Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Physics
Hochgeladen von
Raj GuptaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Physics
Hochgeladen von
Raj GuptaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
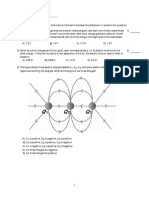
Spherical Shell Insulator (4 points) IE Spherical Shell Insulator An insulator in the shape of a spherical shell is shown in cross-section above.
The insulator is defined by an inner radius a = 4 cm and an outer radius b = 6 cm and carries a total charge of Q = + 9 C (1 C = 10-6 C). (You may assume that the charge is distributed uniformly thro ughout the volume of the insulator). What is Ey, the y-component of the electric field at point P which is located at (x,y) = (0, -5 cm) as shown in the diagram? Ey N/C Coaxial Cylindrical Conductors (4 points) IE Coaxial Cylindrical Conductors Two coaxial cylindrical conductors are shown in cross-section above. The inner c ylinder has radius a = 2 cm, length 10 m and caries a total charge of Qinner = + 8 nC (1 nC = 10-9 C). The outer cylinder has an inner radius b = 6 cm, outer radius c = 7 cm, length 10 m and cariies a total charge of Qoute r = - 16 nC (1 nC = 10-9 C). What is Ex, the x-component of the electric field a t point P which is located at the midpoint of the length of the cylinders at a distance r = 4 cm from the origin and makes an angle of 30o with the x-axis? Ex = N/C Photocopier Drum (3 points) Photocopier Drum The electric field just above the surface of the conducting charged drum of a ph otocopying machines has a magnitude of 2.5 X105 N/C. The drum has a length of 59 cm and a radius of 20 cm. (a) What is the surface charge density of the drum? (You can ignore any edge effects.) = C/m2 (b) What is the total charge on the drum? q = C (c) The manufacturer wishes to produce a desktop version of this copier. Thi s means we must cut the length of the drum down to 29.50 cm and the radius of th e drum must be cut to 13.33 cm. What must be the charge on the drum if we wish t o keep the electric field at the surface of the drum unchanged? q = C Line of Charge with Conducting Cylindrical Shell (3 points) Line of Charge An infinite line of charge with linear density 1 = -2 C/m is positioned along the axis of a thick conducting cylindrical shell of inner radius a = 4 cm and outer radius b = 5 cm and infinit e length. The conducting shell has a net charge (inner and outer surfaces) per u nit length along its symmetry axis of 2 = 5 C/m. (a) Calculate the surface charge densities on the inner (6a) and outer (6b) surf aces of the cylindrical shell. 6a = C/m2 6b = C/m2 (b) Calculate the net radial electric field component at the following radii: At r = 2 cm: Er = N/C At r = 4.5 cm: Er = N/C At r = 10 cm: Er = N/C
Infinite Sheets of Charge (3 points) Infinite Sheet of Charge An infinite nonconducting sheet of charge, oriented perpendicular to the x-axis, passes through x = 0. It has area density 61 = -2 C/m2. A thick, infinite conduct ing slab, also oriented perpendicular to the x-axis, occupies the region between x = a and x = b, where a = 4 cm and b = 5 cm. The conducting slab has a net cha rge per unit area of 62 = 5 C/m2. (a) Calculate the itions: At x = -2 cm: Ex = At x = 2 cm: Ex = At x = 4.5 cm: Ex = At x = 10 cm: Ex = (b) Calculate the and (6b) faces of the lationship between 6a 6a = C/m2 6b = C/m2 Flux (3 points) Flux Through a Cube net x-component of the electric field at the following pos N/C N/C N/C N/C surface charge densities on the left-hand (6a) and right-h conducting slab.You may also find it useful to note the re and 6b.
A cube is oriented such that one of its corners is at the origin and its edges are parallel to the x, y, and z axes as shown to the left. The length of each of its edges is 1.8 m. (a) What is the flux through the cube if the electric field is given by ? = Nm2/C (b) What is the flux through the cube if the electric field is given by ? = Nm2/C or part (b), how much charge must be enclosed by the cube? (c) q= C Conducting Sphere (3 points) Conducting Sphere A point charge of strength q1 = -2 C is located at the center of a thick, conducting spherical shell of inner radius a = 4 cm and outer radius b = 5 cm. The conducting shell has a net charge of q2 = 5 C. (a) Calculate the surface charge densities on the inner (6a) and outer (6b) surf aces of the spherical shell. 7/8/12 6a = C/m2 6b = C/m2 (b) Calculate the net radial electric field component at the following radii : At r = 2 cm: Er = N/C At r = 4.5 cm: Er = N/C At r = 10 cm: Er = N/C (c) If a conducting wire is added that allows electric charge to flow betwee n the location of q1 and the conducting shell, calculate the resulting values of the net radial components of the electric fields at the following radii: At r = 2 cm: Er' = N/C At r = 4.5 cm: Er' = N/C
At r = 10 cm: Er' = N/C Plate and Ball (3 points) Plate and Ball As shown to the left, a small non-conducting ball of mass m = 3 mg and c harge q = 21 nC hangs from from an insulating thread that makes an angle of 35 with a vert ical uniformly charged non-conducting sheet (shown in cross section). Assuming the sheet extends far vertically and out of the drawing, calculate the surface charge density, , on the sheet. = C/m2 Two Plates (3 points) Two Plates Two large metal plates of area 2 m2 face each other. They are 3.4 cm apart and h ave equal but opposite charges on their inner surfaces. The strength of the elec tric field between them is 45 N/C. (a) What is the charge on each plate? (You may ignore edge effects). q = C (b) What if we wished to double the distance between the plates while keepin g the strength of the electric field the same. What would the required charge be on each plate? q = C Solid Cylinder (3 points) Solid Non-conducting Cylinder A long, solid, non-conducting cylinder of radius 9 cm has a non-uniform volume d ensity, , that is a function of the radial distance r from the axis of the cylind er. = A*r2 where A is a constant of value 3 C/m5. (a) What is the magnitude of the electric field 7 cm from the axis of the cy linder? |E| = N/C (b) What is the magnitude of the electric field 11 cm from the axis of the c ylinder? |E| = N/C 10 problems 32 points
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyVon EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23 HRW 0506Dokument6 Seiten23 HRW 0506chanttelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Previous Exams Questions Ch23-24-With NotesDokument11 SeitenPrevious Exams Questions Ch23-24-With NotesaamerbolookiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci 404 - Physics 2 - Midterm - Part IiDokument2 SeitenSci 404 - Physics 2 - Midterm - Part IiJezreel GamboaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test1 16FDokument8 SeitenTest1 16FJasper LuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 24-Gauss's Law: Multiple ChoiceDokument19 SeitenChapter 24-Gauss's Law: Multiple ChoiceRoberto De La PazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prac FinaleDokument14 SeitenPrac FinaleadadafasfasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics ProblemsDokument2 SeitenElectrostatics Problemsquasar2138Noch keine Bewertungen
- In Your Name Where Indicated in The Upper Right Corner Then (2) Do The Same With YourDokument12 SeitenIn Your Name Where Indicated in The Upper Right Corner Then (2) Do The Same With YouradadafasfasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 08 I FinalDokument9 Seiten07 08 I FinalMahmoud FariedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gauss'LawDokument7 SeitenGauss'LawKavish CserNoch keine Bewertungen
- p240w12 Mid1-2Dokument14 Seitenp240w12 Mid1-2shlaeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Questions Chs 21-24 1Dokument40 SeitenPractice Questions Chs 21-24 1jevanjunior0% (1)
- Clicker Chapter 22 PhysicsDokument67 SeitenClicker Chapter 22 PhysicsAnie DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ihw 3Dokument9 SeitenIhw 3LogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Assignment II Las Date of Submission: 26/01/2022Dokument2 SeitenHome Assignment II Las Date of Submission: 26/01/2022Md. Imran AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 220 Homework: Spring 2008Dokument27 SeitenPhysics 220 Homework: Spring 2008Jeff Pratt100% (1)
- W2016 PHYS259 Final Booklet I AnswersDokument12 SeitenW2016 PHYS259 Final Booklet I AnswersYasmeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM MCDokument3 SeitenEM MCسفير بني شهرNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys102 Oldexams Chap23aDokument5 SeitenPhys102 Oldexams Chap23aOny OussNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSE 9e CH 24 CH 25 26 Combined SerwayDokument60 SeitenPSE 9e CH 24 CH 25 26 Combined SerwayYaas BahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap23 10Dokument10 SeitenChap23 10litrakhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 2019Dokument2 SeitenFinal 2019Ashraf WaleedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exam - 1 + Answers Winn F10Dokument13 SeitenPractice Exam - 1 + Answers Winn F10Billy PozehlNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYF125 Tutorial Questions Tri 2 201617Dokument11 SeitenPHYF125 Tutorial Questions Tri 2 201617Sufian PianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ExamA1-2019-1Dokument4 SeitenFinal ExamA1-2019-1trinh.lenukieuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions: D or 2d As Drawn, and A Central Point Is Shown MidwayDokument4 SeitenQuestions: D or 2d As Drawn, and A Central Point Is Shown MidwayFirdous ANoch keine Bewertungen
- 24Dokument19 Seiten24anon_33083814Noch keine Bewertungen
- S.N Questions 1.: BA CB CADokument8 SeitenS.N Questions 1.: BA CB CAkush jindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatic 1 Shot DPP 1Dokument8 SeitenElectrostatic 1 Shot DPP 1Ayush JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics 3Dokument2 SeitenElectrostatics 3bys628h8skNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTHU Electrical Engineering Department EE2140 Electromagnetics Spring 2024 HW #2Dokument1 SeiteNTHU Electrical Engineering Department EE2140 Electromagnetics Spring 2024 HW #2superhense55123Noch keine Bewertungen
- PROBLEMS - University Physics 2 - Homework 2 - Gauss's LawDokument3 SeitenPROBLEMS - University Physics 2 - Homework 2 - Gauss's LawNguyễn Hoàng ĐăngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Assignment, XLL PhysicsDokument5 SeitenHome Assignment, XLL PhysicsaachintsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Charges and Fields DPP 1Dokument4 SeitenElectric Charges and Fields DPP 1deepbag79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exam1 PHYS 193 Spring2014-M2Dokument12 SeitenExam1 PHYS 193 Spring2014-M2alkingkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam1 Phys 193 Fall 2014-m2Dokument12 SeitenExam1 Phys 193 Fall 2014-m2alkingkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 22 Gauss's Law: University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman)Dokument17 SeitenChapter 22 Gauss's Law: University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman)Rachelle SaavedraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4: S M S MDokument4 SeitenTutorial 4: S M S MMatataTomato M30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 272 Final Exam PracticeDokument16 SeitenPhys 272 Final Exam Practiceheehee2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- ch32 PDFDokument14 Seitench32 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS (Pyq)Dokument5 SeitenELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS (Pyq)Abhishek ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23 - Gauss' LawDokument9 SeitenChapter 23 - Gauss' LawVV CepheiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ginn Reading 360 Little Books. Level 3Dokument12 SeitenGinn Reading 360 Little Books. Level 3Aya AbidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NDokument4 SeitenNBHAAJI0001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Potential & CapacitorDokument3 SeitenElectric Potential & CapacitorSayan BhowmickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 2018Dokument3 SeitenFinal 2018Ashraf WaleedNoch keine Bewertungen
- WORKSHEET12Dokument8 SeitenWORKSHEET12Anfeli JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework The Gauss Law SolutionDokument6 SeitenHomework The Gauss Law SolutionTikTok LikeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 210 MCweek 2Dokument3 Seiten210 MCweek 2worktoka3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics 1Dokument2 Seiten12 Physics 1Aman ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ ElectrostaticsDokument4 SeitenMCQ ElectrostaticsqesuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Test 1314Dokument11 SeitenReview Test 1314Hassan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank For May 2017 PhysicsDokument5 SeitenQuestion Bank For May 2017 PhysicsKushagra MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Hannan Saadeh Solved Problems PDFDokument50 SeitenDR - Hannan Saadeh Solved Problems PDFAbdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Dokument7 Seiten3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Eng MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revisions Chapter 24Dokument5 SeitenRevisions Chapter 24Agag HsgsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsVon EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Digital Thermometer Using Arduino: Mini Project Report ONDokument5 SeitenDigital Thermometer Using Arduino: Mini Project Report ONNeha PintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daikin LXE10E-A - Service Manual (TR 01-09B) PDFDokument238 SeitenDaikin LXE10E-A - Service Manual (TR 01-09B) PDFmail4ksnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng Essay For PresentationDokument8 SeitenEng Essay For Presentationctn batrisyiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- APCO CSAA ANS2 101 1webfinalDokument38 SeitenAPCO CSAA ANS2 101 1webfinalJUAN CAMILO VALENCIA VALENCIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared For: Assignment On Workforce DiversityDokument28 SeitenPrepared For: Assignment On Workforce DiversityGolam RabbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avanti II 04-05Dokument137 SeitenAvanti II 04-05Donald SimsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extenso MeterDokument8 SeitenExtenso MeterVijayanandh Raja100% (1)
- Geometallurgical Modelling of The Collahuasi Flotation CircuitDokument6 SeitenGeometallurgical Modelling of The Collahuasi Flotation CircuitFrancisco CampbellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operator'S Manual AND Set-Up Instructions For The: WDL-2070-FADokument49 SeitenOperator'S Manual AND Set-Up Instructions For The: WDL-2070-FAМаксим ЛитвинNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slot 22-23-24 Real Time CommunicationDokument50 SeitenSlot 22-23-24 Real Time CommunicationLinh BuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siasun Company IntroDokument34 SeitenSiasun Company IntromoneeshveeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classical Electromagnetism 1st Edition Franklin Solutions ManualDokument21 SeitenClassical Electromagnetism 1st Edition Franklin Solutions ManualBrianYorktnqsw100% (15)
- GRADE 8 3rd Quarter DLP in EnglishDokument484 SeitenGRADE 8 3rd Quarter DLP in EnglishJulius Salas100% (4)
- Minimum Leak Path For TTJDokument3 SeitenMinimum Leak Path For TTJparikshitpadture100% (2)
- Internship Report PDFDokument11 SeitenInternship Report PDFASWIN KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC Course IntroDokument11 SeitenCC Course IntroSaid TahatNoch keine Bewertungen
- BITS Pilani: Scale Up and Post Approval ChangesDokument56 SeitenBITS Pilani: Scale Up and Post Approval ChangesshrikantmsdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arquitectura Objectiva cl2002Dokument9 SeitenArquitectura Objectiva cl2002api-717600385Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vr31a OmDokument5 SeitenVr31a OmrudydanielleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yuasa Technical Data Sheet: The World's Leading Battery ManufacturerDokument1 SeiteYuasa Technical Data Sheet: The World's Leading Battery ManufacturerAshraf Sayed ShabaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gerrard 1966Dokument13 SeitenGerrard 1966AnandhuMANoch keine Bewertungen
- MYP Unit Planner - MathDokument5 SeitenMYP Unit Planner - MathMarija CvetkovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- P16mba7 1Dokument4 SeitenP16mba7 1Vishalatchi MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Communication SystemDokument13 SeitenAdvanced Communication SystemZohaib AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 11 - LAB 2 LEVEL 0 - BS Lab Electrical Supply - Domestic House Wiring & Accessories Including Lighting - DONEDokument6 SeitenWEEK 11 - LAB 2 LEVEL 0 - BS Lab Electrical Supply - Domestic House Wiring & Accessories Including Lighting - DONEMuhd Alif MikhailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Quiz Threads PDFDokument5 SeitenPost Quiz Threads PDFshubham_narkhedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fujikura FSM40S Service Manual PDFDokument67 SeitenFujikura FSM40S Service Manual PDFAndrey Nikollas BuckoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Practical Guide To HL7 Interface DevelopmentDokument5 SeitenA Practical Guide To HL7 Interface DevelopmentmjohnstnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimal Control Development System For ElectricalDokument7 SeitenOptimal Control Development System For ElectricalCRISTIAN CAMILO MORALES SOLISNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCR Control System Interface HandbookDokument17 SeitenCCR Control System Interface Handbooklcastrey23Noch keine Bewertungen