Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Risk Factors For Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Hochgeladen von
Tuffy TufftuffyOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Risk Factors For Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Hochgeladen von
Tuffy TufftuffyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Risk Factors for Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Close contact with someone who has active Tuberculosis TB. Inhalation of airborne nuclei from an infected person is proportional to the amount of time spent in the same air space, the proximity of the person, and the degree of ventilation. Immunocompromised status (e.g. those with HIV infection, cancer, transplanted organs, and prolonged high-dose corticosteroid therapy) Substance abuse (IV or injection drug users and alcoholics) Any person without adequate health care (the homeless, impoverished, minorities, particularly children under age 15 years and young adults between ages 15 and 44 yrs) Preexisting medical conditions or special treatment (e.g. Diabetes Mellitus, chronic renal failure, malnourishment, selected malignancies, hemodialysis, transplanted organ, gastrectomy, or jejunoileal bypass) Immigration from countries with a high prevalence of Tuberculosis TB (southeastern Asia, Africa, Latin America, Caribbean) Institutionalization (e.g. long-term care facilities, psychiatric institutions, prisons) Living in overcrowded, substandard housing Being a health care worker performing high-risk activities: administration of aerosolized pentamidine and other medications, sputum induction procedures, Bronchoscopy, suctioning, coughing procedures, caring for the immunosuppressed patient, home care with the high-risk population, and administering anesthesia and related procedures (e.g. intubation, suctioning)
Lung Cancer Causes
Considering that lung cancer has the highest rate of of all cancer related deaths, it is important to know the risk factors. There are several known risk factors in lung cancer development such as:
Smoking and secondhand smoke Asbestos exposure Use of beta carotene Exposure to radon
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- New Patient History FormDokument6 SeitenNew Patient History Formعبدالله الكافNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Ridge Split Technique Using Piezosurgery - A Case ReportDokument6 SeitenRidge Split Technique Using Piezosurgery - A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts of Food, Nutrition and Hygiene 23 NovDokument39 SeitenConcepts of Food, Nutrition and Hygiene 23 NovanamikapokhariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to the History and Development of Medical TechnologyDokument23 SeitenIntroduction to the History and Development of Medical TechnologyAnne TGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8 JoanneDokument9 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8 JoanneLANI JOY TABAMONoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Dysfunction in Patients With Head and Neck.10Dokument14 SeitenOral Dysfunction in Patients With Head and Neck.10Yeni PuspitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidance Template Source Doc PlanDokument5 SeitenGuidance Template Source Doc PlanFatin NajihaNoch keine Bewertungen
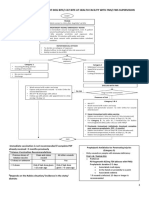
- MANAGING DOG/CAT BITES AT HEALTH FACILITYDokument5 SeitenMANAGING DOG/CAT BITES AT HEALTH FACILITYleo89azman100% (1)
- ScheduleDokument52 SeitenSchedulerohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joseph Constantine Carpue and The Bicentennial of The Birth of Modern Plastic SurgeryDokument11 SeitenJoseph Constantine Carpue and The Bicentennial of The Birth of Modern Plastic Surgerysmansa123Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Significant Association Between Maternity Waiting Homes Utilization and Perinatal Mortality in Africa: Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDokument6 SeitenThe Significant Association Between Maternity Waiting Homes Utilization and Perinatal Mortality in Africa: Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisTegenne LegesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- CGAtoolDokument17 SeitenCGAtoolGlory Anne Joy WillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Legal Letter of Notice To Principles and School NursesDokument2 SeitenSample Legal Letter of Notice To Principles and School NursesJimUKNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Position Paper About "Giving Condoms To High School Student"Dokument2 SeitenA Position Paper About "Giving Condoms To High School Student"Cristine Joy Remerata Villarosa93% (14)
- AtulabhcvDokument13 SeitenAtulabhcvTarun MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Management TemplateDokument5 SeitenCase Management TemplateEncik AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teori 7 Pilar Dasar IKMDokument41 SeitenTeori 7 Pilar Dasar IKMIntan Putri Wirahana ShantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonconventional Formocresol Pulpotomy Saves Tooth StructureDokument6 SeitenNonconventional Formocresol Pulpotomy Saves Tooth StructureMayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lebanese Medical LSK - pdf2Dokument96 SeitenLebanese Medical LSK - pdf2Alaor LopesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunizationDokument2 SeitenImmunizationannamcconkeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emma D'epagnier 3/12/202 0 4 Jenny PerryDokument3 SeitenEmma D'epagnier 3/12/202 0 4 Jenny PerryEmma d'EpagnierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Issu in Midwifery ICM PDFDokument9 SeitenQuality Issu in Midwifery ICM PDFFarhatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomedical Admissions Test - Past Paper 2009 Section 1: Answer KeyDokument2 SeitenBiomedical Admissions Test - Past Paper 2009 Section 1: Answer Keyhirajavaid246Noch keine Bewertungen
- Extra-Intestinal and Long Term Consequences of GiardiaDokument13 SeitenExtra-Intestinal and Long Term Consequences of GiardiaDulce Nalleli Aguilar TejedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Kidney Injury: New Concepts in Definition, Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and TreatmentDokument7 SeitenAcute Kidney Injury: New Concepts in Definition, Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and TreatmentMuhamad RizauddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crisis Management Covid 19Dokument22 SeitenCrisis Management Covid 19jon elleNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOAP Handout 2010Dokument4 SeitenSOAP Handout 2010wawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bites and Stings - Dermatology - MKSAP 17Dokument4 SeitenBites and Stings - Dermatology - MKSAP 17Ciara Marjorie HannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ards Prone PositionDokument9 SeitenArds Prone PositionAnonymous XHK6FgHUNoch keine Bewertungen
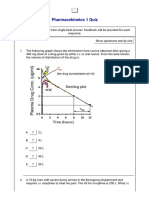
- Pharmacokinetcs 1 QuizDokument5 SeitenPharmacokinetcs 1 QuizCarlos MaingeNoch keine Bewertungen