Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NCP Fluid Volume Excess
Hochgeladen von
Angel MoorerOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
NCP Fluid Volume Excess
Hochgeladen von
Angel MoorerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
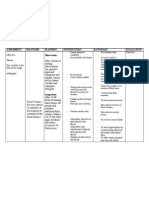
NURSING CARE PLAN
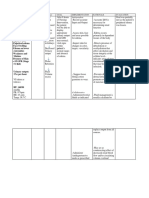
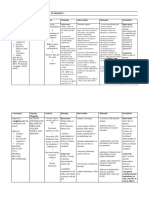
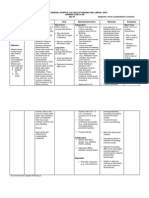
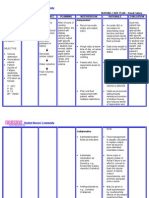
ASSESSMENT S> 0 O> > Generalized edema > difficulty of breathing >shortness of breath >Vital Signs taken as follows: BP-150/80 mmHg T-37 P-81 R-26 NURSING DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION
PLANNING
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Assess patients condition Record Intake and Output
RATIONALE
For baseline data Accurate I and O is necessary for determining renal function and fluid replacement needs and reducing risk of fluid overload Fluid management is usually calculated to prevent further fluid retention Daily body weight is best monitor of fluid status To determine fluid retention To prevent pressure ulcers May indicate increase in fluid retention May indicate cerebral edema To excrete excess fluids
EXPECTED OUTCOME Goal met as manifested by patient was able to demonstrate behaviors to monitor fluid status and reduce recurrence of fluid excess stabilizefluid volume AEB balance I & O, normal VS, stableweight, and freefrom signs of edema.
Fluid Volume Excess related to inability of the kidneys to maintain body fluid balance.
Renal failure blood flow to the kidneys perfusion in kidney urinary output water retention Fluid volume excess
After 8 hours of nursing intervention ,the patient shall demonstrate behaviors to ` monitor fluid status and reduce recurrence of fluid excess
Restrict fluids
Weigh patient daily at the same time each day Record occurrence of dyspnea Change position of client timely Note presence of edema Evaluate mental status Administer Diuretic as ordered
After 24-48 hours of nursing intervention, the patient will manifest stabilizefluid volume AEB balance I & O, normal VS, stableweight, and freefrom signs of edema.
Administer Anti hypertensive as ordered
To treat hypertension by counteracting effects of decreased renal blood flow
and/or circulating volume overload
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Clinician's Guide To Nuclear MedicineDokument409 SeitenA Clinician's Guide To Nuclear Medicineayodeji7886% (7)
- Hemodialysis NCPDokument2 SeitenHemodialysis NCPAfia Tawiah100% (1)
- Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity and Readiness For Enhanced PowerDokument3 SeitenRisk For Impaired Skin Integrity and Readiness For Enhanced PowerdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDokument3 SeitenRisk For Decreased Cardiac OutputSid Artemis FriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume ExcessDokument2 SeitenFluid Volume ExcessRodel Yacas100% (5)
- Fluid Volume Excess (CRF)Dokument4 SeitenFluid Volume Excess (CRF)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For ESRDDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan For ESRDChester Manalo94% (17)
- NCP Altered Mental StatusDokument2 SeitenNCP Altered Mental StatusACVP1188% (16)
- NCP - Fluid Volume ExcessDokument2 SeitenNCP - Fluid Volume ExcessIngrid Sasha Fong100% (4)
- NCP CKDDokument9 SeitenNCP CKDDanica Salinas100% (1)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDokument3 SeitenNCP Excess Fluid VolumeJ.G RNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP CKDDokument6 SeitenNCP CKDBenjie Dimayacyac100% (2)
- Excess Fluid VolumeDokument3 SeitenExcess Fluid VolumeStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodDokument2 SeitenIneffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodYllejann Manez60% (20)
- Ineffective Renal Tissue PerfusionDokument2 SeitenIneffective Renal Tissue PerfusionHendra Tanjung100% (4)
- Respiratory System QuizDokument2 SeitenRespiratory System Quizapi-281108263100% (1)
- 5 Altered Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlansDokument3 Seiten5 Altered Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care Plansjustin_sane40% (5)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDokument2 SeitenImpaired Urinary EliminationHaon Anasu67% (3)
- CKD NCPDokument2 SeitenCKD NCPMark Angelo Chan100% (13)
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDokument4 SeitenAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- Float Pool - Orientation - RN Critical Care Competency ChecklistDokument19 SeitenFloat Pool - Orientation - RN Critical Care Competency Checklistpurwadis100% (2)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDokument2 SeitenIneffective Tissue PerfusionClaidelyn De Leyola100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion NCPDokument5 SeitenIneffective Tissue Perfusion NCPJasmin Calata50% (2)
- Liver NCPDokument5 SeitenLiver NCPMerrill HansNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Dokument3 SeitenNCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce100% (3)
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume Related Compromised Regulatory Mechanism (Renal Failure) (Acute Renal Failure)Dokument3 SeitenNCP - Excess Fluid Volume Related Compromised Regulatory Mechanism (Renal Failure) (Acute Renal Failure)Kian Herrera100% (1)
- NCP EdemaDokument1 SeiteNCP EdemaKurtt Evan Valino100% (1)
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sDokument4 Seiten"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sAllisson BeckersNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDokument4 SeitenNCP Excess Fluid VolumeTrixia CamporedondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFDokument2 SeitenNCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFNoel Cabamongan88% (8)
- Fluid Volume Excess NCPDokument3 SeitenFluid Volume Excess NCPƦя de GuzмѧN80% (5)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDokument2 SeitenNCP Excess Fluid VolumeMei Payumo100% (1)
- NCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSODokument3 SeitenNCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSOtinatin9890% (1)
- 1 Fluid Volume Excess Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlansDokument3 Seiten1 Fluid Volume Excess Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlansMichael Baylon DueñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKD NCPDokument4 SeitenCKD NCPArlene Macatangay100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathyDokument2 SeitenDecreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To Cardiomyopathywen_pil75% (8)
- Esrd NCPDokument7 SeitenEsrd NCPSharmaine Camille de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume Excess NCPDokument3 SeitenFluid Volume Excess NCPAfia TawiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypervolemia NCPDokument2 SeitenHypervolemia NCPAlroi Abrantes50% (2)
- NCP Risk For Bleeding Related To Decreased Platelet CountDokument2 SeitenNCP Risk For Bleeding Related To Decreased Platelet CountKC Ignacio83% (24)
- Fluid Volume ExcessDokument4 SeitenFluid Volume ExcessTamil Villardo100% (2)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDokument4 SeitenNCP Excess Fluid VolumeIngrid Nicolas100% (1)
- NCP For Liver CirrhosisDokument25 SeitenNCP For Liver CirrhosisWendy Escalante100% (1)
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDokument3 SeitenNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- NCP Edema (Emdc)Dokument2 SeitenNCP Edema (Emdc)pitchijaneco76% (17)
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDokument3 SeitenFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Renal FailureMark Jason Rabadan100% (1)
- NCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeDokument4 SeitenNCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDokument1 SeiteActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDokument2 SeitenImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPDokument3 SeitenCRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPchubbielitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pain NCPDokument2 SeitenAcute Pain NCPBobby Valencerina100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument2 SeitenNursing Care PlanAldrein GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDokument2 SeitenRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 1Dokument1 SeiteNCP 1hsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Renal Failure (NCP)Dokument2 SeitenA Renal Failure (NCP)Julie Aranda Hapin100% (1)
- Revised NCPDokument4 SeitenRevised NCPJeboy SadioaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatic Dysfunction: Nursing Disease AnalysisDokument74 SeitenHepatic Dysfunction: Nursing Disease AnalysisAisha Valles MalintadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume Excess..Dokument1 SeiteVolume Excess..Tere GuillermoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing DiagnosisDokument4 SeitenNursing DiagnosisMavy AndresNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 3 DEFICIT IN FLUID VOLUMEDokument2 SeitenNCP 3 DEFICIT IN FLUID VOLUMEGenEsis CarandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Liver CirrosisDokument2 SeitenNCP Liver CirrosisRosebud RoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP Acute Renal Failure Chap7Dokument128 SeitenCP Acute Renal Failure Chap7Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Template - 3SHS-Module-Practical Research 1Dokument15 SeitenTemplate - 3SHS-Module-Practical Research 1Jeanny Mae PesebreNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT Information For Contract PreparationDokument7 SeitenCT Information For Contract PreparationAnime loverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On Performance Appraisal SystemDokument2 SeitenCase Study On Performance Appraisal SystemDivya100% (1)
- Grammar CheckDokument2 SeitenGrammar CheckCharles AlmadronesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kendler InfographicsDokument4 SeitenKendler InfographicsMaría Fernanda Ramírez100% (1)
- Formulir Klaim Rawat InapDokument2 SeitenFormulir Klaim Rawat InapGoris DonkeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AsbestosDokument18 SeitenAsbestosvivek463Noch keine Bewertungen
- HACCPDokument21 SeitenHACCPAINA SAHIRAH ABDUL AZISNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Program 240423Dokument26 SeitenAll Program 240423NoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP 1 Methods and Tools in Social WorkDokument23 SeitenGROUP 1 Methods and Tools in Social WorkJade Cadaoas MagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mets Direction Our Strategy 2018 2025Dokument41 SeitenThe Mets Direction Our Strategy 2018 2025nobbynobbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recording and Reporting in HealthDokument6 SeitenRecording and Reporting in HealthBela CilolitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dosimetric Effects of Using Generalized Equivalent Uniform Dose (gEUD) in Plan OptimizationDokument60 SeitenDosimetric Effects of Using Generalized Equivalent Uniform Dose (gEUD) in Plan OptimizationolgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah 9 - Microorganisms As Xenobiotics Degraders - Ekologi Mikroorganisme 2020 - Ver1 Aoe PDFDokument36 SeitenKuliah 9 - Microorganisms As Xenobiotics Degraders - Ekologi Mikroorganisme 2020 - Ver1 Aoe PDFizhamil hidayahNoch keine Bewertungen
- DivorceDokument3 SeitenDivorceKlein MorisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kristian Thalai - July, 2016Dokument36 SeitenKristian Thalai - July, 2016Mizoram Presbyterian Church SynodNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCPCH Progress Level 1 Paediatrics and Child Health CurriculumDokument16 SeitenRCPCH Progress Level 1 Paediatrics and Child Health CurriculumSabera KapasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anabolic SteroidsDokument5 SeitenAnabolic SteroidsGideon MurathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeopathic Facial Analysis Grant Bentley.03455 1contentsDokument7 SeitenHomeopathic Facial Analysis Grant Bentley.03455 1contentsab moonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Words Matter!: Language Statement & Reference GuideDokument7 SeitenWords Matter!: Language Statement & Reference GuideJonas von HoffmannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Microbiology: Final Report: No Growth Obtained After 5 Days of Incubation at 37°C. (Bact / Alert System)Dokument3 SeitenDepartment of Microbiology: Final Report: No Growth Obtained After 5 Days of Incubation at 37°C. (Bact / Alert System)Muhammad Shahbaz AkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid 19 The Pandemic Situation Challenge or Opportunity For Human Resource Management in Context of HRISDokument13 SeitenCovid 19 The Pandemic Situation Challenge or Opportunity For Human Resource Management in Context of HRISrhythmNoch keine Bewertungen
- ER NOTESsDokument2 SeitenER NOTESsKriz Anthony HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Nasmin.S, MBBS: ObjectiveDokument4 SeitenDR - Nasmin.S, MBBS: ObjectiveNasmin AneeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- RNTCP at A GlanceDokument28 SeitenRNTCP at A Glanceamanjo1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Team Development InterventionsDokument24 SeitenTeam Development InterventionsKhushbu Bavishi100% (1)
- Teacher-Made-Test BEVDokument3 SeitenTeacher-Made-Test BEVMaureen Madriaga100% (1)