Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 30 Homologous Series of Carbon Compounds
Hochgeladen von
sliversniper0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
26 Ansichten2 SeitenHomologous series are groups of compounds that can be represented by a general formula. The document discusses homologous series of carbon compounds including alkanes, alkenes, alkanols, and alkanoic acids. It provides examples of compounds from each series and asks multiple choice and fill-in-the-blank questions about identifying compounds and determining molecular formulas from structural formulas or experimental data.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
30
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenHomologous series are groups of compounds that can be represented by a general formula. The document discusses homologous series of carbon compounds including alkanes, alkenes, alkanols, and alkanoic acids. It provides examples of compounds from each series and asks multiple choice and fill-in-the-blank questions about identifying compounds and determining molecular formulas from structural formulas or experimental data.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
26 Ansichten2 SeitenChapter 30 Homologous Series of Carbon Compounds
Hochgeladen von
sliversniperHomologous series are groups of compounds that can be represented by a general formula. The document discusses homologous series of carbon compounds including alkanes, alkenes, alkanols, and alkanoic acids. It provides examples of compounds from each series and asks multiple choice and fill-in-the-blank questions about identifying compounds and determining molecular formulas from structural formulas or experimental data.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
98 Part 7
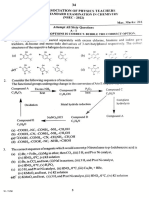
Chapter 30 Homologous Series of Carbon Compounds
A. Multiple Choice Questions 7.98 g
=
1.0 g mol 1
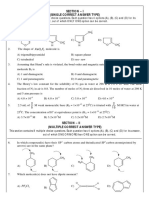
1. B. (1) and (3) only
= 7.98 mol
2. B.
(b) General formula of alkanols:
CnH2n+1OH
Number of moles of H in 1 mole of
CnH2n+1OH = 2n + 1 + 1
7.98 = 2n + 2
3. A. Their general formula is CnH2n+2. n = 2.99 ( 3)
4. A. (1) only Since n = 3, the molecular formula
5. C. They are gases at room temperature of Y is C3H7OH.
and pressure.
6. C. CnH2n+1OH
(c)
7. D. butan-2-ol
8. D. 3,3-Dimethylbutan-2-ol
9. C. 2-Methylpropane
B. Fill in the Blanks
4. (a) 2,2,3-trimethylbutane
1. organic compounds (b) 3,3-dimethylbut-1-ene
2. Structural formula (c) 2,2-dimethylpropanoic acid
3. Hydrocarbons, saturated, unsaturated (d) 2,3-dimethylbut-2-ene
4. functional group (e) 2,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol
(f) 2,3-dimethylbutanoic acid
C. Comprehensive Questions
5. (a)
1. Homologous series is a group of
compounds which can be represented by a
general formula.
2. Alkanes, alkenes, alkanols and alkanoic (b)
acids
3. (a) Mass of 1 mole of Y = 60.0 g
Mass of hydrogen in 1 mole of Y
= 60.0 g 13.3 % (c)
= 7.98 g
Number of moles of hydrogen in 1
mole of Y
Mass of hydrogen in 1 mole of Y
=
Molar mass of H
Chapter 30 Solutions (EE).doc
Chapter 30 99
(d) (f) Molar mass of HX
Mass of HX
=
Number of moles of HX
7.4 g
=
0.10 mol
(e)
= 74.0 g mol1
(g) General formula of alkanoic acids:
CnH2n+1COOH
12.0 (n + 1) + 2n + 2 + 16.0 2
(f) = 74.0
14n + 46.0 = 74.0
14n = 28
n=2
Structual formula of X:
(g) CH3CH2COOH
Name: ethanoic acid
(h)
6. (a) Hydrogen gas
(b) Using a burning splint to test the gas,
it will give a “pop” sound.
(c) 2HX(aq) + Mg(s)
MgX2 + H2(g)
(d) Number of moles of H2
Volume
=
Molar volume
1 200
dm 3
1 000
=
24 dm 3 mol -1
= 0.05 mol
(e) According to the equation, the mole
ratio of HX and H2 = 2 : 1
Number of moles of HX reacted
= 0.05 mol 2
= 0.10 mol
Chapter 30 Solutions (EE).doc
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MHT-CET 2021 Question Paper: 25 September 2021Dokument3 SeitenMHT-CET 2021 Question Paper: 25 September 2021Sank DamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Sci Paper IIDokument7 SeitenChem Sci Paper IIprivateinfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Paper Chem3333333333333333333Dokument1 SeiteSample Paper Chem3333333333333333333maria b chackoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate 2000 CyDokument9 SeitenGate 2000 CyYocobSamandrewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved Gate Papers PDFDokument326 SeitenSolved Gate Papers PDFPreeti Singh100% (3)
- KIITEE Chemistry PaperDokument7 SeitenKIITEE Chemistry PaperPrasan NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Test-1 - MoleDokument2 SeitenClass Test-1 - MoleShashwat PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Review QuestionsDokument2 SeitenChemistry Review QuestionsEMİRCAN İPEKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry QP2Dokument6 SeitenChemistry QP2Jinendra UvarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse Class 12Dokument15 SeitenCbse Class 12ArchitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GT Based On 2018 JEE Paper-1Dokument5 SeitenGT Based On 2018 JEE Paper-1Ravi Kiran KoduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plkno1whcc Chemistry 2122 P1aDokument8 SeitenPlkno1whcc Chemistry 2122 P1aChun Kit LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Chem 5 WorksheetDokument6 SeitenAP Chem 5 WorksheetenesffsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggestion Anwer Scheme PSPM Sem 2 2014Dokument15 SeitenSuggestion Anwer Scheme PSPM Sem 2 2014.....Noch keine Bewertungen
- 04 HT Jee-Pc 14-12-2022Dokument4 Seiten04 HT Jee-Pc 14-12-2022Srinibas DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main 24-06-2022 (Evening) : QuestionsDokument35 SeitenJEE Main 24-06-2022 (Evening) : Questionsychiru540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice+Test+01+Arjuna+ (NEET) + (Chemistry) +-+Practice+Test-01 Arjuna+ (NEET) (Chemistry)Dokument9 SeitenPractice+Test+01+Arjuna+ (NEET) + (Chemistry) +-+Practice+Test-01 Arjuna+ (NEET) (Chemistry)suraj gholapNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOPIC1QuantitativeQ&A PracticeDokument11 SeitenTOPIC1QuantitativeQ&A PracticePreyhunter ?Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 With Ans ChemistryDokument7 SeitenPaper 2 With Ans ChemistryChanikya Naidu GajjarapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number of Atoms in 558.5 Gram Fe (At. Wt. of Fe 55.85 G MolDokument3 SeitenNumber of Atoms in 558.5 Gram Fe (At. Wt. of Fe 55.85 G MolGowri ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 PT Jee-Pc Ce&ie 11-12-2022Dokument4 Seiten09 PT Jee-Pc Ce&ie 11-12-2022Srinibas DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 2 - Test PracticeDokument8 SeitenChem 2 - Test PracticemyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CET Org Chem HydrocarbonsDokument9 SeitenCET Org Chem HydrocarbonsSourabh ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 117 Exam I Summer 2006Dokument2 SeitenCH 117 Exam I Summer 2006smr13Noch keine Bewertungen
- IB CHE P1, TeacherDokument10 SeitenIB CHE P1, TeacherTrương Quốc HuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Chem F5Dokument4 SeitenMS Chem F5Muhamad Aizuddin Abd RazakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDokument6 SeitenTerm-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDarshan NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nsec 2022Dokument13 SeitenNsec 2022Ayushmaan DhanaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Paper 2017Dokument6 SeitenChemistry Paper 2017vishal jassalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-7Dokument8 SeitenBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-7DikshantNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Chemical EquilibriumDokument3 Seiten4 Chemical Equilibriummatty kafwimbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat 8Dokument3 SeitenCat 8Ravi Kiran KoduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gcesoln 6Dokument26 SeitenGcesoln 6api-3734333100% (1)
- Adobe Scan Apr 14, 2023Dokument7 SeitenAdobe Scan Apr 14, 2023shivamgarg1939Noch keine Bewertungen
- S PLE: Answer Any of Two Questions From This Section. Question No 1 Is CompulsoryDokument2 SeitenS PLE: Answer Any of Two Questions From This Section. Question No 1 Is CompulsoryDavid MaranzhyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Exam SL Paper P1 New Material 2016 SyllabusDokument4 SeitenSample Exam SL Paper P1 New Material 2016 SyllabusJota CarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Baulkham Hills Trial Exam With SolutionsDokument24 Seiten2019 Baulkham Hills Trial Exam With SolutionsOzzy PingBoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Super 500 Questions With SolutionsDokument90 SeitenChemistry Super 500 Questions With SolutionsApurv MalviyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: (1) (1) Total 10Dokument2 SeitenAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: (1) (1) Total 10MazlinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical EquilibriumDokument11 SeitenChemical EquilibriumYuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Stereo Isomerism by Mka SirDokument43 SeitenComplete Stereo Isomerism by Mka Sirarryan keshan100% (1)
- 114 Class Test 1 2023 - MEMODokument7 Seiten114 Class Test 1 2023 - MEMOmphenzosinencebaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial SolutionsDokument26 SeitenTutorial SolutionsshubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulae, Equations and Amounts of Substance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPDokument20 SeitenFormulae, Equations and Amounts of Substance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPMuhammad Sameer AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 13 Amount of Substance PPQsDokument49 SeitenYear 13 Amount of Substance PPQsNotes NotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET 2019 Question PaperDokument19 SeitenNEET 2019 Question Paperanunay.mishra4141Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Paper1 Quest With SolDokument20 SeitenChemistry Paper1 Quest With SolDHANUSHTEJ VUNNAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulae, Equations, Amounts of Substance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPDokument19 SeitenFormulae, Equations, Amounts of Substance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPveronica burlacuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Paper1 Quest With AnsDokument15 SeitenChemistry Paper1 Quest With AnsSn PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example Problems For Lecture 15: Umass Boston Chem 115 Spring 2009 Prof. SevianDokument4 SeitenExample Problems For Lecture 15: Umass Boston Chem 115 Spring 2009 Prof. Seviankamal touilebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple ChoiceDokument513 SeitenMultiple ChoiceRaJA ViNoDNoch keine Bewertungen
- KD 1: Hydrocarbon and Crude OilDokument4 SeitenKD 1: Hydrocarbon and Crude OilJocellyn AurelliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Pre Board 1Dokument10 SeitenChemistry Pre Board 1Aadrika DeokatheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mole Concept Full Chapter Practice Sheet - 220627 - 1 - 220627 - 155952Dokument7 SeitenMole Concept Full Chapter Practice Sheet - 220627 - 1 - 220627 - 1559522005anushkasharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Eq DPP 24 Jan 2024Dokument9 SeitenChem Eq DPP 24 Jan 2024adityaat460Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 PDFDokument8 Seiten2010 PDFprakhar vishwakarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2 Thermochemistry Exercise PDFDokument25 SeitenChap 2 Thermochemistry Exercise PDFRanveer Gautam100% (1)
- LPP - 1 - StoichiometryDokument4 SeitenLPP - 1 - StoichiometryAashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Iit-Jee 2009 CHEMISTRY: Paper-I (Code: 06)Dokument21 SeitenSolutions To Iit-Jee 2009 CHEMISTRY: Paper-I (Code: 06)what_the_f22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsVon EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Physics 2006 Paper2 (E)Dokument13 SeitenCE Physics 2006 Paper2 (E)08150815whoimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2005paper 1Dokument16 Seiten2005paper 1sliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2005paper 2Dokument13 Seiten2005paper 2sliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2004 Paper I Marking SchemeDokument12 Seiten2004 Paper I Marking SchemesliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2004paper IIDokument13 Seiten2004paper IIsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2003 Paper IIDokument14 SeitenPhysics 2003 Paper IIapi-26423290Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2004paper IDokument10 Seiten2004paper IsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple-Choice Question 1985 Take G 10 m/s2.: Velocity/msDokument16 SeitenMultiple-Choice Question 1985 Take G 10 m/s2.: Velocity/mssliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2003paper IDokument8 Seiten2003paper IsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2002 Paper 1Dokument20 SeitenPhysics 2002 Paper 1api-3739499100% (2)
- 1 2 3cm 4cm 5cm 6cm CM CM: Multiple-Choice Questions 1986 Take G 10 m/s2Dokument16 Seiten1 2 3cm 4cm 5cm 6cm CM CM: Multiple-Choice Questions 1986 Take G 10 m/s2sliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1985 Physics Paper1 Syl 2Dokument7 Seiten1985 Physics Paper1 Syl 2api-3736914100% (2)
- IOGP S-616 - 2022 - Supp. Specification To API SPEC 5L & ISO 3183 Line PipeDokument187 SeitenIOGP S-616 - 2022 - Supp. Specification To API SPEC 5L & ISO 3183 Line PipeFerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE BT 2019 Solved Question PaperDokument15 SeitenGATE BT 2019 Solved Question PaperXyrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chills General RulesDokument36 SeitenChills General RulesMuthu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solef Hylar PVDFDokument60 SeitenSolef Hylar PVDFribeiro30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Attachment - 1 Document No. 081113B-CL-303-R0 Permissible Elastic Bend Limit Calculation (48in Hassyan Gas Pipeline Location Class 4)Dokument4 SeitenAttachment - 1 Document No. 081113B-CL-303-R0 Permissible Elastic Bend Limit Calculation (48in Hassyan Gas Pipeline Location Class 4)ISRAEL PORTILLONoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 Leaves - The Food Factory of PlantsDokument4 SeitenLesson 2 Leaves - The Food Factory of PlantsRama Nathan0% (2)
- What Is A Pollen AllergyDokument13 SeitenWhat Is A Pollen AllergyHuria MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cold Black FXDokument3 SeitenCold Black FXpankaj chaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abrasive Wear Analysis Using Factorial Experiment DesignDokument6 SeitenAbrasive Wear Analysis Using Factorial Experiment DesignMislav TeskeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capillary Elevation in Capillary TubesDokument2 SeitenCapillary Elevation in Capillary TubesJeffries ThabangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remediation Project 1Dokument26 SeitenRemediation Project 1api-508660724Noch keine Bewertungen
- United States Patent: (21) Appl - No .: 16 / 120, 651Dokument6 SeitenUnited States Patent: (21) Appl - No .: 16 / 120, 651Treerat VacharanukrauhNoch keine Bewertungen
- SilaneCouplingAgents eDokument24 SeitenSilaneCouplingAgents eElisabeth Kurnia Bloom100% (1)
- Electric Arc Furnace SteelmakingDokument55 SeitenElectric Arc Furnace SteelmakingIIT SRININoch keine Bewertungen
- Hasil Uji Emisi Incenerator.2Dokument2 SeitenHasil Uji Emisi Incenerator.2UrlialyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper CodeDokument4 SeitenQuestion Paper CodeBalaji ArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHM 3104 Chemical Thermodynamics: 1) Pn. HayatiDokument8 SeitenCHM 3104 Chemical Thermodynamics: 1) Pn. HayatiFatimah zafirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: SyllabusDokument24 SeitenEnhanced Oil Recovery: SyllabusAkmuhammet MammetjanovNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS MEGAFLOC 515 Revisi OkDokument5 SeitenMSDS MEGAFLOC 515 Revisi OkYafie Al IslamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Physica B: Physics of Condensed MatterDokument29 SeitenAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Physica B: Physics of Condensed MatteryassinebouazziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyro FormulasDokument121 SeitenPyro FormulasMichael Beasley100% (4)
- Ubiquitin-Like CGAS Chain Formation by A Super Enzyme Activates Anti-Phage ResponseDokument43 SeitenUbiquitin-Like CGAS Chain Formation by A Super Enzyme Activates Anti-Phage ResponseGreater K. OYEJOBINoch keine Bewertungen
- Metron Fuel Quality Final PDFDokument67 SeitenMetron Fuel Quality Final PDFpersadanusantara100% (1)
- Reichold, Corrosion Guide 12.15.2010Dokument45 SeitenReichold, Corrosion Guide 12.15.2010Pradeep Srivastava100% (1)
- Full Solution Manual For Chemistry For Changing Times 14Th Edition John W Hill Terry W Mccreary PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDokument34 SeitenFull Solution Manual For Chemistry For Changing Times 14Th Edition John W Hill Terry W Mccreary PDF Docx Full Chapter Chapterseesaw.insearchd8k4100% (15)
- Design For External Pressure-13022018Dokument14 SeitenDesign For External Pressure-13022018Toni100% (1)
- BS en 10222-2 - 2017 PDFDokument32 SeitenBS en 10222-2 - 2017 PDFАртем Титов75% (4)
- Chelidonium Majus PDFDokument40 SeitenChelidonium Majus PDFbhaskarsgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distillation Column Autocad Drawing Design: July 2017Dokument3 SeitenDistillation Column Autocad Drawing Design: July 2017Tera EducativoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci AvogadroDokument3 SeitenSci AvogadroFiona Antoinette BesaNoch keine Bewertungen