Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ir 2108
Hochgeladen von
robertofurlancriOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ir 2108
Hochgeladen von
robertofurlancriCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Data Sheet No.
PD60161-R
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
Features
Fully operational to +600V Packages Tolerant to negative transient voltage dV/dt immune 14-Lead SOIC 8-Lead SOIC Gate drive supply range from 10 to 20V IR21084S IR2108S Undervoltage lockout for both channels 3.3V, 5V and 15V input logic compatible 14-Lead PDIP Cross-conduction prevention logic IR21084 Matched propagation delay for both channels High side output in phase with HIN input 8-Lead PDIP Low side output out of phase with LIN input IR2108 Logic and power ground +/- 5V offset. Internal 540ns dead-time, and 2106/2301//2108//2109/2302/2304 Feature Comparison programmable up to 5us with one external RDT resistor (IR21084) CrossInput conduction Lower di/dt gate driver for better Dead-Time Ground Pins Part logic prevention noise immunity logic Available in Lead-Free 2106/2301 COM
Floating channel designed for bootstrap operation
HALF-BRIDGE DRIVER
Description
Programmable 0.54~5 s The IR2108(4)(S) are high voltage, high speed Internal 540ns IN/SD yes power MOSFET and IGBT drivers with depenProgrammable 0.54~5 s dent high and low side referenced output yes Internal 100ns HIN/LIN COM 2304 channels. Proprietary HVIC and latch immune CMOS technologies enable ruggedized monolithic construction. The logic input is compatible with standard CMOS or LSTTL output, down to 3.3V logic. The output drivers feature a high pulse current buffer stage designed for minimum driver cross-conduction. The floating channel can be used to drive an N-channel power MOSFET or IGBT in the high side configuration which operates up to 600 volts.
21064 2108 21084 2109/2302 21094
HIN/LIN
no
none
HIN/LIN
yes
Internal 540ns
VSS/COM COM VSS/COM COM VSS/COM
Typical Connection
up to 600V VCC
VCC
HIN LIN
VB HO VS LO
TO LOAD
HIN LIN COM
up to 600V
IR2108
VCC HIN LIN
HO VCC HIN LIN DT V SS RDT VSS COM LO VB VS
IR21084
TO LOAD
(Refer to Lead Assignments for correct pin configuration). This/These diagram(s) show electrical connections only. Please refer to our Application Notes and DesignTips for proper circuit board layout.
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute maximum ratings indicate sustained limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. All voltage parameters are absolute voltages referenced to COM. The thermal resistance and power dissipation ratings are measured under board mounted and still air conditions.
Symbol
VB VS VHO VCC VLO DT VIN VSS dV S/dt PD
Definition
High side floating absolute voltage High side floating supply offset voltage High side floating output voltage Low side and logic fixed supply voltage Low side output voltage Programmable dead-time pin voltage (IR21084 only) Logic input voltage (HIN & LIN ) Logic ground (IR21084 only) Allowable offset supply voltage transient Package power dissipation @ TA +25C (8 lead PDIP) (8 lead SOIC) (14 lead PDIP) (14 lead SOIC)
Min.
-0.3 VB - 25 VS - 0.3 -0.3 -0.3 VSS - 0.3 VSS - 0.3 VCC - 25 -50
Max.
625 VB + 0.3 VB + 0.3 25 VCC + 0.3 VCC + 0.3 VCC + 0.3 VCC + 0.3 50 1.0 0.625 1.6 1.0 125 200 75 120 150 150 300
Units
V/ns
RthJA
Thermal resistance, junction to ambient
(8 lead PDIP) (8 lead SOIC) (14 lead PDIP) (14 lead SOIC)
C/W
TJ TS TL
Junction temperature Storage temperature Lead temperature (soldering, 10 seconds)
Recommended Operating Conditions
The Input/Output logic timing diagram is shown in figure 1. For proper operation the device should be used within the recommended conditions. The V S and VSS offset rating are tested with all supplies biased at 15V differential.
Symbol
VB VS VHO VCC VLO VIN DT VSS
Definition
High side floating supply absolute voltage High side floating supply offset voltage High side floating output voltage Low side and logic fixed supply voltage Low side output voltage Logic input voltage IR2108 IR21084 Programmable dead-time pin voltage (IR21084 only) Logic ground (IR21084 only)
Min.
VS + 10 Note 1 VS 10 0 COM VSS VSS -5
Max.
VS + 20 600 VB 20 VCC VCC VCC VCC 5
Units
C TA Ambient temperature -40 125 Note 1: Logic operational for VS of -5 to +600V. Logic state held for VS of -5V to -VBS. (Please refer to the Design Tip DT97-3 for more details).
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
Dynamic Electrical Characteristics
VBIAS (VCC, VBS) = 15V, VSS = COM, CL = 1000 pF, TA = 25C, DT = VSS unless otherwise specified.
Symbol
ton toff MT tr tf DT MDT
Definition
Turn-on propagation delay Turn-off propagation delay Delay matching | ton - toff | Turn-on rise time Turn-off fall time Deadtime: LO turn-off to HO turn-on(DTLO-HO) & HO turn-off to LO turn-on (DTHO-LO) Deadtime matching = | DTLO-HO - DTHO-LO |
Min.
400 4
Typ.
220 200 0 150 50 540 5 0 0
Max. Units Test Conditions
300 280 30 220 80 680 6 60 600 usec nsec nsec VS = 0V VS = 0V RDT= 0 RDT = 200k (IR21084) RDT=0 RDT = 200k (IR21084) VS = 0V VS = 0V or 600V
Static Electrical Characteristics
VBIAS (VCC , VBS) = 15V, VSS = COM, DT= VSS and TA = 25C unless otherwise specified. The VIL, VIH and IIN parameters are referenced to VSS/COM and are applicable to the respective input leads: HIN and LIN. The VO, IO and Ron parameters are referenced to COM and are applicable to the respective output leads: HO and LO.
Symbol
VIH VIL VOH VOL ILK IQBS IQCC IIN+ IINVCCUV+ VBSUV+ VCCUVVBSUVVCCUVH VBSUVH IO+ IO-
Definition
Logic 1 input voltage for HIN & logic 0 for LIN Logic 0 input voltage for HIN & logic 1 for LIN High level output voltage, VBIAS - VO Low level output voltage, VO Offset supply leakage current Quiescent V BS supply current Quiescent VCC supply current Logic 1 input bias current Logic 0 input bias current VCC and VBS supply undervoltage positive going threshold VCC and VBS supply undervoltage negative going threshold Hysteresis Output high short circuit pulsed current Output low short circuit pulsed current
Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions
2.9 20 0.4 8.0 7.4 0.3 120 250 0.8 0.3 75 1.0 5 8.9 8.2 0.7 200 350 0.8 1.4 0.6 50 130 1.6 20 2 9.8 9.0 V mA VO = 0V, PW 10 s VO = 15V, PW 10 s A A mA V VCC = 10V to 20V VCC = 10V to 20V IO = 20 mA IO = 20 mA VB = VS = 600V VIN = 0V or 5V VIN = 0V or 5V RDT=0 HIN = 5V, LIN = 0V HIN = 0V, LIN = 5V
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
Functional Block Diagram
VB
2108
HIN
VSS/COM LEVEL SHIFT HV LEVEL SHIFTER PULSE GENERATOR
UV DETECT R PULSE FILTER R S Q
HO
VS
DT
DEADTIME & SHOOT-THROUGH PREVENTION UV DETECT
VCC
+5V
LO
LIN
VSS/COM LEVEL SHIFT
DELAY
COM
VSS
VB
21084
HIN
VSS/COM LEVEL SHIFT HV LEVEL SHIFTER PULSE GENERATOR
UV DETECT R PULSE FILTER R S Q
HO
VS
DT
+5V
DEADTIME & SHOOT-THROUGH PREVENTION UV DETECT
VCC
LO
LIN
VSS/COM LEVEL SHIFT
DELAY
COM
VSS
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
Lead Definitions
Symbol Description
HIN Logic input for high side gate driver output (HO), in phase (referenced to COM for IR2108 and VSS for IR21084) Logic input for low side gate driver output (LO), out of phase (referenced to COM for IR2108 and VSS for IR21084) DT VSS VB HO VS VCC LO COM Programmable dead-time lead, referenced to VSS. (IR21084 only) Logic Ground (21084 only) High side floating supply High side gate driver output High side floating supply return Low side and logic fixed supply Low side gate driver output Low side return
LIN
Lead Assignments
1 2 3 4 VCC HIN LIN COM VB HO VS LO
8
7 6 5
1 2 3 4
VCC HIN LIN COM
VB HO VS LO
8
7 6 5
8 Lead PDIP
8 Lead SOIC
IR2108
IR2108S
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
VCC HIN LIN DT VSS COM LO VB HO VS
14
13 12 11 10 9 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
VCC HIN LIN DT VSS COM LO VB HO VS
14
13 12 11 10 9 8
14 Lead PDIP
14 Lead SOIC
IR21084
www.irf.com
IR21084S
5
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
HIN
LIN
HO
LIN
50% 50%
LO
ton
Figure 1. Input/Output Timing Diagram
tr 90%
toff 90%
tf
LO
10%
10%
50%
50%
HIN
ton tr 90%
HIN LIN
50% 50%
toff 90%
tf
HO
90%
10%
10%
Figure 2. Switching Time Waveform Definitions
HO LO
DT LO-HO 90%
10% DT HO-LO
10% MDT= DT LO-HO - DT
HO-LO
Figure 3. Deadtime Waveform Definitions
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
Turn-on Propagation Delay (ns)
Turn-on Propagation Delay (ns)
500 400 300 200 100 0 -50
T yp.
500 400 300 200 100 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V BIAS Supply Voltage (V) Figure 4B. Turn-on Propagation Delay vs. Supply Voltage
T yp. Max .
Max.
-25
25
50
o
75
100 125
Temperature ( C) Figure 4A. Turn-on Propagation Delay vs. Tem perature
Turn-off Propagation Delay (ns)
Turn-off Propagation Delay (ns)
500 400 300 200 100
Max .
500 400 300 200 100 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V BIAS Supply Voltage (V) Figure 5B. Turn-off Propagation Delay vs. Supply Voltage
Max . T yp.
T yp.
0 -50
-25
25
50
75
100 125
Temperature (oC) Figure 5A. Turn-off Propagation Delay vs.Tem perature
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
500 Turn-on Rise Time (ns) 400 300 200 100
Max .
500 Turn-on Rise Time (ns) 400 300 200
T yp. Max.
T yp.
100 0
0 -50
-25
25
50
75
100 125
10
12
14
16
18
20
Temperature ( oC) Figure 6A.Turn-on Rise Tim e vs. Tem perature
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V) Figure 6B. Turn-on Rise Time vs. Supply Voltage
200 Turn-off Fall Time (ns) 150 100
Max.
200 Turn-off Fall Time (ns) 150 100 50 0
-25 0 25 50
o
Max.
50
T yp.
T yp.
0 -50
75
100 125
10
12
14
16
18
20
Temperature ( C) Figure 7A. Turn-off Fall Tim e vs. Tem perature
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V) Figure 7B. Turn-off Fall Tim e vs. Supply Voltage
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
1000 800
Max.
1000 800 600 400 200
0 25 50 75 100 125
Deadtime (ns)
Deadtime (ns)
Max. T yp.
600
T yp.
Min.
400
Mi n.
200 -50 -25
10
12
14
16
18
20
Temperature (oC) Figure 8A. Deadtim e vs. Tem perature
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V) Figure 8B. Deadtime vs. Supply Voltage
7 6 Deadtime ( s) 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 50 100 RDT (K) Figure 8C. Deadtim e vs. RDT (IR21084 Only) 150 200
T yp. Mi n.
8 7 Input Voltage (V)
Max .
6 5 4 3 2 1 0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Max .
Temperature ( oC) Figure 9A. Logic "1" Input Voltage vs. Tem perature
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
8 7 Input Voltage (V) 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V CC Supply Voltage (V) Figure 9B. Logic "1" Input Voltage vs. Supply Voltage
Max .
4.0 Input Voltage (V) 3.2 2.4 1.6 0.8
Min.
0.0 -50
-25
25
50
75
100 125
Temperature (oC) Figure 10A. Logic "0" Input Voltage vs. Tem perature
Input Voltage (V)
3.2 2.4 1.6 0.8 0.0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V CC Supply Voltage (V) Figure 10B. Logic "0" Input Voltage vs. Supply Voltage
Min.
High Level Output Voltage (V)
4.0
4 3 2 1
Max .
T yp.
0 -50
-25
25
50
o
75
100
125
Temperature ( C) Figure 11A. High Level Output vs. Temperature
10
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
High Level Output Voltage (V)
Low Level Output Voltage (V)
4 3 2 1 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V CC Supply Voltage (V) Figure 11B. High Level Output vs. Supply Voltage
1.5 1.2 0.9 0.6 0.3
T yp.
Max.
Max.
T yp.
0 -50
-25
25
50
o
75
100
125
Temperature ( C) Figure 12A. Low Level Output vs. Temperature
Low Level Output Voltage (V)
1.5 1.2 0.9
Max .
Offset Supply Leakage Current ( A)
500 400 300 200 100
Max .
0.6
T yp.
0.3 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V CC Supply Voltage (V) Figure 12B. Low Level Output vs. Supply Voltage
0 -50
-25
25
50
o
75
100 125
Temperature ( C) Figure 13A. Offset Supply Leakage Current vs. Tem perature
www.irf.com
11
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
Offset Supply Leakage Current ( A)
500 400 300 200 100 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 V B Boost Voltage (V) Figure 13B. Offset Supply Leakage Current vs. Tem perature V BS Supply Current ( A)
400 300 200 100
Max . T yp. Min.
Max .
0 -50
-25
0 25 50 75 Temperature ( oC)
100 125
Figure 14A. V BS Supply Current vs. Tem perature
400
Vcc Supply Current (mA)
3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5
T yp. Max.
V BS Supply Current ( A)
300 200 100 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V BS Supply Voltage (V) Figure 14B. V BS Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
Max. T yp. Min.
1.0 0.5
Min.
0.0 -50
-25
25
50
o
75
100 125
Temperature ( C) Figure 15A. V CC Supply Current vs. Tem perature
12
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
3.0 V CC Supply Current (mA) 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 10 12 14 16 18 V CC Supply Voltage (V) 20
Max . T yp. Min.
60 Logic "1" Input Current ( A) 50 40 30 20 10
Max . T yp.
0 -50
-25
25
50
75
100
125
Temperature ( oC) Figure 16A. Logic "1" Input Current vs. Tem perature
Figure 15B. V CC Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
60 Logic "1" Input Current ( A) 50 40 30 20 10 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V CC Supply Voltage (V) Figure 16B. Logic "1" Input Current vs. Supply Voltage
Max.
5 Logic "0" Input Current ( A) 4 3
Max .
2 1 0 -50
T yp.
-25
25
50
75
100
125
Temperature ( oC) Figure 17A. Logic "0" Input Current vs . Te m pe rature
www.irf.com
13
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
5
V CC UVLO Threshold (+) (V)
12 11 10 9 8 7 -50
Max . T yp.
Logic "0" Input Current ( A)
4 3 2 1 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V CC Supply Voltage (V) Figure 17B. Logic "0" Input Current vs. Supply Voltage
Max.
Mi n.
-25
25
50
75
100
125
Temperature (oC) Figure 18. V CC Undervoltage Threshold (+) vs. Tem perature
11 VCC UVLO Threshold (-) (V) 10 9 8
Mi n. Max.
12 V BS UVLO Threshold (+) (V) 11 10 9 8
Max . T yp.
T yp.
7 6 -50
Min.
-25
25
50
75
100
125
7 -50
-25
25
50
o
75
100
125
Temperature ( oC) Figure 19. V CC Undervoltage Threshold (-) vs. Tem perature
Temperature ( C) Figure 20. V BS Undervoltage Threshold (+) vs. Tem perature
14
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
11 V BS UVLO Threshold (-) (V) 10 9 8
Min. Max . T yp.
500 Output Source Current ( A) 400 300
T yp.
200
Min.
7 6 -50
100 0 -50
-25
25
50
75
100 125
-25
25
50
o
75
100
125
Temperature (oC) Figure 21. V BS Undervoltage Threshold (-) vs. Tem perature
Temperature ( C) Figure 22A. Output Source Current vs. Tem perature
500 Output Source Current ( A) Output Sink Current (mA) 400 300 200 100 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V BIAS Supply Voltage (V) Figure 22B. Output Source Current vs. Supply Voltage
T yp.
600 500
T yp.
400 300 200 100 0 -50
Min.
Min.
-25
25
50
75
100
125
Temperature (oC) Figure 23A. Output Sink Current vs. Tem perature
www.irf.com
15
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
600 500 400 300
T yp.
0 V S Offset Supply Voltage (V) -2 -4 -6 -8 -10
T yp.
Output Sink Current ( A)
200 100 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 V BIAS Supply Voltage (V) Figure 23B. Output Sink Current vs. Supply Voltage
Min.
10
12
14
16
18
20
V BS Flouting Supply Voltage (V) Figure 24. Maxim um V s Negative Offset vs. Supply Voltage
140 120 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz) Figure 25. IR2108 vs. Frequency (IRFBC20), Rgate=33 , V CC=15V
140V 70V 0V
140 120 Temperature (oC) 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz)
Figure 26. IR2108 vs. Frequency (IRFBC30), Rgate =22: , VC C=15V
140V 70V 0V
Temprature (oC)
16
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
140 120 Temperature (oC) 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz) Figure 27. IR2108 vs. Frequency (IRFBC40), Rgate=15 , V CC=15V
140 120 Temperature (oC)
1 40V 70V 0V
1 40V 70V
0V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz) Figure 28. IR2108 vs. Frequency (IRFPE50), Rgate=10 , V CC=15V
140 120 Temperature (oC) 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz) Figure 29. IR21084 vs. Frequency (IRFBC20), Rgate=33 , V CC=15V
140V 70V 0V
140 120 Temperature (oC) 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz) Figure 30. IR21084 vs. Frequency (IRFBC30), Rgate=22 , V CC=15V
1 40V 70V 0V
www.irf.com
17
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
140V
70V
140 120 Temperature (oC)
Temperature (oC)
140 120 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100
100
140V
0V
80 60 40 20 1 10 100
70V 0V
1000
1000
Frequency (KHz) Figure 31. IR21084 vs. Frequency (IRFBC40), Rgate=15 , V CC=15V
Frequency (KHz) Figure 32. IR21084 vs. Frequency (IRFPE50), Rgate=10 , V CC=15V
140 120 Temperature (oC) Temperature (oC) 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz) Figure 33. IR2108S vs. Frequency (IRFBC20), Rgate=33 , V CC=15V
1 40V 70V 0V
140 120
140V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100
70V 0V
1000
Frequency (KHz) Figure 34. IR2108S vs. Frequency (IRFBC30), Rgate=22 , V CC=15V
18
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
140 120 Temperature (oC) 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100
140V70V
140 120 Tempreture (oC)
140V 70V 0V
0V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000
1000
Frequency (KHz) Figure 35. IR2108S vs. Frequency (IRFBC40), Rgate=15 , V CC=15V
Frequency (KHz) Figure 36. IR2108S vs. Frequency (IRFPE50), Rgate=10 , V CC=15V
140 120
140 120 Temperature (oC) 100 80 60 40 20
1 10 100 1000
1 40V 70V 0V
Temperature (oC)
100 80 60 40 20 Frequency (KHz) Figure 37. IR21084S vs. Frequency (IRFBC20), Rgate=33 , V CC=15V
140V 70V 0V
10
100
1000
Frequency (KHz)
Figure 38. IR21084S vs. Frequency (IRFBC30), Rgate =22 , VCC =15V
www.irf.com
19
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
140 Temperature (oC) Temperature (oC) 120 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz) Figure 39. IR21084S vs. Frequency (IRFBC40), Rgate=15 , V CC=15V
1 40V 70V 0V
140 120 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100
140V 70V 0V
1000
Frequency (KHz) Figure 40. IR21084S vs. Frequency (IRFPE50), Rgate=10 , V CC=15V
20
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
Case outlines
8-Lead PDIP
DIM
F OOT PRINT 8X 0.72 [.028]
01-6014 01-3003 01 (MS-001AB)
D A 5
INCHES MIN .0532 .013 .0075 .189 .1497 MAX .0688 .0098 .020 .0098 .1968 .1574
MILLIMETERS MIN 1.35 0.10 0.33 0.19 4.80 3.80 MAX 1.75 0.25 0.51 0.25 5.00 4.00
A b c D
A1 .0040
6 E
5 H 0.25 [.010] A
E
6.46 [.255]
e e1 H K L y
.050 BAS IC .025 BAS IC .2284 .0099 .016 0 .2440 .0196 .050 8
1.27 BAS IC 0.635 BAS IC 5.80 0.25 0.40 0 6.20 0.50 1.27 8
6X
3X 1.27 [.050]
8X 1.78 [.070]
e1
K x 45
C 0.10 [.004]
y 8X c
8X b 0.25 [.010]
NOT ES :
A1 C A B
8X L 7
1. DIMENSIONING & TOLE RANCING PER AS ME Y14.5M-1994. 2. CONT ROLLING DIMENSION: MILLIME TER 3. DIMENSIONS ARE S HOWN IN MILLIMET ERS [INCHE S]. 4. OUTLINE CONFORMS T O JEDEC OUT LINE MS-012AA.
5 DIMENS ION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROT RUS IONS. MOLD PROTRUSIONS NOT T O E XCEED 0.15 [.006]. 6 DIMENS ION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROT RUS IONS. MOLD PROTRUSIONS NOT T O E XCEED 0.25 [.010]. 7 DIMENS ION IS T HE LE NGT H OF LEAD FOR SOLDERING T O A SUBS TRAT E.
8-Lead SOIC
www.irf.com
01-6027 01-0021 11 (MS-012AA)
21
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
14-Lead PDIP
01-6010 01-3002 03 (MS-001AC)
14-Lead SOIC (narrow body)
01-6019 01-3063 00 (MS-012AB)
22
www.irf.com
IR2108(4) (S) & (PbF)
ORDER INFORMATION Basic Part (Non-Lead Free) 8-Lead PDIP IR2108 8-Lead SOIC IR2108S 14-Lead PDIP IR21084 14-Lead SOICIR21084S order order order order IR2108 IR2108S IR21084 IR21084S Lead-Free Part 8-Lead PDIP IR2108 8-Lead SOIC IR2108S 14-Lead PDIP IR21084 14-Lead SOIC IR21084S order order order order IR2108PbF IR2108SPbF IR21084PbF IR21084SPbF
This product has been designed and qualified for the Industrial market. Qualification Standards can be found on IRs Website. Data and specifications subject to change without notice. IR WORLD HEADQUARTERS: 233 Kansas St., El Segundo, California 90245, USA Tel: (310) 252-7105 TAC Fax: (310) 252-7903 Visit us at www.irf.com for sales contact information.09/08/04 www.irf.com 23
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsVon EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2184Dokument24 SeitenIr 2184buiphuoclaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2109Dokument25 SeitenIr 2109Chavi AlmeidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir2181 Igbt Driver PDFDokument21 SeitenIr2181 Igbt Driver PDFismifaizulNoch keine Bewertungen
- High and low side driver data sheet summaryDokument16 SeitenHigh and low side driver data sheet summaryguiknopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features Packages: Data Sheet No. PD60161-PDokument18 SeitenFeatures Packages: Data Sheet No. PD60161-PPafuncio de AlecrimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Half-Bridge Driver (S) : Features Product SummaryDokument9 SeitenHalf-Bridge Driver (S) : Features Product SummaryMahmoued YasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet Summary for Half-Bridge Driver IRS2103(S)PbFDokument14 SeitenData Sheet Summary for Half-Bridge Driver IRS2103(S)PbFViệt LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2101Dokument14 SeitenIr 2101Willard DmpseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2010Dokument17 SeitenIr 2010Naveed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2304Dokument8 SeitenIr 2304Rajo AmehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir2103 DatasheetDokument12 SeitenIr2103 DatasheetToma HaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2104Dokument14 SeitenIr 2104Néstor BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- S2127Dokument21 SeitenS2127RICHIHOTS2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2111Dokument15 SeitenIr 2111Kutsal KaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR2110/IR2113 : High and Low Side Driver SDokument15 SeitenIR2110/IR2113 : High and Low Side Driver SPandu Sandi PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2110Dokument17 SeitenIr 2110Nguyen KhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drive high and low side MOSFETs and IGBTs up to 500V or 600VDokument15 SeitenDrive high and low side MOSFETs and IGBTs up to 500V or 600VPepe ModstNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2213Dokument14 SeitenIr 2213Lampros LampropoulosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir2117 Igbt Driver PDFDokument18 SeitenIr2117 Igbt Driver PDFismifaizulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2127Dokument16 SeitenIr 2127kimonspNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2105Dokument12 SeitenIr 2105Manuel Villegas AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2111Dokument15 SeitenIr 2111Miltongrimi GrimilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Driving Half-Bridges up to 600 VDokument30 SeitenDriving Half-Bridges up to 600 VphieuxuatkhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irs2101 (S) PBF: High and Low Side DriverDokument15 SeitenIrs2101 (S) PBF: High and Low Side Driverdesin01Noch keine Bewertungen
- High and Low Side Driver: Features Product SummaryDokument14 SeitenHigh and Low Side Driver: Features Product SummaryFernando Camargo100% (1)
- Ir 2103Dokument18 SeitenIr 2103Hồ Trung ChíNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAN7382 High-And Low-Side Gate Driver: Features DescriptionDokument15 SeitenFAN7382 High-And Low-Side Gate Driver: Features DescriptionRiza BaduaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Audio Driver With Discrete Dead-Time and ProtectionDokument25 SeitenDigital Audio Driver With Discrete Dead-Time and Protectiongotcha75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Oscillating Half-Bridge Driver: Ir2153 (D) (S) & (PBF)Dokument9 SeitenSelf-Oscillating Half-Bridge Driver: Ir2153 (D) (S) & (PBF)Zoltán HalászNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2153Dokument9 SeitenIr 2153SteveAbonyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2136Dokument36 SeitenIr 2136Viet VietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irs 20965Dokument16 SeitenIrs 20965Eduardo CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2151Dokument6 SeitenIr 2151RintheGreatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir2112 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverDokument17 SeitenIr2112 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverMugahed DammagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features Product Summary: Led Buck Regulator Control IcDokument20 SeitenFeatures Product Summary: Led Buck Regulator Control IcJess AJNoch keine Bewertungen
- cd4066 DatasheetDokument9 Seitencd4066 DatasheetAbubakar SidikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Phase Bridge Driver up to 600V or 1200VDokument12 Seiten3-Phase Bridge Driver up to 600V or 1200VAlex Navas FonsecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir 2153Dokument9 SeitenIr 2153Carlos Marinho SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irs27951s - RESONANT HALF-BRIDGE CONVERTER CONTROL ICDokument29 SeitenIrs27951s - RESONANT HALF-BRIDGE CONVERTER CONTROL ICAnonymous R0s4q9X8Noch keine Bewertungen
- LM358Dokument7 SeitenLM358llollo21Noch keine Bewertungen
- LTC 1661Dokument14 SeitenLTC 1661mneagu123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Features Applications: SBOS141Dokument11 SeitenFeatures Applications: SBOS141eslovenitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Oscillating Half-Bridge Driver Preliminary Data SheetDokument9 SeitenSelf-Oscillating Half-Bridge Driver Preliminary Data Sheetamijoski6051Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fan 7392NDokument18 SeitenFan 7392NKhaleel MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universal DC/DC Converter: (Top View)Dokument11 SeitenUniversal DC/DC Converter: (Top View)Engine Tuning UpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsVon EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (6)
- Digital Power Electronics and ApplicationsVon EverandDigital Power Electronics and ApplicationsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Audio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsVon EverandAudio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorVon Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Switching in Electrical Transmission and Distribution SystemsVon EverandSwitching in Electrical Transmission and Distribution SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesVon EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (7)
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsVon EverandHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Build Your Own Low-Power Transmitters: Projects for the Electronics ExperimenterVon EverandBuild Your Own Low-Power Transmitters: Projects for the Electronics ExperimenterBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- 03.job Specification Instrumentaton PDFDokument27 Seiten03.job Specification Instrumentaton PDFshareyhouNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9853 1239 01 - COP 54 Service Poster - LOWDokument1 Seite9853 1239 01 - COP 54 Service Poster - LOWValourdos LukasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Support Orca3D HelpDokument281 SeitenSupport Orca3D Helplavrik100% (1)
- DMD Documentation Error - Freetronics ForumDokument3 SeitenDMD Documentation Error - Freetronics ForumapofviewNoch keine Bewertungen
- A320 Aircraft CharacteristicsDokument387 SeitenA320 Aircraft CharacteristicsEder LucianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50TJDokument56 Seiten50TJHansen Henry D'souza100% (2)
- Generation of Electrical Energy - B. R. GuptaDokument171 SeitenGeneration of Electrical Energy - B. R. GuptaIbrahim Ahmed43% (23)
- EZ-THUMP™ Series: Portable Fault Location SystemsDokument2 SeitenEZ-THUMP™ Series: Portable Fault Location Systemsriyad abdulhafeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Causes and Prevention of Crowd DisastersDokument10 SeitenThe Causes and Prevention of Crowd DisastersVarun SwaminathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ExamDokument30 SeitenPhysics Examjomar bolasocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Munsell Color Charts and GaugesDokument2 SeitenMunsell Color Charts and GaugesMario DalengkadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme B36.10M-2018Dokument36 SeitenAsme B36.10M-2018امينNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Pressure Vessels With Ellipsoidal HeadsDokument8 SeitenStrength of Pressure Vessels With Ellipsoidal Headsنصرالدين ادريسNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propeller DesignDokument74 SeitenPropeller DesignBambang Teguh Setiawan75% (4)
- 6GK52160BA002AA3 Datasheet en PDFDokument6 Seiten6GK52160BA002AA3 Datasheet en PDFgrace lordiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of A Fluidized Drum GranulatorDokument6 SeitenDesign of A Fluidized Drum GranulatorditchcheNoch keine Bewertungen
- 95 - 737-General-InformationDokument3 Seiten95 - 737-General-InformationffontanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffraction of Laser Beam Using Wire Mesh, Cross Wire and GratingDokument2 SeitenDiffraction of Laser Beam Using Wire Mesh, Cross Wire and GratingPriyesh PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, Uet Lahore Refrigeration and Air Conditioning LaboratoryDokument7 SeitenDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, Uet Lahore Refrigeration and Air Conditioning LaboratoryTauQeer ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium Citrate AUDokument3 SeitenSodium Citrate AUKrishna OgotNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITU ISUP Release Cause CodesDokument5 SeitenITU ISUP Release Cause Codesdelgado08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Online Institute Reporting Slip of The Application Number - 200310422837 PDFDokument1 SeiteOnline Institute Reporting Slip of The Application Number - 200310422837 PDFRohith RohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering Reference BooksDokument2 SeitenCivil Engineering Reference Booksdevbrat boseNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRI 20RS-12-B Data SheetDokument6 SeitenGRI 20RS-12-B Data SheetJMAC SupplyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wire Rope Maintenance enDokument12 SeitenWire Rope Maintenance ensriabolfazlNoch keine Bewertungen
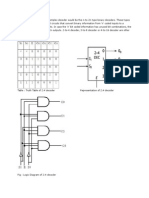
- 2:4 Decoder: DECODER: A Slightly More Complex Decoder Would Be The N-To-2n Type Binary Decoders. These TypesDokument6 Seiten2:4 Decoder: DECODER: A Slightly More Complex Decoder Would Be The N-To-2n Type Binary Decoders. These TypesPavithraRamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osha 1926.452Dokument14 SeitenOsha 1926.452Binoy GopinathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deventer04 MACDokument201 SeitenDeventer04 MACFrancisco Solano Reyes EspinozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manage Safety Changes (MOCDokument5 SeitenManage Safety Changes (MOCWirawan Adi Setya RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixers Towable Concrete Essick EC42S Rev 8 Manual DataId 18822 Version 1Dokument84 SeitenMixers Towable Concrete Essick EC42S Rev 8 Manual DataId 18822 Version 1Masayu MYusoffNoch keine Bewertungen