Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Steady State Performance Equations of Induction Motor: B Raja Deepak Srinivas.R
Hochgeladen von
v_thomasOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Steady State Performance Equations of Induction Motor: B Raja Deepak Srinivas.R
Hochgeladen von
v_thomasCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
STEADY STATE PERFORMANCE EQUATIONS OF INDUCTION MOTOR
By, RAJA DEEPAK SRINIVAS.R
STEADY STATE PERFORMANCE EQUATIONS OF THE INDUCTION MOTOR
Key variables in the machine are as follows: 1) Air gap power 2) Mechanical and Shaft output power 3) Electromagnetic torque
Real power transmitted from the stator to the air gap is the difference between total input power to the stator windings and copper losses in the stator is given by the eqn
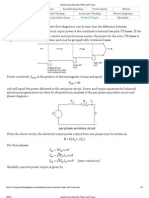
PHASOR DIAGRAM OF THE INDUCTION MOTOR
Neglecting the core losses the air gap power is equal to the total power dissipated as /s in the three phases of the machine. The equation(1) for air gap power is given by
It can also be written as
In the above equation the first term is denoted as rotor copper loss and hence the second term gives the power converted into mechanical form. Rotor copper losses are equal to the product of the slip and air gap power from the equation(1) and this is known as slip power. The mechanical power output is obtained as the equation(3)
Mechanical power output is equal to the electromagnetic torque and rotor speed is given by the equation(4)
where Te is the internal or electromagnetic torque. From the equation(3)
Sub for rotor speed in terms of slip and stator frequency is given by
The electromagnetic or air gap torque is obtained as
The shaft output power of the machine is obtained by subtracting the windage and frictional losses of the rotor from the mechancial output power of the machine. The equation(5) is given by
Friction and windage losses are two distinct and separate losses and these two losses are proportional and square of the speed.They have to be represented as a function of speed for variable speed performance of induction motor.
There are also other losses due to stray magnetic fields in the machine and they are covered by the term stray load losses. The stray load losses may vary from 0.25 to 0.5 percent of the rated machine output.
The stray load losses are obtained from the measurements on the machine under the load from the remainder of the difference between the input power and sum of the losses such as stator and rotor copper losses,friction and windage losses and power output.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Power & TorqueDokument2 SeitenPower & Torquemjh1906893Noch keine Bewertungen
- Losses & Efficiency of Three Phase Induction Motor: Dr. Saif Thamer Al-ZubaidiDokument10 SeitenLosses & Efficiency of Three Phase Induction Motor: Dr. Saif Thamer Al-ZubaididelvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power and Torque in Induction MotorDokument19 SeitenPower and Torque in Induction Motormuhammadarsalank01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Synchronous GeneratorDokument2 SeitenSynchronous GeneratorBrandon LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mesin InduksiDokument40 SeitenMesin InduksiZafid MaulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Equivalent Circuit and Torque of Three-Phase Induction MotorDokument11 SeitenThe Equivalent Circuit and Torque of Three-Phase Induction Motorعمر تاليونNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Power and Torque of Induction MotorDokument30 SeitenPresentation On Power and Torque of Induction MotorNewCandle100% (1)
- Scim Design and PerformanceDokument12 SeitenScim Design and PerformanceLilanda RichardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - V Three Phase Induction Motor DesignDokument14 SeitenUnit - V Three Phase Induction Motor DesignPrema ElizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction Motor (Part 3)Dokument44 SeitenInduction Motor (Part 3)Niha chowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black Box" Model For DC-fed Trains Equipped With VSI Traction Drives and Three-Phase Induction MotorsDokument19 SeitenBlack Box" Model For DC-fed Trains Equipped With VSI Traction Drives and Three-Phase Induction MotorsCPiresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 TransformadorDokument27 Seiten7 TransformadorMarkovic Ávila MartínezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stray Loss Estimation in Induction MotorDokument7 SeitenStray Loss Estimation in Induction MotorIAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Commands For High-Eff Iciency Torque Control of DC Shunt MotorDokument6 SeitenCurrent Commands For High-Eff Iciency Torque Control of DC Shunt Motorcarolain_msNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Armature Reaction On The Performance ofDokument3 SeitenEffect of Armature Reaction On The Performance ofHamood Saqer AbuobaydaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Word - 4 - Induction Machines PDFDokument16 SeitenMicrosoft Word - 4 - Induction Machines PDFMegat Ahmad FaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improved Estimation of Induction Motor Circuit Parameters With Published Motor Performance DataDokument4 SeitenImproved Estimation of Induction Motor Circuit Parameters With Published Motor Performance DataRoberto SuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parameter Estimation of Three Phase Induction Motor An Innovative Approach ThesisDokument58 SeitenParameter Estimation of Three Phase Induction Motor An Innovative Approach ThesisIrfan Ashraf0% (1)
- IM - Motors To GensDokument4 SeitenIM - Motors To Gensmenilanjan89nLNoch keine Bewertungen
- MachinesDokument2 SeitenMachinesShreyas YewaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electic MotorsDokument22 SeitenElectic MotorsAshutosh ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction MotorsDokument47 SeitenInduction MotorsPurushothaman KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 907continuous & Discontinuous Conduction of DC MotorDokument21 Seiten907continuous & Discontinuous Conduction of DC MotorMary Morse0% (1)
- 001 Bien KowskiDokument5 Seiten001 Bien KowskikarnatisharathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Paper2Dokument8 SeitenSeminar Paper2Disha NayarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Motors: RLB EDokument6 SeitenDC Motors: RLB Ehafiz_jaaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design 1Dokument36 SeitenMachine Design 1stanely njogooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Motors: Syllabus Electric Motors: Types, Losses in Induction Motors, Motor Efficiency, Factors AffectingDokument12 SeitenElectric Motors: Syllabus Electric Motors: Types, Losses in Induction Motors, Motor Efficiency, Factors AffectingAjay kunwar singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.efficiency Synch MachinesDokument15 Seiten7.efficiency Synch MachinesJodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 2marksDokument6 SeitenUnit 2 2marksKannan TindivanamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pebn009 Sizing of Electrical Machines PDFDokument2 SeitenPebn009 Sizing of Electrical Machines PDFvishiwizardNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIGURE 3.1 Switched Reluctance Motor Configurations. (A) One Tooth Per Pole. (B) Two Teeth Per Pole (12/10 Poles)Dokument32 SeitenFIGURE 3.1 Switched Reluctance Motor Configurations. (A) One Tooth Per Pole. (B) Two Teeth Per Pole (12/10 Poles)starboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3. Design of 3 Phase Induction MotorDokument43 SeitenModule 3. Design of 3 Phase Induction MotorVivek Pawar83% (6)
- Physical Modeling of PM Synchronous Motors For Integrated Coupling With Machine DrivesDokument4 SeitenPhysical Modeling of PM Synchronous Motors For Integrated Coupling With Machine DrivesMadhu Sudhan MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimum Motor Protection en - LIBRODokument80 SeitenOptimum Motor Protection en - LIBROEdgardo Kat ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec4 Polyphase Induction Motor IIDokument14 SeitenLec4 Polyphase Induction Motor IIMohammed Dyhia AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECEN 441-504: Electronic Motor Drive: Lab 3: Operating Characteristics of The Separately Excited DC MotorDokument6 SeitenECEN 441-504: Electronic Motor Drive: Lab 3: Operating Characteristics of The Separately Excited DC Motorapi-241454978Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Four Weeks) : (Ambala Cantt) Krishan Kumar (11101032)Dokument33 Seiten(Four Weeks) : (Ambala Cantt) Krishan Kumar (11101032)crys suryo prayogo100% (1)
- Efficiency Maps of Electrical MachinesDokument9 SeitenEfficiency Maps of Electrical Machinesmdht1556Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Phase ImDokument43 Seiten3 Phase Imvibhash kumar dwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.0 DC Machine Classification 2Dokument5 Seiten3.0 DC Machine Classification 2Dorothy UdosenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecx3232 Ass3 2010 2011Dokument2 SeitenEcx3232 Ass3 2010 2011tdiddeniyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 226 Electrical Machine-IIDokument99 Seiten226 Electrical Machine-IINuri BerishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Phase Induction MotorDokument23 Seiten3-Phase Induction MotorAshish Verma100% (1)
- Advanced in Control Engineeringand Information ScienceDokument5 SeitenAdvanced in Control Engineeringand Information ScienceLuemba DayzesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2 Electric Motors - Revised (Table Format)Dokument8 Seiten3.2 Electric Motors - Revised (Table Format)Sumit AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Electric Generators and Control: Isha T.BDokument9 SeitenWind Electric Generators and Control: Isha T.BeuginepaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 143-Module VDokument7 SeitenEe 143-Module VDELIZO ARNOLD LEMUEL S.Noch keine Bewertungen
- EM - Solutions To Question Bank 2022-23Dokument53 SeitenEM - Solutions To Question Bank 2022-23Kubera U100% (2)
- Induction motor-UNIT-IVDokument23 SeitenInduction motor-UNIT-IVVaibhav SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume (8) Issue (4) 493-507Dokument15 SeitenVolume (8) Issue (4) 493-507Seid BegovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Modeling and Speed Torque Analysis of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Using Matlab Simulink For Electrical Machines LaboratoryDokument10 SeitenMathematical Modeling and Speed Torque Analysis of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Using Matlab Simulink For Electrical Machines LaboratoryjhonnydesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MoappDokument5 SeitenMoappluanleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersVon EverandVariable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkVon EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesVon EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybrid Systems Based on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Modelling and DesignVon EverandHybrid Systems Based on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Modelling and DesignNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Von EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Centrifugal CompressorsVon EverandDesign and Analysis of Centrifugal CompressorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PGTP Paper FullDokument29 SeitenPGTP Paper FullKantesh DembraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reluktanzmotoren EndDokument16 SeitenReluktanzmotoren EndRamanujam O SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Borderland Research - Vol XLV, No 5, September-October 1989Dokument32 SeitenJournal of Borderland Research - Vol XLV, No 5, September-October 1989Thomas Joseph Brown100% (3)
- Optimal Vector Control ofDokument7 SeitenOptimal Vector Control ofVinay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birds Electrical Circuit Theory and Technology 7Th Edition John O Bird Full ChapterDokument67 SeitenBirds Electrical Circuit Theory and Technology 7Th Edition John O Bird Full Chapterbeverly.bustos487100% (4)
- 943 0019Dokument40 Seiten943 0019Pablo Martir100% (1)
- Heidenhain Motors 938Dokument48 SeitenHeidenhain Motors 938rccarlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCI634H - Winding 311 and 312: Technical Data SheetDokument9 SeitenHCI634H - Winding 311 and 312: Technical Data SheetAlberto AraripeNoch keine Bewertungen
- KUDU Top Tag: Accurate Rotor Placement DeviceDokument1 SeiteKUDU Top Tag: Accurate Rotor Placement DevicePuneet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synchronous MotorDokument33 SeitenSynchronous Motorvnyshreyas100% (2)
- Manual Kohler 5ekd (01 40)Dokument40 SeitenManual Kohler 5ekd (01 40)edgar luis100% (1)
- Brushless ExciterDokument7 SeitenBrushless ExcitervgarudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMUP Electronics V1.5 - With Answers PDFDokument196 SeitenMMUP Electronics V1.5 - With Answers PDFMohammed Faiz MangalasseryNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM734C - Technical Data Sheet Winding 07Dokument6 SeitenPM734C - Technical Data Sheet Winding 07LeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Investigatory PROJECT: Name: Rahul MeenaDokument26 SeitenPhysics Investigatory PROJECT: Name: Rahul MeenaRahul MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selection of Generator For The Micro Hydro Power PlantDokument5 SeitenSelection of Generator For The Micro Hydro Power PlantMuhammad NomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines-IIDokument137 SeitenElectrical Machines-IIgnathbl100% (1)
- Pump XJ - SeriesDokument36 SeitenPump XJ - SeriesFERNANDA ANDRADENoch keine Bewertungen
- EE109XElectrical Machinery Question BankDokument511 SeitenEE109XElectrical Machinery Question BankJaniel Malit100% (1)
- Construction of Synrel MotorDokument18 SeitenConstruction of Synrel MotorAshok Kumar100% (4)
- Smith Turbine Meter 6 Inch Sentry SeriesDokument4 SeitenSmith Turbine Meter 6 Inch Sentry SeriesMuhammad Darussalam HerdaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Phase IMDokument16 Seiten3-Phase IMk rajendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comsol - Guidelines For Modeling Rotating Machines in 3DDokument30 SeitenComsol - Guidelines For Modeling Rotating Machines in 3DtiberiupazaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Fault Diagnostics Based On Current Signatures A ReviewDokument19 SeitenMotor Fault Diagnostics Based On Current Signatures A ReviewBadre BellaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRE BOARD EE (No Solutions)Dokument121 SeitenPRE BOARD EE (No Solutions)John Lloyd Santos0% (1)
- Commutator (DC Machines) 1Dokument29 SeitenCommutator (DC Machines) 1adevirgieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical SectionDokument142 SeitenElectrical Sectionclaudiux78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test Report OM3 - 180L - 4: 22,00 KW: ISO14000 ISO9001Dokument13 SeitenTest Report OM3 - 180L - 4: 22,00 KW: ISO14000 ISO9001Desmon GultomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of 8051 MicrocontrollersDokument23 SeitenApplications of 8051 MicrocontrollersUsama Spiffy100% (1)
- Advanced Motor Starting Analysis ProgramDokument66 SeitenAdvanced Motor Starting Analysis ProgramgilbertomjcNoch keine Bewertungen