NOV 28-Dec 2,2022Dokument4 SeitenSCIENCE 9-SY 2022-2023-Q2-W5-NOV 28-Dec 2,2022NOVA LESLIE AGAPAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument2 SeitenPhysicsjyoti joshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formato ExamenDokument19 SeitenFormato ExamenGuillermo HerasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Science 5 Q3 W6Dokument6 SeitenDLL Science 5 Q3 W6Tin Tin TinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic cable ratings deliver smarter gridsDokument6 SeitenDynamic cable ratings deliver smarter gridsLisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CED Textbook Student Learning Outcomes Performance Indicators Examples/NotesDokument5 SeitenCED Textbook Student Learning Outcomes Performance Indicators Examples/NotesReena NasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- CO3-SCIENCE (4a's) - Series and Parallel CircuitsDokument7 SeitenCO3-SCIENCE (4a's) - Series and Parallel CircuitsmagnojoanmaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Year 2nd Sem Syllabus KukDokument9 Seiten1st Year 2nd Sem Syllabus KukHarshit SalwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016-Edouard - Parameter Sensitivity Analysis of A Simplified Electrochemical Oand Thermal Model For Li-Ion Batteries AgingDokument13 Seiten2016-Edouard - Parameter Sensitivity Analysis of A Simplified Electrochemical Oand Thermal Model For Li-Ion Batteries Agingsofiane maïzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Physics Lab: Course ObjectivesDokument2 SeitenEngineering Physics Lab: Course ObjectivesDarren NehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self InductionDokument5 SeitenSelf InductionThanh DinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fow Seng Joe (B1757) - 2023 Laboratory Assignment 4 Strain Gauges LaboratoryDokument14 SeitenFow Seng Joe (B1757) - 2023 Laboratory Assignment 4 Strain Gauges LaboratoryRobert Fow JOENoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Syllabus: United International UniversityDokument6 SeitenCourse Syllabus: United International UniversityZaid Bin Abdul MalekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5th Semester Course OutlineDokument13 Seiten5th Semester Course Outlineumarwaheed1997Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Development of Image-Based Distance MeasuremenDokument8 SeitenThe Development of Image-Based Distance MeasuremenArpit KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Phase Full Wave Rectification ResearchDokument8 SeitenThree Phase Full Wave Rectification ResearchMonjed AlHaddadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Vibrations Modal Analysis Project With Arduinos: Computers in Education Journal December 2017Dokument8 SeitenMechanical Vibrations Modal Analysis Project With Arduinos: Computers in Education Journal December 2017Crazy FireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demonstration Lesson Plan For Grade 9 Copper SplicingDokument5 SeitenDemonstration Lesson Plan For Grade 9 Copper SplicingGerean Abeleda-VillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity Unit Prac and WRKSHTDokument52 SeitenElectricity Unit Prac and WRKSHTDiana GanapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC IV Year Practical Index 2080Dokument2 SeitenB.SC IV Year Practical Index 2080Sagar SatyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 2 MVT Labsheet Bev40702Dokument8 SeitenExercise 2 MVT Labsheet Bev40702Nur DaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edy 424-Assignment #1Dokument4 SeitenEdy 424-Assignment #1Martias WambiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Science 5 q3 Week 6Dokument6 SeitenDLL Science 5 q3 Week 6Jam SnowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal Semister ProjectDokument7 SeitenProposal Semister ProjectMuket AgmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuits II Lab SyllabusDokument8 SeitenCircuits II Lab SyllabusJuan Glicerio C. ManlapazNoch keine Bewertungen
- NT - CDM Theory - UGDokument14 SeitenNT - CDM Theory - UGAnju GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan - Wiring A Wall OutletDokument2 SeitenLesson Plan - Wiring A Wall Outletapi-733838230Noch keine Bewertungen
- Determine Laser Beam DivergenceDokument18 SeitenDetermine Laser Beam DivergenceSiddhant ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH8151 Py1 Iq Jan2019 Rejinpaul PDFDokument2 SeitenPH8151 Py1 Iq Jan2019 Rejinpaul PDFRGNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP 03-21Dokument4 SeitenDLP 03-21Jannah Palcis Lacdo-oNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schaum's Outline of Electronic Devices and Circuits, Second EditionVon EverandSchaum's Outline of Electronic Devices and Circuits, Second EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (6)
- IB Lab - Torsional Pendulum (D DCP CE)Dokument2 SeitenIB Lab - Torsional Pendulum (D DCP CE)ringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Rate Lab, Modified, Manuel GottiDokument3 SeitenHeart Rate Lab, Modified, Manuel Gottiringo_tiger100% (1)
- Rocket Design Lab, Arjun, For EARCOSDokument5 SeitenRocket Design Lab, Arjun, For EARCOSringo_tiger100% (1)
- IB Lab - 09 Projectile Motion (DCP CE)Dokument3 SeitenIB Lab - 09 Projectile Motion (DCP CE)ringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Lab - 03 Measurement Instrument Circus (DC)Dokument2 SeitenIB Lab - 03 Measurement Instrument Circus (DC)ringo_tiger100% (1)
- Why Rockets Are Awesome, An EARCOS PresentationDokument30 SeitenWhy Rockets Are Awesome, An EARCOS Presentationringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Lab - 08 G From Freefall (DCP CE)Dokument2 SeitenIB Lab - 08 G From Freefall (DCP CE)ringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Lab - 06 Vectors (DCP)Dokument3 SeitenIB Lab - 06 Vectors (DCP)ringo_tiger0% (1)
- IB Lab - 07 Loaded Metre Rule (DCP)Dokument3 SeitenIB Lab - 07 Loaded Metre Rule (DCP)ringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Lab - 04 Errors - Microscope Slide (DC DPP)Dokument2 SeitenIB Lab - 04 Errors - Microscope Slide (DC DPP)ringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Lab - 01 Murphys Law (Pla PLB DC DPP CE)Dokument2 SeitenIB Lab - 01 Murphys Law (Pla PLB DC DPP CE)ringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Lab - 02 Pendulum (Pla PLB DC DPP CE)Dokument3 SeitenIB Lab - 02 Pendulum (Pla PLB DC DPP CE)ringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Torsional Pendulum Design Lab (D)Dokument1 SeiteTorsional Pendulum Design Lab (D)ringo_tiger100% (1)
- IB Lab - 05 Hacksaw Blade Oscillation (DC DPP CE)Dokument4 SeitenIB Lab - 05 Hacksaw Blade Oscillation (DC DPP CE)ringo_tiger50% (4)
- Instructions For Coffee Filter Design LabDokument1 SeiteInstructions For Coffee Filter Design Labringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Welcome Letter, General PhysicsDokument2 SeitenWelcome Letter, General Physicsringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Force LabDokument1 SeiteMagnetic Force Labringo_tigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ib Lab - Density of Ethanol, DCPDokument2 SeitenIb Lab - Density of Ethanol, DCPringo_tiger100% (2)
- Ib Lab - Acceleration of Cart Down A RampDokument1 SeiteIb Lab - Acceleration of Cart Down A Rampringo_tiger100% (2)
- Regular Manual Cleaning: Mimaki Printer Maintenance and Long-Term Storage OptionsDokument3 SeitenRegular Manual Cleaning: Mimaki Printer Maintenance and Long-Term Storage OptionshumbyxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng ThreePDokument192 SeitenEng ThreePMr Ahmed AbdallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modicon TM172PDG42R DatasheetDokument14 SeitenModicon TM172PDG42R DatasheetRonnie SolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hobby 01: COD. 9942062.01 REV. 00Dokument9 SeitenHobby 01: COD. 9942062.01 REV. 00Alexander SharamiginNoch keine Bewertungen
- DG350 ManualDokument17 SeitenDG350 ManualCareergamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit explores Christian morality and conscienceDokument1 SeiteUnit explores Christian morality and conscienceRose Angela Mislang Uligan100% (1)
- Large and Medium Manufacturing Industry Survey Report 2018Dokument778 SeitenLarge and Medium Manufacturing Industry Survey Report 2018melakuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1B Cosmos-Standard - Technical - Guide - v40Dokument45 Seiten1B Cosmos-Standard - Technical - Guide - v40carla deiddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carta Psicrometrica PDFDokument2 SeitenCarta Psicrometrica PDFJuliethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Below WaterDokument10 SeitenLife Below Watertrisha sobito0% (1)
- GreyFox Intercom Install GuideDokument12 SeitenGreyFox Intercom Install GuideAbdallah HashemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collab#2 (Edited)Dokument14 SeitenCollab#2 (Edited)Yani BatoctoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CERT Basic Training Participant Manual - 2011Dokument332 SeitenCERT Basic Training Participant Manual - 2011jegodfreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 ESC Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart FailureDokument137 Seiten2021 ESC Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart FailuredianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Cat 924HZDokument6 SeitenMotor Cat 924HZAdemilson Rangelvieira100% (1)
- Procedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20Dokument6 SeitenProcedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20ChocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTE56004 Thru NTE56010 TRIAC, 15 Amp: FeaturesDokument2 SeitenNTE56004 Thru NTE56010 TRIAC, 15 Amp: FeaturesFreddy SarabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tracking sports training efficiency with surface EMGDokument8 SeitenTracking sports training efficiency with surface EMGsdjuknicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Niryana Shoola DasaDokument7 SeitenNiryana Shoola DasaSuryasukraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quant One Analyser – endless possibilitiesDokument6 SeitenQuant One Analyser – endless possibilitiesSamuel SuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 89HPES24T3G2 Hardware Design Guide: NotesDokument10 Seiten89HPES24T3G2 Hardware Design Guide: NotesDavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7H17-28 Clearances and Wear Limits PDFDokument3 Seiten7H17-28 Clearances and Wear Limits PDFDimitris K100% (1)
- Demo DLLDokument2 SeitenDemo DLLArlene Diokno100% (1)
- 10 01 Breather Filters GBDokument8 Seiten10 01 Breather Filters GBosuengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrating Kuleana Rights and Land Trust PrioritesDokument50 SeitenIntegrating Kuleana Rights and Land Trust PrioritesKeala Rodenhurst-JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Larrabee JChem Educ 1990,67,267Dokument3 SeitenLarrabee JChem Educ 1990,67,267κ.μ.α «— Brakat»Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gold Grade of Epithermal Gold Ore at Lamuntet, Brang Rea, West Sumbawa District, West Nusa Tenggara Province, IndonesiaDokument10 SeitenGold Grade of Epithermal Gold Ore at Lamuntet, Brang Rea, West Sumbawa District, West Nusa Tenggara Province, Indonesiasukri arjunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F588 PDFDokument8 SeitenF588 PDFOscar Gutiérrez-JuncoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limbah PabrikDokument2 SeitenLimbah Pabrikindar dewaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETHICS NOTES PART 1 - IAS PCS PathshalaDokument15 SeitenETHICS NOTES PART 1 - IAS PCS PathshalaATULNoch keine Bewertungen