Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Biology Class 5
Hochgeladen von
Jon Williams0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten2 SeitenComplete Notes from Biology 1 (2007)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenComplete Notes from Biology 1 (2007)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten2 SeitenBiology Class 5
Hochgeladen von
Jon WilliamsComplete Notes from Biology 1 (2007)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
“Cell Surface and Cytoskeleton”_ Biology 5th Class
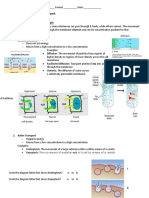
A. Cell Membrane Structure
Cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with mobile proteins.
Types of membrane proteins
• Transport Proteins – move substances across membrane
• Cell Surface Proteins – establish “self”
• Cellular Adhesion Molecules (CAMs) – enable cells to stick
together
• Receptor Proteins – transmit messages into a cell
B. Movement across Membranes (selectively permeable)
1. Simple Diffusion (passive)
- Substances move across phospholipids from high to low concentration,
(no energy)
OSMOSIS is the movement of WATER
Water is driven to move because the membrane is impermeable to solute(s)
2. Facilitated Diffusion
- Substance moves through a transport protein from high concentration to
low concentration
3. Active Diffusion
- Substance moves through a transport protein from low concentration to
high concentration (requires energy).
Substance moves against its concentration gradient
4. Exocytosis & Endocytosis
- Movement of large particles across membranes with the help of vesicles.
• Exocytosis – vesicles move particles OUT of the cells
• Endocytosis – vice/versa
Three types of endocytosis
1. Pinocytosis – cell drinking (liquid)
2. Phagocytosis – cell eating (solid)
3. Receptor mediated endocytosis
C. Cytoskeleton
The Structural framework of a cell
1. Microtubules – hollow, thick, elements made of the protein tubulin
Functions: 1. move chromosomes apart during cell division
2. form cilia and flagella
2. Microfilaments – long, thin elements made of the protein actin
Functions: 1. connect cells to each other
2. move vesicles and organelles within cytoplasm
3. help cells move
D. Intercellular Junctions (connect cells of multicellular organisms to form tissues)
1. Animal Cell Connections
Tight Junctions – cell membranes of adjacent cells are fused,
creating a tight cell
Gap Junctions – channels that allow exchange of materials
2. Plant Cell Connections
Plasmodesmata – channels that link the cytoplasm of adjacent
plant cells
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- OMM Study GuideDokument53 SeitenOMM Study Guideshadowcrest12100% (5)
- Cell Cheat SheetDokument5 SeitenCell Cheat SheetAJ Coots100% (2)
- Anaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDokument27 SeitenAnaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsVince Martin ManaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell 1Dokument48 SeitenCell 1Mihai ChirniciniiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act2 Bio SciDokument4 SeitenAct2 Bio SciPamaran, Kristel DenishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrane Structure and FunctionDokument46 SeitenMembrane Structure and FunctionHurmat AmnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane and Cell TransportDokument4 SeitenCell Membrane and Cell TransportAtasha MojecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1 Reviewer 1Dokument5 SeitenGeneral Biology 1 Reviewer 1Shane Patricia CalmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell StructureDokument3 SeitenCell StructureKYLA LORENZ BALUMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Cells ReviewerDokument3 SeitenAnaphy Cells ReviewerPlacido Edgar MagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport MechanismDokument31 SeitenTransport MechanismCecillia Evan100% (1)
- AnaPhy - Reviewer (Final)Dokument7 SeitenAnaPhy - Reviewer (Final)HyvieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Overview: Subject Name The Cell Topic 1 Week 1Dokument9 SeitenChapter Overview: Subject Name The Cell Topic 1 Week 1VeiliLookNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELL 1 2022 Materials Part 1Dokument27 SeitenCELL 1 2022 Materials Part 1Mutahir AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Biology Review Sheet Prokaryotic Bacteria Eukaryotic (Other Living Things)Dokument4 SeitenAP Biology Review Sheet Prokaryotic Bacteria Eukaryotic (Other Living Things)api-286357921Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDokument13 SeitenThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisMaxellLanceClementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology AML NMAT ReviewerDokument15 SeitenBiology AML NMAT ReviewerJocelyn Mae CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells: The Little Chamber in Plants and Animals: Eb 2005-Introductory BiologyDokument50 SeitenCells: The Little Chamber in Plants and Animals: Eb 2005-Introductory BiologyPatricia Jayshree Samuel JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cornell Notes 1Dokument2 SeitenCornell Notes 1api-333316198100% (1)
- AnaphyDokument8 SeitenAnaphykathrine montebonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout 4 Cell TransportDokument4 SeitenHandout 4 Cell TransportCrissan Jejomar AbanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membran Sel Dan TransportDokument67 SeitenMembran Sel Dan TransportAlbet SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Reviewer SeeleysDokument2 SeitenCell Reviewer Seeleysmarielle castroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotech 2 Cell TransportDokument5 SeitenBiotech 2 Cell TransportClinton YmbongNoch keine Bewertungen
- (L9) Transport Across MembranesDokument22 Seiten(L9) Transport Across MembranesJhon TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrane - FunctionDokument4 SeitenMembrane - Functionphuong anhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrane - FunctionDokument4 SeitenMembrane - Functionphuong anhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 Cell TransportDokument114 SeitenLesson 2 Cell TransportGlimar GacayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Cell Structures FunctionsDokument2 Seiten3 Cell Structures FunctionsKYLA LORENZ BALUMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDokument9 SeitenUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4) Cell MembraneDokument17 Seiten4) Cell Membranescobi doNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellsDokument6 SeitenCellsaryam aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4 - GenBio1 CELL MEMBRANE TRANSPORT 1st Term SY 2021-2022Dokument3 SeitenWeek 4 - GenBio1 CELL MEMBRANE TRANSPORT 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell Theory States ThatDokument2 SeitenThe Cell Theory States ThatMike MesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology: Cytology, The Study of The Structure and Function of CellsDokument48 SeitenHistology: Cytology, The Study of The Structure and Function of CellsZmeu CristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L9 Cellular TransportDokument2 SeitenL9 Cellular TransportStephanie SyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell StructuresDokument54 SeitenCell StructuresWilliam DC RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GenBio9 051716Dokument35 SeitenGenBio9 051716salihuddinalkaizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Your Own Fluid Mosiac Model of The Cell Membrane RESOURCESDokument16 SeitenBuilding Your Own Fluid Mosiac Model of The Cell Membrane RESOURCESVienne MonroidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - Chapter 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationDokument7 SeitenNotes - Chapter 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationRogie P. BacosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology Dr. Noelyn Bernal Cytoplasm-September 7,2018: Page - PEREZDokument13 SeitenHistology Dr. Noelyn Bernal Cytoplasm-September 7,2018: Page - PEREZA18- Jessa Mae DayagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Handouts: I.Cell and Cellular ProcessesDokument37 SeitenBiology Handouts: I.Cell and Cellular ProcessesIanDiel ParagosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell 1Dokument48 SeitenCell 1Pavel GaladiucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDokument16 SeitenOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneDokument15 SeitenCell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneMariane CarandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Cell Structures FunctionsDokument2 Seiten3 Cell Structures FunctionsPia Clarisse Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Transport NotesDokument39 SeitenCellular Transport NotesShen ZuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active TransportDokument11 SeitenActive TransportDARLENE JANE MAYNESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 11 FinalDokument16 SeitenGrade 11 FinalAbdi Fettah AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Physiology Theory 2Dokument18 SeitenAnimal Physiology Theory 2ao868598Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Module 4Dokument6 SeitenBiology - Module 4ASHLEY MONICA PLATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell StructureDokument35 SeitenCell Structure2W10Noch keine Bewertungen
- PlasmalemmaDokument15 SeitenPlasmalemmaRam Nivas AhirwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled PresentationDokument24 SeitenUntitled PresentationFreyacresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Cells PDFDokument51 SeitenBiology Cells PDFTanaka ChirawuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Reviewer 3 CellsDokument13 SeitenAnaphy Reviewer 3 CellsJohn Niño CasuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)Dokument4 SeitenGeneral Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)alfonsogwenmnqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Reviewer Seeley'sDokument2 SeitenCell Reviewer Seeley'smarielle castroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Cell StructureDokument6 Seiten3.1 Cell StructureVienna GilmoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument112 SeitenCellHeydrick GuyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Class Review - Exam 3Dokument4 SeitenBiology Class Review - Exam 3Jon Williams100% (4)
- Biology Class Review - Exam 3Dokument4 SeitenBiology Class Review - Exam 3Jon Williams100% (4)
- Biology Chapter 27Dokument2 SeitenBiology Chapter 27Jon WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes CH 26Dokument4 SeitenBiology Notes CH 26Jon Williams100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 13Dokument6 SeitenBiology Chapter 13Jon Williams100% (3)
- Biology Chapter 24Dokument1 SeiteBiology Chapter 24Jon WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Chapter 10Dokument2 SeitenBiology Chapter 10Jon Williams75% (4)
- Notes For Biology Chapter 9Dokument3 SeitenNotes For Biology Chapter 9Jon Williams91% (11)
- Biology Chapter 15Dokument2 SeitenBiology Chapter 15Jon Williams100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 12Dokument2 SeitenBiology Chapter 12Jon Williams100% (4)
- Biology Chapter 14Dokument1 SeiteBiology Chapter 14Jon Williams100% (1)
- Biology Class 6Dokument2 SeitenBiology Class 6Jon Williams100% (2)
- Biology Class 3Dokument3 SeitenBiology Class 3Jon Williams100% (2)
- The Chemistry of LifeDokument31 SeitenThe Chemistry of LifeJon WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Class 7Dokument4 SeitenBiology Class 7Jon Williams100% (4)
- Biology Class 4Dokument3 SeitenBiology Class 4Jon Williams100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 7Dokument2 SeitenBiology Chapter 7Jon Williams100% (2)
- Biology Class Review - Exam 1Dokument5 SeitenBiology Class Review - Exam 1Jon Williams100% (2)
- Fracture and Dislocation-Rahardyan Magetsari (2016) PDFDokument105 SeitenFracture and Dislocation-Rahardyan Magetsari (2016) PDFRobertOktaChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- O. Tauri: 3-D Ultrastructure Of: Electron Cryotomography of An Entire Eukaryotic CellDokument14 SeitenO. Tauri: 3-D Ultrastructure Of: Electron Cryotomography of An Entire Eukaryotic CellMARIA ANGGIE CANTIKA DEWANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney NotesDokument5 SeitenKidney Notesnad2samNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cardiac System LOBDokument3 SeitenThe Cardiac System LOBbdhhuhddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quran and EmbryologyDokument36 SeitenQuran and EmbryologyISLAMICULTURE67% (3)
- Abdominal Organs Essay SolutionDokument77 SeitenAbdominal Organs Essay SolutionEmmanuel IshiomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microscopic Examination of UrineDokument93 SeitenMicroscopic Examination of UrineJayniel Erys Molleno100% (1)
- 9 ICSE Biology Full Test SECTION I (40 Marks) Attempt All Questions From This SectionDokument4 Seiten9 ICSE Biology Full Test SECTION I (40 Marks) Attempt All Questions From This SectionYash SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology MeaslesDokument3 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology MeaslesCamila DaludadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neculaes. Lucaci. New Therapeutic Approaches To The Treatment of Low Back PainDokument11 SeitenNeculaes. Lucaci. New Therapeutic Approaches To The Treatment of Low Back PainPaul LucaciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histo CompilationDokument217 SeitenHisto CompilationNico LokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluating The Effects of Injected Calcium Hydroxylapatite On Changes in Human Skin Elastin and Proteoglycan FormationDokument5 SeitenEvaluating The Effects of Injected Calcium Hydroxylapatite On Changes in Human Skin Elastin and Proteoglycan FormationChris LicínioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Script For Head To NeckDokument7 SeitenScript For Head To NeckRhelina MinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infanticide: A Case Report: Abdul Gafar Parinduri, Oktafianna Malau, Roland Sanggam P. Tambunan, Eben Debora PurbaDokument7 SeitenInfanticide: A Case Report: Abdul Gafar Parinduri, Oktafianna Malau, Roland Sanggam P. Tambunan, Eben Debora PurbaSelfi AsmrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Principios de Biofarmacia PDFDokument96 Seiten3 Principios de Biofarmacia PDFAnonymous Se5IdneSpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo EyeDokument25 SeitenEmbryo EyeMarera DomnicNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Dokument7 SeitenBIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Tonet LapeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeDokument100 Seiten1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeAyush KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal GlandsDokument18 SeitenAdrenal GlandsNitesh BhuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GNM 1st Year Trhering Topic Handout 2020Dokument13 SeitenGNM 1st Year Trhering Topic Handout 2020shapan biswaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Sciences Answers For Remote Learning Workbook Term 3Dokument24 SeitenLife Sciences Answers For Remote Learning Workbook Term 3Anathiey Certified Jnr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive OrgansDokument8 SeitenReproductive OrgansSelim HanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of DeglutitionDokument23 SeitenPhysiology of DeglutitionMkhaimar NihadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Abo Blood Group SystemDokument3 SeitenThe Abo Blood Group Systemchippai123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous TissueDokument22 SeitenNervous TissuePRIYA DARSHINI GUNALANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition by Whitaker Isbn 10 1439059438 Isbn 13 9781439059432Dokument7 SeitenTest Bank For Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition by Whitaker Isbn 10 1439059438 Isbn 13 9781439059432trangdatif0Noch keine Bewertungen
- VanPutte Seeleys Essentials 11e Chap06 PPT AccessibleDokument149 SeitenVanPutte Seeleys Essentials 11e Chap06 PPT AccessibleCyrille Aira AndresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosing Congenital Malformations in The FetusDokument34 SeitenDiagnosing Congenital Malformations in The FetusMonica SurduNoch keine Bewertungen
- MyonecrosisDokument5 SeitenMyonecrosisJennifer ArangoNoch keine Bewertungen