Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
STREPTOMYCIN
Hochgeladen von
Chad Inong0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten3 SeitenStreptomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis and infections caused by gram-negative bacteria. It works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria. While effective, it can cause serious side effects such as ototoxicity (damage to the inner ear), nephrotoxicity (kidney damage), and neuromuscular blockade. As a result, patients receiving streptomycin require close monitoring of hearing, balance, kidney function, and signs of toxicity.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenStreptomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis and infections caused by gram-negative bacteria. It works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria. While effective, it can cause serious side effects such as ototoxicity (damage to the inner ear), nephrotoxicity (kidney damage), and neuromuscular blockade. As a result, patients receiving streptomycin require close monitoring of hearing, balance, kidney function, and signs of toxicity.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten3 SeitenSTREPTOMYCIN
Hochgeladen von
Chad InongStreptomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis and infections caused by gram-negative bacteria. It works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria. While effective, it can cause serious side effects such as ototoxicity (damage to the inner ear), nephrotoxicity (kidney damage), and neuromuscular blockade. As a result, patients receiving streptomycin require close monitoring of hearing, balance, kidney function, and signs of toxicity.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
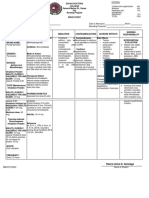
STREPTOMYCIN
Classification: anti-infectives (therapeutic), aminoglycosides (pharmacologic)
INDICATIONS ACTION CONTRAINDICATI ADVERSE & SIDE NURSING
ONS & EFFECTS IMPLICATIONS
PRECAUTIONS
o In o Inhibits protein Contraindicated in: o EENT: o Assess patient
combination synthesis in o Hypersensitivity ototoxicity for infection (VS,
with other bacteria at level o Most parenteral (vestibular & wound
agents in the of 30S ribosome products contain choclear) appearance,
management of o Most bisulfites & o GU: sputum, urine &
active aminoglycoside should be nephrotoxicity stool, WBC) at
tuberculosis s notable for avoided in o F&E: beginning of &
activity against: patients with hypomagnesemi throughout
P. aeruginosa known a therapy.
Klebsiella intolerance o MS: muscle o Obtain
pneumoniae o Products paralysis (high specimens for
Escherichia containing parenteral C&S before
coli benzyl alcohol doses) initiating
Proteus should be o Misc: therapy. First
avoided in hypersensitivity dose may be
Serratia
neonates reactions given before
Acinetobacter
o Cross-sensitivity receiving results.
Staphylococc o Evaluate 8th
among
us aureus
aminoglycosides cranial nerve
o In treatment of
may occer function by
enterococcal audiometry
infections, before &
Use cautiously in:
synergy with a throughout
o Renal
penicillin is therapy. Also
impairments
required monitor for
(dosage
o Also active vestibular
adjustments
against dysfunction
necessary; blood
mycobacterium level monitoring (vertigo, ataxia,
useful in nausea &
preventing vomiting).
ototoxicity & o Monitor intake &
nephrotoxicity) output and daily
o Hearing weight to assess
impairment hydration status
o Geriatric patients & renal function.
& premature o Asess patient for
infants (difficulty signs of
in assessing superinfection.
auditory &
vestibular
function; age-
related renal
impairment)
o Neuromuscular
diseases such as
myasthenia
gravis
o Obese patients
(dosage should
be based on
ideal body
weight)
o Pregnancy (may
cause congenital
deafness)
o Neonates
(increased risk of
neuromuscular
blockade;
difficulty in
assessing
auditory &
vestibular
function;
immature renal
function)
o Lactation,
infants, and
neonates (safety
not established)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Drug Study QIDokument8 SeitenDrug Study QImaeDonitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- StreptomycinDokument1 SeiteStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- AcetazolamideDokument2 SeitenAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- Drug Study - ClarithromycinDokument2 SeitenDrug Study - ClarithromycinTrisha Lapid MatulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study PyrazinamideDokument1 SeiteDrug Study PyrazinamideEphraim MaravillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epirubicin 10Dokument1 SeiteEpirubicin 10PdianghunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: D IphenhydramineDokument5 SeitenDrug Study: D IphenhydramineAnthonette DaquioagNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChlorphenamineDokument1 SeiteChlorphenaminereinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study 04-21-09Dokument2 SeitenDrug Study 04-21-09obietobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcetylcysteineDokument1 SeiteAcetylcysteineLouie Pericon0% (1)
- Drug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient MonitoringDokument2 SeitenDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient Monitoringpoleene de leonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonDokument2 SeitenSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study FORTDokument3 SeitenDrug Study FORTLysa Mae EleazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocortisone Ointment-Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteHydrocortisone Ointment-Drug StudyTrisha CayabyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prednisone Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenPrednisone Drug StudyNiziu BearsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Romeo Victor M. Valderrama BSN-2A: CNS: Confusion, Depression, BeforeDokument8 SeitenRomeo Victor M. Valderrama BSN-2A: CNS: Confusion, Depression, BeforeitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinDokument4 SeitenCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinhahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnasynDokument1 SeiteUnasynrachieeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRZE (Kid's Kit), Toradol, CiprobayDokument4 SeitenHRZE (Kid's Kit), Toradol, CiprobayiloveanneNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeclizineDokument2 SeitenMeclizineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- ONDANSETRONDokument1 SeiteONDANSETRONJugen Gumba Fuentes Alquizar0% (1)
- Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSDokument4 SeitenTrimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSAnika Pleños100% (1)
- CEFUROXIMEDokument1 SeiteCEFUROXIMEJose Luis HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Dokument2 SeitenBeclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- N AcetylcysteineDokument2 SeitenN AcetylcysteineGinena BelarminoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study DoxycylineDokument3 SeitenDrug Study DoxycylineMethaGod GameNoch keine Bewertungen
- AzithromycinDokument1 SeiteAzithromycinjennelyn losantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug-Study CefepimeDokument2 SeitenDrug-Study Cefepimeprince gonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDokument1 SeiteDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cebu Normal University College of Nursing: Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenCebu Normal University College of Nursing: Drug StudyNiño Naryana Luke PanchoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Dokument2 SeitenFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - ClopidogrelDokument2 SeitenDrug Study - Clopidogrelryan100% (1)
- CeftriaxoneDokument1 SeiteCeftriaxoneJayson Almario Aranas100% (2)
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudyGeleen Margaret Atienza100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramDokument1 SeiteDRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramJ-lie GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMINOPHYLLINEDokument2 SeitenAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Drug Study CaseDokument3 SeitenDrug Study CaseKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- CetirizineDokument1 SeiteCetirizineGabby Robles PajeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budesonide Inhalation Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenBudesonide Inhalation Drug StudyAijeelene NalapoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyrazinamide Drug StudyDokument1 SeitePyrazinamide Drug Studyanreilegarde100% (2)
- IrbesartanDokument3 SeitenIrbesartanJohnrick VenturaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gaviscon Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenGaviscon Drug StudyJOANNA MAE ABIA SALOMONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prednisolone Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenPrednisolone Drug StudyKristine Acasio100% (2)
- Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleDokument1 SeiteTrimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleRenmico Aquino0% (1)
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDokument3 SeitenCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementAnika PleñosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Duavent.Dokument1 SeiteDrug Study Duavent.Clariss AlotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study For AntaminDokument1 SeiteDrug Study For AntaminJILLIAN MARIE BARREDO100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyFlorenz Gatchalian100% (1)
- Generic Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida InfectionsDokument1 SeiteGeneric Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida Infectionscen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- SHEENA Clomid Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenSHEENA Clomid Drug StudyNur SetsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propylthiouracil DSDokument6 SeitenPropylthiouracil DSAlexandrea MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenAzithromycin Drug StudySHEILA MAE SACLOTNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG STUDY CLOBETASOL CREAMrevisedDokument2 SeitenDRUG STUDY CLOBETASOL CREAMrevisedswitchlers anneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study EntecavirDokument4 SeitenDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudySunshine Jaranilla0% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyGladys Joy Peña100% (1)
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Generic NameDokument2 SeitenDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Generic NamehahahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OfloxacinDokument2 SeitenOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- NALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsDokument6 SeitenNALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsBeth100% (1)
- Streptomycin Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenStreptomycin Drug Studym B100% (1)
- MCQ April 2015Dokument15 SeitenMCQ April 2015Sylphana Astharica LawalataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vaccine Card - 20231120 - 175739 - 0000Dokument2 SeitenVaccine Card - 20231120 - 175739 - 0000MarilynNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Mastitis Council 2018Dokument137 SeitenNational Mastitis Council 2018Lysett CoronaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Physiotherapy in Antenatal and Post-Natal Care: Dr. Venus Pagare (PT)Dokument74 SeitenRole of Physiotherapy in Antenatal and Post-Natal Care: Dr. Venus Pagare (PT)Haneen Jehad Um Malek100% (1)
- Master Drug ChartDokument22 SeitenMaster Drug ChartMahadhir AkmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glucocorticoids in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ten Questions and Some IssuesDokument13 SeitenGlucocorticoids in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ten Questions and Some IssuesSundas EjazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nnaca Sop 302Dokument6 SeitenNnaca Sop 302Thusitha LakpriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr.H.O.GUNEWARDENE (Folder)Dokument38 SeitenDr.H.O.GUNEWARDENE (Folder)Ian GardnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medtronic Earnings Presentation FY16Q4 FINALDokument21 SeitenMedtronic Earnings Presentation FY16Q4 FINALmedtechyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diarrhea ThesisDokument15 SeitenDiarrhea ThesisIshuWary100% (2)
- Ejercicio: Choose The Best Answer. What Do You Do?Dokument4 SeitenEjercicio: Choose The Best Answer. What Do You Do?LenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glaucoma: by Tekia BuntynDokument18 SeitenGlaucoma: by Tekia BuntynTekia BuntynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hospital ThesisDokument47 SeitenHospital ThesisninsNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid Quiz ResultsDokument2 SeitenFirst Aid Quiz ResultsAyse Duru YildirimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cycle BeadsDokument2 SeitenCycle Beadsgihan200100% (2)
- U S. Medical Eligibility Criteria For Contraceptive Use, 2010Dokument77 SeitenU S. Medical Eligibility Criteria For Contraceptive Use, 2010gerte_yuewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Grafts PDFDokument112 SeitenSkin Grafts PDFalinutza_childNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Medical AbbreviationsDokument12 SeitenCommon Medical AbbreviationsShania Kate Ledesma ManabatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colonoscopy Instructions Using PegLyteDokument2 SeitenColonoscopy Instructions Using PegLyteRomelia CampuzanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LaporanDokument214 SeitenLaporankadek sariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of The Childhood Autism Rating Scale CARS For PDFDokument10 SeitenUse of The Childhood Autism Rating Scale CARS For PDFmahwishmahmood 444Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vitreous Hemorrhage: Retina Eye Specialists Retina Eye SpecialistsDokument2 SeitenVitreous Hemorrhage: Retina Eye Specialists Retina Eye SpecialistsMarcel Antek CivilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Independent Medical Assessments - A Multi-Jurisdictional Analysis Iggy Kosny ACHRF 2013Dokument15 SeitenUnderstanding Independent Medical Assessments - A Multi-Jurisdictional Analysis Iggy Kosny ACHRF 2013ISCRRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antithrombotic DrugsDokument11 SeitenAntithrombotic DrugsKatyBrnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debra Hall Fisher ResumeDokument4 SeitenDebra Hall Fisher Resumeapi-347999772Noch keine Bewertungen
- Great Critical Care ReliefDokument9 SeitenGreat Critical Care ReliefBenedict FongNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABCDEFGHI Systematic Approach To Wound Assessment and ManagementDokument36 SeitenABCDEFGHI Systematic Approach To Wound Assessment and ManagementsaerodinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artsanto R, Doso Sutiyono, Witjaksono : Bagian Anestesiologi Dan Terapi Intensif FK Undip/ RSUP Dr. Kariadi, SemarangDokument12 SeitenArtsanto R, Doso Sutiyono, Witjaksono : Bagian Anestesiologi Dan Terapi Intensif FK Undip/ RSUP Dr. Kariadi, SemarangAdhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Define Infertility: Objectives: Intended Learning Outcomes That TheDokument2 SeitenA. Define Infertility: Objectives: Intended Learning Outcomes That TheJc Mae CuadrilleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name - IDDokument2 SeitenName - IDbasheNoch keine Bewertungen