Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DJ Stenting
Hochgeladen von
Edison Kristine Tolentino DangkeoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DJ Stenting
Hochgeladen von
Edison Kristine Tolentino DangkeoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
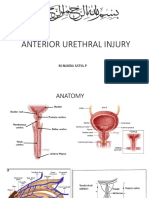
PROCEDURE DEMONSTRATION DJ Stenting
Double-J stents are silicone tubes with a J formed on each end by a fine strand of silicone rubber. While the stent is passed up the ureter, the J hooks are straightened with a wire and when the wire is removed, the J's are formed. Indications for stent use 1. Ureteral injury: a. Cicatricial obstruction (scarring) b. Suture obstruction (adhesions) c. Obstructive edema (hydroureter) 2. External pressure on ureter (e.g. Tumors, impacted feces etc.) 3. Post-operative drainage 4. Retroperitoneal fibrosis 5. Multiple calculi (MOST IMPORTANT INDICATION) Problems and complications during stent drainage 1. Hematuria - usually due to traumatic insertion (maybe early or late complication) 2. Infection - foreign body reaction (late complication) 3. Crystalloid encrustations 4. Reflux 5. Trigonal erosion (due to wrong positioning of distal J of the stent in the bladder) 6. Inadequate drainage (due to encrustations or external obstruction) 7. Stent migration in proximal and distal directions. A DJ stent can be placed for a maximum of 6 months following which it has to be replaced. With time the risk of the above complications esp. infection increases. Measures to be taken a) High fluid intake b) Adjuvant medications, urine acidifiers, antibiotics to increase the solubility of urinary crystalloids. c) Close patient follow-up (control of stent position and patency with pyelogram, cystogram and endoscopically). Retrieval of DJ stents This is well accomplished by the use of: a) A cystoureteroscope with C-arm consult b) A transurethral biopsy forceps
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 25: Trauma: (Also See Chapter 19, Pediatrics)Dokument70 SeitenChapter 25: Trauma: (Also See Chapter 19, Pediatrics)poddataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frontiers of Fluid Mechanics: Proceedings of The Beijing International Conference on Fluid Mechanics, Beijing, People's Republic of China 1—4 July 1987Von EverandFrontiers of Fluid Mechanics: Proceedings of The Beijing International Conference on Fluid Mechanics, Beijing, People's Republic of China 1—4 July 1987Shen YuanBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Trauma de UretraDokument7 SeitenTrauma de UretraJhoel QuellcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erosion in Geomechanics Applied to Dams and LeveesVon EverandErosion in Geomechanics Applied to Dams and LeveesStephane BonelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angga Prasetiyo S.Ked 150611034Dokument43 SeitenAngga Prasetiyo S.Ked 150611034surya gunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Replacement of Double J Stent Without FluorosDokument5 SeitenManual Replacement of Double J Stent Without FluorosqwerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 42 - Orthopedic PrinciplesDokument14 Seiten42 - Orthopedic PrinciplesJeffrey Ariesta PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trauma To The FaceDokument24 SeitenTrauma To The FaceAravind SubhaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparitive Study of Fifty Cases of Open Pyelolithotomy and Ureterolithotomy With or Without Double J Stent InsertionDokument4 SeitenComparitive Study of Fifty Cases of Open Pyelolithotomy and Ureterolithotomy With or Without Double J Stent InsertionSuril VithalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Fixator in Orthopaedics and TraumatologyDokument39 SeitenExternal Fixator in Orthopaedics and TraumatologyAltine Aliyu NuradeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patellar Fracture 1Dokument39 SeitenPatellar Fracture 1Syafiq ShahbudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ureteral Trauma: DR. Sunaryo Hardjowidjoto, dr.,Sp.B.,Sp.UDokument10 SeitenUreteral Trauma: DR. Sunaryo Hardjowidjoto, dr.,Sp.B.,Sp.UIronBladderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medip, ISJ-5905 ODokument7 SeitenMedip, ISJ-5905 OPrasad SrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Successful Retrieval of A Dislodged Zotarolimuseluting Coronary Stent in The Ascending AortaDokument3 SeitenSuccessful Retrieval of A Dislodged Zotarolimuseluting Coronary Stent in The Ascending AortaShira michaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Successful Retrieval of A Dislodged Zotarolimuseluting Coronary Stent in The Ascending AortaDokument3 SeitenSuccessful Retrieval of A Dislodged Zotarolimuseluting Coronary Stent in The Ascending AortaShira michaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Distal Tibial Fractures With Ilizarov Methodology. Maurizio A. CatagniDokument15 SeitenTreatment of Distal Tibial Fractures With Ilizarov Methodology. Maurizio A. CatagniNuno Craveiro LopesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endolymphatic Sacshunt, Labyrinthectomy, Andvestibularnerve Sectioninmeniere'S DiseaseDokument21 SeitenEndolymphatic Sacshunt, Labyrinthectomy, Andvestibularnerve Sectioninmeniere'S Diseasedisk_la_poduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ureteral Stent For Ureteral Stricture: James F. Borin and Elspeth M. McdougallDokument13 SeitenUreteral Stent For Ureteral Stricture: James F. Borin and Elspeth M. McdougallOoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healing of Extraction SocketDokument21 SeitenHealing of Extraction SocketSushant Pandey100% (1)
- Mishaps JIMMYDokument21 SeitenMishaps JIMMYhoho2019kuNoch keine Bewertungen
- T Tube by Daldoul2012Dokument7 SeitenT Tube by Daldoul2012Suhenri SiahaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salivary Glands (3 - SialolithiasisDokument36 SeitenSalivary Glands (3 - SialolithiasisSaleh Ahmed Saleh AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patellar FractureDokument25 SeitenPatellar FractureSyafiq ShahbudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Os Finals ReviewerDokument33 SeitenOs Finals ReviewerGuen ColisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of FracturesDokument59 SeitenComplications of FracturesFathimahAzZahraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HKDJ 0401Dokument4 SeitenHKDJ 0401Yiu Kai WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why When and HowDokument11 SeitenWhy When and Howamrit koiralaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pelvic FracturesDokument32 SeitenPelvic FracturesAgeng BudianantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bladder TraumaDokument3 SeitenBladder TraumaHarris Khan NiaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fractures and DislocationsDokument53 SeitenFractures and Dislocationsagha_sajjad90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spilled Gallstones - Review of The Literature PDFDokument3 SeitenSpilled Gallstones - Review of The Literature PDFZeeshaan Ahmed KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rupture Urethra Anterior DR Sule FixDokument36 SeitenRupture Urethra Anterior DR Sule FixkadinfathiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stump LeakageDokument3 SeitenStump LeakageNuraqila Mohd murshidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sub 15787Dokument6 SeitenSub 15787Yessenia SarabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCNL Consent FormDokument4 SeitenPCNL Consent FormSaisabelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sir 23205Dokument4 SeitenSir 23205ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of Teeth ExtractionDokument13 SeitenComplications of Teeth Extractionfbbqbcht6yNoch keine Bewertungen
- IlizarovDokument16 SeitenIlizarovNanda Gema100% (1)
- Fracture of Both Bone of LEG: AFMG: 46-60Dokument24 SeitenFracture of Both Bone of LEG: AFMG: 46-60Lovesh DagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amputations and Ex ArticulationsDokument24 SeitenAmputations and Ex ArticulationsTesmal FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Falling From The Tightrope: Double Versus Single Tightropes in Patients With Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocations: Technique and ComplicationsDokument6 SeitenFalling From The Tightrope: Double Versus Single Tightropes in Patients With Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocations: Technique and ComplicationsChrysi TsiouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecr2011 C-0318Dokument11 SeitenEcr2011 C-0318zulvaasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giant Bladder Diverticulum Due To Previous Bullet Injury: Findings of Gadolinium-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance ImagingDokument4 SeitenGiant Bladder Diverticulum Due To Previous Bullet Injury: Findings of Gadolinium-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance ImagingIrma Suriani DarwisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Classifications of FracturesDokument33 Seiten1 Classifications of Fracturesرغد شاكر محمود أحمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL (Dokument31 SeitenExtracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL (emirilejlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of ImmobilizationDokument27 SeitenPrinciples of ImmobilizationSivaneasan KandiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- CaseDokument7 SeitenCaseAia JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Infection - Chronic BoneDokument34 Seiten03 Infection - Chronic Boneمحمد عبدالوهابNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fracture CrurisDokument44 SeitenFracture CrurisAnonymous turPUJtErNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary DiversionDokument11 SeitenUrinary Diversionvlad910Noch keine Bewertungen
- (RADIO 250) LEC 08 Introduction To Interventional RadiologyDokument4 Seiten(RADIO 250) LEC 08 Introduction To Interventional RadiologyWilliam PinzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CystotomyDokument34 SeitenCystotomycrazieelorraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 20Dokument14 SeitenChapter 20Syafithria WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of FracturesDokument50 SeitenTypes of FracturesMariah Rosette Sison HandomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complication of FractureDokument79 SeitenComplication of FractureAhmad SyahmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fracture: Suchithra.P.V 1 Year Msc. Nursing College of Nursing AlappuzhaDokument96 SeitenFracture: Suchithra.P.V 1 Year Msc. Nursing College of Nursing AlappuzhaAakash A. AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Encrusted Ureteral Stent Retrieval Using Flexible Ureteroscopy With A Ho Yag LaserDokument5 SeitenEncrusted Ureteral Stent Retrieval Using Flexible Ureteroscopy With A Ho Yag LaserMer UtsavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of FractureDokument80 SeitenIntroduction of Fracturealsead798Noch keine Bewertungen
- SurgeryDokument3 SeitenSurgeryVandra PrinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (32)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (82)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryVon EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (46)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesVon EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1412)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (170)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (8)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)