Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Automated User Acceptance Testing of Web Applications With Selenium
Hochgeladen von
Onur YamanCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Automated User Acceptance Testing of Web Applications With Selenium
Hochgeladen von
Onur YamanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
AUTOMATED USER ACCEPTANCE TESTING OF WEB APPLICATIONS WITH SELENIUM
Presented by Onur Yaman 2010719258 Bogazici University Software Engineering
Overview
General Definitions Problem Statement Solutions Proposal Why Selenium? What is Selenium? Demo Whats next? References
General Definitions
User Acceptance Testing
Final testing based on
Specifications of the end-users or customer Use by end-users or customer over some limited period of time
1/3
Completed system vs. requirements Verification testing Validation testing Audit testing Performed by users of the system
General Definitions
Test Automation
Use of software to control the execution of tests Comparison of actual outcomes to predicted outcomes Setting up
Test preconditions Test control and reporting functions
2/3
Automating a manual process already in place that uses a
formalized testing process
General Definitions
Web Application
Application that is accessed over a network Client-server architecture
3/3
Ability to update and maintain without distributing and installing on
potentially thousands of clients
Cross-platform compatibility
Problem Statement
User acceptance testing of web applications is
Costly
Browser (client) compatibility Web applications tend to get updated frequently Many possible inputs
Slow
Tied to browser performance Clients and servers communicate over network
Solution
Automating user acceptance tests
Usage of proprietary software Many tools exist
FitNesse HtmlUnit HttpUnit Watir, Vapir, Watij, WatiN, Win32-Watir, Watir for Rails Celerity iMacros Canoo WebTest Selenium
Why Selenium?
Handles JavaScript well
Other tools are not reliable in handling in-page JavaScript
Provides maintainable tests
Other tools tend to break after small page changes
Works well with TDD Easy-to-write scripts Open source
Possibility of extending
Supports many browsers Supports many programming languages
What is Selenium?
Automated acceptance testing tool Developed by ThoughtWorks, now open source
1/10
Portable Deploys on Windows, Linux and MacOSX Supports various programming languages including C#, Java, Python, PHP, Perl, Ruby, Groovy Supports most modern web browsers including Firefox, Safari, Google Chrome, Opera, Internet Explorer Supports popular smart phones like Android and iPhone Tool suite Selenium 1 (a.k.a. Selenium RC or Remote Control) Selenium 2 (a.k.a. Selenium WebDriver) Selenium IDE Selenium Grid
10
What is Selenium?
Selenium 1 (a.k.a. Selenium RC or Remote Control)
Was the main Selenium project Still actively supported Supports several languages
Java, JavaScript, Ruby, PHP, Python, Perl, C#
2/10
Supports almost every browser out there Composed of components
Selenium Server
Manages browsers, runs Selenese commands, acts as HTTP proxy between the browser and the AUT
Client libraries
Provide interface between any programming language and the Selenium Server
11
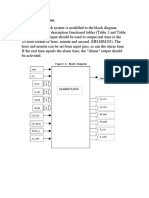
What is Selenium?
Selenium 1 (a.k.a. Selenium RC or Remote Control)
Architecture
3/10
12
What is Selenium?
Example for Selenium 1 (a.k.a. Selenium RC or Remote Control)
4/10
1- Run the Selenium Server
2- Run the language specific tests using the corresponding client API
13
What is Selenium?
Selenium 2 (a.k.a. Selenium WebDriver)
Provides a simple, concise programming interface Better supports dynamic web pages (AJAX) Supplies a well-designed object-oriented API
5/10
Makes direct calls to the browser using browsers native support for
automation (browser dependent)
Possibility of not using Selenium-Server
14
What is Selenium?
Example for Selenium 2 (a.k.a. Selenium WebDriver)
6/10
15
What is Selenium?
Selenium IDE
Tool to develop Selenium test cases Uses Selenese (Selenium script language) Firefox plug-in Allows saving macros (like Microsoft Office macros)
7/10
Allows exporting saved test cases to any desired language that uses
the Client API
Allows grouping test cases as test suites Allows running previously saved test cases/suites Provides results of tests
16
What is Selenium?
Example for Selenium IDE
8/10
17
What is Selenium?
Selenium Grid
Builds on the traditional Selenium setup
More than one machine can be used
9/10
Selenium RC and the browser are not tied to a specific application (they can
be shared by multiple applications and projects)
Possibility of a distributed grid system of Selenium RCs
Shared across builds, applications, projects, organizations
Scalable
Selenium Hub
Allocates a Selenium RC to a specific test (transparently) Limits the number of concurrent test runs on each RC Shields the tests from the actual grid infrastructure
18
What is Selenium?
Selenium Grid Setup
10/10
19
Demo
Live demo
Bingo! Java Web Application Very simple test cases Selenium WebDriver is used Implementation is made in Python 2.7
20
Whats next?
Writing good tests
Keep tests self-contained Write own extensions if needed Write tests before development (TDD) Refactor tests (if possible)
Selenium and FitNesse Integration
Everyone (including the customers) see, track and run tests
Continuous Integration
Running selenium tests is possible (in-memory X window system) Test coverage analysis
21
References
Selenium Documentation (Release 1.0) / May 10, 2012
<URL: http://seleniumhq.org/docs/book/Selenium_Documentation.pdf>
Selenium Grid: How It Works / 2008
<URL: http://selenium-grid.seleniumhq.org/how_it_works.html>
Holmes, A.; Kellogg: Automating functional tests using Selenium.
M.Agile Conference, 2006.
Bruns, A.; Kornstadt, A.; Wichmann, D.: Web Application Tests with
Selenium. Software, IEEEVolume: 26 , Issue: 5.
Razak, R.A.; Fahrurazi, F.R.: Agile testing with Selenium. Software
Engineering (MySEC), 2011 5th Malaysian Conference in Digital Object Identifier: 10.1109/MySEC.2011.6140672.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- UNIT 5 Part1Dokument90 SeitenUNIT 5 Part1Abhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 5 Part1Dokument101 SeitenUNIT 5 Part1Mahammad SHAIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absolute Beginner (Part 1) Selenium WebDriver for Functional Automation TestingVon EverandAbsolute Beginner (Part 1) Selenium WebDriver for Functional Automation TestingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Assignment 2 Final ExamDokument30 SeitenAssignment 2 Final Examsibhat mequanintNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium Testing Tools Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Second EditionVon EverandSelenium Testing Tools Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Second EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Web Testing With Selenium: Deepak Mittal Dec 15, 2007Dokument35 SeitenAutomated Web Testing With Selenium: Deepak Mittal Dec 15, 2007raviskskskNoch keine Bewertungen
- SeleminumDokument9 SeitenSeleminumonkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SeleniumDokument20 SeitenSeleniumabirami mayakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA - Manual Automation Interview Questions - Prasad HiwaleDokument37 SeitenQA - Manual Automation Interview Questions - Prasad HiwaleAneet GulshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stqa Mini Project 2Dokument18 SeitenStqa Mini Project 2SakshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium-The Content MaterialDokument80 SeitenSelenium-The Content Materialvenkatesh SuganyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium Webdriver Interview Question PDFDokument24 SeitenSelenium Webdriver Interview Question PDFDhanashekhar Jayapal100% (1)
- Selenium Web Automation Testing ToolDokument15 SeitenSelenium Web Automation Testing ToolMai Công ChínhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium WebDriver 3x (Java)Dokument111 SeitenSelenium WebDriver 3x (Java)Ana CasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium: Dr. Madhusmita Sahu Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Information TechnologyDokument59 SeitenSelenium: Dr. Madhusmita Sahu Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Information TechnologySubir KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium Interview QuestionsDokument15 SeitenSelenium Interview QuestionsAnonymous PZGvcrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium An Effective Weapon in The Open Source ArmoryDokument30 SeitenSelenium An Effective Weapon in The Open Source ArmoryHitzy SoulriderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web Browser Automation For Testing Web Apps Using Selenium 2Dokument34 SeitenWeb Browser Automation For Testing Web Apps Using Selenium 2Srikar KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 200+ Selenium Interview QuestionsDokument40 Seiten200+ Selenium Interview QuestionsdhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium Interview QuestionsDokument27 SeitenSelenium Interview Questionsvishnuvr143Noch keine Bewertungen
- 200+ Selenium Interview QuestionsDokument39 Seiten200+ Selenium Interview QuestionsJagannath DNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST - Unit3Dokument59 SeitenST - Unit3Aditya vtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium - Testing ToolDokument38 SeitenSelenium - Testing ToolSeshukumar MathampalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium PresentationDokument12 SeitenSelenium PresentationAdriana PanaeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium Interview QuestionsDokument16 SeitenSelenium Interview Questionsshefali0% (1)
- 2 - Introduction To SeleniumDokument28 Seiten2 - Introduction To SeleniumKashish ChhibberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Software Testing ToolsDokument51 SeitenDifferent Software Testing Toolssidhhart kunkololNoch keine Bewertungen
- TestTool SeleniumDokument28 SeitenTestTool SeleniumPalanichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium PART1Dokument33 SeitenSelenium PART1sri_plnsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Most Important Selenium Interview QuestionsDokument14 SeitenMost Important Selenium Interview Questionsnagub100% (2)
- Selenium Interview Q & A - Part 1Dokument27 SeitenSelenium Interview Q & A - Part 1Shruti NimjeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium & Unix Intervoew QuestionsDokument50 SeitenSelenium & Unix Intervoew QuestionsroobhiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is SeleniumDokument6 SeitenWhat Is SeleniumpoorilonavalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium Interview QuestionsDokument15 SeitenSelenium Interview Questionsjadipa123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Regression Test Cases Selenium Webdriver: What Is Automation Testing?Dokument34 SeitenRegression Test Cases Selenium Webdriver: What Is Automation Testing?manuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium and Database QuestionsDokument159 SeitenSelenium and Database QuestionsRudra ShivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium ToolDokument24 SeitenSelenium ToolSayali NagarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium Top InterviewqDokument13 SeitenSelenium Top InterviewqPavan Kumar ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selinium Introduction 1 and 2Dokument28 SeitenSelinium Introduction 1 and 2akshay jondhaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automation - IntroductionDokument17 SeitenAutomation - IntroductionPaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q #1) What Is Automation Testing?Dokument21 SeitenQ #1) What Is Automation Testing?devadas26Noch keine Bewertungen
- 0.selenium CourseContentDokument7 Seiten0.selenium CourseContentsudheerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium PresentationDokument13 SeitenSelenium Presentationsuraj waghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium 1: Introduction To SeleniumDokument7 SeitenSelenium 1: Introduction To SeleniumpriyanshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium 1: Introduction To SeleniumDokument7 SeitenSelenium 1: Introduction To SeleniumswapnilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium IntroductionDokument7 SeitenSelenium Introductionrahul badigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuous Integration With Hudson1Dokument24 SeitenContinuous Integration With Hudson1AbhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium QuestionsDokument52 SeitenSelenium QuestionsrangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium Interview Questions and Answers, Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument6 SeitenSelenium Interview Questions and Answers, Multiple Choice QuestionsvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automation Testing Basics - IntroductionDokument6 SeitenAutomation Testing Basics - IntroductionEric Kartman LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is SeleniumDokument6 SeitenWhat Is SeleniumAryan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To SeleniumDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To SeleniumNeelamohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Introduction To Selenium PDFDokument6 Seiten1 - Introduction To Selenium PDFNeelamohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selenium TrainingDokument114 SeitenSelenium TrainingOshi Lice100% (1)
- Toshiba Motor Control FlyerDokument2 SeitenToshiba Motor Control FlyerkaikakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gatp TcodesDokument2 SeitenGatp TcodesDheerajKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISMS Statement of Applicability For ISMS Course Participant ExerciseDokument12 SeitenISMS Statement of Applicability For ISMS Course Participant ExerciseCyber Guru100% (1)
- Libsvm For MATLABDokument8 SeitenLibsvm For MATLABLuis Oliveira SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Downloading and Installing Cisco Router and Security Device Manager (SDM) Sdmin12Dokument14 SeitenCisco Downloading and Installing Cisco Router and Security Device Manager (SDM) Sdmin12Florin StanciulescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airline Reservation System Project ReportDokument32 SeitenAirline Reservation System Project ReportPardeepJhandi100% (9)
- Nondeterministic Trellis Automata: InputDokument3 SeitenNondeterministic Trellis Automata: InputHello misterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Graphics Question BankDokument7 SeitenComputer Graphics Question Bankniranjani0408Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shutdown Command Via Command PromptDokument2 SeitenShutdown Command Via Command PromptmobilecrackersNoch keine Bewertungen
- College Management SystemDokument9 SeitenCollege Management SystemBhagirath Chahar67% (3)
- CAPTCHA PresentationDokument28 SeitenCAPTCHA Presentationbsbharath198770% (10)
- Multiclass Classification Method Based On Deep Learning For Leaf Identification For FarmersDokument4 SeitenMulticlass Classification Method Based On Deep Learning For Leaf Identification For FarmersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MySQL Interview QuestionsDokument8 SeitenMySQL Interview Questionsvaishu_385Noch keine Bewertungen
- Database Programming With SQL 2-1: Working With Columns, Characters, and Rows Practice ActivitiesDokument5 SeitenDatabase Programming With SQL 2-1: Working With Columns, Characters, and Rows Practice Activitiesstenly94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Specification: FS - FI - VAT - Profit Center Jan - 18Dokument7 SeitenFunctional Specification: FS - FI - VAT - Profit Center Jan - 18Anonymous 0SLsR9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Luxand FaceSDK DocumentationDokument71 SeitenLuxand FaceSDK DocumentationFrancisco Raúl DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARM Cortex Portfolio - Public Version - V7Dokument4 SeitenARM Cortex Portfolio - Public Version - V7Aaron FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ms SQL Server Always On Io Reliability Storage System On Hitachi VSPDokument25 SeitenMs SQL Server Always On Io Reliability Storage System On Hitachi VSPrajiv_ndpt8394Noch keine Bewertungen
- A10 DS AdcDokument20 SeitenA10 DS AdcSupattra SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Bellmanford and SP in DAG - Algorithms (Series Lecture)Dokument40 Seiten10 Bellmanford and SP in DAG - Algorithms (Series Lecture)turjo987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Radiograph TreeDokument957 SeitenDigital Radiograph TreecutefrenzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP2016 SP2019 Enterprise Search Architecture Model PDFDokument1 SeiteSP2016 SP2019 Enterprise Search Architecture Model PDFjohnanticonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Operating Procedures Manual For WebSAMS 2.0 - English - Version 1.1Dokument79 SeitenComputer Operating Procedures Manual For WebSAMS 2.0 - English - Version 1.1shilratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Methods Using MATLAB 4ed Solution ManualDokument171 SeitenNumerical Methods Using MATLAB 4ed Solution Manualnoobispriest2343% (23)
- Dcon Utility User ManualDokument45 SeitenDcon Utility User ManualPedro BortotNoch keine Bewertungen
- VerilogDokument5 SeitenVerilogLoiLeVanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PowerVault MD3600f Spec SheetDokument2 SeitenPowerVault MD3600f Spec SheetOscar Alexander Ojeda AriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual BasicDokument43 SeitenVisual Basickvsureshmysore100% (2)
- Railway Reservation in CDokument36 SeitenRailway Reservation in CShûbhî ShreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frame Problem in Artificial Intelligence: Patrick J. HayesDokument29 SeitenFrame Problem in Artificial Intelligence: Patrick J. HayesVinod GangalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsVon EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (722)
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityVon EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyVon EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (51)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldVon EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Cyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItVon EverandCyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (66)
- System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootVon EverandSystem Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldVon EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (55)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveVon EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewVon EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Chaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyVon EverandChaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (111)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindVon EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyVon EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumVon EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (12)
- Solutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesVon EverandSolutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderVon EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (398)
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andVon EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (709)
- Four Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceVon EverandFour Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessVon EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyVon EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (24)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeVon EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (99)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyVon EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (228)
- Mini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreVon EverandMini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (76)
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldVon EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (107)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda Cans (Father's Day Gift for Science and Engineering Curious Dads)Von EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda Cans (Father's Day Gift for Science and Engineering Curious Dads)Noch keine Bewertungen