Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRF
Hochgeladen von
Noel CabamonganOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
NCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRF
Hochgeladen von
Noel CabamonganCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
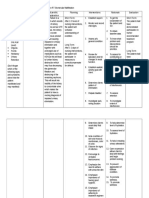
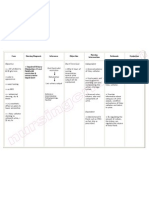
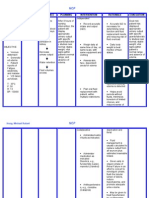
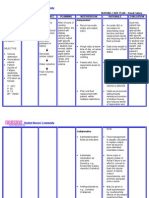
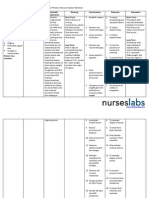
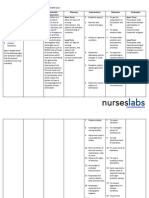
Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Urinary Elimination RT Glomerular Malfiltration Assessment Subjective: (none) Objective: Increase
e in Lab results (BUN, Creatinine, Uric Acid Level) Oliguria Anuria Hesitancy Urinary Retention (Dont forget which of the following signs and symptoms above that the patient manifested and may manifest) Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Urinary Elimination R/T glomerular Malfiltration AEB Impaired excretion of nitrogenous products 2O Renal Failure Scientific Explanation Renal Failure is a problem which results to loss of kidney functions and as GFR decrease, the kidney cannot excrete nitrogenous product and fluid causing impaired in Urinary elimination and together with prolonged use of medications such as NSAIDs this will lead to further kidney destruction which may thus decreasing the glomerular filtration and destroying of the remaining nephrons. This will result into inability of the kidney to concentrate urine which makes the patient to have a nursing diagnosis of impaired urinary elimination. Planning Short Term: After 2-3 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will verbalize understanding of condition Long Term: After 1-2 days of nursing interventions, the patient will participate in measures to correct/compensate for defects Interventions 1. Establish rapport. 2. Monitor and record vital signs. Rationale 1. To get the cooperation of the patient and SO. 2. To obtain baseline data. 3. Assess pts general condition 3. To know what problem and interventions should be prioritize. 4. To assess for contributing or causative factors. 5. Enhance commitments to promoting optimal outcomes. 6. To assess degree of interference. 7. To assess retention 8. To investigate extent of interference Evaluation Short Term: The patient shall have demonstrated participation in his/her recommended treatment program Long Term: The patient shall have demonstrated behavior/lifestyle changes to prevent complications
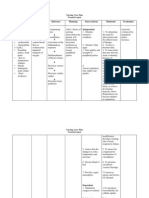
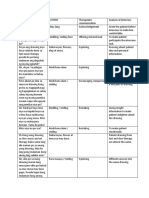
4. Review for laboratory test for changes in renal function. 5. Establish realistic activity goal with client.
6. Determine clients pattern of elimination 7. Palpate bladder 8. Investigate pain, noting location
9. Determine clients usual daily fluid intake 10. Note condition of skin and mucous membranes, color of urine. 11. Observe for signs of infection 12. Encourage to verbalize fear/concerns 13. Emphasize the need to adhere with prescribe diet 14. Emphasize importance of having good hygiene. 15. Emphasize importance of adhering to treatment regimen
9. To help determine level of hydration. 10. To assess level of hydration. 11. To help in treating urinary alterations 12. Open expression allows client to deal with feelings and begin problem solving. 13. To prevent aggravation of disease condition. 14. To promote wellness. 15. To promote wellness
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fluid Volume ExcessDokument4 SeitenFluid Volume ExcessTamil Villardo100% (2)
- 3 Altered Renal Tissue Perfusion Chronic Renal Renal Failure Nursing Care PlansDokument4 Seiten3 Altered Renal Tissue Perfusion Chronic Renal Renal Failure Nursing Care Planssapiah raman100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFDokument2 SeitenNCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFAnonymous FgT04krgymNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDokument3 SeitenImpaired Urinary Eliminationcamziii89% (18)
- NCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSODokument3 SeitenNCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSOtinatin9890% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionReginald Julia100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Urinary EliminationDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan Impaired Urinary Eliminationderic86% (14)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDokument2 SeitenImpaired Urinary EliminationHaon Anasu67% (3)
- NCP For Urinary RetentionDokument5 SeitenNCP For Urinary RetentionColeen Comelle Huerto60% (5)
- NCP CKDDokument9 SeitenNCP CKDDanica Salinas100% (1)
- NCP DysuriaDokument1 SeiteNCP DysuriaJerico Geronimo DacutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary Retention, RevisedDokument2 SeitenUrinary Retention, RevisedKim Beverly100% (5)
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDokument2 SeitenNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKD NCPDokument2 SeitenCKD NCPMark Angelo Chan100% (13)
- NCP LeukemiaDokument2 SeitenNCP LeukemiaNichole Audrey Saavedra0% (1)
- NCP - Fluid Volume ExcessDokument2 SeitenNCP - Fluid Volume ExcessIngrid Sasha Fong100% (4)
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Expected Outcome Implementation Rationale EvaluationDokument5 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Expected Outcome Implementation Rationale EvaluationRazzel Daza100% (1)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDokument4 SeitenNCP Excess Fluid VolumeTrixia CamporedondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP UtiDokument1 SeiteNCP Utitsunami_cutieNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDokument2 SeitenNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- Fluid Volume Excess (CRF)Dokument4 SeitenFluid Volume Excess (CRF)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Planjovanney100% (10)
- Abdominal Pain NCPDokument3 SeitenAbdominal Pain NCPRo-anne Aku100% (1)
- NCP CKDDokument6 SeitenNCP CKDBenjie Dimayacyac100% (2)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPDokument2 SeitenBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- NCP For UtiDokument3 SeitenNCP For UtiAaron Sanchez100% (1)
- To Promote Good Hygiene and Physical Comfort.: Coli (E. Coli), NormallyDokument2 SeitenTo Promote Good Hygiene and Physical Comfort.: Coli (E. Coli), NormallyFran LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDokument1 SeiteActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDokument3 SeitenNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Impaired Oral Mucous Membrane - NCP SLHDokument2 SeitenImpaired Oral Mucous Membrane - NCP SLHNolan Cabral100% (1)
- Reports No Pain During Urination. There Will Be No Tension in Bladder The Patient Will Appear CalmDokument4 SeitenReports No Pain During Urination. There Will Be No Tension in Bladder The Patient Will Appear CalmDenise Louise PoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDokument2 SeitenImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume ExcessDokument2 SeitenFluid Volume ExcessRodel Yacas100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Renal FailureMark Jason Rabadan100% (1)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDokument2 SeitenNCP Excess Fluid VolumeMei Payumo100% (1)
- NCP 1Dokument1 SeiteNCP 1hsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan - UtiDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan - Utisweet_karisma05100% (6)
- NCP - ConstipationDokument3 SeitenNCP - ConstipationDaniel Dave KapunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDokument3 SeitenFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Tissue PerfusionDokument2 SeitenNCP Tissue PerfusionNiña Montejo Ealdama100% (1)
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDokument1 SeiteImpaired Skin IntegrityHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract InfectionsDokument4 SeitenNCP Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract InfectionsRaveen mayi89% (9)
- NCP HemoDokument2 SeitenNCP HemoJigs HechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 Patient's NameDokument4 SeitenMedical Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 Patient's NameHadeer Mahmoud Abuslima100% (1)
- NCP - Yeast InfectionDokument2 SeitenNCP - Yeast InfectionChelzie Laserna100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlansDokument4 SeitenNursing Care PlansanreilegardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaDokument6 SeitenDecreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaNursesLabs.com100% (7)
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDokument4 SeitenNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Urinary Tract InfectionDokument19 SeitenNCP Urinary Tract InfectionYudistiro Adi Nugroho100% (1)
- Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFDokument3 SeitenImpaired Urinary Elimination CRFOscar CocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altered Renal Perfusion CRFDokument4 SeitenAltered Renal Perfusion CRFKristel Anne Nillo ZepolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altered Renal Perfusion CRFDokument5 SeitenAltered Renal Perfusion CRFGen Ramos- SolisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Term: Evaluation Rationale Interventions Goals Nursing Diagnosis AssessmentDokument4 SeitenShort Term: Evaluation Rationale Interventions Goals Nursing Diagnosis AssessmentMidoOo AL3JMINoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP DMDokument21 SeitenNCP DMKate ManalastasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CuesDokument1 SeiteCuesJoanne SaabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Blood ChemDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Blood ChemMary Gold EleveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of The TheoryDokument8 SeitenReview of The TheoryPriskaCliquersNoch keine Bewertungen
- GastroenteritisDokument8 SeitenGastroenteritistanlimdania100% (3)
- Uti NCPDokument3 SeitenUti NCPHamdy Pagilit Dimaporo0% (1)
- Drug Study 2Dokument7 SeitenDrug Study 2Jediale CarcelerNoch keine Bewertungen
- U World Renal-Urinary FinalDokument7 SeitenU World Renal-Urinary FinalNoel CabamonganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delegation RationaleDokument2 SeitenDelegation RationaleNoel Cabamongan0% (1)
- Clin Nurs Res 2013 Resnick 7 29Dokument23 SeitenClin Nurs Res 2013 Resnick 7 29Noel CabamonganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cefazolin Sodium and CelecoxibDokument6 SeitenCefazolin Sodium and CelecoxibNoel CabamonganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)Dokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)Michael Vincent DuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)Dokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)Michael Vincent DuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study H MOLEDokument11 SeitenCase Study H MOLEmaori_martinez82% (11)
- 2120Dokument285 Seiten2120NYONGKER100% (2)
- Hipertension in Pregnancy - QuestionDokument3 SeitenHipertension in Pregnancy - QuestionkoassspkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- HIMAS Handbook On Spa and MassageDokument36 SeitenHIMAS Handbook On Spa and MassageBenjie Eugenio67% (6)
- Counseling Children With Emotional DisturbanceDokument15 SeitenCounseling Children With Emotional DisturbanceLaKenya BrowderNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiferenteDokument5 SeitenDiferenteGabriela ScarlatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Cycle of Breathing TechniqueDokument3 SeitenActive Cycle of Breathing TechniqueSurya KalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lawyer As Counselor: in My Second Year of Law SchoolDokument4 SeitenThe Lawyer As Counselor: in My Second Year of Law SchoolKirsten Denise B. Habawel-VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- People v. VenturaDokument1 SeitePeople v. VenturaAphrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transparency and Self-Disclosure.Dokument20 SeitenTransparency and Self-Disclosure.Fausto Adrián Rodríguez López100% (1)
- Critical Thinking QuestionsDokument2 SeitenCritical Thinking QuestionsJulie Ann EscartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- NGV Journal Edition 2 January 2018Dokument116 SeitenNGV Journal Edition 2 January 2018oakyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnisocoriaDokument11 SeitenAnisocoriaChaturangaNSenerathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persistence Market ResearchDokument8 SeitenPersistence Market Researchapi-302003482Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arum Hastuti Dwi Sofiati Jurnal Persalinan B.inggrisDokument5 SeitenArum Hastuti Dwi Sofiati Jurnal Persalinan B.inggrisArum HastutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark NpiDokument2 SeitenMark NpiBianca Ysabelle RegalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers Mock Exam 5Dokument6 SeitenAnswers Mock Exam 5Muhammed Talha QureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UpdrsDokument8 SeitenUpdrsHanny Novia RiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRICHOMONIASISDokument39 SeitenTRICHOMONIASISAlunaficha Melody KiraniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SelfefficacyDokument4 SeitenSelfefficacyapi-481958145Noch keine Bewertungen
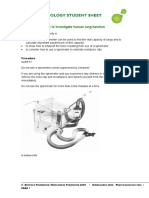
- PB - Using A Spirometer To Investigate Human Lung Function SsDokument6 SeitenPB - Using A Spirometer To Investigate Human Lung Function SsMariam AymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn Massage (Pindot Sarap) in Ten (10) Easy StepsDokument2 SeitenLearn Massage (Pindot Sarap) in Ten (10) Easy StepsBenjie EugenioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pendekatan Kaunseling Dalam Rawatan & Pemulihan Penagihan DadahDokument23 SeitenPendekatan Kaunseling Dalam Rawatan & Pemulihan Penagihan Dadahadib emirNoch keine Bewertungen
- XAlzheimerDokument657 SeitenXAlzheimerHassan MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protect Yourself From The Damage of Chronic Inflammation.: What Is Trypanophobia?Dokument3 SeitenProtect Yourself From The Damage of Chronic Inflammation.: What Is Trypanophobia?Jessie Pasian Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Asthma by ConsensusDokument87 SeitenAsthma by ConsensusSatnam KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- ObturatorDokument15 SeitenObturatorBibek RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychooncology PsychoneuroimmunologyDokument4 SeitenPsychooncology PsychoneuroimmunologypazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topnotch Integrative MedicineDokument65 SeitenTopnotch Integrative Medicinemefav7778520Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vibrational Nos Ws NotesDokument2 SeitenVibrational Nos Ws NotesAmi Patel Mehta100% (1)
- Module 9 - Urinary EliminationDokument4 SeitenModule 9 - Urinary EliminationPaulette Poseskie CoatesNoch keine Bewertungen