Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CH 25 - The Reproductive Systems and Development
Hochgeladen von
Ken1901Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CH 25 - The Reproductive Systems and Development
Hochgeladen von
Ken1901Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
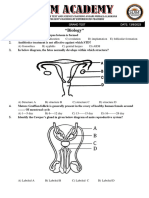
Name: __________________________ Date: _____________ Link to: 25.1 The scrotum 1.
This structure protects and regulates the temperature of the testes A) Dartos muscle B) Cremaster muscle C) D) E) Tunica albuginea Scrotum Tunica vaginalis
Ans: D
Link to: 25.1 The scrotum 2. This structure is the site of sperm production. A) Vas deferens B) Seminiferous tubules C) D) E) Albuginea Epididymis Raphe
Ans: B
Link to: 25.1 The scrotum 3. How many seminiferous tubules are found in the lobules? A) 1-3 B) 50-100 C) D) E) 200-300 500 or more Millions
Ans: A
Page 1
Link to: 25.1 The scrotum 4. These cells may eventually become spermatozoa A) Sertoli cells B) Sustentacular cells C) D) E) Spermatogenic cells Chief cells Speciation cells
Ans: C
Link to: 25.1 The scrotum 5. These cells secrete testosterone. A) Sertoli cells B) Spermatogenic cells C) D) E) Leydig cells Oogonia Chief cells
Ans: C
Link to: 25.1 The scrotum 6. This hormone stimulates Leydig cells to secrete testosterone. A) GnRH B) LH C) D) E) FSH DHT None of the above
Ans: B
Link to: 25.2 Sperm travel 7. The straight tubules in the testis lead into the: A) Efferent ducts B) Afferent ducts C) D) E) Rete testis Ductus epididymis Epididymis
Ans: C
Link to: 25.2 Sperm travel 8. The function of the epididymis is A) Sperm maturation B) Produce sperm C) D) E) Speratid storage Provide nutrition to sperm Absorption of calcium
Ans: A
Link to: 25.2 Sperm travel 9. This is formed by the union of the duct from the seminal vesicle and the ampulla of the vas deferens. A) Urtethra B) Spermatic cord C) D) E) Inguinal canal Ejaculatory duct Prostate
Ans: D
Page 3
Link to: 25.2 Sperm travel 10. This structure lies posterior to the bladder and anterior to the rectum and secretes an alkaline, fructose-filled fluid. A) Prostate B) Bulbourethral gland C) D) E) Seminal vesicles Spongy urethra Prostatic urethra
Ans: C
Link to: 25.2 Sperm travel 11. These are located inferior to the prostate on other side of the membranous urethra within the deep muscles of the perineum. A) Bulbourethral glands B) Seminal vesicles C) D) E) Ejaculatory ducts Urethral ducts Prostate
Ans: A
Link to: 25.2 Sperm travel 12. This structure is composed of three cylindrical masses of erectile tissue each surrounded by a fibrous tissue. A) Testes B) Prostate C) D) E) Bladder Penis Urethra
Ans: D
Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 13. What is produced by the ovaries? A) Primary oocytes, insulin and estrogen B) Secondary oocytes, progesterone and cortisol C) D) E) Tertiary oocytes, insulin and estrogen Secondary oocytes, estrogen and progesterone Primary oocytes, estrogen and testosterone
Ans: D
Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 14. This structure attaches the ovaries and the uterus to the pelvic wall. A) Broad ligament B) Mesovarium C) D) E) Ovarian ligament Suspensory ligament Hilum
Ans: A
Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 15. This is the site of fertilization. A) Ureters B) Urethra C) D) E) Uterine tubes Ovaries Vagina
Ans: C
Page 5
Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 16. This is the portion of the uterus that opens into the vagina. A) Urethra B) Cervix C) D) E) Uterine tubes Inguinal canal Ovaries
Ans: B
Link to: 25.4 The vagina 17. Anterior to the vagina and urethral openings is the A) Labia majora B) Labia minor C) D) E) Mons pubis Cervical sphincter Labial frenulum
Ans: C
Link to: 25.5 The female reproductive 18. __________ hormone, secreted by the __________ , controls the ovarian and uterine cycles. A) FSH, anterior pituitary B) LH, anterior pituitary C) D) E) GnRH, hypothalamus HGH, hypothalamus Estrogens, ovaries
Ans: C
Link to: 25.1 19. This hormone promotes spermatogenesis. A) Relaxin B) Testosterone C) D) E) Inhibin Estrogen Aldosterone
Ans: B
Link to: 25.5 The female reproductive 20. This hormone triggers ovulation. A) GnRH B) LH C) D) E) FSH Estrogen Progesterone
Ans: B
Link to: 25.5 The female reproductive 21. This is secreted by the corpus luteum after ovulation. A) Progesterone B) Relaxin C) D) E) LH FSH HGH
Ans: A
Page 7
Link to: 25.5 The female reproductive 22. This is the uterine phase when the thickness of the endometrium doubles. A) Menstrual phase B) Preovulatory phase C) D) E) Proliferative phase Follicular phase Postovulatory phase
Ans: C
Link to: 25.5 The female reproductive 23. This is the ovarian phase between the end of menstruation and beginning of ovulation. A) Menstrual phase B) Preovulatory phase C) D) E) Proliferative phase Follicular phase Postovulatory phase
Ans: B
Use the following to answer questions 24-26:
Reference: Ref 25-1 Link to: 25.1 24. What does line A point to? A) Lymphatic vessels B) Pampiniform plexus C) D) E) Internal spermatic fascia Spermatic cord Fundiform ligament
Ans: D
Page 9
Reference: Ref 25-1 Link to: 25.1 25. Which structure has a portion removed in a vasectomy? A) A B) D C) D) E) E G I
Ans: B
Reference: Ref 25-1 Link to: 25.1 26. What does line G point to? A) Dartos muscle B) Cremaster muscle C) D) E) Fascia Tunica albuginea Tunica vaginalis
Ans: E
Use the following to answer questions 27-29:
Reference: Ref 25-2 Link to: 25.1 27. What is line C pointing to? A) Efferent duct B) Body of epididymis C) D) E) Straight tubule Seminiferous tubule Lobule
Ans: B
Page 11
Reference: Ref 25-2 Link to: 25.1 28. Where are the straight tubules? A) A B) B C) D) E) C D E
Ans: E
Reference: Ref 25-2 Link to: 25.1 29. What is line F pointing to? A) Ductus epididymis B) Rete testis C) D) E) Efferent duct Afferent duct Seminiferous tubules
Ans: E
Use the following to answer questions 30-33:
Reference: Ref 25-3 Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 30. Which structure is part of the connection of the uterus to the pelvic cavity? A) B B) C C) D) E) E G H
Ans: C
Page 13
Reference: Ref 25-3 Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 31. What is line C pointing to? A) Bladder B) Fimbriae C) D) E) Ovary Uterus Perineum
Ans: C
Reference: Ref 25-3 Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 32. This is the site for implantation of a fertilized ovum. A) A B) B C) D) E) C D F
Ans: D
Reference: Ref 25-3 Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 33. This opens from the uterus to the vagina. A) E B) F C) D) E) G H None of the above
Ans: B
Use the following to answer questions 34-38:
Reference: Ref 25-4 Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 34. This consists of primary oocyte that is surrounded by several layers of cuboidal granulosa cells. A) A B) B C) D) E) C F H
Ans: B
Page 15
Reference: Ref 25-4 Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 35. Where is the mature (graafian) follicle? A) A B) B C) D) E) C F H
Ans: D
Reference: Ref 25-4 Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 36. Where is the corpus albicans? A) F B) G C) D) E) H I None of the above
Ans: E
Reference: Ref 25-4 Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 37. This structure will produce progesterone, estrogens, relaxin and inhibin. A) D B) E C) D) E) G I None of the above
Ans: D
Reference: Ref 25-4 Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 38. What is line D pointing to? A) Follicular fluid B) Germinal epithelium C) D) E) Ovarian cortex Ovarian medulla None of the above
Ans: B
Link to: 25.6 The zygote divides 39. Fertilization normally occurs within which structure? A) Ovary B) Fallopian tube C) D) E) Ovarian ligament Body of uterus Vagina
Ans: B
Link to: 25.6 The zygote divides 40. This is a series of functional changes that sperm go through when they are in the female reproductive tract. A) Acrosomal reaction B) Maturation C) D) E) Fertilization Capacitation Polyspermy
Ans: D
Page 17
Link to: 25.6 The zygote divides 41. The fusion of the male pronucleus and the female pronucleus results in which developmental stage? A) Female pronucleus B) Male pronucleus C) D) E) Zygote Blastomeres Morula
Ans: C
Link to: 25.6 The zygote divides 42. This is the part of the blastocyst that promotes implantation and produces hCG. A) Blastocyte B) Blastosphere C) D) E) Trophoblast Blastocyst cavity Uterine cavity
Ans: C
Link to: 25.6 The zygote divides 43. This is the portion of the endometrium that lies between the embryo and the stratum basalis. A) Decidua basalis B) Decidua capsularis C) D) E) Decidua parietalis Lamina propria Adventitia
Ans: A
Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 44. This develops from the epiblast and carries a protective fluid. A) Cytotrophoblast B) Yolk sac C) D) E) Exocoelomic membrane Amnion Lacunae
Ans: D
Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 45. This will become the primary structure for exchange of material between the mother and the fetus. A) Chorionic villi of the placenta B) Amnion C) D) E) Amnionic fluid Embryonic disc Endoderm
Ans: A
Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 46. This is the connection between the placenta and the embryo. A) Amnion B) Chorion C) D) E) Umbilical cord Placenta Capillary beds
Ans: C
Page 19
Link to: 25.8 During pregnancy 47. During pregnancy stroke volume can increase by A) 10% B) 20% C) D) E) 30% 40% 50%
Ans: C
Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 48. This is the time from the onset of labor to the complete dilation of the cervix. A) Stage of dilation B) Stage of expulsion C) D) E) Placental stage Gestation Effacement
Ans: A
Link to: 25.9 Labor 49. Involution is A) when the placenta is expelled B) when the umbilical cord is cut C) D) E) when the uterus decreases in size when the cervix dilates None of the above
Ans: C
Link to: 25.10 50. This is a principle hormone that releases milk into the mammary ducts. A) Prolactin B) PIH C) D) E) PRH Oxytocin GnRH
Ans: D
Use the following to answer questions 51-53:
Page 21
Reference: Ref 25-5 Link to: 25.3 After a secondary oocyte 51. Which one represents the morula stage? A) A B) B C) D) E) C D E
Ans: C
Reference: Ref 25-5 Link to: 25.6 The zygote divides 52. Which one represents the blastocyst stage? A) A B) B C) D) C D
Ans: D
Reference: Ref 25-5 Link to: 25.6 The zygote divides 53. What does diagram A represent? A) Cleavage of embryo B) Cleavage of zygote C) D) E) Cleavage of morula Cleavage of blastocyst Cleavage of fetus
Ans: B
Link to: 25.6 The zygote divides 54. What is line A pointing to?
A) B) C) D) E)
Endometrial gland Trophoblast Embryoblast Blastocyst Dermatome
Ans: B
Page 23
Use the following to answer questions 55-56:
Reference: Ref 25-6 Link to: 25.6 The zygote divides 55. What stage happens 3-4 days after fertilization? A) A B) B C) D) E) C D E
Ans: C
Reference: Ref 25-6 Link to: 25.6 The zygote divides 56. What stage happens 6 days after fertilization? A) A B) B C) D) E) C D E
Ans: E
Use the following to answer questions 57-61:
Page 25
Reference: Ref 25-7 Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 57. This was formerly called the blastocyst cavity. A) C B) D C) D) E) E F G
Ans: D
Reference: Ref 25-7 Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 58. This is composed of the syncytiotrophoblast and the cytotrophoblast. A) A B) B C) D) E) C D E
Ans: C
Reference: Ref 25-7 Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 59. Where is the amniotic cavity? A) E B) D C) D) E) C B A
Ans: A
Reference: Ref 25-7 Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 60. Where is the yolk sac? A) A B) B C) D) E) E F G
Ans: D
Reference: Ref 25-7 Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 61. What is line G pointing to? A) chorion B) chorionic villi C) D) E) sinusoid extraembryonic mesoderm None of the above
Ans: E
Use the following to answer questions 62-64:
Page 27
Reference: Ref 25-8 Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 62. What is line G pointing to? A) chorionic villi B) amnion C) D) E) umbilical vein umbilical artery amnionic capillary bed
Ans: A
Reference: Ref 25-8 Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 63. Where are the fetal blood vessels? A) C B) D C) D) E) E F G
Ans: C
Reference: Ref 25-8 Link to: 25.7 During the embryonic period 64. What is line F pointing to? A) umbilical arteries B) umbilical vein C) D) E) fetal blood vessels maternal endometrial arteriole chorionic villi
Ans: D
Link to: 25.9 Labor 65. Uterine contractions during labor are stimulated by a positive feedback loop involving a pituitary hormone called A) vasopressin. B) oxytocin. C) D) E) prolactin. relaxin. estrogen.
Ans: B
Link to: 25.2 Sperm travel 66. Trace the path of a sperm cell from the site of its maturation to the site where it leaves the male body. Include descriptions of fluids added along that path. Ans: Sperm mature in the epididymis. From there, they travel through the ductus (Vas) deferens through the abdominal cavity to the ampulla of the ductus deferens which merges with the duct of the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct. Sperm and the alkaline, fructose-rich fluid from the seminal vesicle move from the ejaculatory duct into the prostatic urethra, where they are mixed with a slightly acidic mucoid fluid from the prostate. Next the sperm and fluid pass through the membranous urethra and are mixed with additional alkaline secretions from the bulbourethral glands. The combination of sperm and secretions is called semen. The mixture travels through the penile urethra as it is ejaculated. Link to: 25.1 67. Describe the functions of testosterone. Ans: Testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male secondary sex characteristics, protein anabolism, development of sexual function (behavior, libido, spermatogenesis), and the male pattern of development during prenatal life. Link to: 25.5 The female reproductive 68. Describe the roles of estrogens and progesterone. Ans: Estrogens stimulate the growth, development and maintenance of the female reproductive structures. They stimulate the development of female secondary sex traits including the development of breasts and the pattern deposition of subcutaneous body fat. Estrogens cause the build up of the endometrial lining that prepares the uterus for implantation of the embryo. Estrogens also stimulate protein synthesis. Progesterone works with estrogens to prepare the endometrium for implantation and to prepare the breasts for milk production. Progesterone is critical to maintaining the endometrium throughout a pregnancy.
Page 29
Link to: 25.5 The female reproductive 69. Describe the positive feedback loop involved in ovulation. Ans: FSH and LH promote follicular development, thus increasing estrogen production. High levels of estrogen during the late preovulatory phase stimulate release of GnRH from the hypothalamus. GnRH promotes release of more FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary. Peak levels of LH trigger ovulation Link to: 25.9 Labor 70. Describe the stages of labor. Ans: 1. The stage of dilation is the time from the onset of labor to the complete dilation of the cervix. 2. The stage of expulsion is the time from complete cervical dilation to delivery. 3. The placental stage is the time after delivery of the offspring until the placenta is expelled.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Anatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsVon EverandAnatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (15)
- Imat 2021 Italian Exam (ENG)Dokument13 SeitenImat 2021 Italian Exam (ENG)Mert Tan Tari100% (1)
- Human Anatomy 7th Edition Marieb Test BankDokument20 SeitenHuman Anatomy 7th Edition Marieb Test BankKerriAdamsdwroi100% (14)
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 2: The Female Reproductive System and The Menstrual CycleDokument25 SeitenScience: Quarter 3 - Module 2: The Female Reproductive System and The Menstrual Cyclejane mamon100% (1)
- Ain Shams MCQDokument84 SeitenAin Shams MCQAhmed M. Haroun67% (6)
- Multi Choice Questions Surg IrhDokument58 SeitenMulti Choice Questions Surg IrhFan Eli100% (13)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In HumanVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In HumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- D) Seminal Vesicle: C) EpididymisDokument3 SeitenD) Seminal Vesicle: C) EpididymisEfanPutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH27Dokument18 SeitenCH27Nataliya ShefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 43 Reproductive Systems: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument23 SeitenChapter 43 Reproductive Systems: Multiple Choice QuestionsAnonymous Azxx3Kp9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 4 A and P 2Dokument8 SeitenQuiz 4 A and P 2Agartha HenewaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-3 MCQDokument10 SeitenChapter-3 MCQPriya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTS-3 STARS Academy Multan Campus-Secure PDFDokument14 SeitenCTS-3 STARS Academy Multan Campus-Secure PDFHanzala ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- MarsiiDokument35 SeitenMarsiiMariel Magtalas100% (1)
- Human Reproduction Udaan DPPDokument15 SeitenHuman Reproduction Udaan DPPxxjksvddukebNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10th Foundation - Biology-July-2023Dokument6 Seiten10th Foundation - Biology-July-2023prince2216jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human ReproductionDokument15 SeitenHuman ReproductionkarthibaashokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Appleton 7Dokument16 SeitenSoal Appleton 7Robertus HajaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HUMAN REPRODUCTION-1 Madhu - QuestionDokument69 SeitenHUMAN REPRODUCTION-1 Madhu - QuestionAyan Sarkar100% (1)
- Human ReproductionDokument107 SeitenHuman ReproductionYashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam AnatomyDokument8 SeitenFinal Exam Anatomybillrn21Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 Anatomy MCQsDokument10 Seiten2009 Anatomy MCQsAndrew Kalaw100% (2)
- Human Sexuality in A Changing World 10th Edition Rathus Test BankDokument17 SeitenHuman Sexuality in A Changing World 10th Edition Rathus Test BankLindaCruzDDSncfge100% (15)
- Reproductive HealthDokument103 SeitenReproductive HealthShaibu HamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReproductionDokument17 SeitenReproductionkaran79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kolfe Keranyo Sub City Educational Office Grade 8 Biology Final Examination 2010Dokument5 SeitenKolfe Keranyo Sub City Educational Office Grade 8 Biology Final Examination 2010Emma Mohamed KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 EmbryologyDokument13 Seiten2 EmbryologyManisanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.6 and 11.4 Bio QuestionsDokument14 Seiten6.6 and 11.4 Bio QuestionsJennifer BracyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY, PT1 QuestionsDokument8 SeitenBIOLOGY, PT1 QuestionsAbhishek ratnooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Entry Mock Test-1Dokument16 SeitenPre Entry Mock Test-1ainalashari69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Human Reproduction MCQs IDokument13 SeitenHuman Reproduction MCQs IMahendhiran MariappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shum 104811Dokument12 SeitenShum 104811Daniel GtsadkanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Sexuality in A Changing World 10th Edition Rathus Nevid Test BankDokument17 SeitenHuman Sexuality in A Changing World 10th Edition Rathus Nevid Test Bankamy100% (23)
- Nustmedical Test01Dokument15 SeitenNustmedical Test01MuhammadAbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam MCQ عين شمس + AnswersDokument118 SeitenExam MCQ عين شمس + AnswersIsmail Ahmed0% (1)
- Nikhil Bio ExamDokument15 SeitenNikhil Bio ExamHein Thant SweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Review QuestionsDokument104 SeitenAnatomy Review QuestionsVince CabahugNoch keine Bewertungen
- 123 Human Reproduction NCERTDokument20 Seiten123 Human Reproduction NCERTtashukumar33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Answer KeyDokument16 SeitenAnatomy Answer Keylovelots1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Embryology Questions: Husain MohammadDokument25 SeitenGeneral Embryology Questions: Husain MohammadMoiez AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive System TestDokument12 SeitenReproductive System TestVân vui vẻNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Principles of Human Physiology 4th Edition by StanfieldDokument23 SeitenTest Bank For Principles of Human Physiology 4th Edition by Stanfieldmangcornuntune6o9xNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESIC IMO Grade II Gynaecology Obstetrics PaperDokument12 SeitenESIC IMO Grade II Gynaecology Obstetrics PaperSubhrajit GhantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank MCQ BSMTDokument14 SeitenQuestion Bank MCQ BSMTHifza KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmbryologyDokument29 SeitenEmbryologySara Gblabi50% (2)
- Zoology MCQsDokument26 SeitenZoology MCQsUmair KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 12Dokument177 SeitenChapter1 12Robertus Hajai0% (1)
- Medicine - MAY 2010Dokument34 SeitenMedicine - MAY 2010qudsia_niaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy End of YearDokument9 SeitenAnatomy End of YearmudendasiambulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ S ZoologyDokument102 SeitenMCQ S ZoologySapath GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Lab Sas-44Dokument2 SeitenAnaphy Lab Sas-44Francis Steve RipdosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 1 09-QuestionsDokument16 SeitenBio 1 09-QuestionsYousef AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imperial Guide1Dokument21 SeitenImperial Guide1dawosika2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology 1st Semester BSN Mcqs AD, Educational PlatformDokument18 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology 1st Semester BSN Mcqs AD, Educational PlatformPrince Masroor Ali Abro100% (1)
- Paper 1 Biology Form 5Dokument11 SeitenPaper 1 Biology Form 5GerlJerlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model MCQ Histo Embryo GADokument8 SeitenModel MCQ Histo Embryo GAMuhammad kamran ameerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument21 SeitenChapter 1Allyson OffreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dictionary of Stem Cells, Regenerative Medicine, and Translational MedicineVon EverandDictionary of Stem Cells, Regenerative Medicine, and Translational MedicineNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In HumansVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In HumansBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (2)
- FRCPath Part 1: Examination Preparation Guide: eBookVon EverandFRCPath Part 1: Examination Preparation Guide: eBookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colorectal Surgery: Clinical Care and ManagementVon EverandColorectal Surgery: Clinical Care and ManagementBruce GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MenstrualcyclelecturedrirabonDokument32 SeitenMenstrualcyclelecturedrirabonHananya ManroeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 3rd Grading Module 1 REPRODUCTIVESYSTEMDokument32 SeitenScience 10 3rd Grading Module 1 REPRODUCTIVESYSTEMvinesse100% (1)
- NCERT Class 12 Biology Human ReproductionDokument15 SeitenNCERT Class 12 Biology Human ReproductionSrajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fertility AwarenessDokument5 SeitenFertility AwarenessGabriela GascaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive Endocrinology and HyperandrogenismDokument11 SeitenReproductive Endocrinology and HyperandrogenismaamnakamalkqNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 2 IMDokument215 SeitenGeneral Biology 2 IMPatrick Verroya100% (1)
- Unit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleDokument20 SeitenUnit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleMARIANNE SORIANO100% (2)
- Test Bank For Nutrition Through The Life Cycle 5th Edition Judith e BrownDokument36 SeitenTest Bank For Nutrition Through The Life Cycle 5th Edition Judith e Brownmyositisenigmakoh3100% (44)
- Injection ContraceptionDokument3 SeitenInjection ContraceptionEzyan SyaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science10 Q3 SLM5 1 PDFDokument17 SeitenScience10 Q3 SLM5 1 PDFBien DivinaflorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Reproduction PyqsDokument7 SeitenHuman Reproduction PyqsMrityunjay PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay On King LearDokument7 SeitenEssay On King Learyezfvwwhd100% (2)
- Menstrual CycleDokument8 SeitenMenstrual Cyclejeni antonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estros Cycle in DogsDokument3 SeitenEstros Cycle in DogsnessimmounirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menstrual CycleDokument9 SeitenMenstrual Cyclevarshasharma05100% (2)
- Hormonal Cycle Lesson PlanDokument7 SeitenHormonal Cycle Lesson Plannisha kaushik100% (2)
- The Female Reproductive System Is Designed To Carry Out Several FunctionsDokument2 SeitenThe Female Reproductive System Is Designed To Carry Out Several FunctionsArdie MingayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Menstrual CycleDokument28 SeitenNormal Menstrual CycleCristóbal ConchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive Endocrinology FinalDokument98 SeitenReproductive Endocrinology FinalChino Paolo SamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- HUMAN SEXUAL BEH Flash Cards - KoofersDokument15 SeitenHUMAN SEXUAL BEH Flash Cards - Koofersmode4723Noch keine Bewertungen
- OB CompiledDokument156 SeitenOB CompiledMikeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biosintesis Dan Mekanisme Kerja Hormon Repro Wanita PDFDokument39 SeitenBiosintesis Dan Mekanisme Kerja Hormon Repro Wanita PDFsallynorcelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQDokument99 SeitenMCQhemazzzz80% (5)
- Folliculogenesis: R. RUTHRAKUMAR M. V. SC., ScholarDokument37 SeitenFolliculogenesis: R. RUTHRAKUMAR M. V. SC., ScholarRuthrakumar RavichandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Pathology Reference Range 2017Dokument19 SeitenChemical Pathology Reference Range 2017Shobana RaveendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08-Female Athlete Triad UpdateDokument21 Seiten08-Female Athlete Triad Updateapi-3851239100% (1)
- Maternal Ob NotesDokument103 SeitenMaternal Ob NotesBoris OrbetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repro Costanzo NotesDokument11 SeitenRepro Costanzo NotesAbeebs SalahouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gonadotropins and Their Analogs Current and Potential Clinical ApplicationsDokument27 SeitenGonadotropins and Their Analogs Current and Potential Clinical ApplicationsErika AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen