Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Anatomy of The Skin Dianne
Hochgeladen von
Judith CabañeroOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anatomy of The Skin Dianne
Hochgeladen von
Judith CabañeroCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
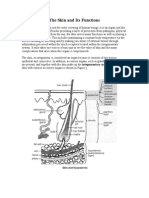
Anatomy of the Skin
Anatomy of the Skin
Click Image to Enlarge
Facts about the skin:
The skin is the body's largest organ, covering the entire body. In addition to serving as a
protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection, the skin also:
• regulates body temperature.
• stores water and fat.
• is a sensory organ.
• prevents water loss.
• prevents entry of bacteria.
Throughout the body, the skin's characteristics (thickness, color, texture) vary. For
instance, the head contains more hair follicles than anywhere else, while the soles of the
feet contain none. In addition, the soles of the feet and the palms of the hands are much
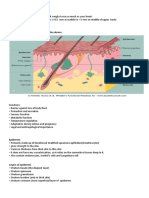
thicker. The skin is made up of the following layers, with each layer performing specific
functions:
• epidermis
• dermis
• subcutaneous fat layer
epidermis The epidermis is the thin outer layer of the skin and consists of three parts:
• stratum corneum (horny layer)
This layer consists of fully mature keratinocytes which contain fibrous
proteins (keratins). The outermost layer is continuously shed. The
stratum corneum prevents the entry of most foreign substances as well
as the loss of fluid from the body.
• keratinocytes (squamous cells)
This layer, just beneath the stratum corneum, contains living
keratinocytes (squamous cells), which mature and form the stratum
corneum.
• basal layer
The basal layer is the deepest layer of the epidermis, containing basal
cells. Basal cells continually divide, forming new keratinocytes that
replace the cells that are shed from the skin's surface.
The epidermis also contains melanocytes, which are cells that produce
melanin (skin pigment).
dermis The dermis is the middle layer of the skin. The dermis contains the following:
• blood vessels
• lymph vessels
• hair follicles
• sweat glands
• collagen bundles
• fibroblasts
• nerves
The dermis is held together by a protein called collagen, made by fibroblasts.
This layer also contains pain and touch receptors.
subcutis The subcutis is the deepest layer of skin. The subcutis, consisting of a
network of collagen and fat cells, helps conserve the body's heat and protects
the body from injury by acting as a shock absorber.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Anatomy of SkinDokument2 SeitenAnatomy of SkinneharikaranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Skin: Ectodermal Tissue Muscles Bones Ligaments Internal OrganDokument4 SeitenAnatomy of The Skin: Ectodermal Tissue Muscles Bones Ligaments Internal OrganKaizen Science Academy100% (1)
- 04 The Integumentary SystemDokument37 Seiten04 The Integumentary SystemRuthie MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 The Structure and Functions of The SkinDokument16 SeitenLesson 4 The Structure and Functions of The SkinNguyễn Gia LộcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Integumentary SystemDokument38 SeitenPhysiology of Integumentary SystemAnisa AnisatusholihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Integumentary System - Cliffnotes A&pDokument4 SeitenThe Integumentary System - Cliffnotes A&pdbelmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intergumentary System 10Dokument40 SeitenIntergumentary System 10Mike BasantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntrotointegumentarypptDokument25 SeitenIntrotointegumentarypptapi-294162496Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.anatomy & Physiology SKINDokument10 Seiten1.anatomy & Physiology SKINMASCULINE DEACONNoch keine Bewertungen
- I) Skin Largest Organ of The Body in Surface Area and Weight. There Are Three Layers of The Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutaneous TissueDokument44 SeitenI) Skin Largest Organ of The Body in Surface Area and Weight. There Are Three Layers of The Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutaneous TissueSaralitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of SkinDokument19 SeitenStructure of SkinFiqi Lampard100% (1)
- Unit-II Skin Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument9 SeitenUnit-II Skin Anatomy and Physiologykamal devdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument135 SeitenIntegumentary SystemTrishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Integumentary SystemDokument8 SeitenAnatomy of The Integumentary SystemChristine Joy MadronioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System Anatomy in Under 40Dokument10 SeitenIntegumentary System Anatomy in Under 40Bago CPSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of the integumentary systemDokument54 SeitenOverview of the integumentary systemAmanuel MaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System - Pptx-For Fundamentals of Zoology 2020Dokument25 SeitenIntegumentary System - Pptx-For Fundamentals of Zoology 2020Islam SamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument30 SeitenLecture 1Dr. Rabail MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANAPHY ReviewerDokument10 SeitenANAPHY ReviewerChristyl AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument9 SeitenIntegumentary SystemxoxogeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System, EdDokument42 SeitenIntegumentary System, EdGirmay GebrehiwotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument13 SeitenIntegumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD0% (1)
- Integumentray System by Hasnairah M. LimbotonganDokument47 SeitenIntegumentray System by Hasnairah M. LimbotonganHasnairah LimbotonganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The SkinDokument25 SeitenAnatomy of The SkinMikylla HuertasNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Anatomy - 4Dokument22 SeitenGeneral Anatomy - 4Divya JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Reviewer SHS General Biology 2 PDFDokument14 SeitenINTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Reviewer SHS General Biology 2 PDFKeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter II IntegumentaryDokument9 SeitenChapter II IntegumentaryTitoMacoyTVNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Integumentary System?Dokument6 SeitenWhat Is The Integumentary System?Jerneth Nyka FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-1: 1.1 Anatomy of SkinDokument59 SeitenChapter-1: 1.1 Anatomy of SkinLydia Elezabeth AlappatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument32 SeitenIntegumentary SystemSurvivors DreamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument18 SeitenIntegumentary SystemRenjyl Gay DeguinionNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnaphyDokument18 SeitenAnaphyIsabela Jelian AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 Integumentary SystemDokument64 SeitenLecture 9 Integumentary Systemhafiz patahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumen - Anatomi, Histologi Dan Fisiologi - ArinSDokument42 SeitenIntegumen - Anatomi, Histologi Dan Fisiologi - ArinSJack Flow ClickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Stratum GerminativumDokument5 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Stratum GerminativumChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANATOMY OF SKIN IN 40 CHARACTERSDokument25 SeitenANATOMY OF SKIN IN 40 CHARACTERSaimi Batrisyia100% (1)
- The integumentary system overview for nursing studentsDokument48 SeitenThe integumentary system overview for nursing studentsAmanuel MaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Integumentary SystemDokument23 SeitenThe Integumentary Systemtareqhaddad123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The SkinDokument25 SeitenAnatomy of The SkinJanak KcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The SkinDokument25 SeitenAnatomy of The SkinJanak KcNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReviewerDokument15 SeitenReviewerYza Grace S. PayangdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SESSION 13 - Integumentary System ENGLISH IIDokument39 SeitenSESSION 13 - Integumentary System ENGLISH IImzunigamendivil148Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy&Physiology of SkinDokument45 SeitenAnatomy&Physiology of Skinpreet kaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument21 SeitenIntegumentary SystemMythily manivannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Policy For B.ed HonsDokument67 SeitenPolicy For B.ed HonsJameelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of Integumentary SystemDokument5 SeitenFunctions of Integumentary SystemgrapikmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology of The SkinDokument32 SeitenHistology of The SkinAbdishakur AdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin AnatomyDokument14 SeitenSkin Anatomyjellymot3474Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument54 SeitenIntegumentary SystemKhaela Mercader100% (2)
- Integumentary System ReportDokument46 SeitenIntegumentary System ReportMarilou Dacles IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Ana PhyDokument7 SeitenAna PhyChyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barlis The Integumentary SystemDokument30 SeitenBarlis The Integumentary SystemBlackKnight ZeusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin AnatomyDokument17 SeitenSkin AnatomyAnonymous 1gH7ra9ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System 1Dokument12 SeitenIntegumentary System 1Akemi LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Integumentary Study GuideDokument3 SeitenChapter 5 Integumentary Study GuideSuperjunior8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 Protection (Integumentary Systems)Dokument25 SeitenPart 1 Protection (Integumentary Systems)Muhammad UsamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 176 Anatomy Integumentary SystemDokument29 Seiten176 Anatomy Integumentary SystemJoana Mae PortezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 3 - Integumentary System PDFDokument28 SeitenChap 3 - Integumentary System PDFRommel Abaya TioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Large Volume Parenterals: Guidelines and Quality Control TestsDokument36 SeitenLarge Volume Parenterals: Guidelines and Quality Control TestsRákêsh MãttàNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcidifiersDokument17 SeitenAcidifiersKarim Khalil100% (3)
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDokument70 SeitenAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisLorenz Hernandez100% (1)
- IRB Definitions (Is It Research? and Definitions of Exempt, Expedited and Full)Dokument4 SeitenIRB Definitions (Is It Research? and Definitions of Exempt, Expedited and Full)analyn123Noch keine Bewertungen
- PTP1 - Reading Test 5Dokument17 SeitenPTP1 - Reading Test 5Anh DucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Pressure Log 30Dokument2 SeitenBlood Pressure Log 30Yousab KaldasNoch keine Bewertungen
- HOHF Witch of The Wilderlands VsubhaDokument30 SeitenHOHF Witch of The Wilderlands VsubhaDom100% (1)
- Procedure of General AnaesthesiaDokument4 SeitenProcedure of General AnaesthesiaNuridayu Sedek100% (1)
- Gardens For Patients With Alzheimer's DiseaseDokument3 SeitenGardens For Patients With Alzheimer's DiseaseKritikou1547Noch keine Bewertungen
- EFN - PPTX 3Dokument9 SeitenEFN - PPTX 3Suheni Khotimah IndrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Manufacturing Units With Valid Ayush 64 Technology Transfer Agreement As On 15.06.2021Dokument5 SeitenList of Manufacturing Units With Valid Ayush 64 Technology Transfer Agreement As On 15.06.2021Sunira EnterprisesNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of MicrobiologyDokument3 SeitenHistory of MicrobiologyAngeli ButedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAFTAR OBAT LASA (Look Alike Sound AlikeDokument4 SeitenDAFTAR OBAT LASA (Look Alike Sound Aliketri tanayawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiarrheaDokument24 SeitenDiarrheaash ashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonifacio V. Romero High School Tle Beauty Care 9 1st Quarter Examination S.Y. 2018-2019Dokument6 SeitenBonifacio V. Romero High School Tle Beauty Care 9 1st Quarter Examination S.Y. 2018-2019Virginia Saavedra100% (1)
- Modified Release Dosage FormDokument24 SeitenModified Release Dosage FormSuraj ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kriya For Balancing The ChakrasDokument5 SeitenKriya For Balancing The ChakrasFedra Fox Cubeddu100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Physiology Case 9Dokument50 SeitenCardiovascular Physiology Case 9Kim AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiogenic Shock Causes and TreatmentDokument43 SeitenCardiogenic Shock Causes and TreatmentGalih Arief Harimurti WawolumajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological Point of ViewDokument3 SeitenPsychological Point of ViewForam PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Divine Message of Yog Rishi.: Swastha Ho Jan, Gan, Man and The Nation 'Dokument68 SeitenThe Divine Message of Yog Rishi.: Swastha Ho Jan, Gan, Man and The Nation 'Aniket ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lawsuit Against Small Smiles Dental Center Aka Alabany Access Dental Center Et. Al.Dokument52 SeitenLawsuit Against Small Smiles Dental Center Aka Alabany Access Dental Center Et. Al.DebHgnNoch keine Bewertungen
- OrthosisDokument35 SeitenOrthosissinghmenkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CasestudynervoussystemDokument2 SeitenCasestudynervoussystemapi-265854240Noch keine Bewertungen
- Administering Corticosteroids in Neurologic Diseases3724Dokument12 SeitenAdministering Corticosteroids in Neurologic Diseases3724Carmen BritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turmeric:: Plant Origin and HistoryDokument8 SeitenTurmeric:: Plant Origin and HistoryCuber Anay GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FISIOGRAFT ENG Set 17 PDFDokument28 SeitenFISIOGRAFT ENG Set 17 PDFmaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring 2011 21st AnniversaryDokument56 SeitenSpring 2011 21st AnniversaryRajesh SekhriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Employment Occupational Health FormDokument7 SeitenPre Employment Occupational Health Formlinks2309Noch keine Bewertungen
- Konsep Latihan Plyometric PDFDokument27 SeitenKonsep Latihan Plyometric PDFDwinda Abi PermanaNoch keine Bewertungen