Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Methods CAS2 2009 Formulas
Hochgeladen von
Jeff TsaiOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Methods CAS2 2009 Formulas
Hochgeladen von
Jeff TsaiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS)
Written examination 2
FORMULA SHEET
Directions to students
Remove this formula sheet during reading time.
This formula sheet is provided as a reference.
Copyright © Insight Publications 2009
2
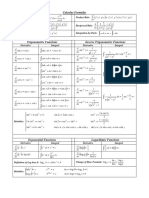
Mathematical Methods Formulas
Mensuration
1 1
area of a trapezium: (a + b) h volume of a pyramid: Ah
2 3
4 3
curved surface area of a cylinder: 2π rh volume of a sphere: πr
3
1
volume of a cylinder: π r 2h area of a triangle: bc sin A
2
1 2
volume of a cone: πr h
3
Calculus
d n
dx
( )
x = nx n −1 ∫ x dx = n + 1 x
n 1 n +1
+ c, n ≠ −1
d ax
dx
( )
e = aeax ∫e
ax
dx =
1 ax
a
e +c
d
dx
( log e ( x ) ) =
1
x
1
∫ x dx = log e x +c
d
dx
( sin ( ax ) ) = a cos ( ax ) 1
∫ sin ( ax ) dx = − a cos ( ax ) + c
d 1
dx
(cos(ax)) = − a sin(ax) ∫ cos ( ax ) dx = a sin ( ax ) + c
d
dx
( tan ( ax ) ) =
a
cos ( ax )
2
= a sec 2 ( ax )
d dv du du dv
product rule: ( uv ) = u + v d ⎛u⎞
v −u
dx dx dx = dx dx
dx ⎜⎝ v ⎟⎠
quotient rule:
v2
dy dy du approximation: f ( x + h ) ≈ f ( x ) + hf ′ ( x )
chain rule: =
dx du dx
Probability
Pr( A) = 1 − Pr ( A′ ) Pr ( A ∪ B ) = Pr ( A ) + Pr ( B ) − Pr ( A ∩ B )
Pr ( A ∩ B )
Pr ( A B ) =
Pr ( B )
mean: μ = E ( X ) variance: var ( X ) = σ 2 = E ( X − μ ) ( 2
) = E( X ) − μ
2 2
probability distribution mean variance
discrete Pr ( X = x ) = p ( x ) μ = ∑ x p ( x) σ 2 = ∑ ( x − μ ) p ( x)
2
continuous ∞ ∞
Pr ( a < X < b ) = ∫ f ( x ) dx x f ( x ) dx ( x − μ )2 f ( x ) dx
b
μ=∫ σ2 =∫
a −∞ −∞
END OF FORMULA SHEET
Copyright © Insight Publications 2009
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Maths Formula SheetDokument3 SeitenMaths Formula SheetHendrix HamalainenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjusted Formula Sheet - MMEDokument4 SeitenAdjusted Formula Sheet - MMEDhruvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Képlet TáblázatDokument1 SeiteKéplet TáblázatMáté KucseraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Képlet TáblázatDokument1 SeiteKéplet TáblázatMáté KucseraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration FomulaeDokument1 SeiteIntegration FomulaezexoditeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel A Level Maths Formula SheetDokument3 SeitenEdexcel A Level Maths Formula SheetSanveer GroverNoch keine Bewertungen
- KépletgyűjteményDokument3 SeitenKépletgyűjteménycsodaelmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A B C A B C A B C A B C BC A B A C Ac B C A B Ab C: Identidades Trigonométricas Fórmulas de DerivaciónDokument2 SeitenA B C A B C A B C A B C BC A B A C Ac B C A B Ab C: Identidades Trigonométricas Fórmulas de DerivaciónGael Garcia VazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sciaga - CalkiDokument1 SeiteSciaga - Calkiapi-3716595Noch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Calculus Formulas and ConceptsDokument5 SeitenDifferential Calculus Formulas and ConceptsDroffilc Nav Cm MulihamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16-17 Spring FinalDokument8 Seiten16-17 Spring FinalAmeer Hazim Ghazi Assa’dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus 12 Formula Sheet : Pythagorean: DerivativesDokument2 SeitenCalculus 12 Formula Sheet : Pythagorean: DerivativesDhaval PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- AddMath Formula SheetDokument5 SeitenAddMath Formula SheetHidayah TeacherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulasintegrales BNDokument1 SeiteFormulasintegrales BNVicente MachinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 12 Math 163 2015-16Dokument2 SeitenMe 12 Math 163 2015-16Ron H LetwinskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution & Answer For Kcet-2009 Version - A-2: (Mathematics)Dokument6 SeitenSolution & Answer For Kcet-2009 Version - A-2: (Mathematics)Rahul DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathmethods Formula WDokument4 SeitenMathmethods Formula WbrrtybeetleNoch keine Bewertungen
- RulesDokument1 SeiteRulesBil's Top 5Noch keine Bewertungen
- (123dok - Com) Bab Xvi Integral 2Dokument4 Seiten(123dok - Com) Bab Xvi Integral 2Yahya IrfansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Differentiation and Integration FormulasDokument2 SeitenMaths Differentiation and Integration FormulasYeshmitha AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tableau Primitives Usuelles8494949Dokument2 SeitenTableau Primitives Usuelles8494949kibutsujimuzan940Noch keine Bewertungen
- MVR 320 document covers continuous systems, sound, vibration isolationDokument2 SeitenMVR 320 document covers continuous systems, sound, vibration isolationRamzes47Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integration ResultsDokument1 SeiteIntegration ResultsctbijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PURE MATHEMATICSDokument3 SeitenPURE MATHEMATICSpatricia eileenNoch keine Bewertungen
- JAMBMath FormulasDokument2 SeitenJAMBMath Formulaszacq18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Specmaths Formula W PDFDokument4 SeitenSpecmaths Formula W PDFAO TutoringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Further Applications of IntegrationDokument3 SeitenChapter 8 Further Applications of Integration祈翠Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus II formulas for derivativesDokument1 SeiteCalculus II formulas for derivativesrichy_eg185834Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Concepts: Algebra CalculusDokument1 SeiteMathematical Concepts: Algebra Calculusrandom guyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Notes On Integral Calculus For JEE Main 2022 - PDF DownloadDokument7 SeitenRevision Notes On Integral Calculus For JEE Main 2022 - PDF DownloadMiriam SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulaphase 2Dokument1 SeiteFormulaphase 2nagham khaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Calculus BC 2006 Scoring Guidelines Form B: The College Board: Connecting Students To College SuccessDokument7 SeitenAP Calculus BC 2006 Scoring Guidelines Form B: The College Board: Connecting Students To College SuccessMr. PopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Math IntegrationDokument12 SeitenAdd Math Integrationkamil muhammad100% (1)
- AP Calculus AB BIBLE SheetDokument9 SeitenAP Calculus AB BIBLE SheetElizabeth RankinNoch keine Bewertungen
- TABLA DE INTEGRALES v1Dokument2 SeitenTABLA DE INTEGRALES v1Valeria Pinzón VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics SummaryDokument7 SeitenMathematics SummaryMoses KabeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic integration rules and antiderivativesDokument1 SeiteBasic integration rules and antiderivativessalnasu100% (1)
- PRINT4 - Derivatives Cheat Sheet - SymbolabDokument2 SeitenPRINT4 - Derivatives Cheat Sheet - SymbolabPamela RicaforteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus FormulasDokument2 SeitenCalculus FormulasMahamud Hossain ArnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector & Basic Maths - Short Notes - JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2024Dokument2 SeitenVector & Basic Maths - Short Notes - JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2024Comical comicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wjec Gce Mathematics Unit 3 7 IntegrationDokument2 SeitenWjec Gce Mathematics Unit 3 7 IntegrationSubiraj RamanjoolooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Memory Aid 2Dokument2 SeitenMemory Aid 2julsaujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus 2Dokument305 SeitenCalculus 2nicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Problems On VolumesDokument2 SeitenSolutions To Problems On VolumesteachopensourceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Formula Book - First YearDokument18 SeitenMathematics Formula Book - First Year20S1002 Joel DsouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mat2 SalabahterDokument1 SeiteMat2 SalabahterAntonio ArihNoch keine Bewertungen
- 38 Integration Full Part 4 of 5Dokument10 Seiten38 Integration Full Part 4 of 5nandagopanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of integrals formula guideDokument1 SeiteTable of integrals formula guideFrankBordaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tablica Izvoda I Integrala PDFDokument1 SeiteTablica Izvoda I Integrala PDFDunja VidicNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 4.1 FormulasDokument2 SeitenHW 4.1 FormulasAbdiakim AbdikadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mensuration R: Pure MathematicsDokument8 SeitenMensuration R: Pure Mathematicsquang hưngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus FormulaDokument2 SeitenCalculus FormulaGeramagliquiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATE - Tabele Integrale Si DerivateDokument2 SeitenMATE - Tabele Integrale Si Derivatecrocodilu100% (1)
- ### - Tabel de Integrale PDFDokument2 Seiten### - Tabel de Integrale PDFFaur CristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Maths Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenSenior Maths Formula SheetMark Riley100% (2)
- FormulasDokument3 SeitenFormulassaeed khaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regras de Deriva C AoDokument1 SeiteRegras de Deriva C AoWendel MeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regras de derivação e identidades trigonométricasDokument1 SeiteRegras de derivação e identidades trigonométricasHermenegildo valorNoch keine Bewertungen
- DerivadasDokument1 SeiteDerivadasLeandro Aparecido Do NascimentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Productivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionVon EverandProductivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCME-TBW Course OutlineDokument6 SeitenSCME-TBW Course Outlineinam ullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE 330 Fall 2015 Course OutlineDokument6 SeitenChE 330 Fall 2015 Course Outlinecjkim93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Production DepartmentDokument2 SeitenProduction Departmentavinash peddintiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Tensor CalculusDokument300 SeitenVector Tensor CalculusDiogo Martins100% (3)
- 6.3 Additional Practice PDFDokument2 Seiten6.3 Additional Practice PDFTyler VanvleetNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparison of Two Linear Algebra BooksDokument3 SeitenA Comparison of Two Linear Algebra BooksAnton Van WykNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization Lecture 6: BITS PilaniDokument32 SeitenOptimization Lecture 6: BITS PilaniSeshu BollineniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1.1 - Relation and FunctionDokument34 SeitenLesson 1.1 - Relation and Functionkate deguzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- (A State University Established Under Govt. of Haryana Act. No. 29 of 2006) Accredited "A" Grade by NAACDokument5 Seiten(A State University Established Under Govt. of Haryana Act. No. 29 of 2006) Accredited "A" Grade by NAACMohit NaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linton, David Cloud Charts, Trading Success With The Ichimoku TechniqueDokument119 SeitenLinton, David Cloud Charts, Trading Success With The Ichimoku TechniqueJuan Luis Lopez Martinez65% (20)
- Chapter 1 Understanding ResearchDokument23 SeitenChapter 1 Understanding ResearchDimas Pratama PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 微积分公式大全Dokument5 Seiten微积分公式大全Samuel YehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Technique Laboratory PDFDokument56 SeitenNumerical Technique Laboratory PDFRAMEYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Real Analysis by Christopher HeilDokument416 SeitenIntroduction To Real Analysis by Christopher HeilDipendranath Mahato100% (4)
- Numerical Optimization-Based Extremum Seeking Control With Application To ABS DesignDokument14 SeitenNumerical Optimization-Based Extremum Seeking Control With Application To ABS DesignDouglas CairesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean Median ModeDokument20 SeitenMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean Median ModeRia BarisoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gretl Empirical Exercise 2 - KEY PDFDokument3 SeitenGretl Empirical Exercise 2 - KEY PDFDaniel Lee Eisenberg JacobsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Random VariableDokument7 Seiten8 Random VariableNoor MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.loridon 60 ML SuspensionDokument5 Seiten10.loridon 60 ML SuspensionShorup GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Research IntrodutionDokument38 SeitenLecture Notes Chapter 1 Research IntrodutionMitikuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ill-posed problems in image and signal processingDokument50 SeitenIll-posed problems in image and signal processingOmar Enrique Garcia CaicedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3 Lab 3Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 3 Lab 3Sohar AlkindiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Hanbook - Project - Ebtp4106 - BTM & BMMG & BPFMDokument23 Seiten1-Hanbook - Project - Ebtp4106 - BTM & BMMG & BPFMSuwit HannieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data CAT-2 NotesDokument26 SeitenBig Data CAT-2 NotesAditiya GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 2: Solutions: Damien Klossner Damien - Klossner@epfl - CH Extranef 128 October 18, 2018Dokument14 SeitenProblem Set 2: Solutions: Damien Klossner Damien - Klossner@epfl - CH Extranef 128 October 18, 2018ddd huangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Analytics Chapter 1Dokument50 SeitenBusiness Analytics Chapter 1ricardo enriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AB WS 041 Reimann Sum Approximation 1Dokument2 SeitenAB WS 041 Reimann Sum Approximation 1Justin CooleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Fourier TransformDokument42 SeitenDigital Fourier Transformsnake teethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 5.3, Exercise 10Dokument3 SeitenSection 5.3, Exercise 10Carlos LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Exercise 2: Simple Linear Regression and Hypothesis TestingDokument4 SeitenSolutions To Exercise 2: Simple Linear Regression and Hypothesis TestingAna-Maria BadeaNoch keine Bewertungen