Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Advanced Computer Networks Class Test -1 Questions Answers
Hochgeladen von
Vijay UkaniOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Advanced Computer Networks Class Test -1 Questions Answers
Hochgeladen von
Vijay UkaniCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Advanced Computer Networks
Class Test -1
Max Marks: 30 Q.1 A Do as directed ATM breaks all traffic into 53-Byte cells because [2 marks] a) 53-Byte cells are the ideal size for the voice communication b) 53-Byte cells are the ideal size for data communication c) 53-Byte cells are the ideal size for circuit switching d) 53-Byte cells are the compromised size for both voice and data communication What gives ATM network the ability to operate at different data rates and why? [2 marks] a) Its short, fixed length cells: Allows the prediction of the size of buffers to be used. b) Its short, fixed length cells: Enables the cells to be transported via different routes. c) Its short, fixed length cells: Short delays for voice traffic. d) Its short, 5-Byte header: Less delay for routing the cells. Why is Frame Relay's throughput lower than that of ATM? [2 marks] a) Frame Relaying have error control (ARQ) functionality but not ATM. b) ATM does not need to have CRC checking/generation or bit stuffing functionality in the packets as in Frame Relay. c) Frame Relaying needs to do multiplexing of logical channels but not ATM. d) Although both Frame relay and ATM have frame boundary recognition (flags), ATM doesnt have bit stuffing as in frame Relaying. ATM is said to be a connection oriented technology. What does this mean and why is it necessary? [2 marks] a) Cells travel through the same path to the receiver. By this, cell does not have to be rearranged. b) Cells travel through different paths. Therefore cells can reach the receiver faster. c) A path is reserved exclusively for one user. Arrangement of cells is not necessary d) Cells are transmitted using fiber optic cables. Cells would be less susceptible to errors. Which three Layer 2 encapsulation types would be used on a WAN rather than a LAN? (Choose three) [3 marks] a) HDLC b) Ethernet c) Token Ring d) PPP e) FDDI f) Frame Relay Which three statements properly describe Frame Relay? [3 marks] a) Frame Relay works at the application layer. b) The connection to the network edge is often a leased line, but dialup connections are available from some providers using ISDN or xDSL lines. c) Frame Relay implements no error or flow control. d) Available data rates for Frame Relay are commonly up to 10 Mbps. e) Most Frame Relay connections are SVCs rather than PVCs. f) Frame Relay provides both PVC and SVC service using shared mediumbandwidth connectivity that carries both voice and data traffic. Which three statements accurately describe ATM? [3 marks] a) ATM is implemented by using virtual circuits. b) An ATM network comprises ATM routers, which are responsible for forwarding cells and packets. c) Virtual circuits provide a bidirectional communications path from one ATM endpoint to another. d) An ATM virtual circuit is a physical circuit-switched connection created AN S D
A D F
B C F
A C F
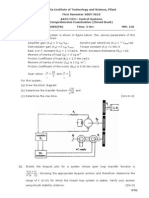
between two computer endpoints across an ATM network. e) ATM can run only over coaxial cable using DS3. f) ATM is a type of cell-switched connection technology that is capable of transferring voice, video, and data through private and public networks. H What is the difference between ATM and frame relay networks? [3 marks] Ans. ATM has more support for QoS and support for variety of traffic as compared to Frame Relay. ATM has higher bandwidth compared to Frame Relay. ATM has fixed size cell where as Frame Relay has variable frame length. I Suppose that the TCP congestion window is set to 64 KB and a timeout occurs. The receiver (sliding) window is 100 KB and the maximum segment size is 1 KB. Assume there is no linear mode. [4 marks] a) How big will the congestion window be after the next six transmission bursts allowed by the congestion window are all successful? b) Now the 7th transmission burst has a timeout. How big will the congestion window be after the next three transmission bursts are all successful? Ans. Cwnd = 64 KB, rwnd = 100 KB, MSS = 1 KB, because of timeout cwnd = 1 MSS=1KB a) 1st transmission cwnd = 1 KB, after transmission, cwnd = 2 KB 2nd transmission burst, cwnd = 4 KB, likewise next 8, 16, 32, 64 KB b) 7th burst timesout, so cwnd = 1 MSS = 1KB, next 3 are successful, so cwnd will be 2,4 and 8KB Suppose you are browsing www.yahoo.com from your machine cse.nirmauni.ac.in. If the round-trip time between yahoo and cse is 100ms; timeout value is 200ms; Maximum Segment Size (MSS) of TCP is 1KB; the congestion window is 1 MSS; the congestion threshold is 8KB; the available buffer size is 64KB and transmission bandwidth is 200 KB/sec. [6 marks] a) What is the transmission time for a TCP segment? b) How long will it take to download a page of 6KB from yahoo? Assume there is no prior TCP connection between yahoo and your machine, there is no packet loss or retransmission. Ignore transmission time for this part. c) How will the result in (b) change if the 4th. TCP segment is dropped and the client gets to detect this loss by timeout? Ans. RTT = 100ms, Timeout = 200 ms, MSS = 1KB, cwnd = 1MSS, ssthresh = 8KB, rwnd = 64KB, BW=200KBPS a) 1/200 Sec b) Page Size = 6 KB. Establish TCP connection will take one RTT = 100 ms 1st transmission, cwnd = 1MSS, 1 more RTTT = 100ms 2nd RTT, cwnd = 2MSS, 1 more RTT = 100 ms 3rd RTT, cwnd=4MSS of which 3 KB of data is transmitted in 1 more RTT = 100 ms So total time needed to download page = 400 ms. c) 4th TCP segment is lost. So 1st and 2nd transmission with 3 MSS sent successfully in 300 ms. To detect the loss of 4th segment, it will take one more RTT = 100 ms. Now cwnd = 1 MSS again, 4th segment in 1 RTT = 100 ms Cwnd = 2 MSS, 5th and 6th MSS in 1 more RTT = 100 ms So total time needed = 600 ms.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fundamentals of Computer Networks Quiz - 1 - With AnswersDokument5 SeitenFundamentals of Computer Networks Quiz - 1 - With AnswersKhandakar Farhan NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers 3Dokument5 SeitenAnswers 3Carl SigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Media Types and CharacteristicsDokument73 SeitenTransmission Media Types and Characteristicshardcore85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Signalling: Inchannel Versus Common Channel Signalling: Inchannel Common ChannelDokument16 SeitenSignalling: Inchannel Versus Common Channel Signalling: Inchannel Common ChannelAruna GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Rev Ist220Dokument2 SeitenChapter 2 Rev Ist220ktdf08Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 271 Course Covers Fundamentals of Telecom NetworksDokument58 SeitenECE 271 Course Covers Fundamentals of Telecom NetworksBhagaban DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRC error detection methodDokument11 SeitenCRC error detection methodUthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question BankDokument5 SeitenQuestion BankSwati AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages of Coaxial CableDokument24 SeitenAdvantages of Coaxial CableBurhanudheen KodiyathoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS313 Computer Communication and Networking (Spring 2018) Assignment # 1Dokument5 SeitenCS313 Computer Communication and Networking (Spring 2018) Assignment # 1razaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE-351 Communication Systems Course Outline-UpdatedDokument5 SeitenEE-351 Communication Systems Course Outline-UpdatedRabail InKrediblNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument5 SeitenAssignment 1Parker Bollinger IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- CS535 Assignment QuestionDokument2 SeitenCS535 Assignment QuestionhackermlfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Assignment Technology Park MalaysiaDokument25 SeitenIndividual Assignment Technology Park MalaysiaSamir GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- hwk2 Sol 7Dokument9 Seitenhwk2 Sol 7Shereen QassemNoch keine Bewertungen
- DataComm N Networking Solved ExamplesDokument10 SeitenDataComm N Networking Solved ExamplesMiguel CotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00 - Mobile Communication (404189) - Syllabus - OKDokument32 Seiten00 - Mobile Communication (404189) - Syllabus - OKvydeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Lab - 15ecl57 Part - IDokument37 SeitenDSP Lab - 15ecl57 Part - Ivsuresha25% (4)
- CS 601 Data Communication Latest File Spring 2021Dokument111 SeitenCS 601 Data Communication Latest File Spring 2021mc210202582 MUEEN HASANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16-Bit RISC PROCESSORDokument16 Seiten16-Bit RISC PROCESSORCroitoru Adrian100% (1)
- Assign 2Dokument3 SeitenAssign 2Kamran KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network Principles - Revision Exam PaperDokument18 SeitenComputer Network Principles - Revision Exam PaperEse KelvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Telecom and NetworkingDokument25 SeitenBasics of Telecom and NetworkingSujeet KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab ReportDokument7 SeitenMatlab ReportMUHAMAD_REHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programing LabDokument3 SeitenC Programing LabManasa Gowda100% (1)
- Wimax Bit Error Rate (Ber) With Awgn Channel For Variable Modulation TechniquesDokument9 SeitenWimax Bit Error Rate (Ber) With Awgn Channel For Variable Modulation TechniquesIzza AnshoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment#1Dokument5 SeitenAssignment#1Nabil ToorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science Formula BookDokument27 SeitenComputer Science Formula BookAnand KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource Planning Guide for Finding & Retaining TalentDokument15 SeitenHuman Resource Planning Guide for Finding & Retaining TalentSreekala SudheeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMP 103 3 Programming in C 3 0 3Dokument2 SeitenCMP 103 3 Programming in C 3 0 3Dinesh PudasainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExamDokument4 SeitenExamKiru Bagari VellaisamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument184 SeitenUntitledKathiravan ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTTP and FTP Chapter ProblemsDokument10 SeitenHTTP and FTP Chapter ProblemsFarhan Sheikh MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Outline ADCDokument3 SeitenCourse Outline ADCmnotcoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2marks & 16 MarksDokument4 Seiten2marks & 16 MarksJeremiah ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Aaoc C321 642 C 2009 1Dokument2 SeitenAaoc C321 642 C 2009 1Tushar GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN Unit1 8-7-10Dokument20 SeitenCN Unit1 8-7-10nallapatiharika0% (1)
- Data Communication Chapter 1 TestDokument14 SeitenData Communication Chapter 1 Testticktacktuck100% (2)
- Antenna Tutorials Question & AnswersDokument4 SeitenAntenna Tutorials Question & Answerscrazy about readingNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN Module I & IIDokument99 SeitenCN Module I & IIsaumya ranjan sahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Answers HW3Dokument5 SeitenModel Answers HW3John100% (1)
- Presentation About Computer NetworkingDokument55 SeitenPresentation About Computer NetworkingAbhishek AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network 1st AssignmentDokument3 SeitenComputer Network 1st AssignmentRodney AlexanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems and Digital Networks PDFDokument2 SeitenCommunication Systems and Digital Networks PDFChrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Dokument3 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)krithikgokul selvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Question Answers-MTDokument9 SeitenReview Question Answers-MTmad maran100% (1)
- HW9 SolDokument3 SeitenHW9 SolTài LâmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Switching Systems Course ContentDokument31 SeitenDigital Switching Systems Course ContentravimhattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP versions 0-5 and socket programming exercisesDokument6 SeitenIP versions 0-5 and socket programming exercisesS Sam100% (1)
- Introduction On Telephone TrafficDokument35 SeitenIntroduction On Telephone TrafficJanicePeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking Short Questions and AnswersDokument81 SeitenComputer Networking Short Questions and AnswersMuhammad AkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ FundamentalsDokument207 SeitenC++ Fundamentalsbrm1shubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Assignment - #01 - 29-08-2012Dokument3 SeitenClass Assignment - #01 - 29-08-2012Rahul Saxena50% (2)
- Final Exam 6340.Doc1May20161Dokument3 SeitenFinal Exam 6340.Doc1May20161waukeshajodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the Internet: A Glimpse into the Building Blocks, Applications, Security and Hidden Secrets of the WebVon EverandUnderstanding the Internet: A Glimpse into the Building Blocks, Applications, Security and Hidden Secrets of the WebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relational Data Model A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandRelational Data Model A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems Programming: Designing and Developing Distributed ApplicationsVon EverandSystems Programming: Designing and Developing Distributed ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0BzHu7MURhtkHbWxyZk9wRWpSTXJhLTNMUVZvR0dHNHZfajBj 1 PDFDokument2 Seiten0BzHu7MURhtkHbWxyZk9wRWpSTXJhLTNMUVZvR0dHNHZfajBj 1 PDFscribdaccount078Noch keine Bewertungen
- EC3023 2015-6 Problemsheet#2Dokument2 SeitenEC3023 2015-6 Problemsheet#2markNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birla Institute of Technology & Science Computer Networks Exam QuestionsDokument4 SeitenBirla Institute of Technology & Science Computer Networks Exam QuestionsChaitanyaLukkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mpeg 4 CCTVDokument1 SeiteMpeg 4 CCTVVijay UkaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 10 Use Case Modeling ErrorsDokument1 SeiteTop 10 Use Case Modeling ErrorsVijay UkaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network BasicsDokument87 SeitenNetwork BasicsVijay UkaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reliable Multicast Protocols and Applications CiscoDokument18 SeitenReliable Multicast Protocols and Applications CiscoVijay UkaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poster Wvs NDokument1 SeitePoster Wvs NVijay UkaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- WLAN HandoffDokument6 SeitenWLAN HandoffVijay UkaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular IP: 2 Cellular Internet 3 Protocol Overview 3.1 Features 3.2 Routing 3.3 Handoff 3.4 Paging ReferencesDokument6 SeitenCellular IP: 2 Cellular Internet 3 Protocol Overview 3.1 Features 3.2 Routing 3.3 Handoff 3.4 Paging ReferencesVijay UkaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable Net 2020 BrochureDokument124 SeitenCable Net 2020 BrochureBen PressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initial Script (3059)Dokument14 SeitenInitial Script (3059)lucky chandelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transceiver Data SheetDokument26 SeitenTransceiver Data SheetROGELIO GARCIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Atheros 6 G Mini-Pci Adapter Emp-8602 Plus-S: 2.4 / 5.0 GHZ 802.11A/B/G 54 MbpsDokument2 SeitenAtheros 6 G Mini-Pci Adapter Emp-8602 Plus-S: 2.4 / 5.0 GHZ 802.11A/B/G 54 MbpsAudiofilo84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Switching Basics.Dokument272 SeitenCisco Switching Basics.Vipin AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- WeekEndAssignment 01 1Dokument5 SeitenWeekEndAssignment 01 1adityadas.657Noch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial EthernetDokument398 SeitenIndustrial EthernetisaacsavioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Level OneDokument80 SeitenCatalogo Level Onemedo amgdNoch keine Bewertungen
- E400 Indoor Access Point: CnpilotDokument3 SeitenE400 Indoor Access Point: CnpilotsotodolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Quiz Connectivity QuestionsDokument2 SeitenLab Quiz Connectivity QuestionsAamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- PowerCube - 24.12.2020Dokument32 SeitenPowerCube - 24.12.2020Mustaf MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAC Protocols For Ad-Hoc Wireless NetworksDokument55 SeitenMAC Protocols For Ad-Hoc Wireless NetworksIqra HanifNoch keine Bewertungen
- SG350-28MP Datasheet: Get A QuoteDokument3 SeitenSG350-28MP Datasheet: Get A QuoteKali LinuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCN Unit - 4Dokument115 SeitenDCN Unit - 4Rohan SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerohive Certified Networking Professional (Acnp) : ConfidentialDokument622 SeitenAerohive Certified Networking Professional (Acnp) : ConfidentialAlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS6450 AOS 6.6.2 R02 CLI Reference GuideDokument1.864 SeitenOS6450 AOS 6.6.2 R02 CLI Reference GuideXavier BelondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lista de componentes del Servicio de TelefoníaDokument8 SeitenLista de componentes del Servicio de TelefoníaHHESCOBARF100% (1)
- Wifi Phy TestDokument44 SeitenWifi Phy TestNgo Tan BinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring Auto MdixDokument6 SeitenConfiguring Auto MdixTrịnh TrọngNoch keine Bewertungen
- AFDX - Real-Time EthernetDokument33 SeitenAFDX - Real-Time EthernetVarun AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- VLAN Basics PDFDokument4 SeitenVLAN Basics PDFAnuja AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AO DataSheet SFP ReferenciaDokument2 SeitenAO DataSheet SFP ReferenciaAntero CasaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aruba Ds Rap 100Dokument6 SeitenAruba Ds Rap 100Karimul Wafa AuvensevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEEDokument141 SeitenIEEEAdfgatLjsdcolqwdhjpNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMU-CS S252 - Introduction To Network - Telecommunication Technology - 2020S - Lecture Slides - 5Dokument24 SeitenCMU-CS S252 - Introduction To Network - Telecommunication Technology - 2020S - Lecture Slides - 5Quang Trần MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carrier Ethernet Academy: MEF-CECP Boot Camp Course Module 5-1Dokument27 SeitenCarrier Ethernet Academy: MEF-CECP Boot Camp Course Module 5-1Julio Carla Duda PintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stop-and-Wait ARQ Protocol: Unit 02.01.01 CS 5220: Computer CommunicationsDokument9 SeitenStop-and-Wait ARQ Protocol: Unit 02.01.01 CS 5220: Computer CommunicationsLong Trần Văn HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Training Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol RSTP TutorialDokument8 SeitenCCNA Training Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol RSTP TutorialMasterDefcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28GHz LMDS Datasheet Point To MultiPointDokument2 Seiten28GHz LMDS Datasheet Point To MultiPointyoiussefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ieee 802.11 Wireless Lan TechnologyDokument24 SeitenIeee 802.11 Wireless Lan Technologyvarsha rajNoch keine Bewertungen