Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Meristematic Tissues2
Hochgeladen von
Aman ChaudharyOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Meristematic Tissues2
Hochgeladen von
Aman ChaudharyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
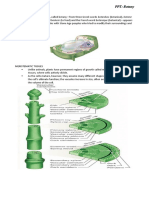
Meristematic Tissues
Meristematic tissues are cells or group oI cells that have the ability to divide. These tissues in a
plant consist oI small, densely packed cells that can keep dividing to Iorm new cells. Meristems
give rise to permanent tissues and have the Iollowing characteristics:
O the cells are small,
O the cells walls are thin,
O cells have large nuclei,
O vacuoles are absent or very small, and
O there are no intercellular spaces.
Meristematic tissues is Iound in the Iollowing 4cati43s:
O near tips oI roots and stems. This is called apical meristems.
O in the buds and nodes oI stems.
O in the cambium between the xylem and phloem in dicotyledonous trees and shrubs.
O under the epidermis oI dicotyledonous trees and shrubs (cork cambium).
O in the pericycle oI roots, producing branch roots.
Types a3/ Fu3cti43 41 Meristematic Tissue
Apica Meristem: Apical meristems are located near the tips oI roots and shoots. A typical
meristem cell is relatively small, cuboid,with a thin cellulose cell walland dense cytoplasmic
contents.When the cell divided by mitosis one cell remain in the neristemwhile the other
increase in size and diIIerentiates to become a part oI the permanent plant body. Apical
meristem is responsible Ior primary growth and thus responsible Ior the increase in length oI the
plant. The apical initials may occur in one or more tiers.
Latera Meristem: Lateral meristems are laterally situated in older parts oI the plant parallel
with the long axis oI the organs. They occur in thin layers. It is responsible Ior secondary growth.
Vascular cambium gives rise to secondary vascular tissue. Phellogen gives rise to the periderm
which replaces the epidermis and includes cork. It is responsible Ior the increase in girth oI the
plants.
I3tercaary Meristems: Intercalary meristems are located between the regions oI permanent
tissue, at the nodes oI many cotyledons, such as at the base oI grass leaves. It allows an increase
oI length. The lateral meristems gives rise to the tissues responsible Ior this thickening oI stems
and roots. The main Iunction oI this type oI meristem is to increase the length oI the organin
which they occur. They are short lived and gradually merge with the surrounding tissues and
become permanent.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Plant Tissue PDFDokument63 SeitenPlant Tissue PDFJitendra Kumar100% (1)
- Plant TissuesDokument32 SeitenPlant TissuesVikneswaran Gunahlan Nesh100% (2)
- Plant & Animal TissueDokument39 SeitenPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- Definition of Plant TissueDokument3 SeitenDefinition of Plant TissueCrash Zerocool67% (3)
- Plant Tissue SystemDokument123 SeitenPlant Tissue SystemAnkit Bansal100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Points To RememberDokument7 SeitenChapter 6 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)Dokument12 SeitenDetailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)suman_das1983100% (7)
- Biology Presentation Class 7Dokument11 SeitenBiology Presentation Class 7binu biju100% (2)
- Plant Anatomy Class 12Dokument63 SeitenPlant Anatomy Class 12Ranjeet Pandey100% (1)
- Meristematic TissuesDokument13 SeitenMeristematic Tissueskripa v k nair100% (1)
- BIOL223-Lab 10Dokument60 SeitenBIOL223-Lab 10chicken friesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meristematic TissuesDokument4 SeitenMeristematic TissuesNur Syiffa RosmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Tissues: Epidermis Ground Tissue Vascular Tissue Biomass Leaves Xylem Phloem Differentiated PhotosynthesisDokument12 SeitenPlant Tissues: Epidermis Ground Tissue Vascular Tissue Biomass Leaves Xylem Phloem Differentiated Photosynthesismurari_sahu100% (1)
- Plant Histology and AnatomyDokument39 SeitenPlant Histology and AnatomyN Madhusudhan50% (2)
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDokument40 SeitenAnatomy of Flowering PlantsChaitali DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Shobhit NirwanDokument15 SeitenAnatomy of Flowering Plants - Shobhit NirwanPrakhar SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Tissue - Study NotesDokument10 SeitenPlant Tissue - Study Notesjjoshin10Noch keine Bewertungen
- TissueDokument2 SeitenTissueMason PeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sa Nka LP: Sankalp EducationDokument3 SeitenSa Nka LP: Sankalp Educationshalini priyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.anatomy of Flowering Plants-FDokument28 Seiten6.anatomy of Flowering Plants-Fshrutianand8915Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Tissue and Anatomy NotesDokument15 SeitenPlant Tissue and Anatomy Noteskhan kashif100% (1)
- Storage - Emulated - 0 - Whatsapp - Media - WhatsApp Documents - NOTES CLASS 9 TISSUESDokument14 SeitenStorage - Emulated - 0 - Whatsapp - Media - WhatsApp Documents - NOTES CLASS 9 TISSUESdubeymaya153Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant PrintsDokument11 SeitenPlant PrintsWARDAH SHOAIBNoch keine Bewertungen
- ROOTSDokument10 SeitenROOTSKaren ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy.. Paper ADokument6 SeitenAnatomy.. Paper ASoha Ch100% (1)
- The Plant Body: Tissues and MeristemDokument11 SeitenThe Plant Body: Tissues and MeristemClarissa CuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Tissues WordDokument5 SeitenPlant Tissues WordJeannie de leonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.meristematic TissuesDokument4 Seiten4.meristematic Tissuesdr.anmolmishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Info Sheets On Plant TissuesDokument6 SeitenInfo Sheets On Plant TissuesjasmineecasttNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Biology Notes Ch06 Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDokument8 Seiten11 Biology Notes Ch06 Anatomy of Flowering PlantsPriyanshu BhadanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes of CH Tissues Class 9Dokument20 SeitenNotes of CH Tissues Class 9PrabhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strucrtures of Plant PartsDokument95 SeitenStrucrtures of Plant Partsfatima100% (1)
- Plant TissueDokument19 SeitenPlant TissueKAMESH .G100% (1)
- Ke L-SciDokument5 SeitenKe L-SciMaricar BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botany Notes 101Dokument7 SeitenBotany Notes 101Ma. Lilian Jem MonteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 June Support and Transport Systems in PlantsDokument25 Seiten8 June Support and Transport Systems in Plantsmaduanekabelo08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tissue - Class 9Dokument9 SeitenTissue - Class 9Rohit Jain100% (1)
- Edu246 Botany 2Dokument8 SeitenEdu246 Botany 2ANNE MARGUERITE BARETENoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsDokument12 SeitenChapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsKeerthana IX-C [370]Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jaringan Tumbuhan Dalam Bahasa InggrisDokument5 SeitenJaringan Tumbuhan Dalam Bahasa InggrisRijal Algifari100% (1)
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Revision NotesDokument72 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Revision Noteschakrabortytrisha.2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- MeristemDokument20 SeitenMeristemMurad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tissues - YTDokument94 SeitenTissues - YTRaima Sharma100% (3)
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDokument3 SeitenAnatomy of Flowering Plantstamalbio7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Tissue and Ground Tissue (Parenchyma Tissue)Dokument39 SeitenPlant Tissue and Ground Tissue (Parenchyma Tissue)Firly GusnitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant TissueDokument8 SeitenPlant Tissueshaardesh84100% (1)
- Biology Plant TissuesDokument10 SeitenBiology Plant TissuesChandrakala K RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Tissues: Quick ReviewDokument7 SeitenChapter 2 Tissues: Quick ReviewPrathmesh NamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio - CH 2 TissuesDokument92 SeitenBio - CH 2 TissuesPagli MonkeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022Dokument31 SeitenPlant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022shalu malaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- TISSUESDokument9 SeitenTISSUEStyrtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.plant TissueDokument3 Seiten7.plant TissueRAVINDRA PRASADNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types Meristem JP MSC Sem-IIDokument7 SeitenTypes Meristem JP MSC Sem-IIYusnaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Biology Notes Ch06 Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDokument8 Seiten11 Biology Notes Ch06 Anatomy of Flowering PlantsSyamala NatarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyDokument4 SeitenPlant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Plant Tissue SystemsDokument2 SeitenPlant Tissue SystemsJohn0% (1)
- Botany - Plant TissuesDokument6 SeitenBotany - Plant TissuesKrianne Chris DimaanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells and A Complete OrganismDokument7 SeitenTissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells and A Complete OrganismErneyann BibeyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant TissuesDokument10 SeitenPlant TissuesAndrea CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biography of MathematiciansDokument5 SeitenBiography of MathematiciansAman Chaudhary100% (1)
- The Green Revolution in IndiaDokument6 SeitenThe Green Revolution in IndiaAman ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vedic MathematicDokument11 SeitenVedic MathematicAman ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affect of Salt Water in Plants GrowthDokument1 SeiteAffect of Salt Water in Plants GrowthAman ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ganga AvataranDokument3 SeitenGanga AvataranAman ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thallophyta and BryophytaDokument1 SeiteThallophyta and BryophytaAman ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biography of HeronDokument7 SeitenBiography of HeronAman ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen