Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
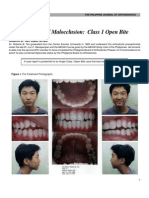
Consideration of Treatment of Open Bite
Hochgeladen von
muumuufistOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Consideration of Treatment of Open Bite
Hochgeladen von
muumuufistCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Consideration of treatment of open bite Schematics: Parameter affecting treatment option: Treatment o Interceptive o Non surgical camo o Surgical
al Open bite malocclusion may exhibit aspects of dental and skeletal types. Predominantly dental open bite can be corrected by orthodontics alone, while skeletal types may require combined orthognathic and orthodontic treatment plan. More severe skeletal pattern: the more surgery is likely. Skeletal pattern is assessed by several methods: 1. Bjork seven signs. Bjork (1969) has listed seven cephalometric features to indicate abnormal growth rotation: Inclination of condylar head Interincisal angle Interpremolar/intermolar angle Curvature of mandibular canal Shape of lower border of the mandible (antegonial notch) Prominence of chin (symphisis) Amount of lower anterior facial height Bjork 1969 and Bjork and Skeiller 1972 found that in growing patient, backward rotators is synonymous with open bite tendency, and opening of the bite might be difficult to prevent. 2. Anterior Facial Height Ratio (AFH vs LFH) Nahoum 1971 Identifies upward cant of the anterior portion of the maxillary plane serves to decrease the upper face height (N-ANS) and increase the lower face height (ANS-Me) He measured UFH:LFH ratio and concluded that : Normal subjects have ratio of 0.809 and open bite subjects have average ratio of 0.699. Therefore Nahoum 1975 UFH : LAFH ratio: >0.900 = deep bite 0.700-0.900 = normal (normal average at 0.800) <0.700 =open bite. a 3. Jarabak ratio (Facial Height Ratio) Used cranial base as reference. One of the parameters: facial height ratio which compares posterior facial height (S-Go) and anterior facial height (N-Me). Siriwat and Jarabak (1985) classified 3 distinct facial pattern based on this measurement. FHR <59% - HYPERdivergent growth pattern o Face rotates downwards and posteriorly o AFH > PFH FHR 59%-63% o Downward and forward growth with same increment anterior and posteriorly o No progressive change in angular relationship FHR>63% o HYPOdivergent growth pattern : predominantly horizontal growth.
4. Overbite Depth Indicator (ODI) Developed by Kim 1974 The Overbite Depth Indicator (ODI) is the arithmetic sum of the angle of the A-B plane to the mandibular plane and the angle of the Palatal plane to Frankfort horizontal plane OVERBITE DEPTH INDICATOR
1. 76). 2.
Measure the angle of the mandibular plane(MP), and AB plane. Write it in corresponding rectangle (MP-AB). (Example:
Measure the angle of the Frankfort horizontal plane (FH), and the Palatal plane (PP). A positive angle occurs when the palate tips downward and forward. A negative angle occurs when the palate tips upward and forward. In case of a positive value, write it in the corresponding positive rectangle, otherwise, write it in the corresponding negative rectangle (Example: -3)
3.
Combine these values to obtain the Overbite Depth Indicator (76-3=73). In this example the ODI is 73 degrees,which is slightly lower than the norm (74.5 , 6); howerver, the diference is 1.5. Considering the standard deviation, it falls within the normal limit with a sligth tendency to be an openbite.
o o
MP-AB = The mandibular plane and the AB plane (Angle). FH-PP = The Frankfort plane and the palatal plane (Angle).
Table 1. Example: ~ MP-AB FH-PP FH-PP ODI 74.5 6 CASE 76 + - 3 = 73 >< OK > Deep <Openbite x x
Lower ODI figure: greater chance of open bite /AOB tendency. Higher ODI figure: greater depth of overbite . Kim 1974 suggested the following values: 50-60s : AOB Low 60s AOB tendency Mid 70s = normal 70-80 = deep bite tendencyp 80-90s = deep bite. Overall Outcome Prediction:
Nahoum 1977 : suggested that UFH/LFH ratio of 0.650 are poor risks for ortho camouflage Kim 1974: ODI with normal range of 70 will be able to be corrected via ortho camouflage. cases with low ODI may require posterior intrusion, anterior extrusion and second molar extraction to remove wedging effect. opponents: Dung and Smith 1988: pretreatment cephalometrics ratio are no predictors of treatment response. Lopez Gavito 1985: no single parameter of dentofacial form proved to be a suitable predictor of post treatment stability or relapse.
1.
Treatment of AOB: Observation: Transitional AOB during mixed dentition usually will close spontaneously. worms 1971, finlay and richardson 1995 (127 subjects , 59% closure in pre pubertal group, 49% in pubertal and 44% in post pubertal group.) 2. Habit control Thumbsucking - straightforward discussion, reminder therapy with plaster , cemented cribs Tongue Habits: tongue exercise by Straub (1960 1961) Crib therapy, Tongue reduction surgery with keyhole excision in true macroglossia. 3.Growth Modification: to correct or intercept hyperdivergent growth pattern. IRE impede Dental eruption to control vertical growth redirect vertical growth via intra or extraoral forces erupt anterior teeth.
1.
GM appliances extraoral high pull headgear vertical chin cap facemask 2.intra oral appliance biteblocks open bite bionator function regulator 4 Growth Mod Appliance Headgear to hold maxillary sutural growth Joffe and Jacobson 1979 - use acrylic splint to create a large anchor unit. superior and distal displacement of maxilla clockwise rotation of palatal plane relative intrusion of upper molars.
Chin cap Pearson 1978, 1986 chincap and FA to reduce mandibular plane angle. prevent extrusion of posterior teeth. Chincap + mandibular bite block : intrusive forces on posterior teeth to close open bite Chincap + kloehn : antero posterior and vertical control. buschang 2002 : chincap increases posterior height, redirect condylar growth , reduce gonial angle. overall effects controversial Facemask conventional facemask causes counterclockwise rotation on the maxilla, increase in mandibular plane angle and open bite tendency (nanda 1980) for true protraction to occur, force must pass through centre of resistance of dentomaxillary complex and parallel to occlusal plane. modification: modified protraction headgear with chincup (nanda 1980) delaire facemask (staggers 1992) petit facemask (keles 2002) staggers and keles managed to rotate maxilla clockwise with closure of AOB.
Intraoral appliance Bite blocks correct AOB with excessive LAFH 3-4mm thick, disrupts freeway space to intrude posterior teeth by stretched muscle when appliance is used. allow differential eruption of anterior teeth. maxillary complex most affected (Mcnamara 1977) Altuna and woodside 1985 - animal studies matured animal - intrusion of buccal teeth growing animal - relative intrusion biteblocks can be modified to active form woodside and linder-aronson 1986 proposed use of spring loaded bite blocks gurton 2004 - molar intruder for mixed dentition Dellinger 1986 - active vertical corrector (magnets) kuster and ingervall 1992- effect of magnet greater. however magnetic appliance are cemented. Kiliaridis 1990 - crossbite and scissorsbite with magnetic appliance. MAD 4 attracting magnet on anterior to guide mandible to midline. Open bite bionator posterior bite blocks to inhibit extrusion of posterior teeth. anterior acrylic as lingual shield labial bow at correct lip closure height. overall simulates a competent seal relationship. Functional Regulator 4 Frankel believes that incompetent lips in AOB are due to poor postural behavious of facial musculature. functional therapy with lip seal training will correct aob provided competent oral seal is established.
Fixed appliance: factors to consider : extractions o premolars most common incisors retract below center of rotation - drawbridge effect mesial movement of molars - reduction in mandibular plane angle indications: proclined maxillary and mandibular incisors little gingival display
o molars o
brachycephalic, not dolicocephalic (hyperdivergent) skeletal pattern incisor at rest < 2-3 mm
when only 2nd molars are occluding and third molars are developing normally. autorotation of mandible and closure AOB eliminates posterior crowding uprights mesially inclined molars
single lower incisors require diagnostic setup on cases with minimal overbite and overjet. canut 1996 - on edge to edge class 3 with AOB tendency. mandibular arch shortens and lower incisor retrudes.
Arch wires MEAW ( modified edgewise archwire ) modified meaw elatics temporary anchorage devices auxilaries rapid molar intruder vertical holding appliance
MEAW Kim 1987 correct inclination of the occlusal plane align maxillary incisors relative to the lip line upright axial inclination of the posterior teeth intrude molars by pitting it against heavy anterior elastics double brackets 0.018 slots post levelling and aligning tip back bends posterior to first premolars upper wire deep curve lower wire reverse curve worsens aob - counteracted with vertical elastics.
Modified meaw enacar 1996 accentuated curve and lower reverse curve instead of meaw wires. kucukkeles 1999 - open bite mainly by lower incisor extrusion. functional occlusal plane levelled by lower premolar exrrusion and uprighting of lower molars. Elastics to extrude incisors not stable does not directly address aetiology. AOB rarely caused by lack of eruption of upper incisors- more due to skeletal factor or excessive eruption of posterior teeth. class 2, 3 elastics - extrude molars, overall overbite decrease - must be used with caution. TAD Umemori 1999 titanium miniplates for intrusion of lower molars used with meaw and lingual arch to prevent flaring of molars during intrusion. sherwood 2002
intrusion of upper molars with normal archwires intrusion range 1.45-3.32 mm mean 1.99mm
park 2006 intrusion of upper and lower molars 3mm AOB to 1.5 mm overbite Choi 2007 miniscrews on either side of mid palatal suture splinted with self curing resin bonded with S sheath to intrude posterior teeth with elastomeric chain. posterior teeth splinted with fiber reinforced composites. upper molars intrude by 2 mm lower molars intrude by 1 mm. Erverdi 2006 zygomatic anchorage to intrude whole segment of posterior teeth.
surgery vs tad Kurado 2007 molar intrusion with tad simpler than 2 jaw surgery. maxillary and mandibular incisors were elongated in surgery group. anterior teeth tend to elongate post surgery during levelling and finishing phases intermaxillary fixation can also cause elongation. RMI modified jasper jumper Carano and Machata 2002 deliver functional,bite jumping forces, headgear or elastic like forces pt bites - devices flexes and exerts intrusive force of 900 g to molars decays to 450 on wk 2, 250g on wk 3. variation of insertion methods alter force direction in sagittal plane. clinical trial carano 2005 adult pt with full dentition full size rectangular arch wire. occlusal contacts other than first molars are eliminated to allow intrusive effects of rmi to take place 2nd molar exo in difficult case, 3rd molar exo when it erupts. cinsar 2007 rmi can be used for early intervention of skeletal open bite correction.
vertical holding appliance. modified TPA with acrylic pad. tongue pressure to reduce vertical development of first molars. DeBerardinis 2000 - vha vs control, Vha is useful in controlling overbite and anterior vertical dimension.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Non XNDokument9 SeitenNon XNNaveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maxillomandibular Relationship RecordDokument93 SeitenMaxillomandibular Relationship Recordsamar yousif mohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edgewise MechanismDokument77 SeitenEdgewise MechanismPuneet Jain100% (1)
- GENIOPLASTYDokument36 SeitenGENIOPLASTYJesus MullinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Considerations of Orientation, Vertical and Horizontal Jaw Relations in Complete Denture-First PartDokument43 SeitenBiological Considerations of Orientation, Vertical and Horizontal Jaw Relations in Complete Denture-First PartArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extraoral ApplianceDokument87 SeitenExtraoral ApplianceDr. Sushil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Class Ii Division 1 MalocclusionDokument67 SeitenManagement of Class Ii Division 1 MalocclusionMahima Gupta100% (2)
- Case Report: Surgical Orthodontic Treatment of Severe Skeletal Class IIDokument6 SeitenCase Report: Surgical Orthodontic Treatment of Severe Skeletal Class IISebas Quiroga GNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Tweeds AnalysisDokument6 Seiten20 Tweeds AnalysisMariyam100% (2)
- Vertical Control in Fixed Orthodontics - A ReviewDokument4 SeitenVertical Control in Fixed Orthodontics - A ReviewThang Nguyen TienNoch keine Bewertungen
- FinalizaçãoDokument57 SeitenFinalizaçãodentalnetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertical Anchorage FinalDokument155 SeitenVertical Anchorage FinalBhawna SagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXPANSION Method of Gaining SpaceDokument66 SeitenEXPANSION Method of Gaining SpaceDr. Sushil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tweeds AnalysisDokument7 SeitenTweeds AnalysisDrmrunalni ChoukseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ortho Case ReportDokument6 SeitenOrtho Case ReportAlex Adille OgaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autorotation & 6 SG Options FishDokument28 SeitenAutorotation & 6 SG Options FishMuhammad Aleem100% (1)
- Finishing and DetailingDokument47 SeitenFinishing and DetailingSparsh Bhaskar SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EdgewiseDokument110 SeitenEdgewiseDhanusha ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 040 060Dokument21 Seiten040 060nhasuonlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herbst ApplianceDokument21 SeitenHerbst Applianceimtiyazorthodontist83% (6)
- Open Bite - Spectrum of Treatment Potentials and LimitationsDokument20 SeitenOpen Bite - Spectrum of Treatment Potentials and LimitationsDr.Thrivikhraman KothandaramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maxillary Protraction Dr.M.M.varadharaja / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDokument121 SeitenMaxillary Protraction Dr.M.M.varadharaja / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Club1 / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDokument19 SeitenJournal Club1 / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNoch keine Bewertungen
- RadiologyDokument55 SeitenRadiologySuganya MurugaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- KimDokument12 SeitenKimIvanna H. A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Gaining Space. / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDokument70 SeitenMethods of Gaining Space. / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academy100% (2)
- Standard Edgewise 2.6.2020Dokument110 SeitenStandard Edgewise 2.6.2020nikita100% (3)
- Open Bite CaseDokument10 SeitenOpen Bite CaseezfreshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthognathic Surgery RonalDokument56 SeitenOrthognathic Surgery Ronaldrghempik100% (2)
- Nonextraction Treatment of An Open Bite With Microscrew Implant AnchorageDokument12 SeitenNonextraction Treatment of An Open Bite With Microscrew Implant AnchorageCYNTHIA MARLEN HORTA SANCHEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Considerations of Orientation, Vertical and Horizontal Jaw Relations in Complete Denture-First PartDokument43 SeitenBiological Considerations of Orientation, Vertical and Horizontal Jaw Relations in Complete Denture-First Partkhaled alahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthognathic SurgeryDokument26 SeitenOrthognathic Surgerym.n.n .q.c.fNoch keine Bewertungen
- BANDANDLOOPDokument21 SeitenBANDANDLOOPcanaborbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- IZC Bone Screw Anchorage For Conservative Treatment of Bimaxillary Crowding in An Asymmetric Class II/I Subdivision 1 MalocclusionDokument19 SeitenIZC Bone Screw Anchorage For Conservative Treatment of Bimaxillary Crowding in An Asymmetric Class II/I Subdivision 1 MalocclusionAly OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maxillary Protraction / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDokument86 SeitenMaxillary Protraction / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservative Adult Treatment For Severe Class IIIDokument14 SeitenConservative Adult Treatment For Severe Class IIIJULIAN ANDRES CAICEDO RIVERANoch keine Bewertungen
- Scenario 3 Groub 3Dokument30 SeitenScenario 3 Groub 3kharismayulia kamarullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles and Management of Panfacial TraumaDokument43 SeitenPrinciples and Management of Panfacial TraumaDR NASIM100% (1)
- Anchorage: N.Mothi Krishna Ii Mds Department of OrthodonticsDokument83 SeitenAnchorage: N.Mothi Krishna Ii Mds Department of OrthodonticsMothi KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bimaxillary Protrusion - A Case ReportDokument4 SeitenBimaxillary Protrusion - A Case ReportLisbethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growth PredictionDokument64 SeitenGrowth PredictionMothi KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Space in The Mixed Dentition: The Use of Lip BumperDokument6 SeitenManagement of Space in The Mixed Dentition: The Use of Lip BumperRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Headgear 160921221446Dokument63 SeitenHeadgear 160921221446s pradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaw Relation: DR Gayathri GangadharanDokument65 SeitenJaw Relation: DR Gayathri GangadharanGayathri GangadharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rims & Occlusal Record PDFDokument63 SeitenRims & Occlusal Record PDFAmanda AmaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correction of Severe Bimaxillary ProtrusionDokument37 SeitenCorrection of Severe Bimaxillary ProtrusionRobbyRamadhonieNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOMAC: An Orthognathic Treatment Planning System Part 1 Soft-Tissue AnalysisDokument89 SeitenTOMAC: An Orthognathic Treatment Planning System Part 1 Soft-Tissue AnalysisDrKamran Momin100% (1)
- Prostho AmdadDokument23 SeitenProstho AmdadAman GaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBT Appliance: Mclaughlin Bennett TrevisiDokument247 SeitenMBT Appliance: Mclaughlin Bennett TrevisiJustFine DolittleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growth RotationDokument57 SeitenGrowth RotationAtul Koundel100% (1)
- Biomechanics of Deep Bite TreatmentDokument66 SeitenBiomechanics of Deep Bite TreatmentMaitreye PriyadarshiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Club / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDokument19 SeitenJournal Club / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asymmetric Maxillary Expansion (AMEX)Dokument29 SeitenAsymmetric Maxillary Expansion (AMEX)Monojit DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clase III No QuirurgicoDokument8 SeitenClase III No QuirurgicoNadia Vite SáenzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Twinblockshilpa 170129085958 PDFDokument130 SeitenTwinblockshilpa 170129085958 PDFWaqar JeelaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hobo-Twin Stage by IndrajeetDokument108 SeitenHobo-Twin Stage by Indrajeetindra_jeet2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Full-Cusp Class II Malocclusion With BilateralDokument20 Seiten2 Full-Cusp Class II Malocclusion With BilateralJULIAN ANDRES CAICEDO RIVERANoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone Regeneration After Alveolar Dehiscence Due To Orthodontic Tooth Movement - A Case ReportDokument7 SeitenBone Regeneration After Alveolar Dehiscence Due To Orthodontic Tooth Movement - A Case ReportRabab Abd El-HafezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Rules For Steel ErectionDokument71 SeitenBasic Rules For Steel Erectionfoller2Noch keine Bewertungen
- David Burlock LamoreauxDokument21 SeitenDavid Burlock LamoreauxLeena RogersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kullu Tamam Merged - Cropped - TextDokument345 SeitenKullu Tamam Merged - Cropped - TextEuro-trading GroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 9 Radical Reactions 1Dokument19 SeitenCH 9 Radical Reactions 1Darth VADERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 RespirationDokument3 SeitenClass 10 RespirationHimanshu singh100% (1)
- Open CVDokument11 SeitenOpen CVXavier Ibarra CorteNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRENCH Grade 6 UnlockedDokument50 SeitenFRENCH Grade 6 UnlockedWainaina MuriukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AttentionDokument26 SeitenAttentionKarn KunteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Planning For Implementing E-Government in Iran: Formulating The StrategiesDokument8 SeitenStrategic Planning For Implementing E-Government in Iran: Formulating The StrategiesTantri Mulia KarinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Chemistry Project (Electochemistry)Dokument10 SeitenClass 12 Chemistry Project (Electochemistry)Raghvendra Pandey0% (1)
- MaintGuideUSA PDFDokument118 SeitenMaintGuideUSA PDFfotopredicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Cover LetterDokument6 SeitenSample Cover LettermohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 14Dokument2 SeitenQuiz 14warning urgentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submarines and SubmersiblesDokument28 SeitenSubmarines and Submersiblespraveench1888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amazing Race Math QuestionsDokument2 SeitenAmazing Race Math QuestionsROSALEN M. CUNANANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Op 275Dokument13 SeitenOp 275cvbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mse 110l Fall 15 - Lab 4Dokument25 SeitenMse 110l Fall 15 - Lab 4Billy JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 180-SCF-3314 - Job DescriptionDokument17 Seiten180-SCF-3314 - Job DescriptionUmair AshfaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morocco Expat GuideDokument10 SeitenMorocco Expat GuidefredNoch keine Bewertungen
- 曼昆《经济学原理第三版》宏观分册原版中英文双语PPT课件Chap 25Dokument76 Seiten曼昆《经济学原理第三版》宏观分册原版中英文双语PPT课件Chap 25Jia Wei MiaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PREQ3-1 Shrouded VisionsDokument47 SeitenPREQ3-1 Shrouded VisionsVelenar ShadowalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agesitab OP850: Electronic Operating TableDokument4 SeitenAgesitab OP850: Electronic Operating TableMuhammad NaomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach SlabDokument2 SeitenApproach SlabMahmood Mufti100% (1)
- Ideco E-2100 Parts List-OcrDokument48 SeitenIdeco E-2100 Parts List-OcrMarcelino Payro TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- 060610at617pm Mayday Re Are We Under Terrorist Attack YesDokument12 Seiten060610at617pm Mayday Re Are We Under Terrorist Attack YesRalph Charles Whitley, Sr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crossroads #10 - Roger Zelazny's Amber - Seven No-TrumpDokument254 SeitenCrossroads #10 - Roger Zelazny's Amber - Seven No-TrumplerainlawlietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marciniak Barbara The PleiadiansDokument89 SeitenMarciniak Barbara The Pleiadiansaman100% (3)
- Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsDokument3 SeitenWeek 10 Tutorial QuestionsIsha ChandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Z370 AORUS Gaming 3: User's ManualDokument48 SeitenZ370 AORUS Gaming 3: User's ManualAtrocitus RedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invariant and MonovariantDokument3 SeitenInvariant and MonovariantQuốc ĐạtNoch keine Bewertungen