Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
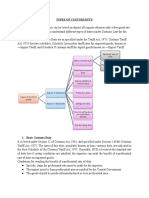
Types of Customs Duties in India
Hochgeladen von
Surbhi SofatOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Types of Customs Duties in India
Hochgeladen von
Surbhi SofatCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Custom duties
Custom duty is the duty imposed on export and import of goods to avoid flow of unwanted good or products form one nation to another. The Customs Act of India began in 1962.
Types of customs Duties in India While Customs Duties include both import and export duties, but as export duties contributed only nominal revenue, due to emphasis on raising competitiveness of exports, import duties alone constituted major part of the revenue from Customs Duties and include the following: Basic Customs Duty All goods imported into India are chargeable to a duty under Customs Act, 1962 .The rates of this duty, popularly known as basic customs duty, are indicated in the First Schedule of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 as amended from time to time under Finance Acts. The duty may be fixed on ad -valorem basis or specific rate basis. The duty may be a percentage of the value of the goods or at a specific rate. The Central Government has the power to reduce or exempt any good from these duties. Additional (Countervailing) Duty of Customs This countervailing duty is livable as additional duty on goods imported into the country and the rate structure of this duty is equal to the excise duty on like articles produced in India. The base of this additional duty is c.i.f. value of imports plus the duty levied earlier. If the rate of this duty is on ad-valorem basis, the value for this purpose will be the total of the value of the imported article and the customs duty on it (both basic and auxiliary).
Export Duties Under Customs Act, 1962, goods exported from India are chargeable to export duty The items on which export duty is chargeable and the rate at which the duty is levied are given in the customs tariff act,1975 as amended from time to time under Finance Acts. However, the Government has emergency powers to change the duty rates and levy fresh export duty depending on the circumstances. Auxiliary Duty of Customs This duty is levied under the Finance Act and is leviable all goods imported into the country at the rate of 50 per cent of their value. However this statutory rate has been reduced in the case of certain types of goods into different slab rates based on the basic duty chargeable on them. Cesses Cesses are leviable on some specified articles of exports like coffee, coir, lac, mica, tobacco (unmanufactured), marine products cashew kernels, black pepper, cardamom, iron ore, oil cakes and meals, animal feed and turmeric. These cesses are collected as parts of Customs Duties and are then passed on to the agencies in charge of the administration of the concerned commodities. Education cess on customs duty An education cess has been imposed on imported goods w.e.f. 9-7-2004. The cess will be 2% and wef 01.03.2007 2%+1% of the aggregate duty of customs excluding safeguard duty, countervailing duty,Anti Dumping Duty. Protective Duties Tariff Commission has been established under Tariff Commission Act, 1951. If the Tariff Commission recommends and Central Government is satisfied that
immediate action is necessary to protect interests of Indian industry, protective customs duty at the rate recommended may be imposed under section 6 of Customs Tariff Act. The protective duty will be valid till the date prescribed in the notification. Countervailing Duty on Subsidized goods If a country pays any subsidy (directly or indirectly) to its exporters for exporting goods to India, Central Government can impose Countervailing duty up to the amount of such subsidy under section 9 of Customs Tariff Act. Anti Dumping Duty on dumped articles Often, large manufacturer from abroad may export goods at very low prices compared to prices in his domestic market. Such dumping may be with intention to cripple domestic industry or to dispose of their excess stock. This is called 'dumping'. In order to avoid such dumping, Central Government can impose, under section 9A of Customs Tariff Act, anti-dumping duty up to margin of dumping on such articles, if the goods are being sold at less than its normal value. Levy of such anti-dumping duty is permissible as per WTO agreement. Anti dumping action can be taken only when there is an Indian industry producing 'like articles'. Safeguard Duty Central Government is empowered to impose 'safeguard duty' on specified imported goods if Central Government is satisfied that the goods are being imported in large quantities and under such conditions that they are causing or threatening to cause serious injury to domestic industry. Such duty is permissible under WTO agreement. Safeguard duty is a step in providing a need-based protection to domestic industry for a limited period, with ultimate objective of restoring free and fair competition
National Calamity Contingent Duty A National Calamity Contingent Duty (NCCD) of customs has been imposed vide section 129 of Finance Act, 2001. This duty is imposed on pan masala,chewing tobacco and cigarettes. It varies from 10% to 45%. - - NCCD of customs of 1% was imposed on PFY, motor cars, multi utility vehicles and two wheelers and NCCD of Rs 50 per ton was imposed on domestic crude oil, vide section 134 of Finance Act, 2003. 20.3.5 Rate of duty applicable There are different rates of duty for different goods there are different rates of duty for goods imported from certain countries in terms of bilateral or other agreement with such countries which are called preferential rate of duties the duty may be percentage of the value of the goods or at specified rate. .. Types of Customs Duties Export duties are levied occasionally to mop up excess profitability in international prices of goods in respect of which domestic prices may be low at the given time. But the sweep of import duties is quite wide. Import duties are generally of the following types:Basic Duty :- it may be at the standard rate or, in the case of import from some other countries, at the preferential rate. Additional customs duty :- equal to central excise duty leviable on like goods produced or manufactured in India. Additional duty is commonly referred to as Countervailing duty or C.V.D. It is payable only if the imported article is such as, if produced in India, its process of production would amount to 'manufacture' as per the definition in Central Excise Act,1944. Exemption from excise duty has the effect of exempting additional duty of customs. Additional duty is calculated on a value base of aggregate of value of the goods including landing charges and basic customs duty. Other duties like anti-dumping
duty, safeguard duty etc are not taken into account. In case of goods covered by provisions of the Standards of Weights and Measures Act,1976, the value base would be the retail sale price declared on the package of the goods less the rebate as notified under the Central Excise Act,1944 for such goods True Countervailing duty or additional duty of customs :- is levied to offset the disadvantage to like Indian goods due to high excise duty on their inputs. It is levied to provide a level playing field to indigenous goods which have to bear various internal taxes. Value base for this additional duty would be as in the case of C.V.D, under Customs Tariff Act,1975 minus the retail sale price provision. This additional duty will not be included in the assessable value for levy of education cess on imported goods. Manufacturers will be able to take credit of this additional duty for payment of excise duty on their finished products. Anti-dumping Duty/ Safeguard Duty :- for import of specified goods with a view to protecting domestic industry from unfair injury. It would not apply to goods imported by a 100% EOU (Export Oriented Units) and units in FTZ (Free Trade Zones) and SEZ (Special Economic Zones). On export of goods, anti-dumping duty is rebatable only by way of a special brand rate of drawback. Safeguard duties do not require the finding of unfair trade practice such as dumping or subsidy on the part of exporting countries but they must not discriminate between imports from different countries. Safeguard action is resorted to only if it has been established that a sudden increase in imports has caused or threatens to cause serious injury to the domestic industry. Education cess :- at the prescribed rate is levied as a percentage of aggregate duties of customs. If goods are fully exempted from duty or are chargeable to nill duty or are cleared without payment of duty under prescribed procedure such as clearance under bond, no cess would be levied.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Types of Custom DutyDokument3 SeitenTypes of Custom DutyKarina ManafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customs in India Nature & TypesDokument2 SeitenCustoms in India Nature & TypesSaagar Hingorani100% (3)
- Customs DutyDokument17 SeitenCustoms DutyBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)100% (1)
- Kinds of CompaniesDokument18 SeitenKinds of CompaniesAnirudh AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance TaxDokument11 SeitenAdvance TaxAdv Aastha MakkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Planning MergerDokument4 SeitenTax Planning MergerAks SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Security of WorkmenDokument10 SeitenSocial Security of WorkmenPalak JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naresh Chandra Committe, PresentationDokument14 SeitenNaresh Chandra Committe, Presentationrjruchirocks100% (9)
- Nature and Scope of Corporate FinanceDokument1 SeiteNature and Scope of Corporate FinanceSitaKumari100% (3)
- Assignment - Explain Income From Other SourcesDokument9 SeitenAssignment - Explain Income From Other SourcesPraveen SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Indian Financial SystemDokument34 SeitenStructure of Indian Financial SystemmoqimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Protection CouncilsDokument10 SeitenConsumer Protection CouncilsPrachee Chelsea TanejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Meeting NotesDokument14 SeitenCompany Meeting NotesManish RoydaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Education & Research Institute: INTERVIEW FOR MBA/PGDM 2013-15 (Marketing)Dokument2 SeitenManagement Education & Research Institute: INTERVIEW FOR MBA/PGDM 2013-15 (Marketing)ankitverma9716Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Share CapitalDokument42 SeitenChapter 12 Share CapitalOmer UddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trips & TrimsDokument20 SeitenTrips & TrimsMaghilan Arunachalam100% (2)
- Income From SalaryDokument66 SeitenIncome From SalaryShamika LloydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Payment of TaxDokument4 SeitenAdvance Payment of Taxparag03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Titan Ratio Analysis - IDokument10 SeitenTitan Ratio Analysis - INikhil Gulhane0% (1)
- LICDokument39 SeitenLICPrathamesh Wakade50% (2)
- Income Tax Short Notes For C S C A C M A Exam 2014Dokument43 SeitenIncome Tax Short Notes For C S C A C M A Exam 2014Jolly SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Calculate Net Profit For Managerial RemunerationDokument3 SeitenHow To Calculate Net Profit For Managerial Remunerationsonika7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between A Private LTD and Public LTDDokument4 SeitenDifference Between A Private LTD and Public LTDShoaib Shaik0% (1)
- Unit 2 - Income From Business or ProfessionDokument13 SeitenUnit 2 - Income From Business or ProfessionRakhi DhamijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: What Do You Understand by Efficient Frontier (With Diagram) ? IntroductionDokument2 SeitenTopic: What Do You Understand by Efficient Frontier (With Diagram) ? Introductiondeepti sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meetings and ProceedingsDokument11 SeitenMeetings and ProceedingssreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal, Procedural & Tax Aspects of DividendsDokument18 SeitenLegal, Procedural & Tax Aspects of DividendsNavneet Nanda100% (1)
- Agreement On Agriculture WTODokument27 SeitenAgreement On Agriculture WTOPriyankologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Depository ReceiptsDokument11 SeitenIndian Depository ReceiptsZoheb SayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulatory FrameworkDokument15 SeitenRegulatory Frameworkpankajgupta100% (5)
- Harmonizing Accounting Differences Across The CountriesDokument22 SeitenHarmonizing Accounting Differences Across The Countriesankzzy100% (1)
- Balance of PaymentDokument4 SeitenBalance of PaymentAMALA ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Buy Back of Shares Under The Companies Act, 1956 - An InsightDokument4 SeitenBuy Back of Shares Under The Companies Act, 1956 - An InsightHrdk DveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Consideration in Project FinancesDokument18 SeitenTax Consideration in Project FinancesMukesh Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Companies in IndiaDokument14 SeitenTypes of Companies in IndiaGanesh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Tax Planning and ManagemantDokument11 SeitenCorporate Tax Planning and ManagemantVijay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXIM PolicyDokument6 SeitenEXIM PolicyVikas ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fund and Non Fund Based BankingDokument17 SeitenFund and Non Fund Based BankingPrajakta SamantNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Meaning of Customs Duty in India and Its TypesDokument35 SeitenWhat Is The Meaning of Customs Duty in India and Its Typesrohit singh100% (3)
- Anti Dumping Duty and IndiaDokument39 SeitenAnti Dumping Duty and Indiasagarkhedekar999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Buy-Back of SharesDokument19 SeitenBuy-Back of SharesChirag VashishtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customs Notes (Introduction and Types of Duty PDFDokument16 SeitenCustoms Notes (Introduction and Types of Duty PDFJayshree ShettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 Big Advantages and Disadvantages of Foreign Direct InvestmentDokument5 Seiten17 Big Advantages and Disadvantages of Foreign Direct Investmentpatil mamataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Law Lecture Notes - ManagementDokument9 SeitenCompany Law Lecture Notes - ManagementSenelwa Anaya100% (5)
- Definition and FeaturesDokument4 SeitenDefinition and FeaturesnayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foreign Exchange Management ActDokument11 SeitenForeign Exchange Management ActankitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Management With Reference To - Repair, Replace, Renewal or RenovationDokument4 SeitenTax Management With Reference To - Repair, Replace, Renewal or RenovationAkhil1101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emerging Issues in International Marketing-17.02Dokument61 SeitenEmerging Issues in International Marketing-17.02anmolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Liberalisation of The Insurance Sector On The Life Insurance Corporation of IndiaDokument10 SeitenImpact of Liberalisation of The Insurance Sector On The Life Insurance Corporation of IndiaBrijbhushan ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implications of Wto in IndiaDokument16 SeitenImplications of Wto in IndiaDivisha Bhagat100% (1)
- Change in Exim PolicyDokument50 SeitenChange in Exim Policya_aka198986% (7)
- Com.Dokument24 SeitenCom.MALAYALY100% (1)
- Final Tax Planning ProjectDokument14 SeitenFinal Tax Planning ProjectyashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piracy of DesignsDokument13 SeitenPiracy of DesignsArjun NarainNoch keine Bewertungen
- CartelDokument2 SeitenCartelUmesh JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Income From Hous PropertyDokument21 SeitenIncome From Hous PropertyAnsari SufiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customs ActDokument24 SeitenCustoms ActSoujanya NagarajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Custom DutyDokument13 SeitenCustom DutyBoobalan RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Custom DutyDokument2 SeitenCustom DutyNawab SahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customs DutyDokument8 SeitenCustoms DutyBhavana GadagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Khaman Dhokla Recipe CardDokument2 SeitenKhaman Dhokla Recipe CardSurbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Chief Ministers in IndiaDokument1 SeiteCurrent Chief Ministers in IndiaSurbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Account Share CapitalDokument13 SeitenAccount Share CapitalSurbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- International: Labour OrganizationDokument37 SeitenInternational: Labour OrganizationSurbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Labour OrganisationDokument12 SeitenInternational Labour OrganisationSurbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pape-R ID: (C0101) : F R L 6 8 6 F TsselDokument2 SeitenPape-R ID: (C0101) : F R L 6 8 6 F TsselSurbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper ID: (C01691: Organisational Be Havtour Subject Code: MB - 102 (2K9)Dokument2 SeitenPaper ID: (C01691: Organisational Be Havtour Subject Code: MB - 102 (2K9)Surbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Papcr Id: Lc022Ll: 'Fotal No. of Questions: 071 L0Tlw'Ll'I ('Ibtnl No. of I'Agcs: 02Dokument2 SeitenPapcr Id: Lc022Ll: 'Fotal No. of Questions: 071 L0Tlw'Ll'I ('Ibtnl No. of I'Agcs: 02Surbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper ID (MB, 6221: MBA (Sem. - 3'ul4'n7Dokument2 SeitenPaper ID (MB, 6221: MBA (Sem. - 3'ul4'n7Surbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Issues in Consultant Client Relationship1Dokument25 SeitenIssues in Consultant Client Relationship1Surbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 - Issues of Collective BargainingDokument3 Seiten04 - Issues of Collective BargainingSurbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Businmss Laws - Ii Siibtect Code: BB - 4M " Paper ID I lc022llDokument2 SeitenBusinmss Laws - Ii Siibtect Code: BB - 4M " Paper ID I lc022llSurbhi SofatNoch keine Bewertungen
- GsdeDokument6 SeitenGsdeSurbhi Sofat0% (1)
- December 2022 Issue: More Transparency, P S An R T e R o M, y C en Ar P P, y PDokument24 SeitenDecember 2022 Issue: More Transparency, P S An R T e R o M, y C en Ar P P, y Pwpp8284Noch keine Bewertungen
- Checkpoints Before Transformer InstallationDokument3 SeitenCheckpoints Before Transformer InstallationBeaBustosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tawjihi 7Dokument55 SeitenTawjihi 7api-3806314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecological Consideration of Site AnalysisDokument20 SeitenEcological Consideration of Site AnalysisAUST BNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATMPP Diabetes Change and Review Proposal Npa 2012-18Dokument8 SeitenATMPP Diabetes Change and Review Proposal Npa 2012-18Juha TamminenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chen Probable Cause Affidavit 050714Dokument7 SeitenChen Probable Cause Affidavit 050714USA TODAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Hack For The Yoga PoseDokument3 SeitenA Hack For The Yoga PoseAlex NNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWP 4A Syllabus Fall 2021 (Misinformation)Dokument11 SeitenAWP 4A Syllabus Fall 2021 (Misinformation)camNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definite NessDokument398 SeitenDefinite NessKbraNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Communication - Project - File - 455 PDFDokument20 SeitenHistory of Communication - Project - File - 455 PDFlathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UX-driven Heuristics For Every Designer: OutlineDokument7 SeitenUX-driven Heuristics For Every Designer: OutlinemuhammadsabirinhadisNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTCC Project - Fake News and Its Impact On Indian Social Media UsersDokument41 SeitenNTCC Project - Fake News and Its Impact On Indian Social Media UsersManan TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- PS-8955 Zinc Alloy ElectrodepositedDokument8 SeitenPS-8955 Zinc Alloy ElectrodepositedArturo Palacios100% (1)
- LIP Reading Using Facial Feature Extraction and Deep LearningDokument5 SeitenLIP Reading Using Facial Feature Extraction and Deep LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4148-Article Text-14752-1-10-20211029Dokument7 Seiten4148-Article Text-14752-1-10-20211029Daffa AzkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 6 - Performance AppraisalDokument50 SeitenCH 6 - Performance AppraisalMark SullivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatty AcidsDokument13 SeitenFatty AcidsRaviraj MalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual G Ingles - V6Dokument68 SeitenManual G Ingles - V6Phùng Thế Kiên50% (2)
- GlobalisationDokument8 SeitenGlobalisationdummy12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kajima's Three PolicyDokument2 SeitenKajima's Three PolicyBe Seang SeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +917019900128 E-MailDokument5 SeitenCurriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +917019900128 E-MailJay MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PlansDokument12 SeitenLesson Plansapi-282722668Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nanoimprint Lithography: Presented by Group 7Dokument27 SeitenNanoimprint Lithography: Presented by Group 7Samia SafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification For Neoprene Coating On The Riser CasingDokument17 SeitenSpecification For Neoprene Coating On The Riser CasingLambang AsmaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EvoFox Katana-X Mechanical Gaming Keyboard With Outemu Blue Switches Vivid Rainbow Lighting With 13 Preset Effects DedicatedDokument1 SeiteEvoFox Katana-X Mechanical Gaming Keyboard With Outemu Blue Switches Vivid Rainbow Lighting With 13 Preset Effects Dedicatedsaqibdar7051236186Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Teaching PracticeDokument14 SeitenThe Impact of Teaching PracticemubarakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Aspects of Construction Ethics PaperDokument11 SeitenLegal Aspects of Construction Ethics PaperbikaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- RenewalPremium 1123186Dokument1 SeiteRenewalPremium 1123186Suhas Renu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Management Systems and Strategies by Dipak Kumar BhattacharyyaDokument385 SeitenPerformance Management Systems and Strategies by Dipak Kumar Bhattacharyyasayal96amrit100% (3)
- Classical Mechanics MCQ GamecampuscoDokument3 SeitenClassical Mechanics MCQ GamecampuscoFaryal TalibNoch keine Bewertungen