Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
There Are Two Basic Categories of Transmission Media
Hochgeladen von
Abdirahman ElmiOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
There Are Two Basic Categories of Transmission Media
Hochgeladen von
Abdirahman ElmiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
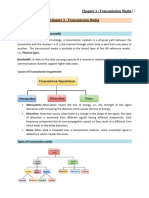
There are two basic categories of transmission media 1. Guided 2.
Unguided Guided Transmission media uses a Cabling system that guides the data signals along a specific path. The data signals are found by the cabling system. Guided media is also known as Bound media. Cabling is meant in a generic sense in the previous sentences and is not meant to be interpreted as copper wire cabling only. Unguided transmission media consists of a means for the data signals to travel but nothing to guide them along a specific path. The data signals are not bound to a cabling media and as such are after called unbounded media. There are four basic types of Guided media (i) Open wire (ii) Twisted pair (iii) Coaxial cable (iv) Optical fiber
Open wire: Open wire is traditionally used to describe the electrical wire strung along power roles. There is single wire strung between poles. No shielding or protection from noise interference. This can include multiconductor cables or single wire. This media is susceptible to a large degree of noise and interference and consequently not acceptable for data transmission except for short distances under 20 ft.
Twisted pair: The wires is twisted pair cabling are twisted together in pairs. Each pair would consist of wire used for the +ve data signal and a wire used for the ve data signal. Any noise that appears on +ve/ve wire of the pair would occur on the other wire. Because the wires are opposite polarities, they are 180 degrees out of phase (180 degree phases or definition of opposite polarity) when the noise appears on both wires, it cancels or nulls itself out at the receiving used. Twisted pair cables are most effectively used in system that use a balanced line method of transmission. Polar line coding ( Manchester encoding) as opposed to unipolar line coding.
The degree of reduction in noise interference is determined specially by the number of turns per foot increasing the number of turns per foot reduces the noise interference. To further improve noise rejection, a foil or wire braid shield is wound around the twisted pair. This shield can be moves around individual pairs or around a multi pair conductor. Cables with the shield are called shielded twisted pair and commonly abbreviated SIP. Cables without a shield are called unshielded twisted pair or UTP. Twisting the wires together results in characteristics impedance for the cable. UTP or unshielded twisted pair cable is used on Ethernet 10 Base T and can also be used with taken ring, It uses the RJ line of connectors (RJ 45, RJ 11 etc). STP or shielded twisted pair is used with the traditional Token Ring Cabling.
Coaxial cable: Coaxial cable consists of 2 conductors. The inner
conductor is held
Inside the insulator with the other conductor waves around it providing a shield, an insulating protective coating called a jacket covers the outer conductor. The outer shield protects the inner conductor from outside electrical signals. The distance between the outer conductor (Shield) and inner conductor plus the type of material used for insulating the inner conductor determine the cable properties or impedance. Typical impedance for coaxial cables is 75 ohm for cable TV, 50 ohm for Ethernet thermite and thicknet. The excellent control of the impedance characteristics of the cable allow higher data rates to be transferred than twisted pair cable. Optical Fiber: Optical fiber consists of thin glass fiber that can carry information at frequencies in the visible light spectrum. The typical optical fiber consists of a very narrow strand of glass called the cladding. A typical core diameter is 62.5 microns. Typically cladding has a diameter of 125 minors. Coating the cladding is a protective coating consisting of plastic, it is called the jacket.
Unguided media transport electromagnetic waves without using a physical conductor. Type of communication is often referred to as wireless communication. There are three types of Unguided Media (i) Radio waves (ii) Micro waves
(iii) Infrared. (i) Radio waves: Electromagnetic wave ranging in frequencies between 3 KHz and TGHz are normally called radio waves. Radio waves are omnidirectional when an antenna transmits radio waves they are propagated in all directions. This means that sending and receiving antenna do not have to he aligned. A sending antenna can send waves that can be received by any receiving antenna. Radio waves particularly those waves that propagate in sky mode, can travel long distances. This makes radio waves a good candidate for long-distance broadcasting such as AM radio. Radio waves particularly those of low and medium frequencies can penetrate walls. It is an advantage because; an AM radio can receive signals inside a building. It is the disadvantage because we cannot isolate a communication to first inside or outside a building. The radio waves band is relatively narrow just under I GHz, compared to the microwave band. When this band is divided into subband, the sidebands are also narrow, leading to a low data rate for digital communications.
Microwaves: Electromagnetic waves having frequencies between I and 300 GFL are called microwaves. Microwaves are unidirectional, when an antenna transmits microwaves they can be narrowly focused. This means that the
sending and receiving antennas need to be aligned. The unidirectional property has an obvious advantage. A pair of antennas can be aligned without interfering with another pair of aligned antennas. On the other hand microwaves. Propagation is line-of-sight. Since the towers with the mounted antennas needs to be in direct sight of each other, towers that are for apart need to he very tall, the curvature of the earth as well as other blocking obstacles do not allow two short towers to communicate using microwaves, Repeaters are often needed for long distance communication very high frequency microwaves cannot penetrate waIls.
Parabolic dish antenna and horn antenna are used for this means of transmission
Infrared: Infrared signals with frequencies ranges from 300 GHz to 400 1Hz can be used for short range communication. Infrared signals, having high frequencies, cannot penetrate walls. This helps to prevent interference between one system and another. in this one room cannot be affected by the infrared waves in another room. fl infrared band, almost 400 THz, has an excellent potential for data transmission. So this will transfer digital data with a very high frequency. There are no. of computer devices which are used to send the data through infrared medium e.g. keyboard mice, PCs and
printers. There are some manufacturers provide a special part called the IrDA port that allows a wireless keyboard to communicate with a PC
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Unit 2Dokument15 SeitenUnit 2sahilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4Dokument12 SeitenLesson 4Kean Rafael MarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guided MediaDokument23 SeitenGuided MediaJohn Ellonye AckahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data CommunicationDokument10 SeitenData CommunicationMuhammad MaazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guided Vs Unguided Transmission MediaDokument14 SeitenGuided Vs Unguided Transmission Mediamuhammad haris aqeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example: For A Written Message, The Transmission Medium Might Be A Mail Carrier, A Truck, or An AirplaneDokument33 SeitenExample: For A Written Message, The Transmission Medium Might Be A Mail Carrier, A Truck, or An AirplaneAnil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument70 SeitenUnit 2Gaytri HogaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Media: A. Guided Transmission Media B. Unguided Transmission MediaDokument4 SeitenTransmission Media: A. Guided Transmission Media B. Unguided Transmission MediaRonit SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission MediaDokument16 SeitenTransmission MediaJames MacalaladNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission MediaDokument6 SeitenTransmission Mediamahar.nomi1039Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission MediaDokument73 SeitenTransmission Mediahardcore85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Networ Techinical Skills ICT1532 Assignement 2Dokument12 SeitenNetwor Techinical Skills ICT1532 Assignement 2mahlatse iven somelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Layer 3Dokument17 SeitenPhysical Layer 3soumen maityNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Transmission MediaDokument24 Seiten4 Transmission MediaRashad MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- MediaDokument19 SeitenMediaDeepak KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 170 Transmission MediaDokument39 Seiten170 Transmission Mediahauwauibrahimmagaji532Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission MediumDokument12 SeitenTransmission MediumSuryanshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trans Miss On MediaDokument13 SeitenTrans Miss On Mediahatim44026Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - NetworkingDokument9 SeitenChapter 3 - Networkingninjamekwan10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Layer: Transmission Media - Guided Transmission MediaDokument185 SeitenPhysical Layer: Transmission Media - Guided Transmission MediaDeepika SheshabutterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission MediaDokument9 SeitenTransmission MediaCatherine KiwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking Transmission MediaDokument42 SeitenNetworking Transmission MediaMaxwell KoomsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit1-Transmission MediaDokument9 SeitenUnit1-Transmission MediaManmohan K GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Channel & Its TypesDokument7 SeitenCommunication Channel & Its TypesShiekhDaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emi AND EmcDokument7 SeitenEmi AND Emcmanojkumar9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No #3: What Is Transmission Media?Dokument5 SeitenAssignment No #3: What Is Transmission Media?ArslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2-: Physical LayerDokument26 SeitenChapter 2-: Physical Layeralish shrsethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument84 SeitenUnit 2Gaytri HogaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Transmission MediaDokument2 SeitenTypes of Transmission MediaFRANCISCO JERHYL KEITH G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission MediaDokument33 SeitenTransmission MediaLYF WITH AK KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fibre Communication With Overview 1.pdf 2Dokument97 SeitenOptical Fibre Communication With Overview 1.pdf 2ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC - Module IIDokument19 SeitenDC - Module IIveenadivyakishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication and Networking: Chapter TwoDokument22 SeitenData Communication and Networking: Chapter TwoMahamud elmogeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Media (Communication Media)Dokument22 SeitenTransmission Media (Communication Media)HarishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of Media: Transmission MediumDokument13 SeitenDifferent Types of Media: Transmission MediumParvesh RishieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Computer NetworksDokument9 SeitenUnit 4 Computer Networkspratyay dhondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication ChannelsDokument3 SeitenCommunication ChannelsMukul BagreNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Physical Layer: Unit - 2Dokument22 SeitenThe Physical Layer: Unit - 2Phani VishwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Media (Communication Media)Dokument22 SeitenTransmission Media (Communication Media)Viral NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Media: Guided: Transmission Capacity Depends Critically On The Medium, The Length, andDokument10 SeitenTransmission Media: Guided: Transmission Capacity Depends Critically On The Medium, The Length, andMONEER THAMEERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data TransmissionDokument7 SeitenData Transmissionantonially24Noch keine Bewertungen
- NET 201 Module 4Dokument13 SeitenNET 201 Module 4RickCy Perucho PccbsitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking NotesDokument13 SeitenComputer Networking Notesanamayasharma2953Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matter - TNT PhysicsDokument5 SeitenMatter - TNT PhysicsTamiranashe Tammie NyunguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research WorkDokument24 SeitenResearch WorkSindhuja VarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Media ProjectDokument10 SeitenTransmission Media ProjectSahil Aggarwal60% (5)
- COM 122 Introduction To Internent Lecture Note 3Dokument8 SeitenCOM 122 Introduction To Internent Lecture Note 3Elijah OlusegunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Media 1. Guided MediaDokument2 SeitenTransmission Media 1. Guided MediaHana hanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment of NetworkingDokument13 SeitenAssignment of NetworkingJyoti BhanotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Transmission MeidaDokument5 SeitenData Transmission MeidaRana Sarfraz NawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Media ManualDokument10 SeitenTransmission Media ManualVarun RankajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Medias and TopologiesDokument49 SeitenCommunication Medias and TopologiesAmjad IrshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 2 - Physical LayerDokument59 SeitenUNIT 2 - Physical Layerpatilamrutak2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission MediaDokument12 SeitenTransmission MediaJatin RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Mod 2Dokument154 SeitenDC Mod 2Athulya M ArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Model NotesDokument18 SeitenCommunication Model NotesjolieprincesseishimweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission MediaDokument31 SeitenTransmission Mediahadirehman488Noch keine Bewertungen
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)Von EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsVon EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- KrauseDokument3 SeitenKrauseVasile CuprianNoch keine Bewertungen
- tdr100 - DeviceDokument4 Seitentdr100 - DeviceSrđan PavićNoch keine Bewertungen
- PartitionDokument5 SeitenPartitionKotagiri AravindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Majalah Remaja Islam Drise #09 by Majalah Drise - Issuu PDFDokument1 SeiteMajalah Remaja Islam Drise #09 by Majalah Drise - Issuu PDFBalqis Ar-Rubayyi' Binti HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCS Valve: Minimizes Body Washout Problems and Provides Reliable Low-Pressure SealingDokument4 SeitenMCS Valve: Minimizes Body Washout Problems and Provides Reliable Low-Pressure SealingTerry SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1grade 9 Daily Lesson Log For Demo 1 4Dokument5 Seiten1grade 9 Daily Lesson Log For Demo 1 4cristy olivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economies and Diseconomies of ScaleDokument7 SeitenEconomies and Diseconomies of Scale2154 taibakhatunNoch keine Bewertungen
- OrganometallicsDokument53 SeitenOrganometallicsSaman KadambNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sun Nuclear 3D SCANNERDokument7 SeitenSun Nuclear 3D SCANNERFranco OrlandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation and Frequency Synthesis X Digital Wireless RadioDokument233 SeitenModulation and Frequency Synthesis X Digital Wireless Radiolcnblzr3877Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elliot WaveDokument11 SeitenElliot WavevikramNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE1000 DC Networks Problem SetDokument7 SeitenEE1000 DC Networks Problem SetAmit DipankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- LICDokument82 SeitenLICTinu Burmi Anand100% (2)
- Application of ARIMAX ModelDokument5 SeitenApplication of ARIMAX ModelAgus Setiansyah Idris ShalehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gmo EssayDokument4 SeitenGmo Essayapi-270707439Noch keine Bewertungen
- Relevant Cost For Decision: Kelompok 2Dokument78 SeitenRelevant Cost For Decision: Kelompok 2prames tiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Price Book 524Dokument1 SeiteABB Price Book 524EliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minor Project Report Format MCADokument11 SeitenMinor Project Report Format MCAAnurag AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kayako Support Suite User Manual PDFDokument517 SeitenKayako Support Suite User Manual PDFallQoo SEO BaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preventive Maintenance - HematologyDokument5 SeitenPreventive Maintenance - HematologyBem GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Between:-Mr. Pedro Jose de Vasconcelos, of Address 14 CrombieDokument2 SeitenBetween:-Mr. Pedro Jose de Vasconcelos, of Address 14 Crombiednd offiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projects: Term ProjectDokument2 SeitenProjects: Term ProjectCoursePinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of SOADokument36 SeitenPrinciples of SOANgoc LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.mukherjee - 2019 - SMM - Customers Passion For BrandsDokument14 Seiten1.mukherjee - 2019 - SMM - Customers Passion For BrandsnadimNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC Building Wiring Installation NC IIDokument72 SeitenCBC Building Wiring Installation NC IIFaysbuk KotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Estimate Template PDFDokument1 SeiteElectrical Estimate Template PDFMEGAWATT CONTRACTING AND ELECTRICITY COMPANYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sciencedirect: Jad Imseitif, He Tang, Mike Smith Jad Imseitif, He Tang, Mike SmithDokument10 SeitenSciencedirect: Jad Imseitif, He Tang, Mike Smith Jad Imseitif, He Tang, Mike SmithTushar singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exoskeleton ArmDokument5 SeitenExoskeleton Armc214ocNoch keine Bewertungen
- PanasonicDokument35 SeitenPanasonicAsif Shaikh0% (1)