Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sports Medicine
Hochgeladen von
Shelby HooklynOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sports Medicine
Hochgeladen von
Shelby HooklynCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SPORTS MEDICINE How are sports injuries classified and managed?
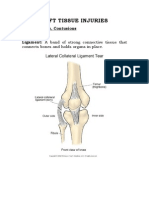
Ways to classify sports injuries Direct and Indirect Direct injuries are caused by direct forces generated from outside the body, result in fractures, dislocations, sprains and bruises. E.g. a dislocated shoulder caused by a tackle in rugby league. Indirect Injuries are caused by an intrinsic force (a force within the body). They are caused by indirect warm up, ballistic movements, excessive movement or a mistake in execution of a skill. Result from excessive strain placed on muscles, tendons and ligaments. May cause damage to body structures. E.g. a sprinter tearing a hamstring during a race. Soft and Hard Tissue Soft tissue injuries include damage to muscle, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, blood vessels, skin, organs and nerves. Either acute or chronic. Acute injuries occur suddenly examples include sprains, strains, dislocations, abrasions, etc. Chronic injuries which are prolonged include the same types of injuries but their severity means long rehabilitation is necessary. Hard tissue injuries cause damage to bones and teeth. Often more serious than soft tissue injuries. Examples include dislodged teeth and broken bones. Fractures are most common. Overuse Overuse injuries are caused by overuse of specific body regions over long periods of time. E.g. shin splints, tendonitis. Contribute to stress fractures.
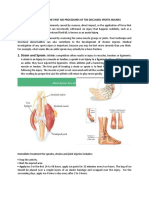
Soft tissue injuries Tears, sprains, contusions A tear occurs when a tissue is excessively stretched or severed. Two types of tear *sprains * strains. A sprain arises from the stretching or tearing or a ligament (connect bone to bone). 3 degrees of sprain. 1st degree = little damage, 2nd degree = moderate damage, 3rd degree = extensive damage. Strains occur when a muscle or tendon is stretched or torn, same levels as sprain (1st, 2nd, 3rd degrees). Contusions are caused by a sudden blow to the body e.g. a bruise. May be close to the skin or penetrate deeply causing bone to bruise. Skin abrasions, lacerations, blisters All are forms of skin trauma. Skin abrasions occur when the player may fall on a dry hard surface. The injury causes pain and shallow bleeding because of the skin being scraped. Treatment requires gentle cleansing and sterilisation top prevent infection. Lacerations are wounds where the flesh has incurred an irregular tear. Care must be taken to prevent infection, must refer to doctor if longer than 1cm. Blisters are caused by a collection of fluid below or within the epidermal layer of the skin, incur intense pain. Caused by new equipment being worn or used, using equipment for a long time and movement with sudden movement causes friction in sport shoe. Inflammatory response when soft tissue is injured it becomes inflamed but responds by activating a self-healing response. This is the inflammatory response, may last up to 3 or 4 days after injury. The injury progresses through phases. Phase 1 Inflammatory stage Pain, redness and swelling of area, loss of mobility, damage to cells, increased blood flow to area, formation of blood vessels to promote healing.
Phase 2 Repair and regenerative stage Elimination of debris, formation of new fibres, production of scar tissue Phase 3 Remodelling stage Increased production of scar tissue and replacement tissue Hard tissue injuries Fractures Either simple or compound. Simple (closed) fractures are when the bone breaks but remains under the skin. Compound (open) fractures are when the bone breaks and protrudes through the skin. Types include greenstick (like a crack), comminuted (broken into parts), depressed (dent of the skull) and oblique (one break). Dislocation Is the displacement of a bone at a joint. Cause deformity, technically a soft tissue injury as the bone although displaced is not damaged. Bone has to be physically reinserted into joint. Symptoms include deformity, swelling, pain, loss of function.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sprain and Strains, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesVon EverandSprain and Strains, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arthur E Chapman-Biomechanical Analysis of Fundamental Human Movements-Human Kinetics (2008) PDFDokument323 SeitenArthur E Chapman-Biomechanical Analysis of Fundamental Human Movements-Human Kinetics (2008) PDFJoao Cunha75% (4)
- 1 Safety Practices in Sports and Exercise PDFDokument44 Seiten1 Safety Practices in Sports and Exercise PDFMark Anthony Nazareth100% (2)
- Pdhpe Sports Medicine HSC NotesDokument18 SeitenPdhpe Sports Medicine HSC Notesamacqueen1230% (3)
- Mythus Character Sheets 002Dokument6 SeitenMythus Character Sheets 002J'uar100% (3)
- Soft Tissue Injuries-2Dokument11 SeitenSoft Tissue Injuries-2api-298014898Noch keine Bewertungen
- SEHS Course OutlineDokument2 SeitenSEHS Course Outlinekevinv10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Book RecomendationsDokument6 SeitenBook RecomendationsAlejandro Martinez100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDokument17 SeitenLesson 1 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseMr. CRAFTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of FractureDokument45 SeitenTypes of Fractureanupama varghese100% (1)
- Fracture PresentationDokument58 SeitenFracture Presentationshejila c hNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sport Injury and ManagementDokument56 SeitenSport Injury and ManagementEva GustianiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report A763319Dokument7 SeitenLab Report A763319David EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recognising and Classifying Injuries 9c Injuries Recognising ClassifyingDokument4 SeitenRecognising and Classifying Injuries 9c Injuries Recognising ClassifyingJake GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 Hazard Biomechanical PDFDokument26 Seiten16 Hazard Biomechanical PDFamirq4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Injury and Overuse Injury.: Classification of Sports InjuriesDokument2 SeitenInjury and Overuse Injury.: Classification of Sports InjuriesVladGrosuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1:concepts of Sports Injury: Mohamad Izzudyn Fariss Bin Mohd HamiziDokument28 SeitenChapter 1:concepts of Sports Injury: Mohamad Izzudyn Fariss Bin Mohd Hamizideepaa gunalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEH Causes of Sports InjuriesDokument7 SeitenPEH Causes of Sports InjuriesFaye TiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2soft Tissue InjuriesDokument11 Seiten2soft Tissue InjurieskevinpoultonNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid - Wound CareDokument18 SeitenFirst Aid - Wound CareKristine BillonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soft Tissue LesionsDokument33 SeitenSoft Tissue Lesionsnimra khaliqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Inuries Soft and HardDokument19 SeitenAssessment of Inuries Soft and HardCaleb FellowesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sports InjuriesDokument2 SeitenSports InjuriesGuwayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fracture: Definition and ClassificationDokument25 SeitenFracture: Definition and ClassificationJacob JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Wound Is A Break in The Continuity of A Tissue of The BodyDokument6 SeitenA Wound Is A Break in The Continuity of A Tissue of The BodyChristine Katherine LibuitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sport InjuriesDokument7 SeitenSport InjuriesChelsea EdwardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ways To Classify Sports Injuries 2Dokument23 SeitenWays To Classify Sports Injuries 2Jereboy Agroup JbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typesofsportsinjuries 150427233008 Conversion Gate01Dokument34 SeitenTypesofsportsinjuries 150427233008 Conversion Gate01Wild RiftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Physiological Reaction To InjuryDokument90 SeitenUnit 2 - Physiological Reaction To InjuryFabian Chapima100% (1)
- Injuries - Forensic Pathology OnlineDokument13 SeitenInjuries - Forensic Pathology OnlinePrashant MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRACTURE First AidDokument15 SeitenFRACTURE First AidAdrian CadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic TraumatologyDokument113 SeitenForensic TraumatologyYasir Latif Chauhdhary100% (1)
- Pe Bblan AssignmentDokument2 SeitenPe Bblan AssignmentOrlando Sanchez RimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FracturesDokument1 SeiteFracturesLarry MarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- P E-ReviewerDokument5 SeitenP E-ReviewerKc SumilhigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open FractureDokument9 SeitenOpen FractureAnnyl LaurelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wijaya Johanes Chendra, DR., SP - OTDokument41 SeitenWijaya Johanes Chendra, DR., SP - OTRiqqah USNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE and HealthDokument3 SeitenPE and HealthRia Ellaine Cornelio LachicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Wounds, Soft Tissue Injuries: ClassificationDokument64 SeitenTypes of Wounds, Soft Tissue Injuries: ClassificationAli ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sports Injury: Organs Through Any Sport Equipment, ActivityDokument9 SeitenSports Injury: Organs Through Any Sport Equipment, Activitywelcome homeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0001.Dokument2 SeitenWa0001.Sumaya NasrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prentice9e Im Chap13Dokument6 SeitenPrentice9e Im Chap13api-281340024100% (1)
- Fracture: Signs and SymptomsDokument6 SeitenFracture: Signs and SymptomsKaran MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jawaban FrakturDokument3 SeitenJawaban FrakturSyipa febri auliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of FracturesDokument50 SeitenClassification of Fracturesmohammad farhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sports InjuriesDokument11 SeitenSports InjuriesShubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soft Tissue InjuriesDokument6 SeitenSoft Tissue InjuriesIshitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHS 512 Lec 01Dokument34 SeitenSHS 512 Lec 01Ayesha ShafiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- FractureDokument4 SeitenFractureCandra P0% (1)
- Hard Tissue Injuries-2Dokument8 SeitenHard Tissue Injuries-2api-298014898Noch keine Bewertungen
- Injury and The Healing ProcessDokument58 SeitenInjury and The Healing ProcessMary Lou San JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson-11-Water SafetyDokument3 SeitenLesson-11-Water SafetyKrystal GailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Athletic Injuries: Task 1 General Vocabulary - QuizDokument3 SeitenUnit 3 Athletic Injuries: Task 1 General Vocabulary - QuizCSbksNoch keine Bewertungen
- SprainDokument2 SeitenSprainFruzsina SomogyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Classifications of FracturesDokument33 Seiten1 Classifications of Fracturesرغد شاكر محمود أحمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid FractureDokument2 SeitenFirst Aid FractureJudea Drizzle BaguidudolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Injuries in ExerciseDokument5 SeitenCommon Injuries in ExercisejinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Injuries Involved in Recreation and First Aid TechniquesDokument20 SeitenCommon Injuries Involved in Recreation and First Aid TechniquesRjay NagilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sports - Injury - Classification 3Dokument36 SeitenSports - Injury - Classification 3zaydawwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Injuries FMTDokument30 SeitenClassification of Injuries FMTkhadzx100% (2)
- Bahaa Motawea. #. & DislocationsDokument51 SeitenBahaa Motawea. #. & DislocationsFathy AlhallagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sports InjuriesDokument18 SeitenSports InjuriesIntan AqilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-The Musculosceletal SystemDokument6 Seiten3-The Musculosceletal SystemEma FröhlichováNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDokument25 Seiten7 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseFirst GhostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Option 3 - Sports MedicineDokument54 SeitenOption 3 - Sports MedicinesshamsalzubaidyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Are You Okay? Sports Injuries: Causes, Types and Treatment - Sports Book 4th Grade | Children's Sports & OutdoorsVon EverandAre You Okay? Sports Injuries: Causes, Types and Treatment - Sports Book 4th Grade | Children's Sports & OutdoorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat GaitDokument32 SeitenReferat GaitAsry WahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPEX 201 Lab 1 - Motion Analysis Techniques - STUDENT - 2023Dokument8 SeitenSPEX 201 Lab 1 - Motion Analysis Techniques - STUDENT - 2023tom mallardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penalty Stroke in Field Hockey A Biomechanical StudyDokument5 SeitenPenalty Stroke in Field Hockey A Biomechanical StudySkunda LagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Berena - Activity 1 in PEHDokument1 SeiteBerena - Activity 1 in PEHMarcus Rhiguel BereñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free English TextbooksDokument50 SeitenFree English TextbooksWENNNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMCH Exam 1 Study GuideDokument14 SeitenBMCH Exam 1 Study Guidemasoud masoudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foot & Ankle Doctor in Delhi, Flat Foot Specialist in Delhi, Hyprocure Specialist in Delhi - DR Abhishek JainDokument1 SeiteFoot & Ankle Doctor in Delhi, Flat Foot Specialist in Delhi, Hyprocure Specialist in Delhi - DR Abhishek JainSatvinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sports Injuries Symptoms & Causes WorksheetDokument3 SeitenSports Injuries Symptoms & Causes WorksheetAlexa :DNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Movable Technological Simulation System For Kinematic Analysis To Provide Immediate Accurate Feedback and Predict Javelin Throw DistanceDokument9 SeitenA Movable Technological Simulation System For Kinematic Analysis To Provide Immediate Accurate Feedback and Predict Javelin Throw DistanceRubigen LaysonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myotonometer GE23M005Dokument5 SeitenMyotonometer GE23M005nurhassen856Noch keine Bewertungen
- SearchOok Results For MechanicDokument30 SeitenSearchOok Results For Mechaniclche0590% (1)
- Basic Biomechanics Hall 7th Edition Test BankDokument14 SeitenBasic Biomechanics Hall 7th Edition Test BankjoelalmayowxuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSIGNMENTDokument6 SeitenASSIGNMENTRùpám KanungoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gait CycleDokument30 SeitenGait Cyclefredrickshein73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Fracture ManagementDokument18 SeitenPrinciples of Fracture ManagementMpanso Ahmad AlhijjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering RapportDokument48 SeitenMechanical Engineering RapportGaurav UpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment and Rehabilitation of Fractures (Stanley Hoppenfeld)Dokument1 SeiteTreatment and Rehabilitation of Fractures (Stanley Hoppenfeld)小蓮花Noch keine Bewertungen
- MPT SyllabusDokument27 SeitenMPT SyllabusvinaymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomechanics NordinDokument1 SeiteBiomechanics NordinKhizar HayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESMC2018 Technical Program Web 0 PDFDokument291 SeitenESMC2018 Technical Program Web 0 PDFSenthilkumar VNoch keine Bewertungen
- What I Have Learned: Suffering A Double Stress FractureDokument5 SeitenWhat I Have Learned: Suffering A Double Stress FractureAshley11 DeCastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomechanics of Kicks in Football Are ViewDokument14 SeitenBiomechanics of Kicks in Football Are ViewAkshat SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomechanics and Muscular-Activity During Sit-to-Stand TransferDokument11 SeitenBiomechanics and Muscular-Activity During Sit-to-Stand TransferAh ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomaterials For Dental Implants: PART II Basic SciencesDokument29 SeitenBiomaterials For Dental Implants: PART II Basic SciencesAna-Maria RoșuNoch keine Bewertungen