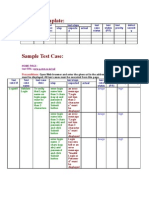
Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Software Test Management
Hochgeladen von
api-3772931Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Software Test Management
Hochgeladen von
api-3772931Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Software Test Management involves planning and monitoring the software
testing efforts at the various life cycle phases or testing levels.
Unit testing is planned and accomplished by the developers.
Integration testing involves testing the combinations of program units and their
interfaces. Integration testing is planned during the design phase and
accomplished with an appropriate balance of developers with design
knowledge and independent testers with minimal design biases.
System testing involves testing the entire system to verify that requirements
are met including specified function, quality, and performance characteristics.
System testing is planned during requirements analysis and accomplished by
independent testers.
Acceptance testing involves testing the system to ensure that it is ready for
delivery and use. Acceptance testing is planned during requirements analysis
and accomplished or witnessed by intended system users.
The effectiveness of the various levels of testing is monitored by collecting
information about the types of defects found and the phase at which the defect
was entered into the software.
Testing coverage is investigated to discern the amount of code exercised and
the requirements tested.
Maintenance and rework of software consumes significant resources in many
organizations. Regression tests are required to ensure that software changes
do not adversely affect the software and cause undesirable side effects.
Efforts to minimize test input efforts by automated means are investigated and
implemented.
Software Test Management also involves controlling the test resources
(testware).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Verification and ValidationDokument22 SeitenVerification and Validationapi-3806986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Regression TestingDokument5 SeitenRegression Testingapi-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal ReportnewdetailvuDokument3 SeitenCrystal Reportnewdetailvuapi-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Testing FundamentalsDokument2 SeitenTesting Fundamentalsapi-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Testing StratagiesDokument3 SeitenTesting Stratagiesapi-3772931100% (1)
- DB - Check ("List1.cdl", "DBVFL") : "Default - XLS"Dokument16 SeitenDB - Check ("List1.cdl", "DBVFL") : "Default - XLS"api-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- VBTipsDokument1 SeiteVBTipsapi-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- DebuggingDokument1 SeiteDebuggingapi-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test Data - Ver 1.0Dokument1 SeiteTest Data - Ver 1.0api-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test Script - Ver 1.0Dokument3 SeitenTest Script - Ver 1.0api-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Traceability Matrix - Ver 1.0Dokument1 SeiteTraceability Matrix - Ver 1.0api-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Software Testing Process and RequirementsDokument3 SeitenSoftware Testing Process and Requirementsapi-3748582Noch keine Bewertungen
- ISOCMM PresentationDokument6 SeitenISOCMM Presentationapi-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Winrunner QtnsDokument10 SeitenWinrunner Qtnsapi-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1) What Is Testing?Dokument20 Seiten1) What Is Testing?api-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Est Case Template:: Home Page: Test URL: WWW - Qatest.co - In/railDokument6 SeitenEst Case Template:: Home Page: Test URL: WWW - Qatest.co - In/railapi-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Testing Qtn&ansDokument4 SeitenBasic Testing Qtn&ansapi-3772931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)