Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hw1 Answers
Hochgeladen von
Cheryl GlorOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hw1 Answers
Hochgeladen von
Cheryl GlorCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MasteringPhysics: Assignment Print View
Page 1 of 5
01 - Motion Graphs
Due: 8:00pm on Wednesday, February 1, 2012
Note: To understand how points are awarded, read your instructor's Grading Policy. [Switch to Standard Assignment View]
[ Print ]
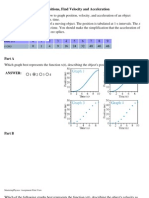
Given Positions, Find Velocity and Acceleration
Learning Goal: To understand how to graph position, velocity, and acceleration of an object starting with a table of positions vs. time. The table shows the x coordinate of a moving object. The position is tabulated at 1-s intervals. The x coordinate is indicated below each time. You should make the simplification that the acceleration of the object is bounded and contains no spikes. time (s) x (m) 0 0 1 1 2 4 3 9 4 16 5 24 6 32 7 40 8 46 9 48
Part A Which graph best represents the function x(t), describing the object's position vs. time?
ANSWER:
1 2 3 4 Correct
Part B Which of the following graphs best represents the function v(t), describing the object's velocity as a function of time?
Hint B.1
Compute and plot the average velocity
Hint not displayed
Hint B.2
Finding the position from the velocity graph
Hint not displayed
Hint B.3
Implications of zero velocity
Hint not displayed
Hint B.4
Characteristics of the velocity function
Hint not displayed
ANSWER:
http://session.masteringphysics.com/myct/assignmentPrintView?assignmentID=1737843
4/16/2012
MasteringPhysics: Assignment Print View
Page 2 of 5
1 2 3 4 Correct Part C Which of the following graphs best represents the function a(t), describing the acceleration of this object? [ Print ]
Hint C.1
Identify the region of constant velocity
Hint not displayed
Hint C.2
Acceleration in the region of constant velocity
Hint not displayed
Hint C.3
Regions of constant acceleration
Hint not displayed
ANSWER:
1 2 3 4 Correct
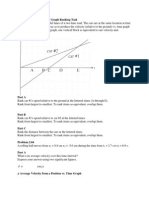
Average Velocity from a Position vs. Time Graph
Learning Goal: To learn to read and interpolate on a graph of position versus time and to change units. In this problem you must find the average velocity from a graph of to indicate the average velocity over the time interval from average velocity over the time interval from 1 to 3 s. . We will use the notation to . Thus is the
Part A Find the average velocity over the time interval from 0 to 1 second. Hint A.1 Definition of average velocity
Hint not displayed
Answer to the nearest integer.
http://session.masteringphysics.com/myct/assignmentPrintView?assignmentID=1737843
4/16/2012
MasteringPhysics: Assignment Print View
Page 3 of 5
ANSWER:
= 0
Correct [ Print ]
Part B Find the average velocity over the time interval from 1 to 3 seconds. Answer to the nearest integer. ANSWER: = 20 Correct
Part C Now that you have and , find .
Give your answer to three significant figures. ANSWER: = 13.3 Correct is not equal to the simple arithmetic average of and , because they are averages for time intervals of different
Note that
length. You would have to double the weight given to
because it is for an interval twice as long.
Part D Find the average velocity over the time interval from 1 to 5 seconds. You will need to interpolate to find the position at time the position or you will likely not be able to obtain the solution to the desired accuracy. Hint D.1 How to interpolate
because the graph is clearly not at one of the horizontal lines (or midway in between). The best way to and and has easy to read values at these times, then use a bit of algebra (or geometry).
. Do not simply eyeball
The most difficult thing here is reading the position at proceed is to note that the graph is straight between Find the position at .
Hint D.1.1
Formula for interpolation
and is 40 . Because the position vs. time graph is linear, at . Mathematically, then: (one-third of the time between
The difference in position between and
) the position will have changed by one-third of the total 40
Round your answer to three significant figures. ANSWER: =
Answer not displayed
Round your answer to two significant figures. ANSWER: = 6.7 Correct
Part E Obtaining this answer required some interpolation on the graph. Now see if you can express this result in terms of kilometers per hour. Hint E.1 Simple method to change units
Hint not displayed
Hint E.2
What other conversion to use
Hint not displayed
Express your answer to the nearest integer. ANSWER: = 24 Correct
Part F Find the average velocity over the time interval from 2.5 to 6.0 seconds. Hint F.1 Determining the displacement
What is the displacement?
http://session.masteringphysics.com/myct/assignmentPrintView?assignmentID=1737843
4/16/2012
MasteringPhysics: Assignment Print View
Page 4 of 5
Answer to the nearest integer. ANSWER: = -30 Correct Determining the time interval
Hint not displayed
[ Print ]
Hint F.2
Express your answer to two significant figures. ANSWER: = -8.6 Correct
Motion of Two Rockets
Learning Goal: To learn to use images of an object in motion to determine velocity and acceleration. Two toy rockets are traveling in the same direction (taken to be the x axis). A diagram is shown of a time-exposure image where a stroboscope has illuminated the rockets at the uniform time intervals indicated.
Part A At what time(s) do the rockets have the same velocity? Hint A.1 How to determine the velocity
Hint not displayed
ANSWER:
at time at time at times
only only and and
at some instant in time between
at no time shown in the figure Correct Part B At what time(s) do the rockets have the same x position? ANSWER: at time at time at times only only and and
at some instant in time between
at no time shown in the figure Correct Part C At what time(s) do the two rockets have the same acceleration? Hint C.1 How to determine the acceleration
http://session.masteringphysics.com/myct/assignmentPrintView?assignmentID=1737843
4/16/2012
MasteringPhysics: Assignment Print View
Page 5 of 5
Hint not displayed
ANSWER:
at time at time at times
only only and and
[ Print ]
at some instant in time between
at no time shown in the figure Correct Part D The motion of the rocket labeled A is an example of motion with uniform (i.e., constant) __________. ANSWER: and nonzero acceleration velocity displacement time Correct Part E The motion of the rocket labeled B is an example of motion with uniform (i.e., constant) __________. ANSWER: and nonzero acceleration velocity displacement time Correct Part F At what time(s) is rocket A ahead of rocket B? Hint F.1 Use the diagram
Hint not displayed
ANSWER:
before after before between
only only and after and
at no time(s) shown in the figure Correct
Score Summary:
Your score on this assignment is 93.1%. You received 27.92 out of a possible total of 30 points.
http://session.masteringphysics.com/myct/assignmentPrintView?assignmentID=1737843
4/16/2012
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (10)
- MP2 DDDokument30 SeitenMP2 DDabeck171344% (9)
- Assignment Mastering PhysicsDokument3 SeitenAssignment Mastering PhysicsreikashinomoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Skill BuildingDokument26 SeitenChapter 2 Skill BuildingSmartGuiye67% (3)
- HWCH 2Dokument7 SeitenHWCH 2abdghfarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP1 WWWDokument16 SeitenMP1 WWWabeck1713Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mastering Physics 2009Dokument6 SeitenMastering Physics 2009ToscaVerdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Skill BuildingDokument21 SeitenChapter 3 Skill BuildingCandice Francois100% (1)
- Mastering Physics 2009Dokument6 SeitenMastering Physics 2009ZixiangLimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastering Physics 2Dokument12 SeitenMastering Physics 2ozilla_26_me80% (5)
- Formal Homework Assignment 3Dokument31 SeitenFormal Homework Assignment 3mhm000666100% (7)
- Formal Homework Assignment 1 - This Assignment, and Other "Formal Homework Assignment"s, Are Graded.Dokument24 SeitenFormal Homework Assignment 1 - This Assignment, and Other "Formal Homework Assignment"s, Are Graded.mhm000666100% (5)
- Chapter 13 Skill BuildingDokument26 SeitenChapter 13 Skill BuildingNKHICQ1mEbIwNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Module 6 q1 General Physics 1Dokument28 Seiten6 Module 6 q1 General Physics 1romel jerichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Projectile Motion: Chapter 3Dokument15 SeitenIntroduction To Projectile Motion: Chapter 3Sebastian Villamizar GarcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Homework Assignment 2Dokument31 SeitenFormal Homework Assignment 2mhm000666100% (13)
- 1.1-1.6 HWDokument14 Seiten1.1-1.6 HWADVITH CHEGUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab-Analysis of Projectile MotionDokument16 SeitenLab-Analysis of Projectile MotionSouvik GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Kinematics Workbook: AP Physics CDokument57 SeitenUnit 1 Kinematics Workbook: AP Physics CNarendra Kumar0% (1)
- Chapter 01 HomeworkDokument15 SeitenChapter 01 HomeworkFatboy91100% (5)
- MP3 FFDokument20 SeitenMP3 FFabeck1713100% (2)
- Masteringphys 13Dokument22 SeitenMasteringphys 13CarlosGomez25% (4)
- MasteringPhysics Answers SOLUTIONSDokument139 SeitenMasteringPhysics Answers SOLUTIONSgdfeiu dionwdn0% (1)
- Chapter 12 Homework: Due: 9:00am On Wednesday, November 11, 2009Dokument8 SeitenChapter 12 Homework: Due: 9:00am On Wednesday, November 11, 2009Chun Ming IpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report-MOTION IN 1D-PART IIDokument12 SeitenReport-MOTION IN 1D-PART IILabrepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematic Vocabulary: DiagnosticsDokument16 SeitenKinematic Vocabulary: DiagnosticsSebastian Villamizar GarcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastering PhysicsDokument10 SeitenMastering Physicsozilla_26_me100% (1)
- HW1 Mastering PhysicsDokument16 SeitenHW1 Mastering Physicszmontgom183% (6)
- PC1431 Assignment 1 AnswersDokument30 SeitenPC1431 Assignment 1 AnswersMikael Lee88% (8)
- Taller de Autoaprendizaje No 1aDokument12 SeitenTaller de Autoaprendizaje No 1ah gNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International As and A Level Physics Revision Guide Cambridge Education Cambridge Uni SamplesDokument5 SeitenCambridge International As and A Level Physics Revision Guide Cambridge Education Cambridge Uni SamplesNalaka Abeysekera50% (6)
- Yb 1507 Phy 0012Dokument4 SeitenYb 1507 Phy 0012Magesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Fall Experiment: Short DescriptionDokument3 SeitenFree Fall Experiment: Short Descriptionjeffrey luis guyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 71 Notes - FinalsDokument21 SeitenPhysics 71 Notes - FinalsCris Reven GibagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 03 HWDokument36 SeitenCH 03 HWClayton KwokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphing Motion Worksheet2Dokument4 SeitenGraphing Motion Worksheet2KIKINoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 KinematicsDokument39 Seiten2 Kinematicsxxhkkfm69xNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch3 SolutionsDokument15 Seitench3 Solutionsizel valerianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CalculusVolume1 SASG 01 04Dokument7 SeitenCalculusVolume1 SASG 01 04Junior PortilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Verification of Assignment Briefs: Evaluation Criteria or 1 Draft Final BriefDokument8 SeitenInternal Verification of Assignment Briefs: Evaluation Criteria or 1 Draft Final BriefOsama HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLM General Physics 1 3rdWk PDFDokument24 SeitenSLM General Physics 1 3rdWk PDFKrestel Faith CabalfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics PracticalsDokument17 SeitenKinematics PracticalsJennifer MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW1 Mastering PhysicsDokument16 SeitenHW1 Mastering PhysicsdominicNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Physics ISP MechanicsDokument41 SeitenAs Physics ISP Mechanicsnazran68Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ugular Adv Mechanics AppendixDokument57 SeitenUgular Adv Mechanics AppendixFiras DiknashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test 14-Mathematical AptitudeDokument12 SeitenPractice Test 14-Mathematical AptituderajatguptNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masteringphys 14Dokument20 SeitenMasteringphys 14CarlosGomez0% (3)
- Internal Verification of Assignment BR Iefs: Evaluation Criteria 1 Draft Final BriefDokument12 SeitenInternal Verification of Assignment BR Iefs: Evaluation Criteria 1 Draft Final BriefOsama HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBADokument10 SeitenPBAsamjshahNoch keine Bewertungen
- WTFDokument6 SeitenWTFDerek BowermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masteringphysics 13 - WithANSDokument19 SeitenMasteringphysics 13 - WithANSgdfeiu dionwdnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 02 Kinematics PDFDokument30 SeitenUnit 02 Kinematics PDFAgness CheweNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics Week 2Dokument10 SeitenGeneral Physics Week 2Velasco, Josiah M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elliott Wave Timing Beyond Ordinary Fibonacci MethodsVon EverandElliott Wave Timing Beyond Ordinary Fibonacci MethodsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (21)
- ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics: Wei-Chih WangDokument86 SeitenME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics: Wei-Chih WanggNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 1 Lesson-8.1Dokument37 SeitenGeneral Physics 1 Lesson-8.1Anjanette RiparipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bouncing Balls Gcse CourseworkDokument5 SeitenBouncing Balls Gcse Courseworkrhpvslnfg100% (2)
- 14Dokument97 Seiten14physicsdocs95% (19)
- Science 9compiled SIPACKS Fourth QuarterDokument73 SeitenScience 9compiled SIPACKS Fourth QuarterB03 - Lapuz UmbrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understeer and OversteerDokument12 SeitenUndersteer and OversteerMuhamad Nur Issam100% (1)
- 7 Physics Nos. 162-232Dokument69 Seiten7 Physics Nos. 162-232Cherry-Ann C. OlajayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force and Motion - Summative TestDokument2 SeitenForce and Motion - Summative TestAiza Conchada100% (2)
- Class Ix Physics Worksheet 4 Work&Energy 2018-19Dokument1 SeiteClass Ix Physics Worksheet 4 Work&Energy 2018-19James KMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling of 2-DOF Robot Arm and ControlDokument13 SeitenModeling of 2-DOF Robot Arm and ControlMourad KattassNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS. Physics NotesDokument141 SeitenCS. Physics NotesOmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compare and Contrast The Aristotelian and GalileanDokument18 SeitenCompare and Contrast The Aristotelian and GalileanReuben John Abalayan83% (6)
- May 2-DLPDokument3 SeitenMay 2-DLPAndrea Jarani LinezoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Physics Assignment 2Dokument4 Seiten11 Physics Assignment 2kaurbatthmandeep80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Science LAS PDFDokument123 SeitenGrade 8 Science LAS PDFRam Candelaria60% (10)
- HOW TO Design A Pump System PDFDokument17 SeitenHOW TO Design A Pump System PDFwidhihartantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IAL Physics FAMXQ Unit 1 Part 1Dokument101 SeitenIAL Physics FAMXQ Unit 1 Part 1Will AndyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Related Rates - ProblemsDokument10 SeitenRelated Rates - ProblemsLenard MerlinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air-Jet Weft Insertion System Part 2Dokument11 SeitenAir-Jet Weft Insertion System Part 2Neeraj BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tut 1Dokument2 SeitenTut 1muhammadmusakhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- District Unified Summative Test in Science 7Dokument2 SeitenDistrict Unified Summative Test in Science 7Mariejoy Vargas Adlawan-SartigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: Pearson EdexcelDokument22 SeitenPhysics: Pearson EdexcelmiltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 JC1 H2 PH BT P2 Question SolutionDokument17 Seiten2014 JC1 H2 PH BT P2 Question Solutionshakthee sivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Analysis of An Evaporator Using ChemcadDokument5 SeitenVibration Analysis of An Evaporator Using ChemcadIJIERT-International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Motion (2) : Experiment - The "Ping-Pong" PistolDokument8 SeitenProjectile Motion (2) : Experiment - The "Ping-Pong" PistolperumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Math NotesDokument67 SeitenApplied Math NotesUgo Buslacchi100% (1)
- SND K ChrsDokument6 SeitenSND K ChrsJustine Laurence VicenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Dynamics-Newton's 1st LawDokument2 Seiten07 Dynamics-Newton's 1st LaweltytanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Api RP 11LDokument10 SeitenApi RP 11LAlberto J Salcedo MNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCELERATION NotesDokument3 SeitenACCELERATION Notes03sylphNoch keine Bewertungen