Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Introduction To Bridge Vs Router
Hochgeladen von
jiha2007Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Introduction To Bridge Vs Router
Hochgeladen von
jiha2007Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
COMPUTER NETWORK CHAPTER 3 : BRIDGE & ROUTER ROUTER
-To connect LAN to outside network ex. WAN -Focus more on separating a network into smaller segments -Known as layer 3 network device because it functions on network layer of OSI -Router breaks broadcast and collision domain
BRIDGE
-To connect between LAN segments in an organization -Focus more on connecting separated LAN segments -Known as layer 2 network device because it functions on data link layer of OSI -Bridge only breaks collision domain
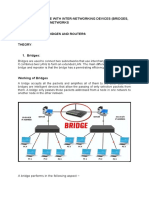
Introduction to Bridge
-Bridge operates in both physical and data link layers. -At physical layer, it regenerates the signal it receives -At data link layer, it check physical addresses of source and destination contained in the frame. -Bridge function is similar to switch but Bridge can only have 4 ports whereas switch can have 4-24 ports per switch. Types of bridge 1. Local : provide direct connection between multiple LAN segments in the same area. 2. Remote : connect multiple LAN segments in different areas over telecommunication lines Types of bridging : 1. Transparent bridging It is found primarily in Ethernet environments. The bridge does forward or filter decision based on a bridging table. 2. Source-route bridging It occurs primarily in Token Ring environments. The sender decides the path that its data should follow.
3. Translational bridging
It provides translation between the formats and transit principles of different media types (usually Ethernet and Token Ring).
4. Source-route Transparent bridging
It combines the algorithms of transparent bridging and source-route bridging to enable communication in mixed Ethernet/Token Ring environments.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVon EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-I PPT2 BasicsDokument34 SeitenUnit-I PPT2 BasicsTejas MahadikNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATSA/IN NotesDokument16 SeitenATSA/IN NotesMaxwell LaurentNoch keine Bewertungen
- NETWORKINGDokument2 SeitenNETWORKINGManish BangiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Intro To Networking and Network DevicesDokument20 Seiten5 Intro To Networking and Network DevicesAbhinav DandareNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSM 478 lecture2-NEWDokument35 SeitenCSM 478 lecture2-NEWOsei SylvesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Area Networks - InternetworkingDokument27 SeitenLocal Area Networks - InternetworkingMohammed MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Physical Layer and Network Media 3Dokument25 SeitenUnit 2 Physical Layer and Network Media 3Sagar wagleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication & NetworkingDokument31 SeitenData Communication & NetworkingHafiz Muhammad Zulqarnain JamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Devices: Repeaters, Hubs, Bridges, Switches, Routers, NIC'sDokument21 SeitenNetwork Devices: Repeaters, Hubs, Bridges, Switches, Routers, NIC'skavi_mt2008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network Devices: Repeaters, Hubs, Bridges, Switches, Routers, NIC'sDokument21 SeitenNetwork Devices: Repeaters, Hubs, Bridges, Switches, Routers, NIC'sAzhar SkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Console Related.: Subnet Mask Default GatewayDokument14 SeitenConsole Related.: Subnet Mask Default GatewayDragos AlexeNoch keine Bewertungen
- D PDFDokument29 SeitenD PDFokienaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Hardware Components: Network Interface CardsDokument2 SeitenBasic Hardware Components: Network Interface CardssathyadhoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cns Practical 4Dokument10 SeitenCns Practical 4How to download AnythingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networks: Access Management: Class Notes # 6 Internetworking September 29, 2003Dokument7 SeitenNetworks: Access Management: Class Notes # 6 Internetworking September 29, 2003utop8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-4 - DevicesDokument8 SeitenUnit-4 - Devicesbobbysingh727272Noch keine Bewertungen
- Repeater - : About Repeaters Is That They Do Not Amplify TheDokument9 SeitenRepeater - : About Repeaters Is That They Do Not Amplify TheCh Abdul MoizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5-Repeaters - Hubs - Switches - Bridges-Routers-19-01-2024Dokument46 Seiten5-Repeaters - Hubs - Switches - Bridges-Routers-19-01-2024vedhatrioathi100Noch keine Bewertungen
- LO3 Develop Topology EditedDokument38 SeitenLO3 Develop Topology Editedbiruk mollaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networks and Networking AICT003-3-2 Local Area Network TechnologiesDokument41 SeitenNetworks and Networking AICT003-3-2 Local Area Network Technologiesyoges_0695Noch keine Bewertungen
- CPH Micro ProjectDokument14 SeitenCPH Micro Projectharshawardhan deshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repeater: Physical Layer OSI ModelDokument4 SeitenRepeater: Physical Layer OSI Modeljhony jonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.0 Repeaters, Bridges, Routers, and Gateways: A Comparative Study: 4.1 RepeatersDokument5 Seiten4.0 Repeaters, Bridges, Routers, and Gateways: A Comparative Study: 4.1 Repeatersvickypatel_63873791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication Notes: Point-to-PointDokument12 SeitenData Communication Notes: Point-to-PointychokhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IIIDokument11 SeitenUnit IIIJayprakash DuveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations: Network DevicesDokument10 SeitenFoundations: Network Devicesanon_310938149Noch keine Bewertungen
- BN002 Yr2 COMP H2015 Jan08 Semester3 Switching Basics & Intermediate RoutingDokument23 SeitenBN002 Yr2 COMP H2015 Jan08 Semester3 Switching Basics & Intermediate RoutingsextonpppNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Area Networks - InternetworkingDokument41 SeitenLocal Area Networks - InternetworkingSalih AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking BasicsDokument222 SeitenNetworking Basicsceren_can_6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Networking Hardware and TopologiesDokument56 SeitenNetworking Hardware and Topologiesskam zacNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN Practical File - MergedDokument94 SeitenCN Practical File - MergedNoobs RageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network DevicesDokument29 SeitenNetwork Devicesmam monNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 GTU Computer Network Mid Sem Exam PaperDokument14 Seiten5 GTU Computer Network Mid Sem Exam PaperNickHenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router and Gateways)Dokument35 SeitenNetwork Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router and Gateways)Aaizah WaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch10 Connecting DevicesDokument45 SeitenCh10 Connecting DevicesFARISHA NABIHA SYAMSURIZAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Reservation ChartDokument66 SeitenElectronic Reservation Chartasharmasp100% (1)
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Dokument3 SeitenNetwork Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Roxanne EspirituNoch keine Bewertungen
- B48 Exp1 CNDokument7 SeitenB48 Exp1 CNNikhil AherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 10Dokument11 SeitenLecture 1023wingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3Dokument21 SeitenLecture 3usamazebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connecting Devices: 1. RepeaterDokument5 SeitenConnecting Devices: 1. RepeaterAadhya JyothiradityaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument42 SeitenChapter 5Bezabh AbebawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Net Notes (3 Files Merged)Dokument17 SeitenNetwork Net Notes (3 Files Merged)RohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connecting DevicesDokument28 SeitenConnecting DevicesNirmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking Devices Hub Switch Router Modem Bridges Brouters GatewaysDokument6 SeitenNetworking Devices Hub Switch Router Modem Bridges Brouters GatewaysAshleyGeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP 301 - Computer Networking FundamentalsDokument18 SeitenEP 301 - Computer Networking FundamentalsShazul Afizi Zulkiflee100% (1)
- Net+2009CP p04Dokument77 SeitenNet+2009CP p04Nigel RamasawmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NetworkingDokument49 SeitenNetworkingSandeep ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication in Dcs & ScadaDokument21 SeitenCommunication in Dcs & ScadaGiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Devices - PPSXDokument37 SeitenNetwork Devices - PPSXMaricris Bejer LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On CcnaDokument69 SeitenProject Report On Ccnanitin111989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network DevicesDokument33 SeitenNetwork Devicesapi-19739889Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking Individual Assignments: Section:-"A"Dokument9 SeitenComputer Networking Individual Assignments: Section:-"A"Abi DemNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrintDokument11 SeitenPrintJelai AlilioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking Devices Unit 1Dokument40 SeitenNetworking Devices Unit 1amaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Error Detection and Correction (CN)Dokument20 SeitenError Detection and Correction (CN)Smart TechNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 IT Section: 7.1 Network AdministrationDokument16 Seiten7 IT Section: 7.1 Network AdministrationRavi K YaddehigeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 5 - Cabling LAN's and WAN'sDokument2 SeitenMODULE 5 - Cabling LAN's and WAN'sGrecu GianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sequence Diagram BasicDokument4 SeitenSequence Diagram Basicjiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Example of Supercomputer Usage in MalaysiaDokument1 SeiteExample of Supercomputer Usage in Malaysiajiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment (OOSAD)Dokument4 SeitenAssignment (OOSAD)jiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- SupercomputerDokument2 SeitenSupercomputerjiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment (OOSAD)Dokument4 SeitenAssignment (OOSAD)jiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment (OOSAD)Dokument4 SeitenAssignment (OOSAD)jiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network Diagram (OOSAD)Dokument4 SeitenNetwork Diagram (OOSAD)jiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- DNS ExplainedDokument16 SeitenDNS Explainedjiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Proposed Seci DiagramDokument2 SeitenProposed Seci Diagramjiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bell LaPadula ModelDokument8 SeitenBell LaPadula Modeljiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Proposed SeciDokument3 SeitenProposed Secijiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short History of ComputerDokument2 SeitenShort History of Computerjiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Bridge Vs RouterDokument2 SeitenSummary of Bridge Vs Routerjiha2007Noch keine Bewertungen