Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Module-2 Lecture #7 & 8 PV Technology (Applied)
Hochgeladen von
9898171006Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Module-2 Lecture #7 & 8 PV Technology (Applied)
Hochgeladen von
9898171006Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Module-2 Lecture #7 & 8 PV Technology (Applied)
Prof. Indrajit Mukhopadhyay Au 2011 indrajit.m@sse.pdpu,ac.in
Solar cell of different generation Processing of Silica to MG-Si and SC-Si
Primary requirement for a solar cell:
Bandgap between 1.1 to 1.7 eV (to absorb Visible spectrum). Direct band gap (Direct photon to exiton) of absorber Consisting of readily available, non-toxic material. Easily reproducible fabrication techniques. Also suitable for large area production. Good PV conversion efficiency. Long-term stability.
Overview of First generation Si- solar cells: It is dominant technology in the commercial production of solar cells, accounting for more than 86% of the solar cell market. Cells are typically made using a crystalline silicon wafer. Consists of a large-area, single layer p-n junction diode. Band gap ~ 1.11 eV
Tradeoffs in First generation Si- solar cells:
Si indirect bandgap material 90% absorption of spectrum requires100 m of Si while only 1 m of GaAs. Larger thickness also demand for higher quality material, generated carrier needs to diffuse longer. Diffusion length should be double of wafer thickness, at least 200 m. Si still is material of choice due to well developed micro-electronics industry
Fabrication technique: Mono (Single) crystalline solar cell: STEP-6: Wafer surface damage removal High degree of damage on wafers by sawing operation 2 problems: (i) bad surface & (ii) defects can lead to wafer fracture
So, about 10-15 m surface is etched by acid/ alkali (later preferred for easy waste disposal) in a chemical bath (temperature & composition controlled)
Thin film Solar cells Highly efficient multi-junction solar cell Concentrated Photovoltaics (CPV)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Photo Voltaic Cell BackupDokument8 SeitenPhoto Voltaic Cell BackupShafaq NigarNoch keine Bewertungen
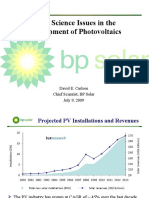
- David Carlson Besac 7 09Dokument23 SeitenDavid Carlson Besac 7 09Abdulhakk AgaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Cell Basics and Future TechnologyDokument37 SeitenSolar Cell Basics and Future TechnologyMuhammad FauzanNoch keine Bewertungen
- احمد ناصر برزنتيشنDokument40 Seitenاحمد ناصر برزنتيشنahmed mahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 5_Fundamentals of solar PV_BMEDokument8 SeitenCHAPTER 5_Fundamentals of solar PV_BMEBIJETA KUNWARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yang 2003Dokument5 SeitenYang 2003Erick Javier Muro MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Photovoltaic Solar Technologies and EfficiencyDokument25 SeitenReview of Photovoltaic Solar Technologies and EfficiencyDhanraj MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defects Impact on Photoelectric ContactsDokument5 SeitenDefects Impact on Photoelectric ContactsСергей ХрипкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class-2&3 Solar PV ModulesDokument59 SeitenClass-2&3 Solar PV ModulesDivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Where Are We Today in y Research in Photovoltaics ?Dokument48 SeitenWhere Are We Today in y Research in Photovoltaics ?sridharkckNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 - Picosecond Laser Patterning For Ultrathin Spectrally Selective Solar Mini Modules With Transparent Metal-Oxide Multilayer ElectrodesDokument6 Seiten2022 - Picosecond Laser Patterning For Ultrathin Spectrally Selective Solar Mini Modules With Transparent Metal-Oxide Multilayer ElectrodesP SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin Film SCDokument6 SeitenThin Film SCalikaya12002Noch keine Bewertungen
- PVT&P 15 Nov 2012Dokument4 SeitenPVT&P 15 Nov 2012Shalini JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bernd Schmid-Solar CellsDokument19 SeitenBernd Schmid-Solar CellsMariya AQ NasutionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nano-Solar Cells: My Anti Fossil Fuel......Dokument20 SeitenNano-Solar Cells: My Anti Fossil Fuel......mula madeen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- History SiDokument1 SeiteHistory SiPutri PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Photovoltaic CellsDokument8 SeitenInorganic Photovoltaic CellsReivax50Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solar CellDokument11 SeitenSolar Cellapi-3808445100% (2)
- Optics Communications: 19%-Efficient and 43 M-Thick Crystalline Si Solar Cell From Layer Transfer Using Porous SiliconDokument1 SeiteOptics Communications: 19%-Efficient and 43 M-Thick Crystalline Si Solar Cell From Layer Transfer Using Porous SiliconPutri PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin Film Solar Cell WikiDokument7 SeitenThin Film Solar Cell Wikivishrao1984Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nano-Solar Cells: My Anti Fossil Fuel......Dokument20 SeitenNano-Solar Cells: My Anti Fossil Fuel......Rajat SethNoch keine Bewertungen
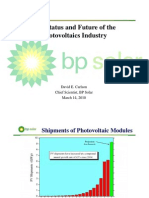
- The Status and Future of The Photovoltaics Industry Photovoltaics IndustryDokument28 SeitenThe Status and Future of The Photovoltaics Industry Photovoltaics IndustryAndyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module2-Solar PV Modules TechnologiesDokument16 SeitenModule2-Solar PV Modules TechnologiesJames K. BitokNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Rystalline and Thin-Film Silicon Solar Cells: State of The Art and Future PotentialDokument12 SeitenC Rystalline and Thin-Film Silicon Solar Cells: State of The Art and Future PotentialRizwan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials:: Thin-Film Technologies Reduce The Amount of ActiveDokument11 SeitenMaterials:: Thin-Film Technologies Reduce The Amount of ActiveParth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin-Film-Silicon Solar Cells: J. Cárabe and J.J. GANDIA CIEMAT, 22 Avda. Complutense, E-28040 Madrid, SpainDokument6 SeitenThin-Film-Silicon Solar Cells: J. Cárabe and J.J. GANDIA CIEMAT, 22 Avda. Complutense, E-28040 Madrid, SpainLong HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wittich2011 SonkusaleVanderveldeDokument1 SeiteWittich2011 SonkusaleVanderveldevishiwizardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Generation Solar CellsDokument4 SeitenSecond Generation Solar CellsAboothahir AfzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar PV Unit 2Dokument101 SeitenSolar PV Unit 2Dhananjay Chandrashekhar KajaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- M2.solar - Part2Dokument49 SeitenM2.solar - Part2shivamjana40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thin Film Solar Cells: A Review: Journal of Information, Knowledge and Research in Electronics and CommunicationDokument3 SeitenThin Film Solar Cells: A Review: Journal of Information, Knowledge and Research in Electronics and CommunicationEndalew kassahunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar 17tiwari PDFDokument0 SeitenSolar 17tiwari PDF928371Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 LectureDokument48 Seiten2 LectureDonavan CheahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin Film Silicon Solar CellDokument41 SeitenThin Film Silicon Solar CellMukesh JindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Cell 1Dokument7 SeitenSolar Cell 1ManishNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN671 Lecture 7 SPV1Dokument20 SeitenEN671 Lecture 7 SPV1percy jacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vincent 09ch043Dokument15 SeitenVincent 09ch043kumaran.DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kosi WorkDokument11 SeitenKosi WorkKermit CloudNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Miro Zeman Delft University of TechnologyDokument46 Seiten4 Miro Zeman Delft University of TechnologyportlandguyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of Solar TechnologyDokument15 SeitenBasic Principles of Solar TechnologykoinsuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Power StationsDokument20 SeitenSolar Power StationsAhmad Al-ThunebatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabrication and Characterization of Highly Efficient Thin-Film Polycrystalline-Silicon Solar Cells Based On Aluminium-Induced CrystallizationDokument5 SeitenFabrication and Characterization of Highly Efficient Thin-Film Polycrystalline-Silicon Solar Cells Based On Aluminium-Induced CrystallizationSarah GloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM ART-CUT@ Techno Logy S 0 1 A New High Volume Application For Ion ImplantationDokument4 SeitenSM ART-CUT@ Techno Logy S 0 1 A New High Volume Application For Ion ImplantationMarco Aurélio DonatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage Electric Current Light Photoelectric EffectDokument15 SeitenVoltage Electric Current Light Photoelectric EffectKool KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dye Solar Cells: Overview of Mechanism, Limitations & SolutionsDokument36 SeitenDye Solar Cells: Overview of Mechanism, Limitations & SolutionsDevendra KhadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pahal Solar PVTDokument21 SeitenPahal Solar PVTPurab PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Generation Solar Cell TypesDokument8 SeitenFirst Generation Solar Cell TypesAan TsaqifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ms. V.Gayathri PDFDokument44 SeitenMs. V.Gayathri PDFAbubakkar SiddiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mse 104 Fall14 Hw5Dokument6 SeitenMse 104 Fall14 Hw5danila007Noch keine Bewertungen
- FP Final DraftDokument9 SeitenFP Final Draftapi-390422023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon Solar Cell TechnologyDokument87 SeitenSilicon Solar Cell TechnologyJack BuzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Causes TransistorDokument4 SeitenThe Effect of Causes TransistoryashasvaagarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - Solar Cell Technology - Overview I: Alan P. MorrisonDokument22 SeitenLecture 3 - Solar Cell Technology - Overview I: Alan P. MorrisonastiChantillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Solar CellsDokument15 SeitenDevelopment of Solar CellsPrithvi HarveNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1016@j Optmat 2019 109433Dokument10 Seiten10 1016@j Optmat 2019 109433khannoussi kamiliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ret PDFDokument14 SeitenRet PDFomkar pubg GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current and Future Photovoltaics: 1G, 2G and 3G TechnologiesDokument17 SeitenCurrent and Future Photovoltaics: 1G, 2G and 3G TechnologiesGowtham SrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Grid: Thin Film Solar CellsDokument5 SeitenSmart Grid: Thin Film Solar CellsSHREYA SHARMA IET Lucknow StudentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallium Nitride-enabled High Frequency and High Efficiency Power ConversionVon EverandGallium Nitride-enabled High Frequency and High Efficiency Power ConversionGaudenzio MeneghessoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wide Band Gap Semiconductor Nanowires 1: Low-Dimensionality Effects and GrowthVon EverandWide Band Gap Semiconductor Nanowires 1: Low-Dimensionality Effects and GrowthVincent ConsonniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Misunderstandings Mar Workplace, by Timothy ChambersDokument2 SeitenMisunderstandings Mar Workplace, by Timothy ChambersTimothy Chambers100% (2)
- Crisis CommunicationDokument5 SeitenCrisis CommunicationArk Group33% (3)
- Partial DerivativeDokument71 SeitenPartial Derivative9898171006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Mesurani Vishal: Analysis of MRF Tyres Advertisement in The Basis of Perceptual Selectivity FrameworkDokument13 SeitenName: Mesurani Vishal: Analysis of MRF Tyres Advertisement in The Basis of Perceptual Selectivity Framework9898171006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matrices: Nishant Parikh School of Petroleum Technology Petroleum University, Gujarat, India Lecture-12 (Part-1)Dokument6 SeitenMatrices: Nishant Parikh School of Petroleum Technology Petroleum University, Gujarat, India Lecture-12 (Part-1)9898171006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial1 MatricesDokument1 SeiteTutorial1 Matrices9898171006Noch keine Bewertungen
- StratigraphyDokument17 SeitenStratigraphy989817100675% (4)