Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Oncogene
Hochgeladen von
drnazzOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Oncogene
Hochgeladen von
drnazzCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
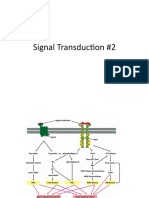
oncogenes
There are several systems for classifying oncogenes,[11][12] but there is not yet a widely accepted
standard. They are sometimes grouped both spatially (moving from outside the cell inwards) and
chronologically (parallelling the "normal" process of signal transduction). There are several categories
that are commonly used:
Category Examples Description
Usually secreted by specialized cells to induce cell
proliferation in themselves, nearby cells, or distant
cells. An oncogene may cause a cell to secrete
Growth factors, or growth factors even though it does not normally do
c-Sis
mitogens so. It will thereby induce its own uncontrolled
proliferation (autocrine loop), and proliferation of
neighboring cells. It may also cause production of
growth hormones in other parts of the body.
Kinases add phosphate groups to other proteins to
turn them on or off. Receptor kinases add phosphate
epidermal growth factor
groups to receptor proteins at the surface of the cell
receptor (EGFR), platelet-
(which receive protein signals from outside the cell
derived growth factor
Receptor tyrosine and transmit them to the inside of the cell). Tyrosine
receptor (PDGFR), and
kinases kinases add phosphate groups to the amino acid
vascular endothelial growth
tyrosine in the target protein. They can cause cancer
factor receptor (VEGFR),
by turning the receptor permanently on
HER2/neu
(constitutively), even without signals from outside
the cell.
Src-family, Syk-ZAP-70
family, and BTK family of
Cytoplasmic
tyrosine kinases, the Abl gene -
tyrosine kinases
in CML - Philadelphia
chromosome
Cytoplasmic
Serine/threonine Raf kinase, and cyclin-
kinases and their dependent kinases (through -
regulatory overexpression).
subunits
Ras is a small GTPase which hydrolyses GTP into
GDP and phosphate. Ras is activated by growth
factor signaling (ie. EGF, TGFalpha) and acting like
Regulatory
Ras protein a binary switch (on/off) in growth signaling
GTPases
pathways. Downstream effectors of Ras include Raf,
MEK, MEKK, MAPK, ERK, most of which in turn
regulate genes that mediate cell proliferation.
Transcription -They regulate transcription of genes that induce cell
myc gene
factors proliferation.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Virus 2Dokument3 SeitenVirus 2faizahmaulidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Growth Factors On CellsDokument6 SeitenEffect of Growth Factors On Cellsv.shivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tyrosine Kinase Receptors in Oncology: Molecular SciencesDokument48 SeitenTyrosine Kinase Receptors in Oncology: Molecular SciencesAnuradha Monga KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signal Transduction Lecture 2Dokument30 SeitenSignal Transduction Lecture 2chrystalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Genetic EngineeringDokument62 SeitenPlant Genetic EngineeringRonaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 38 - Neoplasia IVDokument49 SeitenLecture 38 - Neoplasia IVapi-3703352100% (1)
- 8 CancerDokument17 Seiten8 CancerGianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapk Renal Di: /ERK Signaling in Regulation of FferentiationDokument21 SeitenMapk Renal Di: /ERK Signaling in Regulation of Fferentiationlinda ratna watiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definisi Dan Klasifikasi Faktor PertumbuhanDokument9 SeitenDefinisi Dan Klasifikasi Faktor PertumbuhanArmy Setia KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self - Sufficiency in Growth Signals Cancer.Dokument21 SeitenSelf - Sufficiency in Growth Signals Cancer.siddhant kushareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: Group VDokument20 SeitenReceptor Tyrosine Kinase: Group VNana juniartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stem Cell - The BasicsDokument33 SeitenStem Cell - The Basicsharleen22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Signal Recognition ParticleDokument17 SeitenSignal Recognition ParticleMehak MattooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heldin2002 - Signal Transduction: OverviewDokument7 SeitenHeldin2002 - Signal Transduction: Overview7cmym76z2jNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd PPT Growth Factors and ReceptorsDokument31 Seiten2nd PPT Growth Factors and ReceptorsIndranil BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FALLSEM2023-24 BBIT307L TH VL2023240100208 2023-06-02 Reference-Material-IDokument32 SeitenFALLSEM2023-24 BBIT307L TH VL2023240100208 2023-06-02 Reference-Material-IANOUSHKA ARUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe How Cells GrowDokument1 SeiteDescribe How Cells GrowMichael BriscoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2025 Module 6 Genetics, Evolution and EcosystemsDokument42 Seiten2025 Module 6 Genetics, Evolution and Ecosystemsharman panwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 CarcinogenesisDokument48 Seiten4 CarcinogenesisDipo Mas SuyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hallmarks of CancerDokument21 SeitenHallmarks of CancerAnanya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oncogene Function: Specific Transcript - Ion Factors or Components of Growth Stimulating Signal PathwaysDokument8 SeitenOncogene Function: Specific Transcript - Ion Factors or Components of Growth Stimulating Signal PathwaysRitwik ChakradharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tirosin Kinase Receptor (RTK)Dokument8 SeitenTirosin Kinase Receptor (RTK)Nur Afra YsNoch keine Bewertungen
- OncogenesDokument8 SeitenOncogenesClaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene Regulation, Transposon N Genetic VariationDokument27 SeitenGene Regulation, Transposon N Genetic Variationbishalstha079Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review Article: Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) in Cancers: Overexpression and Therapeutic ImplicationsDokument10 SeitenReview Article: Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) in Cancers: Overexpression and Therapeutic ImplicationsPeter MjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 8 Cell CommunicationDokument28 SeitenPart 8 Cell CommunicationLê Thanh HằngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Signaling Signal TransductionDokument7 SeitenCell Signaling Signal TransductionArslan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swati ImpDokument3 SeitenSwati ImpShrenik MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.016 Recitation 17 - Fall 2018: Summary of Lectures 25 (11/9) & 26 (11/14)Dokument9 Seiten7.016 Recitation 17 - Fall 2018: Summary of Lectures 25 (11/9) & 26 (11/14)Shubham singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Chaperones ReportDokument47 SeitenMolecular Chaperones ReportKristian Cada100% (1)
- Oncogenes - The BasicsDokument4 SeitenOncogenes - The BasicsiamboredtiredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell-Cell Communication in Development: Lee Kui SoonDokument46 SeitenCell-Cell Communication in Development: Lee Kui SoonSayapPutihNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseDokument7 SeitenThe Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseNtando SitholeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Receptor-Ligand Interactions - Cell Signaling, Adhesion, Motility, Cell MigrationDokument31 SeitenReceptor-Ligand Interactions - Cell Signaling, Adhesion, Motility, Cell MigrationLeebo PinPinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signals and ReceptorsDokument28 SeitenSignals and ReceptorsEmilio MurciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signal Transduction PathwaysDokument6 SeitenSignal Transduction PathwaysSHREYA SENTHIL KUMAR IMS21286Noch keine Bewertungen
- Production of Recombinant Pharmaceutical ProteinsDokument25 SeitenProduction of Recombinant Pharmaceutical ProteinsJuliana DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of Gene Expression-1Dokument20 SeitenRegulation of Gene Expression-1Iram MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cell Communication in Development 20240206 060723 0000 1Dokument22 SeitenCell Cell Communication in Development 20240206 060723 0000 1Sai YamanakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RASopatiasDokument20 SeitenRASopatiasLeo YueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 Hallmarks CancerDokument131 SeitenLecture 5 Hallmarks CancerTHANISHTA KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healing and Repair: Facilitator: Prof KitinyaDokument99 SeitenHealing and Repair: Facilitator: Prof KitinyaIbrahimuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signaling Pathways1189Dokument26 SeitenSignaling Pathways1189Mehedi HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- L14 - Cancer Cell Signalling-Part 2-S23Dokument26 SeitenL14 - Cancer Cell Signalling-Part 2-S23waNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiosignallingDokument16 SeitenBiosignallingAsmaa HatemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mosaic Analysis With A Repressible Cell Marker For Studies of Gene Function in Neuronal Morphogenesis (1999)Dokument11 SeitenMosaic Analysis With A Repressible Cell Marker For Studies of Gene Function in Neuronal Morphogenesis (1999)Ana TuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imunologi TumorDokument55 SeitenImunologi Tumortaufik.abdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C & M Bio CancerDokument32 SeitenC & M Bio CancerA PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oncogenes-By Localization of Their Products: Transcription FactorsDokument3 SeitenOncogenes-By Localization of Their Products: Transcription Factorsmixalis4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Membraan Nucleus Voortgang GroeihormonenDokument3 SeitenMembraan Nucleus Voortgang GroeihormonenMeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Peptide Hormones by Sonu FloricultureDokument19 SeitenPlant Peptide Hormones by Sonu FloricultureSonu SheoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Genetic Core of Development: Differential Gene ExpressionDokument35 SeitenThe Genetic Core of Development: Differential Gene ExpressionSayapPutihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proto OncogenesDokument42 SeitenProto OncogenesMedicNoch keine Bewertungen
- OncogenesDokument77 SeitenOncogenesAnand Reghuvaran100% (3)
- Lecture 20 CarcinogenesisDokument84 SeitenLecture 20 CarcinogenesisMohammad_Islam87100% (1)
- New Promoter and Selection System For Transgenics: Submitted By: Kirti PH.DDokument51 SeitenNew Promoter and Selection System For Transgenics: Submitted By: Kirti PH.DSubash SubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cancer RemedialDokument12 SeitenCancer RemedialLee Tung LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10ECMDokument49 Seiten10ECMrameshvibhin poosarlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene ExpressionDokument16 SeitenGene ExpressionmidhunbonumahanthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growth Factors and Their Receptors in Cell Differentiation, Cancer and Cancer TherapyVon EverandGrowth Factors and Their Receptors in Cell Differentiation, Cancer and Cancer TherapyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Q S Table ReviewDokument27 SeitenBiochem Q S Table ReviewMallick KodavantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testbank 4e ch16Dokument13 SeitenTestbank 4e ch16drnazz100% (9)
- Reg GlycDokument6 SeitenReg GlycdrnazzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycolysis "Sugar Splitting" 10 Reactions & Some Mechanisms Energy Enzymes Regulation Pyruvate Fate - Aerobic or Not?Dokument45 SeitenGlycolysis "Sugar Splitting" 10 Reactions & Some Mechanisms Energy Enzymes Regulation Pyruvate Fate - Aerobic or Not?drnazzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sage Handbook For The USMLE Step 1 Class of 2013Dokument17 SeitenSage Handbook For The USMLE Step 1 Class of 2013drnazzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interruption of Bile Salt CirculationDokument2 SeitenInterruption of Bile Salt CirculationdrnazzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01GITDokument50 Seiten01GIThasankababiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Acid-Base ProblemsDokument3 SeitenPractice Acid-Base ProblemsAmanda van TasselNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHD: Host-Parasite InteractionsDokument3 SeitenPHD: Host-Parasite InteractionsAlemayehu DargeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relevanttopicalskincare Productsforprevention AndtreatmentofagingskinDokument6 SeitenRelevanttopicalskincare Productsforprevention AndtreatmentofagingskinenviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell WallDokument4 SeitenCell WallSamia KhandkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Marine BiologyDokument83 Seiten2-Marine BiologyLutfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphocyte TraffickingDokument8 SeitenLymphocyte TraffickingAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fraga - 2005 - Epigenetic Differences Arise During The Lifetime of Mono Zygotic TwinsDokument6 SeitenFraga - 2005 - Epigenetic Differences Arise During The Lifetime of Mono Zygotic TwinstechnopsychNoch keine Bewertungen
- CATS & DOGS Nutrition PDFDokument71 SeitenCATS & DOGS Nutrition PDFErald Renz LaurenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Paper MicrosDokument7 SeitenScientific Paper MicrosThe Gaile-squared ShopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology: Maayan Dadon-Freiberg, Nava Chapnik, Oren FroyDokument9 SeitenMolecular and Cellular Endocrinology: Maayan Dadon-Freiberg, Nava Chapnik, Oren FroyAnnie GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17-Chapter Manuscript-477-1-10-20200501Dokument14 Seiten17-Chapter Manuscript-477-1-10-20200501nikhilkapoor1999Noch keine Bewertungen
- IAL Timetable January 2018 FinalDokument18 SeitenIAL Timetable January 2018 FinalAminul Islam IshmamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterosexism Fact SheetDokument3 SeitenHeterosexism Fact Sheetapi-3595219970% (1)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1 NoteDokument4 SeitenForm 2 Science Chapter 1 Noteseek_4_happinesss100% (1)
- FasciaDokument4 SeitenFasciaNaresh MuttavarapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MY 1st Sem. Presttn DNA Damage & Repair PPT MW 2003Dokument26 SeitenMY 1st Sem. Presttn DNA Damage & Repair PPT MW 2003Samhita Kalita100% (1)
- Free Radicals and The SkinDokument5 SeitenFree Radicals and The SkinTamina PfeifferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assurance Gds Brochure Br2694en MKDokument4 SeitenAssurance Gds Brochure Br2694en MKFatimaezzahraa BouaalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penawaran Harga PCR KitDokument2 SeitenPenawaran Harga PCR KithafizauliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Causal Factors of SchizophreniaDokument6 SeitenBiological Causal Factors of SchizophreniaspartanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Test Bank For Campbell Biology in Focus 1st Edition Urry PDF Full ChapterDokument36 SeitenFull Download Test Bank For Campbell Biology in Focus 1st Edition Urry PDF Full Chapterirefulofterimrgb100% (13)
- Osmosis and Diffusion WorksheetDokument7 SeitenOsmosis and Diffusion WorksheetAbir Omar25% (4)
- Semelparity and IteroparityDokument5 SeitenSemelparity and Iteroparityraz23aletthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herb-All Organic (Treatment For Cancer) : How It WorksDokument44 SeitenHerb-All Organic (Treatment For Cancer) : How It WorksJohn Patrick MuzanyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hem Lab Manual Diff F16Dokument10 SeitenHem Lab Manual Diff F16LAB.RSWB0% (1)
- (Plant Science Research and Practices) White, Monica-Rapeseed - Chemical Composition, Production and Health Benefits-Nova Science Publishers (2016)Dokument177 Seiten(Plant Science Research and Practices) White, Monica-Rapeseed - Chemical Composition, Production and Health Benefits-Nova Science Publishers (2016)Red Red100% (1)
- Root Canal News Release - 2Dokument13 SeitenRoot Canal News Release - 2hanalei77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic System NotesDokument4 SeitenLymphatic System Notestaccxo14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conspectus of The Bulgarian Vascular Flora. Third EditionDokument454 SeitenConspectus of The Bulgarian Vascular Flora. Third EditionBoris AssyovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iji2013 151028Dokument8 SeitenIji2013 151028Kershaun MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscle Physiology: Human Anatomy and Physiology II Oklahoma City Community CollegeDokument45 SeitenMuscle Physiology: Human Anatomy and Physiology II Oklahoma City Community CollegeswitifranzNoch keine Bewertungen