Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
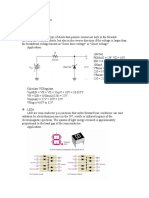
Characteristics of A Varactor Diode
Hochgeladen von
Recardo RamsayOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Characteristics of A Varactor Diode
Hochgeladen von
Recardo RamsayCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Characteristics Of a Varactor Diode
Varactor diodes, also known as varicap diodes, are a simple electronic component. A type of simple semiconductor diode commonly used in electronics such as parametric amplifiers, filters, oscillators and frequency synthesizers, varactor diodes have a variable capacitance, which is a function of the voltage impressed on its terminals. In electronics, varactor diodes are mostly utilized as voltage-controlled capacitors.
Operation
Varactor diodes are constructed in the same way as a capacitor and operate under reverse bias conditions, which gives rise to three currentconducting regions. Currents conduct through positive (P) and negative (N) regions, located at either end of the diode. Near the junction of the P and N regions, a depletion region ensures that no current carriers are available, thus acting as an insulator. Due to this arrangement, a varactor diode's conductive plates are separated by an insulatorlike dielectric, much like a capacitor.
Capacitance
In electronics, capacitance is the ratio of charge impressed on a given conductor. This characteristic determines a diode's frequency of operation. Any capacitor or conductor's capacitance depends on varying factors such as the area of its conductive plates, the dielectric constant of the insulator between the plates and the distance between the two plates. The width of a varactor diode's depletion region increases and decreases via changing the level of the diode's reverse bias. In effect, changing this level alters the distance between the capacitor's plates. As the capacitance range of varactor diodes are controlled by adjusting the gradient and junction width, range changes are applied using reverse voltage. Commonly, varactor diodes operate at a four-to-one capacitance range.
Reverse Breakdown
Varactor diodes are designed to provide voltage-controlled capacitance via operation under reverse bias. A diode's reverse breakdown is defined by the minimum reverse voltage required to make the diode conduct in reverse. As reverse bias increases, capacitance decreases; the maximum voltage that a varactor diode can withstand is determined by its maximum capacitance level. The reverse bias of most varactor diodes operates from around a few volts up to about 20 volts, with some rare exceptions operating up to 60 volts. As a varactor diode's voltage increases, specific energy supplies must be provided for the circuits driving the diode.
a varactor diode or varicap diode is also known as a variable capacitance diode or a
varicap. It provides an electrically controllable capacitance, which can be used in tuned circuits
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Half Wave Rectifier PDFDokument23 SeitenHalf Wave Rectifier PDFArjun SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsVon EverandNonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rs485 GuideDokument140 SeitenRs485 Guidepbhanududi100% (1)
- Name: Chethan Kumar. D USN: 1PI07EC027 Topic: Varactor DiodeDokument19 SeitenName: Chethan Kumar. D USN: 1PI07EC027 Topic: Varactor DiodeVish ShadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor AssignmentDokument9 SeitenVaractor Assignmentjawad_h89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor DiodeDokument8 SeitenVaractor DiodeEva Victoria Ann CarandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: Name: Roll No:: Varactor Diode Abdul Mohiz CS-15-41Dokument21 SeitenTopic: Name: Roll No:: Varactor Diode Abdul Mohiz CS-15-41Ryzza Claire Montes AurinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor DiodeDokument13 SeitenVaractor DiodeRyzza Claire Montes AurinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor DiodeDokument5 SeitenVaractor DiodeSmruti SawantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor DiodeDokument3 SeitenVaractor DiodeKenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Purpose Diodes PDFDokument19 SeitenSpecial Purpose Diodes PDFJhoanna Dacatimbang0% (1)
- VaractorDokument8 SeitenVaractorshwet_vNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor Diodes: Aravind K R & Edwin SebyDokument13 SeitenVaractor Diodes: Aravind K R & Edwin SebyEdwin sebyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor Capacitor & Varactor DiodeDokument9 SeitenVaractor Capacitor & Varactor Diodekjel reida jøssanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Diodes IntroDokument21 SeitenSpecial Diodes Introapi-26100966Noch keine Bewertungen
- Special Purpose DiodesDokument13 SeitenSpecial Purpose DiodesAnoop SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIODES LectureDokument29 SeitenDIODES LecturemunashetakazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Light FinalDokument35 SeitenEmergency Light Finalritesh chauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021MT10892 - Akshat Madhan - ELP Lab Report - Exp 5Dokument8 Seiten2021MT10892 - Akshat Madhan - ELP Lab Report - Exp 5Akshat MadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor DiodeDokument15 SeitenVaractor DiodeOsairas100% (1)
- Transient Voltage SuppressorDokument5 SeitenTransient Voltage SuppressorIim KhotimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power DiodesDokument46 SeitenPower DiodesJay R BallonNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Pavilion G4-G6-G7 Quanta R23 AMD Sabin UMA-Muxless Schematic Diagram 1ADokument14 SeitenHP Pavilion G4-G6-G7 Quanta R23 AMD Sabin UMA-Muxless Schematic Diagram 1AParv PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsDokument20 SeitenPower Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsHassan FrazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components 1. Diode: Semiconductor DiodesDokument8 SeitenComponents 1. Diode: Semiconductor DiodesVaranasi RamakrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 41-44 Lecture Microwave Solid State DevicesDokument61 Seiten41-44 Lecture Microwave Solid State Deviceskumarnpcc0% (3)
- SssssssssDokument23 SeitenSssssssssyohannisyohannis54Noch keine Bewertungen
- PN-junction Diodes and Its ApplicationsDokument37 SeitenPN-junction Diodes and Its ApplicationsRahul sandireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5b Diode - EEDokument90 SeitenChapter 5b Diode - EEHarithZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode SDokument45 SeitenDiode SGanesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3: REGULATORS:Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple FactorDokument12 SeitenUnit-3: REGULATORS:Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple FactorShinde SaikiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode Circuits and Special Purpose Diodes CpEDokument29 SeitenDiode Circuits and Special Purpose Diodes CpEvj hernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode and Its ApplicationsDokument39 SeitenDiode and Its ApplicationsUsama SidhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Purpose DiodesDokument4 SeitenSpecial Purpose DiodeslouiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 4Dokument30 SeitenLec 4muhabamohamed21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Unit IDokument27 SeitenPower Electronics Unit ISatya Sudhakar RasamsettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Power Diode in Power ElectronicsDokument18 SeitenApplication of Power Diode in Power ElectronicsSahale Shera Lutse 18BEE0376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitors: Winkler, Basics of Electricity/Electronics Workshop, p.7Dokument1 SeiteCapacitors: Winkler, Basics of Electricity/Electronics Workshop, p.7sanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edc - 2 Marks With AnswerDokument0 SeitenEdc - 2 Marks With AnswerJoshua DuffyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor: Voltage Current Characteristic Negative Resistance Region OscillatorsDokument2 SeitenVaractor: Voltage Current Characteristic Negative Resistance Region Oscillatorsmohan ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDokument84 SeitenBasic Electronic ComponentsAj RaynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Lecture 2 - RevDokument40 SeitenUnit 1 Lecture 2 - RevMohak KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiments EPLDokument24 SeitenExperiments EPLMonicaSekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Index: Web Space - Website Hosting - Business Hosting - Free Website Submission - Shopping Cart - PHP HostingDokument12 SeitenIndex: Web Space - Website Hosting - Business Hosting - Free Website Submission - Shopping Cart - PHP Hostingcelo81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument32 SeitenChapter 3api-394738731Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deutsch: Register To Download Premium Content!Dokument15 SeitenDeutsch: Register To Download Premium Content!Modesto Marcos Calderon CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency LightDokument12 SeitenEmergency LightEysha qureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Part 2 - DiodeDokument27 SeitenChapter 1 Part 2 - Diodebatrisyia1979Noch keine Bewertungen
- DiodeDokument39 SeitenDiodelim hyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EST 1 Session 1 6Dokument83 SeitenEST 1 Session 1 6ron Joshua QuirapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic CKT RectifierDokument20 SeitenElectronic CKT Rectifieramansumesh2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Schottkey and Pin DiodeDokument28 SeitenSchottkey and Pin DiodeShreya RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode CharacteristicsDokument7 SeitenDiode Characteristicsvimukthi gunasinghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics 2010-2011Dokument68 SeitenPower Electronics 2010-2011Adnan Younus100% (1)
- Basic Analog Electrnics PPT IN PDFDokument67 SeitenBasic Analog Electrnics PPT IN PDFMusa KunrooNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiodeDokument35 SeitenDiodeEdelrose LapitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3::Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple Factor, Full WaveDokument12 SeitenUnit-3::Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple Factor, Full WaveAhsan JalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3::Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple Factor, Full WaveDokument12 SeitenUnit-3::Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple Factor, Full WaveHemant TulsaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3: REGULATORS:Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple FactorDokument12 SeitenUnit-3: REGULATORS:Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple FactorVenkat RajeevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitors: BY: Janaki G. Nair Abhishek GautamDokument14 SeitenCapacitors: BY: Janaki G. Nair Abhishek GautamAbhishek GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dse9150 9130 9155 9255 Data SheetDokument2 SeitenDse9150 9130 9155 9255 Data SheetMohamed Salah Allam100% (1)
- DatasheetDokument1 SeiteDatasheetCalixto Milla EsauNoch keine Bewertungen
- PGF7000Dokument1 SeitePGF7000gphargreavesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Calulation1Dokument1 SeiteBattery Calulation1ma chan wanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT4 (10 Pages)Dokument10 SeitenPT4 (10 Pages)sampath kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSOP382.., TSOP384.., TSOP392.., TSOP394..: Vishay SemiconductorsDokument7 SeitenTSOP382.., TSOP384.., TSOP392.., TSOP394..: Vishay SemiconductorssickdogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Node and Mesh Analysis1Dokument59 SeitenUnit 4 Node and Mesh Analysis1Alerda MaatrixxNoch keine Bewertungen
- No Load Test Report PDFDokument3 SeitenNo Load Test Report PDFYusmin JusohNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2.4.A CircuitCalculationsDokument5 Seiten1.2.4.A CircuitCalculationsCarolay Gabriela Aponte RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AES 301E Basic Electrical and Electronics 2020 2021Dokument2 SeitenAES 301E Basic Electrical and Electronics 2020 2021Cindelle Mariae GomiegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class-12-Physics-Project-On-Full-Wave-Bridge-Rectifier HELLO123Dokument16 SeitenClass-12-Physics-Project-On-Full-Wave-Bridge-Rectifier HELLO123Aryan Budhathoki100% (1)
- Ericsson Krc11822 Tda 2009 TocDokument4 SeitenEricsson Krc11822 Tda 2009 TocEarl LumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Report On Amplitute Modulation: Sanu Kumar Gangwar M.SC Physics 16510072 Sanu - Gangwar@iitgn - Ac.inDokument7 SeitenExperimental Report On Amplitute Modulation: Sanu Kumar Gangwar M.SC Physics 16510072 Sanu - Gangwar@iitgn - Ac.inSanu GangwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Center Computation of A Corrugated Horn PDFDokument10 SeitenPhase Center Computation of A Corrugated Horn PDFwaleed fawwazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase OTDR Coherent DetectionDokument6 SeitenPhase OTDR Coherent DetectiongeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wyard 29Dokument5 SeitenWyard 29deepu4303Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP431A, SC431A, NCP431B, NCP432B Series Programmable Precision ReferencesDokument17 SeitenNCP431A, SC431A, NCP431B, NCP432B Series Programmable Precision ReferencesPedro OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis SheetsDokument12 SeitenThesis Sheetselsa n. calvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Interface ModuleDokument12 SeitenDigital Interface ModuleakramhomriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pioneer Amp Vsx-516 Not Powering Up, Its Not SwitDokument1 SeitePioneer Amp Vsx-516 Not Powering Up, Its Not SwitwilliamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uninterruptible Power Supply System: 5-1. GeneralDokument6 SeitenUninterruptible Power Supply System: 5-1. GeneralRajinikanth RenganathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amplitude Modulation, II: Single Sideband Modulation (SSB) Vestigial Sideband Modulation (VSB)Dokument16 SeitenAmplitude Modulation, II: Single Sideband Modulation (SSB) Vestigial Sideband Modulation (VSB)balkyderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 860 DSPi Manual Section I Chapter 2Dokument3 Seiten860 DSPi Manual Section I Chapter 2trilithicwebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elex - EXPERIMENT 2 .1Dokument8 SeitenElex - EXPERIMENT 2 .1KzenetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ds Bps 700dnc40 12 XG SeriesDokument6 SeitenDs Bps 700dnc40 12 XG Seriesricardogaravito3353Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Hardware ArchitecturesDokument52 SeitenIntroduction To Hardware ArchitecturesUrvashi BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schematic Diagram (Main 1/2) : L CH Power AmpDokument2 SeitenSchematic Diagram (Main 1/2) : L CH Power AmpMiodrag VranjesevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apeapcet2023 2022lastrankdetailsDokument43 SeitenApeapcet2023 2022lastrankdetailsTupakula NarasimharaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haier 2968Dokument50 SeitenHaier 2968Evelyn NaranjoNoch keine Bewertungen