Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Necessary product parameters for aluminum sulphate elevator
Hochgeladen von
Budi Maryanto100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
2K Ansichten1 SeiteCentrifugal discharge conveys usually have a spacing between buckets that is 2 to 3 times the bucket projection, though the spacing can be greater for free-flowing products. The head pulley diameter is the distance from the top dead centre to the bottom of the bucket. The belt speed is determined by the bucket spacing times the number of buckets per second.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Belt Bucket Elevator Design-EXAMPLE
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCentrifugal discharge conveys usually have a spacing between buckets that is 2 to 3 times the bucket projection, though the spacing can be greater for free-flowing products. The head pulley diameter is the distance from the top dead centre to the bottom of the bucket. The belt speed is determined by the bucket spacing times the number of buckets per second.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
2K Ansichten1 SeiteNecessary product parameters for aluminum sulphate elevator
Hochgeladen von
Budi MaryantoCentrifugal discharge conveys usually have a spacing between buckets that is 2 to 3 times the bucket projection, though the spacing can be greater for free-flowing products. The head pulley diameter is the distance from the top dead centre to the bottom of the bucket. The belt speed is determined by the bucket spacing times the number of buckets per second.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
The left-hand column provides descriptive text. The right-hand column provides an example.
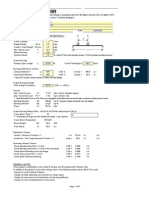
NECESSARY INFORMATION NECESSARY INFORMATION
Required product parameters. Product parameters.
Service use. Raise crushed product from mill outlet to storage silo.
Material chemical name. Aluminium Sulphate.
Bulk density – mass/volume – kg/m3 1700 kg/m3
Maximum duty – kg/hr or m3/hr 5,000 kg/hr
Maximum lump size - dimensions 3 mm max
average size 2 mm
percentage of lumps in total Nil
Height product is to be raised (meters) and angle of incline 5.5 m including length of discharge chute into 4 m high
if any. Provide enough height at the outlet of the discharge storage silo.
chute so the product is always falling following discharge.
Product characteristics – abrasiveness Sharp edges
flowability – free/cohesive/slug Free
dampness – % moisture Less than 2%
friability – firm/breaks/powders Firm
particle shape – Consistent
length/size/volume Ambient
temperature of product 30 degrees
angle of repose Corrosive if damp
corrosiveness Dry and airy
Operating environment, location and conditions –
corrosive/damp
Service required – continuous/intermittent. Intermittent – up to 12 hours per day 6 days a week
Open or closed boot design. Open boot bottom, elevator will sit on a concrete floor.
SELECT BUCKET SIZE AND SPACING SELECT BUCKET SIZE AND SPACING
The size and number of buckets is determined from the 5,000 kg/hr throughput.
required throughput using an iteration process. Select a bucket 150 mm wide x 100 mm projection with a
volume of 0.78 litre.
Select the bucket from the range in the bucket supplier’s
Using 2/3 of the volume give a capacity of 0.5 litre.
catalogue. Only 2/3 (67%) of the bucket’s design capacity
0.5 lt. is 0.0005 m3 and holds 0.85 kg of product. (0.0005
is used in calculations.
m3 x 1700 kg/m3).
Centrifugal discharge conveys usually have a spacing To move 5000 kg/hr using 150 x 100 buckets requires
between buckets that is 2 to 3 times the bucket projection, 6,000 buckets per hour or 100 buckets per minute.
though the spacing can be greater for free-flowing Select a bucket spacing of 300 mm.
products.
DETERMINE BELT SPEED
DETERMINE BELT SPEED
100 buckets per minute/60 sec per minute = 1.7 bucket/sec.
The bucket spacing times the number of buckets per
1.7 bucket/sec x 0.3 m = 0.5 m/sec. This is too low and
second determines the required belt speed. The speed for
will prove to be insufficient for a clearance throw into the
centrifugal bucket elevators is usually in the range of 1 m/s
discharge chute. The bucket spacing will need to be
to 2 m/s to insure the product throws into the chute at the
increased and the calculation repeated.
head pulley.
CALCULATE HEAD PULLEY DIAMETER CALCULATE HEAD PULLEY DIAMETER
A simplifying assumption is made that the throw v2 (0.5m) 2
commences at the top of the head pulley. At this point the r (radius ) = = = 25mm
g 9.8m / sec 2
centrifugal force and gravity force are balanced.
cos β The head pulley diameter is 50 mm. This size, though
Centrifugal force = m ⋅ v 2 ⋅ where accurately calculated, is not practical. It is far too small.
r The buckets cannot deform sufficiently to go around the
m = mass in kg pulley without over-stressing both buckets and belt.
v = belt speed in m/s
= angle from top dead centre The solution is to increase the bucket spacing or to use
r = pulley radius in m smaller buckets. This then requires a proportionate speed
Gravity force = m ⋅ g where increase to maintain the throughput. The greater velocity
g = gravity constant 9.8 m/sec2. needs a larger head pulley revolving at the same RPM.
Putting both forces equal to each other - However as we are using the smallest buckets available it
The right-hand column provides an example. is necessary to increase the bucket spacing.
Postal Address: FEED FORWARD PUBLICATIONS, PO Box 578, BENTLEY, West Australia, 6102. E-mail Address: feedforward@bigpond.com
Because the authors and publisher do not know the context in which the information presented in the flyer is to be used they accept no
responsibility for the consequences of using the information contained or implied in any articles
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Belt Bucket Elevator DesignDokument14 SeitenBelt Bucket Elevator Designking100% (1)
- Bucket Elevator Calculation - Rev. 1Dokument8 SeitenBucket Elevator Calculation - Rev. 1Jose David Jurado100% (4)
- Bucket Elevator Maintenance ManualDokument26 SeitenBucket Elevator Maintenance ManualJ Dany T. Delgado100% (1)
- Bucket Elevator SanweiDokument1 SeiteBucket Elevator SanweiTriết Lãm NgôNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge Screw Conveyors Design SelectionDokument5 SeitenDischarge Screw Conveyors Design SelectionHadid100% (1)
- Calculate Bucket Elevator CapacityDokument2 SeitenCalculate Bucket Elevator CapacityBùi Hắc HảiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bucket Elevator Vs AirliftDokument10 SeitenBucket Elevator Vs AirliftSunil D Pujari100% (1)
- Telescopic ChuteDokument2 SeitenTelescopic Chutebiswajit sabuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pan Conveyors PDFDokument20 SeitenPan Conveyors PDFChristian Makande100% (2)
- Pan Conveyors PDFDokument24 SeitenPan Conveyors PDFcachorrexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Conveyor 2Dokument26 SeitenBelt Conveyor 2gunduanil17100% (2)
- TS of Travelling TripperDokument10 SeitenTS of Travelling TripperShashank HegdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dunlop Conveyor Belt Design Manual - P1Dokument14 SeitenDunlop Conveyor Belt Design Manual - P1perdhana2000100% (1)
- Flexible Pin Bush CouplingDokument3 SeitenFlexible Pin Bush Couplingsunilshinday1_456107Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sturt Air ClassifierDokument6 SeitenSturt Air ClassifierHenry Vladimir VianchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Conveyor Example - Engineering GuideDokument12 SeitenScrew Conveyor Example - Engineering GuideskylineshareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Slide ConveyorDokument12 SeitenAir Slide Conveyorluwky.kitut42Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lubricants Fundamentals IociDokument84 SeitenLubricants Fundamentals IociSrikanth AnchulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dunlop Conveyor Belt Design Manual - P2Dokument15 SeitenDunlop Conveyor Belt Design Manual - P2perdhana2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Designing Belt Conveyors for Bulk Sugar HandlingDokument10 SeitenDesigning Belt Conveyors for Bulk Sugar Handlingmihai90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Conveyor CalculationDokument8 SeitenBelt Conveyor CalculationFarrahxviiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomass Storage Capacity - Rev.01Dokument5 SeitenBiomass Storage Capacity - Rev.01vidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bucket Elevator Capacity Formulas REVISEDDokument1 SeiteBucket Elevator Capacity Formulas REVISEDbrpnaidu2157Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bucket Elevators: Installation and Operation ManualDokument20 SeitenBucket Elevators: Installation and Operation Manualboyka yuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Services For Bulk Material Handling Projects: Project Formulation Phase Project Engineering PhaseDokument29 SeitenServices For Bulk Material Handling Projects: Project Formulation Phase Project Engineering PhasesrichmechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fenner Wedge Belt Drive Selection 299 - Friction - WedgebeltdrivesDokument22 SeitenFenner Wedge Belt Drive Selection 299 - Friction - WedgebeltdrivesSubramanian ChidambaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibratingfeeder 150211110459 Conversion Gate01Dokument18 SeitenVibratingfeeder 150211110459 Conversion Gate01ManekGorisNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCC Bucket Elevators For A Variety of Applications: Catalog No. 201Dokument16 SeitenSCC Bucket Elevators For A Variety of Applications: Catalog No. 201sudheer4079100% (2)
- Failure Analysis of Belt Conveyor Damage Caused by The Falling Material. Part 1 PDFDokument9 SeitenFailure Analysis of Belt Conveyor Damage Caused by The Falling Material. Part 1 PDFCezar PajaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEUMER Bucket ElevatorsDokument12 SeitenBEUMER Bucket ElevatorsIsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Design Features of Bucket Elevator: Package M10: Auxiliary Equipment - Maintenance and RepairDokument56 Seiten1.1 Design Features of Bucket Elevator: Package M10: Auxiliary Equipment - Maintenance and RepairDilnesa EjiguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Conveyor Belts: With Steel Cord and Fabric ReinforcementDokument5 SeitenPipe Conveyor Belts: With Steel Cord and Fabric ReinforcementEugenepaccelli Kolandai SamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Optimization For Modification of Trough Belt Conveyor To Reduce Material Spillage Used in Clinker Transport in Cement PlantDokument11 SeitenDesign Optimization For Modification of Trough Belt Conveyor To Reduce Material Spillage Used in Clinker Transport in Cement PlantBob AntunesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Chain Conveyor Construction DrawingDokument22 SeitenDouble Chain Conveyor Construction DrawingendriaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.5.4. Combined Stacker/Reclaimers and Their LimitationsDokument19 Seiten2.5.4. Combined Stacker/Reclaimers and Their LimitationsMatheus Simões100% (1)
- 243 BUI 1047 BCI Conveyor Belt CatalogDokument19 Seiten243 BUI 1047 BCI Conveyor Belt CatalogBayu SuprayogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Filter BagDokument1 SeiteLong Filter BagAlbar BudimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bucket Elevator ManualDokument37 SeitenBucket Elevator ManualEdwin MarsigliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23 HaverDokument36 Seiten23 HaverkonstantasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDM Bucket Elevators: Centrifugal ContinuousDokument2 SeitenCDM Bucket Elevators: Centrifugal ContinuousOcta IrawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Conveyor PulleysDokument24 SeitenBelt Conveyor PulleysPercy Torres100% (3)
- GSI Bucket Elevator AssemblyDokument38 SeitenGSI Bucket Elevator AssemblyElias ArizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Conveyor and Bucket Elevator Engineering GuideDokument32 SeitenScrew Conveyor and Bucket Elevator Engineering GuideJorge Cronwell Montaño VásquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear and equipment specification summaryDokument4 SeitenGear and equipment specification summaryprashant mishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation and Design of Air-Slide Conveyor for Thermal Power PlantDokument7 SeitenCalculation and Design of Air-Slide Conveyor for Thermal Power PlantHannan yusuf KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 3684 1990Dokument8 SeitenIso 3684 1990joaquin fuentealba moralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bucket Elevator Excel SheetDokument20 SeitenBucket Elevator Excel SheetMaheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kiln Tyre Replacement 13 Nov.. 2013Dokument80 SeitenKiln Tyre Replacement 13 Nov.. 2013muhammad mujahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cast Central Pipe - EN - SmidthDokument4 SeitenCast Central Pipe - EN - SmidthLuis Orlando Villarroel TorrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Bucket Elevator Design NotesDokument12 SeitenBelt Bucket Elevator Design Notesshanto4100% (2)
- Process, Plant and Equipment UP-TIME: Belt Bucket Elevator Design, Use & CareDokument27 SeitenProcess, Plant and Equipment UP-TIME: Belt Bucket Elevator Design, Use & CaresaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- GAODETEC Refractory EquipmentDokument9 SeitenGAODETEC Refractory Equipmentorangel anayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fine and Extra-Fine Vibrating Mill GrindingDokument5 SeitenFine and Extra-Fine Vibrating Mill GrindingdearistyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UOPS 2 - Part 2Dokument3 SeitenUOPS 2 - Part 2Jeoh SilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agitation and MixingDokument19 SeitenAgitation and MixingkrolkjgNoch keine Bewertungen
- AASHTO T 27 - Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse AggregatesDokument4 SeitenAASHTO T 27 - Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse AggregatesBambang DwihargonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample - Belt Bucket Elevator DesignDokument7 SeitenSample - Belt Bucket Elevator DesignAli DandamunNoch keine Bewertungen
- CENTRIFUGATIONDokument2 SeitenCENTRIFUGATIONLily Antonette AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crocheted Hoods and Cowls: 20 Enchanting Designs for Women 7 Adorable Animal Hoods for KidsVon EverandCrocheted Hoods and Cowls: 20 Enchanting Designs for Women 7 Adorable Animal Hoods for KidsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Atap JpocDokument1 SeiteAtap JpocBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRLHM WF000 - Sheet1Dokument2 SeitenTRLHM WF000 - Sheet1Budi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shot Blast Room Modification Plan for PT. Katshusiro IndonesiaDokument1 SeiteShot Blast Room Modification Plan for PT. Katshusiro IndonesiaBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CraneBeam v1 1Dokument39 SeitenCraneBeam v1 1satya_jayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tempat Sampah HssiDokument3 SeitenTempat Sampah HssiBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNP 150 JOIN ORTAL P18 MM2100-Model PDFDokument1 SeiteUNP 150 JOIN ORTAL P18 MM2100-Model PDFBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Schedule Clamp Bracket Pile Salab Zulin-PekanbaruDokument1 SeiteTime Schedule Clamp Bracket Pile Salab Zulin-PekanbaruBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Perbaikan JalanDokument17 Seiten03 Perbaikan JalanBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 Erection Pci Girder-ModelDokument1 Seite0 Erection Pci Girder-ModelBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - Molding Facade PDFDokument1 Seite01 - Molding Facade PDFBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCCC Harbour Bureau 2: Bridge Girder LauncherDokument1 SeiteCCCC Harbour Bureau 2: Bridge Girder LauncherBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection Report Example (Stormwater)Dokument4 SeitenInspection Report Example (Stormwater)Phumla MaSompisi MphembaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 91 Boyd C Bronson 1972 DafDokument58 Seiten91 Boyd C Bronson 1972 DafSlim KanounNoch keine Bewertungen
- Join H Beam200 Bracket Portal Panjang LRT Cikunir-Bekasi-ModelDokument1 SeiteJoin H Beam200 Bracket Portal Panjang LRT Cikunir-Bekasi-ModelBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Construction Method of Original Concrete Block (OCB)Dokument1 SeiteThe Construction Method of Original Concrete Block (OCB)Budi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A.machining Plate t100, 1400x900 Abutmen 600 TDokument1 SeiteA.machining Plate t100, 1400x900 Abutmen 600 TBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExpandedMesh PDFDokument2 SeitenExpandedMesh PDFBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Chimney DesignDokument8 SeitenConcrete Chimney DesignashishopclNoch keine Bewertungen
- Print Large FormatDokument2 SeitenPrint Large FormatBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding ProcedureDokument14 SeitenWelding Procedureamirhazwan100% (2)
- Henderson Component Drawings Track Brackets Channels RailsDokument4 SeitenHenderson Component Drawings Track Brackets Channels RailsBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Box Culvert Sizes 031413Dokument1 SeiteBox Culvert Sizes 031413Budi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Available 3-Sided Box Culvert Sizes:: HaunchDokument1 SeiteAvailable 3-Sided Box Culvert Sizes:: HaunchBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalkulasi Berat Steel Box Abutment 600 TDokument10 SeitenKalkulasi Berat Steel Box Abutment 600 TBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel 2D Truss Analysis 2004 (For Distribution - Limited Analysis)Dokument7 SeitenExcel 2D Truss Analysis 2004 (For Distribution - Limited Analysis)1960jackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compression Testing Machine PDFDokument5 SeitenCompression Testing Machine PDFBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation Vertical Flat Bottom TankDokument2 SeitenInstallation Vertical Flat Bottom TankBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto VentDokument4 SeitenAuto VentBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Tensile Steel 4340Dokument2 SeitenHigh Tensile Steel 4340Arun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spec of End Carriage Indent NoDokument5 SeitenSpec of End Carriage Indent NoBudi MaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Physics Wave Oscillation Damping ResonanceDokument4 SeitenSPM Physics Wave Oscillation Damping ResonanceIVAN TIONG WEI JUN MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drag Coefficient PDFDokument9 SeitenDrag Coefficient PDFphutd09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation of Energy: Physics 20 Unit C: Energy and WorkDokument10 SeitenConservation of Energy: Physics 20 Unit C: Energy and WorkUnzal FatehullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switching Impulse Flashover Performance of Different Types of Insulators at High Altitude Site of Above 2800 MDokument6 SeitenSwitching Impulse Flashover Performance of Different Types of Insulators at High Altitude Site of Above 2800 MdaaanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine MountDokument8 SeitenEngine MountAkash WaitageNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuperconductivityDokument16 SeitenSuperconductivityLakshay VohraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer DesignDokument26 SeitenTransformer DesignVinay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construct Plain Scales and Measure DistancesDokument2 SeitenConstruct Plain Scales and Measure DistancesSumit AgnihotriNoch keine Bewertungen
- McQuiston HVAC Analysis Design 6th SolutionsDokument313 SeitenMcQuiston HVAC Analysis Design 6th SolutionsProsperouscross77% (31)
- South Bihar Power Citizen Charter for ConsumersDokument2 SeitenSouth Bihar Power Citizen Charter for ConsumersAlok AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of Inertia 2Dokument51 SeitenMoment of Inertia 2Kunal kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NPT16 Transformer ControlDokument16 SeitenNPT16 Transformer ControlElver MesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Brushless Excitation SystemDokument35 Seiten5 - Brushless Excitation Systemsamson16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Model LA-ST120: AC Distribution Panel UnitDokument2 SeitenModel LA-ST120: AC Distribution Panel UnitDaniel JovelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIT MESRA RANCHI DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED MECHANICS ENGINEERING MECHANICS SHEET 1Dokument34 SeitenBIT MESRA RANCHI DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED MECHANICS ENGINEERING MECHANICS SHEET 1monumunduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Simulation of Lithium-Ion Battery ConsideringDokument7 SeitenModeling and Simulation of Lithium-Ion Battery ConsideringCarlos Morales ZamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Paper How To Properly Size Surge Protective Devices Solahd en 7635026Dokument4 SeitenWhite Paper How To Properly Size Surge Protective Devices Solahd en 7635026deju nationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistivity by Four Probe Method (Theory) - Solid State Physics Virtual Lab - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabDokument3 SeitenResistivity by Four Probe Method (Theory) - Solid State Physics Virtual Lab - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual Labupanith100% (1)
- HVDC Transmission SystemsDokument1 SeiteHVDC Transmission SystemsDattam ChranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution - Tutorial 3Dokument11 SeitenSolution - Tutorial 3zgalionoooNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOT 2 JEE 2021 Paper PDFDokument18 SeitenMOT 2 JEE 2021 Paper PDFBiswadeep GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Counting Squares A Method To Quickly Estimate PWB Trace ResistanceDokument11 SeitenCounting Squares A Method To Quickly Estimate PWB Trace ResistanceManjunath MjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction: Tec 114: Basic MechanicsDokument4 SeitenFriction: Tec 114: Basic MechanicsGodwin NgenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Presentation On 'Maxwell's Demon'Dokument27 SeitenA Presentation On 'Maxwell's Demon'luciferlightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 3daffy duckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor AnalysisDokument16 SeitenMotor AnalysisRehan MurtazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poster BiasDokument1 SeitePoster Biasapi-320021039Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radar-Measuring PrincipleDokument25 SeitenRadar-Measuring PrincipleBen FranNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW6 SolutionsDokument3 SeitenHW6 SolutionsmithosoykuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Mass&stiffnessDokument14 SeitenEffective Mass&stiffnessjitendraNoch keine Bewertungen