Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ICU Equipment
Hochgeladen von
Lovelyn Joy Abubo CortezOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ICU Equipment
Hochgeladen von
Lovelyn Joy Abubo CortezCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P.
BSN IV 5
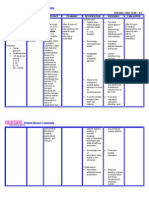
Equipment Mechanical Ventilator/s Definition Use(s) How to Operate Nursing Responsibilities A machine that Controls to makes it easier for adjust the rate patients to breathe and size of each until they are able breath to breathe completely on their A humidifier to own. warm and moisten the air The use of machine going into the to take over active lungs. breathing for a patient. Ensures that adequate oxygen gets into the blood stream and carbon dioxide is exhaled. Used of machine to take over active breathing for a patient. 1. Wear an oxygen mask for 2-3 Monitor for blood mins to ensure enough oxygen in pressure and pulse your system during the oximetry (O2 Sat). procedure. Obtain ABGs 2. Physician will tilt the head back measurements slightly. frequently 10-15 mins after the institution of 3. Then will use a tool called a mechanicalventilation laryngoscope which has a handle, . a light and a smooth dull blade. Used to lift the tongue off the Assess for peak back of the throat so the doctor inspiratory and can see the vocal cords. plateau pressures frequently. Although 4. Then he will stick one end of the it should be breathing tube through them, recognized that both down to lower windpipe. pressures will be increased by 5. Once the tube is in position, the extrapulmonary doctor will remove the scope and pressure. leave the tube in place. 6. The tube will then be taped to the Expiratory volume is corner of the mouth. checked initially and periodically to ensure 7. Next the doctor will attach the that the set tidal tube to a ventilator machine. volume is delivered.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
Endotracheal tube Endotracheal tube: Used to deliver a flexible plastic oxygen in tube that is put higher into the mouth and concentrations then down into the than found in trachea (airway). air, or to administer Tracheostomy other gases. tube: a curved endotracheal tube Used as a route that is inserted for or into the trachea administration through a of certain Tracheostomy tube tracheostomy. medications. 1. Patient is made to lie down on Keep supplies for their back with the neck and reinserting the tube head extended by keeping pillow at bedside, including under the shoulder/back. suctioning equipment, new 2. Local or general anesthesia is tracheostomy tube used for the procedure. with obturator and curved hemostat. 3. A horizontal cut is made across the neck above the sterna notch Oxygen and using a knife. equipment for ET intubation also 4. Skin is separated and should be available. surrounding tissues are dissected to expose the trachea. If decannulation Used for airway occurs, call the management in 5. 2nd or 3rd of the tracheal ring is Emergency response the settings of incised for the tracheostomy tube team to attempt general to be placed. reinsertion. anesthesia, critical 6. A suitable size tracheostomy tube Ventilate gently to care, mechanica is then introduced inside. prevent air from l ventilation, Smallest feasible tube should be escaping through the and emergency used. General rule: tube should stoma and carefully medicine. be of the diameter of trachea. occlude the stoma with a gloved hand, 7. Cuff of tube is inflated by using Provide tracheostomy 2-5 ml of air and held in place by care 4-8 hours. using a necktie. Monitor skin for signs 8. Incision is closed using skin of irritation or sutures by the side of the infection (e.g. tracheostomy tube. erythema, pain or discharge). 9. Dressing is applied for the wound to heal. Maintain
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
humidification. Monitor and record cuff pressures q shift and more often if tube is repositioned or changed, or volume of cuff air changes or leak occurs. Data is collected in one location Monitor patient and transmitted to another. frequently and continuously by using Patient wears electrodes on telemetry. chest which are attached to leads and a telemetry Note for abnormalities transmitter. and arrhythmias and brought to the Transmitter sends signals to a attention of monitoring station where they cardiologists who can can be watched by nurses and use this information cardiologists. in diagnosis and treatment. Wearing portable transmitter allows patients to be mobile, as Always check for the long as the signal stays in range placement of of the monitoring station. electrodes in the chest to note for some displacement that may occur.
Cardiac Monitor with Telemetry
Means of sending a Used for for real-time tracing of continual the electrical observation of activity in the several patients heart to a view screen somewhere Used for within the vicinity continuous of the patients monitoring is telemetry monitor. useful for observation of postoperative patients, patients with severe electrolyte imbalances, and other unstable patients. Used for prompt identification and initiation of treatment for cardiac arrhythmias and other conditions.
1. 2.
3.
4.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
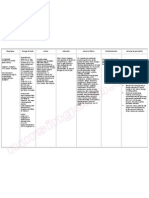
Pacemaker(s) A surgically- Used for 1. Patient undergoes simple surgery In preparation, check implanted electrical pulses to insert pacemaker using either for the presence of electronic device to prompt the local or general anesthetic. hair in the chest. If that regulates a heart to beat at present, hair may be slow or erratic a normal rate. 2. Patient is given drug for clip prior to surgery heartbeat. relaxation before surgery. or using depilatory Used to agent as the surgery treat arrhythmi 3. An antibiotic is typically will involve bandages as. administered to prevent and monitoring infection. equipment to be affixed to the body. Used for monitoring and 4. Inserted in left shoulder area where an incision is made below Always check for the recording your the collar bone creating a small patient data (among heart's electrical pocket where pacemaker is others, symptom activity and actually housed in patients primary, ECG, heart rhythm; body. aetiology), pacemaker monitor your center (doctor, blood 5. Lead/s are fed into the heart hospital), IPG. temperature, through a large vein using a breathing rate, fluoroscope to monitor the When patient is living and other progress of lead insertion. Right with the pacemaker factors ventricular lead would be at home, advise positioned away from apex of patient to check the right ventricle and up on the pacemaker routinely inter ventricular septum, below to ensure device is the outflow tract, to prevent operational and deterioration of the strength of performing the heart. appropriately. 6. Actual surgery may take 30-90 mins.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
Defibrillator(s) An electric device used used to counteract emergency fibrillation of the medicine heart muscle and terminate restore normal ventricular heartbeat by fibrillation applying a brief pulseless electric shock. ventricular tachycardia. in 1. Switch on defibrillator. Some Know your facilitys AEDS may automatically switch policy and procedure to on when the AED lid is opened. for defibrillation and If more than one rescuer is how units present, continue CPR until defibrillator operate. or shock is administered. Check pulse and 2. Remove patients shirt or blouse, rhythm. watch, rings and jewelry. Check for piercings and remove all Responsible for the Used to apply a studs. following activities: controlled - Confirming the electrical shock 3. Apply electrode pads to chest rhythm. to the heart, according the diagram displayed - Setting the which leads to on machine. Place one on upper equipment. depolarization of right side of chest, other on - Defibrillating. the entire lower left. - Documenting. electrical - Time of SCA. conduction 4. Stop CPR. Plug electrode pads to - Cardiac rhythms. system of the connector. Do not touch patient - Times of heart. when defibrillator analyzes the defibrillation and patients heart beat and assess energy discharged. the need for a shock. - Presence and 5. If AED determines that aa shock absence of pulse. is needed, machine will tell you audibly to deliver a shock by pressing the orange button. Yes, it is useful to say Clear: prior to doing so, since no rescuers should be in contact with patient at this time. Machine will examine the victims heart beat to see if another shock is needed.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
6. Check patients breathing and pulse. If the heart has resumed beating, but patient is not breathing, resume CPR. No pulse, repeat defibrillation process.
Dialysis Equipment A special machine Used to cleanse that is used in the the blood and process of balance its cleansing the constituents. blood. Allows patient Used to filter a with kidney failure patient's blood a chance to live to remove productive lives. excess water 2 types: and waste - Hemodialysis products when - Peritoneal the kidneys are dialysis damaged, dysfunctional, or missing.
1. Abdomen is cleaned in Assess the fistula or preparation for surgery, and graft and arm before, catheter is surgically inserted after each dialysis or with one end in the abdomen and every shift; the access other protruding from the skin. flow and complications. 2. Before infusion, are must be cleaned and flow into and out of Assess complication the abdomen tested. of the central venous catheter: the tip 3. A large volume of fluid is placement, exit site, introduced to the abdomen over complication the next 15 mins. documents and notify appropriate health 4. Dwell can be as much as 2.5 L care provider and medication can also be added regarding any to the fluid immediately before concern. infusion. Dwell remains in the abdomen and waste products is Educate patient with diffuse across peritoneum. appropriate cleaning of the fistula and 5. After a period of time (usually 4-6 graft and exit site: hours, fluid is removed and reporting signs and replaced with fresh fluid. symptoms of infection and complication.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
Nasogastric tubes and other feeding tubes A flexible tube Remove good oral 1. Tubes are usually inserted by Provide made of rubber contents of the nurses or junior doctors by the hygiene at regular that is passed stomach and frequent bedside or by anaesthetists in through the nose including air. intervals. Offer water theatre before or during surgery. and down through or mouthwash to the nasopharynx Decompress the rinse the mouth every 2. External measurement from the and esophagus stomach. hour. Assist patient tip of the nose to a point halfway into the stomach. to brush his teeth at between the xiphoid and the Remove small least every 4 hours. solid objects umbilicus distance gives a rough and fluid such idea of the required length. Keep nostrils free of as poison from accumulations of 3. The patient should sit up, the stomach. dried secretions. without any head tilt (chin up). An Put substances appropriately sized tube is chosen Encourage the patient into the to change position and the tip is lubricated by stomach; place frequently, using care smearing aqua gel or local nutrients not to pull on the directly into anaesthetic gel. Anaesthetic gel is a tube and not to lie on stomach when drug so if it is used it must be the drainage tubing. patient cannot prescribed, and precautions taken take food or such as checking for allergies. drink by mouth. 4. The wider nostril is chosen and the tube slid down along the floor of the nasal cavity. Patients often gag when the tube reaches the pharynx. 5. Asking them to swallow their saliva or a small amount of water may help to direct the tube into the oesophagus.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
6. Once in the oesophagus, it may be easy to push it down into the stomach. The correct intragastric position is then verified. 7. The tube is fixed to the nose and forehead using adhesive tapes. The stomach is decompressed by attaching a 60ml syringe and aspirating its contents. Blocked tubes can be flushed open with saline or air. For Feeding: 1. Place patient in semi-high fowlers and remove spigot from NG tube. 2. Aspirate stomach contents with 50 ml syringe and test with blue litmus paper and observe. 3. Attach syringe to tube and hold I to side at level of patients forehead. 4. Fill the syringe with prescribed feed and allow to flow by gravity. 5. Do not allow funnel to become empty. Observe patient during feeding. 6. Conclude feed with water.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
Disconnect the apparatus spigot tube. Then record. Suction Pump(s) and
A common pump Used 1. Check to make sure the suction Patient should be in which the liquid for medical pur pump works and all parts are in periodically assessed to be raised is poses to suction order. The hose should not have a to determine the need pushed by out material proper cap for the job on the end, for suctioning when atmospheric from a person's the hose should have no cracks or the need does not pressure into the lungs or leaks, and power source should obviously present partial vacuum wounds. be charged. Run a diagnostic to itself. under a retreating make sure that the suction turns valved piston on on works properly. Make sure Results and the upstroke and that the storage bin where the observations related reflux is prevented suction will pull the material to is to suctioning should by a valve in the also fixed and attached properly. be recorded to inform pipe that permits and alert other care flow in only one 2. Place the suction hose into the givers. direction. area that you need to suction. If its a medical suction pump, the Monitor for color, you need to place the pump into consistency and odor. the wound area, or if its an industrial type pump, place the hose into the pool that needs to be suctioned. 3. Turn on the suction once the hose in place. Suction the area until youre sure you have all the material out you can safely get then remove the suction hose. You can leave the hose on if its safe to suction the surrounding area, but if not, turn the suction pump off before removing the hose.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
4. Empty the suction receptacle into an appropriate place. Medical waste has to be disposed properly and many industrial chemicals that might be suctioned up also require proper disposal. Syringe Pump(s) A small infusion Used to pump used to gradually admi gradually nister small administer small amounts of fluid amounts of fluid (with or without (with or w/o medication) to a medication) to a patient or for patient or for use use in chemical in chemical and and biomedical biomedical research. research. Used in palliative care to continuously administer analgesics, antiemetics, and other drugs. 1. Wash hands. A PICC line must Confirm physicians remain absolutely sterile. Use order and verify the soap and water. Dry with a paper patients identity towel. using 2 patient identifiers. 2. Rub the lumen (rubber cap of the catheter) with an alcohol prep Reinforce the pad. explanation of alarm system to patient to 3. Draw up the proper amount of prevent anxiety. saline into the syringe. You will be told the right amount prior to Monitor pump and leaving the hospital. Insert the patient frequently to syringe into the lumen unclamp ensure correct the catheter. Inject saline flush operation, proper very slowly. infusion rate, to detect infiltration and 4. Clamp the catheter at the end of to observe for the flush process while you are complications as still flushing to avoid air getting in infection and air the line. embolism.
Used also for delivering IV 5. Remove the syringe and dispose it Change the tubing medications properly. and the cassette every over several 72 hours or accdg. to minutes. 6. Repeat these process with the policy. right amount of heparin. Insert the syringe into the lumen. If electrical power
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
Unclamp the catheter. Slowly inject the heparin. Clamp while still flushing near the end. 7. Remove the syringe. Dispose properly. Drains: Penrose drain Penrose Drain Used to promote -a soft tubedrainage in an shaped rubber or open surgical silicone drain. wound. Named after American Gynecologist Charles Bingham Penrose (18621925). T-tube Drain Used to allow -a narrow flexible bile to drain out tube in the form of of the patient's a T that is used body into a for drainage small pouch, especially of the known as a bile common bile duct. bag. fails, the pump will automatically switches to battery power.
T-tube drain
Jackson Pratt drain
Jackson Pratt Drain -made of a thin Used to remove rubber tube fluid that can inserted into a soft collect inside round squeeze your body after bulb with a surgery, 2. Amount of bile is assessed and Use measurements of removable infection, or measured. fluid loss to assist stopper. injury. intravenous 3. Attached to skin with a stitch. replacement of fluids. Dressing should surround the tube
Penrose Drain Ensure the drain is 1. Wash hands. Peel off pieces of secured tape holding dressing in place. Avoid (dislodgement is likely pulling on the drain itself. Remove to occur when layers of gauze and dispose transferring patients properly. after anesthesia). Dislodgement can 2. Examine wound area for signs of increase the risk for infection. infection and irritation to the 3. Wash hands before applying new surrounding skin. dressing. Use wash cloth to clean and dry with a clean towel. Accurately measure and record drainage 4. Pre-cut pieces of adhesive tape output. and layers of gauze. Monitor changes in 5. Place all materials in plastic bag character or volume and record. of fluid. Identify any complications T-tube Drain resulting in leaking 1. Surgeon place the tube into the fluid (bile or bile duct to drain out patients body pancreatic secretions) into a bile bag. or blood.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
and change at least once daily. Jackson Pratt Drain 1. Aseptic technique should always be observed. To remove drain, absorbent gauze is placed into drain site. 2. With one finger on each side of the skin, drain will gently be removed out of the site and to sterile towel. 3. Then constant pressure is given over the drain site to prevent extensive bleeding. Catheters: Pulmonary artery catheter Also called a Used to 1. Catheter is introduced through a The patient is Swan-Ganz detect heart large vein-often the internal observed for any catheter. A light failure or sepsis jugular, subclavian or femoral signs of infection or flexible balloon, monitor veins. the complications tipped tube that is therapy, and 2. From this entry, is threaded often from the procedure. introduced into evaluate with the aid of fluoroscopy, the pulmonary the effects of dr through the right atrium of the Check patient for artery. ugs. heart, the right ventricle and signs of allergies in subsequently into the pulmonary latex. artery. 3. The portion of the tube that touches the body should be thoroughly cleaned during bath time and anytime it is soiled.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
Intra-aortic Balloon Pump A mechanical Used to 1. Procedure may take place in the device that decrease the cardiac catheterization lab or at increases workload of the your hospital bedside and you myocardial oxygen heart and will remain awake but will be perfusion while at increase blood given medication to help you the same time flow to the heart relax. increasing cardiac and the rest of output. the body. 2. Groin area will be numbed before the puncture site is made to the Used in the femoral artery to insert the treatment of catheter through which the cardiogenic balloon will be threaded to the shock, acute aorta located in chest. heart failure, irregular heart 3. Patient will feel minimal rhythms, discomfort during the procedure cardiac surgery, from the local numbing and PCI. medication applied to groin. (no discomfort associated with IABP). 4. Tube with balloon connect to the balloon pump machine located outside the body. Stay in bed while connected. 5. Removal: It is pulled out from the same puncture site where it was inserted. Manual pressure is applied to the femoral artery for several minutes afterward. Ensure that a set of skin and external leads are connected and functional. Assess both leads for function every shift and confirm assessment of IABP flow sheet. Assess capillary refill and pedal pulses every hour. Observe site and report any signs of infection to the physician.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
Incubator(s) An apparatus with Used to keep a chamber used to the babys provide controlled temperature environmental stable through conditions an element. especially for the cultivation of Used to create microorganisms or an artificial the care and environment for protection of infants who are premature or sick too small or sick babies. to maintain a warm enough body temperature for survival. Used also to help protect an infant from noise, light and germs that may cause sickness and infections. Photolights or Bili lights Refers to a type of Used to reduce 1. phototherapy that the levels of is used to treat bilirubin in an newborn jaundice, infants body. a yellow coloring of the skin related to Used to treat immature liver newborn function. jaundice, a yellow coloring of the skin 1. Pre-warmed to a temperature appropriate to the infants age, size and condition. Monitor 02 flow rate and concentration as prescribed.
2. Use in Air mode and must Replace incubator always be switched on with the every 7 days (Date of motor running if in use for a replacement should baby. be indicated clearly 3. Check and record the incubator on incubator). temperature hourly. 4. Position away from draughts or Inspect mattress direct sunlight. cover carefully for 5. Do not routinely use on the signs of tear or loss of humidity function while in use impermeability. for babies this function is generally required for premature infants only. 6. Default incubator temperature in 35 degrees. 7. Adjust incubator temperature by no more than or less than 0.5 degree at a time. 8. Re check temperature within half an hour of making any adjustment. 1. Strip infant down to a diaper. 2. Cover infants eyes with soft eye patches. 3. Place infant on stable surface where light box can be placed close to her. 4. Cover the infant with the bili Keep accurate logs, as indicated by doctor. This includes taking a babys temperature, skin changes, documenting feeding times and amount and the number of wet and soiled diapers.
ABUBO, LOVELYN JOY P. BSN IV 5
related immature function. to liver blanket, or fiber optic pad, so that the lighted section is Monitor baby against the skin. Secure with frequently, but dont adhesive strips found on the interrupt therapy underside. unless feeding, 5. Turn the light source box on bathing or a diaper after plugging it in, and turn it changes is necessary. to the setting prescribed. Baby can be disturbed every 2o to 6. Swaddle the baby with a light reposition the bili blanket or sleep when blanket and to check necessary. for skin signs of infection or any 7. Monitor baby frequently, but problems. dont interrupt therapy unless feeding, bathing or a diaper Every 4o, babys changes is necessary. temperature should be taken usually 8. Continue phototherapy as many rectally and recorded hours per day as directed until for the health care jaundice subsides. provider. 9. Keep accurate logs, as indicated by doctor. This includes taking a babys temperature, skin changes, documenting feeding times and amount and the number of wet and soiled diapers.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- How Is A NST Performed?Dokument1 SeiteHow Is A NST Performed?Lovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slipDokument2 SeitenPay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slip Pay slipLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resumeresume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resumeDokument1 SeiteResumeresume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resume resumeLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Keeping Mom and Baby Together After Delivery Beneficial-DrDokument1 SeiteKeeping Mom and Baby Together After Delivery Beneficial-DrLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Complications of Labor and DeliveryDokument5 SeitenComplications of Labor and DeliveryLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Forceps and Other Instruments Can Assist Birth-DrDokument2 SeitenForceps and Other Instruments Can Assist Birth-DrLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Nursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Dokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)deric95% (97)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Sample of Job AnalysisDokument7 SeitenSample of Job AnalysisLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Application LetterDokument3 SeitenApplication LetterLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenDrug Studykakienz100% (7)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Organizational Chart (Small, Med, Large)Dokument7 SeitenOrganizational Chart (Small, Med, Large)Lovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hydro CortisoneDokument8 SeitenHydro CortisoneLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polio: Bacteria Clostridium TetaniDokument6 SeitenPolio: Bacteria Clostridium TetaniLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Filipino Scientists and InventorsDokument18 SeitenFilipino Scientists and InventorsTrixia Anne Resuello0% (5)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- By: Christine Kotch, Emily Ferrol, and Alyssa SiposDokument4 SeitenBy: Christine Kotch, Emily Ferrol, and Alyssa SiposLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Polio: Bacteria Clostridium TetaniDokument6 SeitenPolio: Bacteria Clostridium TetaniLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDokument1 SeiteClonidine HydrochlorideLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Problems (FSPR)Dokument6 Seiten5 Problems (FSPR)NMDNMSSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3A: Designing Instruction in The Different Learning Delivery ModalitiesDokument30 SeitenModule 3A: Designing Instruction in The Different Learning Delivery Modalitiesnel baradi67% (9)
- Philippines AFHS - Standards and Implementation GuideDokument37 SeitenPhilippines AFHS - Standards and Implementation GuideShardin Labawan-Juen,RNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Epidemiology: The Basic Science of Public HealthDokument34 SeitenIntroduction To Epidemiology: The Basic Science of Public Healthapi-19641337100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- CSR Activities by TATADokument13 SeitenCSR Activities by TATAMegha VaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Points To Be DiscussedDokument4 SeitenPoints To Be DiscussedShalini ShekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATLABAYAN - Task 4 - Formative Assessment-1Dokument4 SeitenGATLABAYAN - Task 4 - Formative Assessment-1Mary Jelyn Kate GatlabayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Draft HHP Informed Consent FormDokument7 SeitenDraft HHP Informed Consent Formapi-589951233Noch keine Bewertungen
- StoryDokument6 SeitenStoryGerard NicholasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lifestyle Related Diseases HandoutsDokument1 SeiteLifestyle Related Diseases HandoutsJonathan RagadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L TyrosineDokument6 SeitenL TyrosinecpullerNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- NursingDokument18 SeitenNursingKairmela PeriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bulk Stimulants Lubricants Other Laxatives GI StimDokument5 SeitenBulk Stimulants Lubricants Other Laxatives GI Stimrosita d. ramosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Good-Enough Sex Model For Couple Sexual SatisfactionDokument13 SeitenThe Good-Enough Sex Model For Couple Sexual SatisfactionwernikNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSCA Vol10 RoseCheramieDokument9 SeitenHSCA Vol10 RoseCheramiekanashane4794Noch keine Bewertungen
- Playlist AssignmentDokument7 SeitenPlaylist AssignmentTimothy Matthew JohnstoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Quick Trip To 7 Billion Exploring The Timeline PDFDokument9 SeitenA Quick Trip To 7 Billion Exploring The Timeline PDFArn Laurence SibagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health Awareness SpeechDokument2 SeitenMental Health Awareness SpeechThea Angela Longino95% (20)
- Abc Ven 2020Dokument81 SeitenAbc Ven 2020CorneLia JacintaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced German Volume Training - Week 1Dokument9 SeitenAdvanced German Volume Training - Week 1tactoucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Significance of HACCP and SSOP in Food Processing EstablishmentsDokument7 SeitenSignificance of HACCP and SSOP in Food Processing EstablishmentselfiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- D-Ox Benefits of Hydrogen WaterDokument10 SeitenD-Ox Benefits of Hydrogen WaterGabi Del RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Cut-Off Points For Admission Under The Government Sponsorship Scheme For The Academic Year 2015/2016.Dokument4 SeitenCut-Off Points For Admission Under The Government Sponsorship Scheme For The Academic Year 2015/2016.The Campus Times100% (1)
- World AIDS Day - December 1, 2019 Status of HIV Case-Based Surveillance Implementation - 39 U.S. PEPFAR-Supported Countries, May-July 2019Dokument16 SeitenWorld AIDS Day - December 1, 2019 Status of HIV Case-Based Surveillance Implementation - 39 U.S. PEPFAR-Supported Countries, May-July 2019worksheetbookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary Glaucoma IGADokument28 SeitenSecondary Glaucoma IGANur JannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- No. Kode Dan Nama Kode Diagnosa ICD 10 Nama PenyakitDokument11 SeitenNo. Kode Dan Nama Kode Diagnosa ICD 10 Nama PenyakitViki AY15Noch keine Bewertungen
- High PlateletsDokument9 SeitenHigh PlateletsHemal VyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental and Clinical Reconstructive Microsurgery 1st Ed. 2003 EditionDokument559 SeitenExperimental and Clinical Reconstructive Microsurgery 1st Ed. 2003 EditionLuka DamjanovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- DoctrineDokument1 SeiteDoctrinevinay44Noch keine Bewertungen
- P1 Cri 089Dokument2 SeitenP1 Cri 089Joshua De Vera RoyupaNoch keine Bewertungen